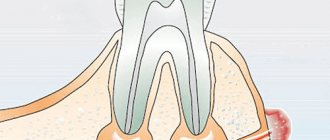
An inflammatory formation affecting the upper part of the tooth root is called granuloma. It is formed during the development of periodontitis. Tooth granuloma is tightly attached to the root, being the initial stage of a granular cyst (cystogranuloma), from which it differs, in fact, only in its slightly smaller size. If the formation is ignored and not treated, it will begin to increase.
What kind of disease is this
Focal damage to the periodontal tissues is caused by bacteria. First, a node appears at the site of the pathology, then it transforms into a sac with a cavity inside, which is filled with purulent exudate. The peculiarity is that the affected area can affect neighboring organs, including causing the formation of sinusitis, fistula, and a number of other disorders.
The appearance of a neoplasm is difficult to notice and localize at the initial stage, since most often it does not give any pronounced symptoms. The only way to see and begin treatment on time is to undergo regular dental examinations.
Causes
Light spots on enamel can appear for various reasons. Here are the most common among them.
- Carious lesion. With caries in the initial stage, the enamel becomes loose and loses its natural shine. These changes are the reaction of hard dental tissues to the effects of bacterial waste products.
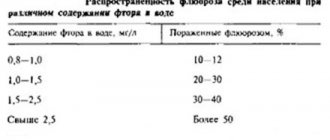
- Fluorosis is an excess of fluoride in the human body. Occurs when drinking fluoridated water, constantly using toothpastes with a high fluoride content, or working in hazardous industries.
- Enamel hypoplasia. Characterized by the appearance of light marks on the incisors and molars. It is a consequence of improper formation of tooth buds.
- Chronic deficiency of minerals - zinc, calcium, phosphorus. These elements participate in the formation of enamel and maintain its strength, therefore, with their acute deficiency, dental health suffers.
- Wearing braces or dentures. White spots on the enamel are caused by microtraumas of the crown and appear at the points of contact of the fasteners with the teeth.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a dentist. Based on the results, the specialist will suggest the optimal treatment method.
Dental granuloma code according to ICD-10
The International Classification of Diseases helps to unify the procedure for diagnosis, therapy, as well as the introduction of new technologies and methods into routine practice. For convenience, all disease classes and specific conditions are assigned alphanumeric codes. Every 10 years the list is updated and corrected in accordance with corrections from the World Health Organization. According to the latest data, granuloma-like pathologies of the oral mucosa are coded K13.4.
How to do dental x-rays
The procedure is carried out by a doctor in a specially equipped room. The implementation mechanism takes place in 4 stages:
- The patient sits in a chair. The doctor examines the problem area.
- A special apron is placed on the patient to reduce the adverse effects of x-rays.
- The doctor fixes the head of the subject to obtain a clear image.
- On the affected area inside the oral cavity behind the teeth or on the front side, using a digital visiograph, the doctor directs the beam.
The whole process takes 3 minutes. After 15 minutes, you will be given a photograph of your teeth on film or electronically (if necessary).
There may be the following reasons for taking a photo:
- Clarification of the development process of pulpitis, periodontal disease and caries;
- Check after removal of damaged teeth;
- Checking the quality of treated teeth;
- Determining the specific structure of teeth before installing a crown or bridge;
- Checking neoplasms.
During endodontic treatment, at least 3 photographs of the tooth are taken: 1. Photograph of the teeth at the diagnostic stage. It is necessary to determine the condition of the tooth, the shape and number of roots, and the treatment method.
2. A photograph at the stage of tooth treatment with endodontic instruments inserted into the tooth canals. The picture is displayed on the computer screen.
3. Control image after completion of treatment to check the sealed tooth canals.
Permissible radiation dose for dental x-rays
The radiation dose for a targeted photograph for a person is 3-5 μ3v. During the year, an adult is allowed to receive up to 1000 microns. Consequently, a patient can take from 80 to 90 images per year using an X-ray machine. The radiovisiograph will make it possible to take up to 400 images. This indicates the harmlessness of this manipulation.
Reasons for the formation of the inflammatory process
The periodontium consists of soft and hard tissues, which are the basis for holding the tooth in the jaw. Therefore, any changes that violate its integrity can lead to inflammation of the gums, bleeding, and even destruction and loss of dental organs. Therefore, the root cause of granuloma is bacteria, which begin to destroy the periodontium. It, in turn, can be caused by caries and its complications - pulpitis and periodontitis - these are the main causes, while the others listed below are only risk factors and increase the likelihood of the formation of the disease. We include:
- Microcracks in the teeth, through which infection can easily enter.
- Poor or irregular oral hygiene. It is not enough to brush; you need to use dental floss, mouthwash, and also make an appointment with your dentist for professional cleaning at least once every six months. This service is provided with high quality in the clinic – “Dentika”.
- Insufficient antiseptic treatment of gums after treatment or surgery.
Provoking factors can also be:
- Smoking.
- Overwork and stress.
- Lack of vitamins and microelements.
- Moving to other climatic conditions.
- Frequent colds and other signs of low immunity. It is especially bad when the disease has a bacterial lesion in the oral cavity.
Pay attention to preventive procedures that are prescribed by doctors for rehabilitation after surgery or other complex processes when it is necessary to disinfect a wound. Everything on the mucous membranes heals quite quickly and well, but even a slight ingress of bacteria can lead to infection. After each meal, be sure to rinse your mouth and also carry out antiseptic treatment.
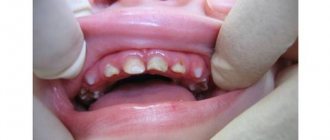
Stains on an adult's teeth
Chalky stains on the teeth of an adult can signal dental caries. Tooth decay destroys teeth if they are not carefully cared for. Then dietary fiber remains in the interdental spaces, which is a breeding ground for pathogenic microbes. They begin to secrete organic acids, which contribute to the leaching of calcium from the teeth.
Diagnosing granuloma on a dental photograph
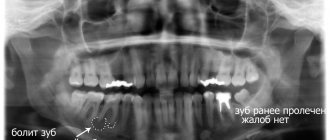
Since the nodule appears deep in the tissue near the root, it is very difficult to determine its presence in the early stages. At first, it will not appear externally as swelling or redness. You can see the symptoms only when the spread is strong enough, when purulent exudate begins to accumulate. It is best to recognize the presence of a problem at a stage when treatment can still be effectively carried out using x-rays or radiovisiography. In the photographs, the disease looks like a dark round spot. The tumor can have different sizes - from 0.1 to 1.2 cm.
The specialist recognizes the presence of the disease at the initial stage when healing adjacent incisors, canines or molars.
At a more advanced stage, you can find out how dental granuloma is treated by diagnosing the following symptoms:
- Acute pain, especially when pressed. Painful sensations also worsen when suffering from infections.
- Swelling, redness and hyperemia of the mucous membranes.
- Pus that flows out when you press on an area of the gum.
- The enamel takes on a darker shade.
- Dizziness begins.
- Enlarged lymph nodes - this does not happen often.
However, symptoms may indicate several other dental diseases. Therefore, the doctor is able to determine the formation of a purulent root node solely by x-ray.
Tooth granuloma: symptoms of the disease
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis based on an x-ray, where a darkening will be visible in the root area. Any darkening in the image is a sign of the presence of a cavity, but if a granuloma occurs, it means that periodontitis, which is chronic in nature, begins to develop.
For a long time, the tooth may not bother a person at all. Sometimes pain may occur when biting or when eating hot food: these are the first signs of the development of chronic periodontitis. An exacerbation of the disease is observed during periods of weakening of the body's immunity: then the pain intensifies significantly, which is especially noticeable when biting. During such periods, as a rule, the gums become swollen, and in the area of inflammation it becomes painful to touch.
How to treat granuloma on the root of a tooth
Treatment is selected by a specialist depending on several factors:
- At what stage is the inflammatory process currently?
- Has the damage affected neighboring areas?
- What conditions accompany the pathology (pinched nerve, stomatitis, multiple caries, etc.).
As a result, drug therapy or surgical intervention is chosen. The second method is more radical; it allows you to cope with the problem when the root, pulp is damaged or a crack has formed.
Conservative way
To exclude a bacterial infection (it is this that leads to suppuration), antibacterial drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling, inflammation, redness and severe pain. The diseased tooth is sanitized. It is opened, the dentist drills a hole down to the root canals to remove all the affected tissue cells. Then the medicine is placed into the formed cavity. Unfortunately, this does not provide a 100% guarantee that a relapse will not occur.
Physiotherapeutic method
You can act on the granuloma, but do not damage the soft tissue. This is done using:
- Depophoresis. In this case, a special medical composition is placed into the dental canals, which have been previously cleaned from the inside. This mixture perfectly eliminates infections and prevents re-infection.
- Laser. This is a very effective technique at the initial stage of development. A laser beam affecting the root system completely disinfects it.
Note that after all the above methods, a temporary filling is installed. This allows the doctor to then re-open and examine the condition of the tissue. If everything is fine there, then he seals the area being sanitized.
Symptoms
Externally it looks like a small bag or round formation. Forms at the root of the tooth. The “sac” has thin walls and is filled with liquid pus inside. Due to the inflammatory process, the destruction of infected cells accelerates over time, decay is activated, and the infected area gradually increases in size until it becomes visible to the naked eye.
Diagnosing dental disease is difficult due to the lack of obvious symptoms.
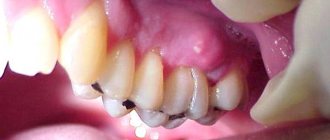
In the initial stages of the disease, there is virtually no pain, so the patient is not even aware of the active inflammatory process. Pain, discomfort, and swelling of the gums near the tooth occur only in the later stages, when the infected sac with purulent fluid grows to large sizes, covering a significant area of the periodontium.
Doctors most often diagnose the disease in a non-acute form incidentally - when treating adjacent teeth or taking x-rays of a large area of the jaw.
Symptoms of a disease that develops into an acute form:
- strong pain;
- the appearance of swelling at the site of suppuration;
- redness of the gums near the sore tooth;
- purulent discharge at the location of the inflamed cavity;
- darkening of the tooth;
- increase in the patient's body temperature.
Since similar symptoms are inherent in other diseases of the teeth and oral cavity, specialists cannot always recognize the problem without taking a high-quality x-ray of the diseased tooth root. On the x-ray, you can clearly see a rounded darkening located at the apex or side of the root - this is what a granuloma sac looks like.
Surgical treatment of gum granuloma
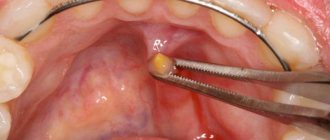
Intervention is necessary in cases where conservative medicine has not had the desired effect. It is required when diagnosing destruction processes in the acute stage. Local or general anesthesia can be used for the operation. The simplest option is gingival excision to expose the purulent sac. The pus flows out, the cavity formed is washed and medicine is placed into it for disinfection and pain relief.
Root resection
During the procedure, the dental surgeon acts as follows:
- The gum tissue is peeled away to gain access to the top of the root system.
- The dental canals are opened and cleaned.
- The formed passages are filled with drugs.
- The granuloma is excised along with the upper part of the tooth.
- The place where the inflamed node used to be is filled with a special bone substitute.
- Filling is being done.
Interradicular hemisection of the root
It is necessary in case of severe damage, when it is no longer possible to cut off only the top while maintaining the main size. Key steps of the operation:
- Removal of the area located inside the alveolus, while the plate itself can be saved.
- Cleaning of periodontal tissues.
- Filling the cavity with a special compound.
- Implant installation.
For preventive purposes, it is necessary to monitor the operated area by regularly taking x-rays. This is an effective and fairly simple method that allows you to preserve a living dental plate, and a neat crown can be installed on the remaining areas in the future.
How to cure granuloma on the root of a tooth with cystotomy
This is a gradual elimination of a large focus of inflammation. To remove all the purulent exudate, an artificial canal is created that connects the inflamed node directly to the oral cavity. After removing the infected fluid, the area is treated with antibiotics and the wound is sutured. The resulting holes can be filled with artificial biomaterial - bone cells. This is a long operation, but it is usually performed without complications.
Removal
It is prescribed as a last resort if other procedures have shown to be ineffective, for example, when:
- Complications arise, an advanced stage.
- An external purulent pocket began to form on the gum.
- A longitudinal crack is formed - the dental plate simply splits into two parts.
- Bone tissue is destroyed (the tooth crumbles).
- Origin of root perforation.
- The canals are destroyed.
During the operation, the root system is completely removed, leaving a hole in the periodontium. It is filled with pus that needs to be washed out. 2-3 months after surgery, a pin can be placed on the healed area to place the implant. Additionally, the doctor prescribes rinsing solutions (for example, Chlorhexidine), gels for local anesthesia and disinfection (Cholisal), as well as antibiotics against bacterial infections and painkillers in tablets or injections.
Tooth granuloma: treatment
Usually treatment is only therapeutic in nature, but its strategy may vary depending on whether the canals have been filled before.
- If the canals have not been filled, the tissues affected by caries are drilled out, and the old filling is removed. This is required to carry out high-quality mechanical treatment of the canals, which are expanded and treated with antiseptic agents. If the granuloma is small (formations up to 3 mm are considered such), then the canal is sealed immediately. If the size of the granuloma exceeds 3 mm, the treatment period increases, since it is necessary to put a medicine into the canal, which includes potassium hydroxide - this substance leads to a decrease in the granuloma or even to its complete disappearance. A temporary filling is placed for the period the medication is placed (approximately 2-3 weeks). Then a repeat x-ray is taken, which should clearly show a significant reduction in the inflammatory formation. If the dynamics are obvious, the canals are sealed and a permanent filling is placed.
- If the canals have been filled, then the first stage of treatment is their unsealing. The further sequence of actions is similar to that described in the previous paragraph. The only thing is that if there is a crown on the tooth, it will have to be removed, and after the treatment is completed, it will have to be made and placed again. Some patients do not want to spend money on re-installing a crown: the solution is to perform a root resection operation, when the upper part with the granuloma attached to it is cut off through a small incision in the gum.
Possible complications
If left untreated or inappropriately selected, the infection can spread and cause unpleasant consequences, including:
- An even greater progression of periodontitis with the formation of a fistula.
- Alveolitis - when the tooth socket becomes inflamed.
- Flux on the periosteum.
- Tissue death.
- Loss of the patient and near standing bone formations.
- Formation of purulent abscess, phlegmon.
- Bacteria enter internal organs, starting with the nearest lymph nodes and ending with the liver, kidneys, heart and brain.
- Asymmetry of the face due to a pinched nerve or displacement of parts of the jaw by an inflamed node.
- Fever, malaise, weakness, nausea and other signs of intoxication of the body.
Causes and course of the disease
To understand what the essence of initial caries is and how to treat it, you need to once again remember the structure of the tooth. The basis of the tooth body is dentin - a hard porous tissue penetrated by microscopic tubules, vessels and nerve endings. It is covered with enamel, the hardest substance in our body. Tooth enamel is a matrix of living protein compounds, which is filled with mineral compounds of phosphorus, fluorine and calcium. The microflora living under dental plaque destroys the mineral compounds of the enamel, loosens it, forming a white spot at the first stage of this destructive process, which indicates the development of the initial stage of caries. At this stage, the dentin is not yet affected, it is still protected by a loose patch of degrading enamel. Tooth enamel, 97 percent consisting of mineral compounds, is completely devoid of nerve endings, so the patient may not subjectively feel the onset of the pathological process.
Granuloma on the root of a tooth: how dangerous it is and what are the prognoses
Please note that this disease cannot be treated at home. If it is detected, an urgent visit to a specialist, the use of drugs and surgical intervention are necessary. The danger of the condition is that self-medication can trigger an inflammatory process.
With prompt diagnosis and timely assistance, the prognosis is very promising. The patient usually does not feel discomfort, quickly recovers from anesthesia, and after a while, specialists begin aesthetic correction - installing a crown or implant. With a conservative method of therapy, relapse is possible, so it is worth carrying out regular examinations and, if necessary, taking x-rays.
Ways to solve the problem
The choice of treatment method for white spots on tooth enamel depends on the cause of the pathology.
- In cases of caries and damage to the crown by orthodontic and orthopedic structures, remineralization of the enamel helps. The procedure consists of strengthening tooth tissue using special solutions, pastes or gels. According to indications, deep fluoridation and fissure sealing is possible. These measures will stop the spread of the disease and prevent further damage.
- Fluorosis is treated with electrophoresis and medications are applied. Diet plays a special role in therapy. The diet should include fish, fresh vegetables, cereals, milk and dairy products. Whitening helps restore the beauty of your smile; in difficult cases, doctors recommend installing veneers.
- Enamel hypoplasia requires combined treatment. In mild forms of pathology, remineralization helps, in complex forms, filling or prosthetics helps.
Prevention
For preventive purposes it is necessary:
- Practice daily oral hygiene using a toothbrush, floss, and gum rinse.
- Get checked by a dentist at least once every six months.
- Reduce the consumption of sweets, coffee, tea, as well as all drinks with dyes - all this negatively affects the enamel and often leads to the formation of caries.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Increase the amount of vitamins and beneficial microelements that enter the body.
In the article we talked about what a granuloma in a tooth is and showed it in the photo. Follow our recommendations and carefully monitor your health! If you find problems, come to the Dentika dental clinic, where we will select a course of treatment for you and eliminate any deficiencies.
Measures to prevent granuloma after an extracted tooth
Preventive measures are aimed at preventing the development of the disease. They include:
- high-quality cleaning of teeth and gums on a daily basis;
- timely treatment of bleeding gums;
- regular visits to the dentist at least once a year (it is better to do this twice);
- replacing toothbrushes (old brushes accumulate bacteria that can provoke the development of the disease);
- contacting the dentist at the slightest pain associated with the gums or teeth;
- treatment of caries, periodontitis and pulpitis - quite often these diseases are the catalyst for the development of granuloma;
- the use of medicated toothpastes and herbal decoctions for rinsing;
- eating foods rich in calcium and other trace elements.