Physiotherapy in dentistry
Physiotherapy is a field of medicine that studies the characteristics and healing properties of physical factors, develops methods of their use for treatment, disease prevention and medical rehabilitation. Recently, physical treatment methods have been increasingly introduced into dental practice, which, in combination with other treatment methods, make it possible to quickly stop various problems. processes in the jaw. Physical factors are used mainly in the treatment of many dental diseases in the phase of incipient or complete remission with inflammatory, dystrophic and functional changes, they are used in organizing dispensary observation of patients, and in the rehabilitation of patients after traumatic injuries of the maxillofacial area. Physical factors allow for more accurate diagnosis of diseases and monitoring the effectiveness of treatment.
General contraindications to physiotherapeutic procedures: severe body conditions, severe exhaustion, malignant neoplasms, tendency to bleeding, blood diseases, severe cardiovascular and respiratory failure, impaired renal and liver function.
In the treatment of dental diseases, natural artificial physical factors are used: direct electric current, pulsed current of low voltage and frequency, alternating electric currents and electric fields of high, ultra-high and ultra-high frequencies. Magnetic therapy, phototherapy, constant high-voltage electric field, aerotherapy, aerosol therapy, ultrasound therapy, cryotherapy are used. In dental practice, hypothermia, paraffin, ozokerite and mud therapy are used, hydrotherapy, vacuum therapy and massage are also used. It is necessary to prescribe no more than 2 procedures, provided that one of them has a predominantly local effect, and physical factors of the opposite effect (sedative and stimulating procedures) are not prescribed simultaneously. In dental practice, physiotherapy is used in combination with other treatment methods, it occupies a worthy place and has great prospects.
Electrotherapy is used in dental practice:
• Direct low voltage electric current (galvanization, medicinal electrophoresis, electrical anesthesia);
• Pulsed currents of low frequency and low voltage (treatment with diadynamic, sinusoidal, modulated, fluctuating currents, pulsed low voltage current used for electrodiagnostics and EDI);
• High frequency alternating electric currents (darsonvalization, diathermocoagulation);
• Electric, magnetic, electromagnetic field (electric field of ultra-high frequency - EG-UHF, alternating magnetic field of ultra-high frequency - MP-UHF, microwave therapy, magnetic therapy).
Efficiency
Physiotherapeutic methods have a huge number of benefits when used as additional treatment .
In combination with other methods of therapy, they show high efficiency, but as independent therapy, they are ineffective or bring only minor temporary relief.
A correctly selected complex allows you to achieve positive results in a short period of time, with no side effects at all.
The main advantage of the therapy is that it can be used equally for both adults and children .
Galvanization and electrophoresis
Galvanization
This is the use for therapeutic purposes of continuous direct current of low strength (up to 50mA), and low voltage (30-80V), which are passed through certain areas of the body.
In dental practice, galvanization is used in the collar area. Galvanic current is a factor that stimulates blood circulation, improves tissue trophism, promotes the removal of metabolic products from the source of inflammation, the resorption of infiltrates and scars at the site of exposure, helps restore the conductivity of nerve elements, increases tissue metabolism, which is associated with increased blood and lymph circulation in the skin, mucous membranes, tissues due to vasodilation, the appearance of hyperemia, with an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall, with an increase in local temperature. This promotes the absorption of medicinal substances introduced into the skin using direct current.
Galvanic effect on the salivary glands:
Galvanization for periodontal disease:
Location of electrodes when affecting the TMJ:
Drug electrophoresis
Drug electrophoresis is the introduction of medicinal substances (DS) into the body through the skin or mucous membranes using direct current.
Advantages of electrophoresis:
♦ Combined action of direct electric current and drug;
♦ Absence of general toxic effect of drugs;
♦ The ability to selectively introduce one or another ion depending on its polarity into tissues that are inaccessible to other methods of drug administration.
Devices for galvanization and medicinal electrophoresis:
Indications for the use of galvanization and electrophoresis:
- Chronic inflammatory processes.
- Gingivitis.
- Periodontitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Arthrosis, arthritis (trismus).
- Scarring.
- Post-traumatic conditions.
- Glossalgia.
- Neuralgia and neuritis.
- Dental diseases.
- Diseases of the salivary glands.
Contraindications for the use of galvanization and electrophoresis:
- Acute inflammatory (purulent) processes.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Cardiac decompensation, blood diseases.
- Severe sclerosis of cerebral vessels.
- Epilepsy.
- Acute skin diseases.
- Tuberculosis in the active phase.
- Toxic condition, cachexia.
- Individual intolerance.
- Second half of pregnancy.
- Feverish condition.
Galvanization and electrophoresis in childhood
Galvanization and electrophoresis can also be used in childhood. When carrying out the procedure, electrodes with wires soldered to them are used, rather than clamps. Electrodes must be secured with bandages. Since the sensitivity of children's skin to direct current is increased, the current strength is increased slowly, bringing it within 3-4 minutes to the value prescribed by the doctor. The current density depends on the age of the child - in the range of 0.03-0.08 mA per 1 cm2 of area. Physiotherapy pads for children are carried out with less power, until a slight tingling sensation appears, for 5-10 minutes.
Galvanic collar according to A.E. Shcherbak:
Galvanization and electrophoresis of the facial area (“Bergonier half mask”):
General indications
Physiotherapy complements the treatment of many dental diseases.
- stomatitis;
- gingivitis;
- pulpitis;
- fluorosis;
- pain syndrome due to damage to the trigeminal nerve;
- post-filling pain;
- sialadenitis;
- glossalgia;
- paresis, paralysis of the soft palate, cheeks, tongue, muscles of the floor of the mouth;
- post-traumatic conditions;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- periodontitis;
- pathologies of facial nerves;
- alveolitis;
- arthritis of the temporomandibular joint;
- inflammatory and purulent-inflammatory diseases with outflow of purulent contents;
- erosive and ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa;
- frostbite;
- hematomas.
Electrical anesthesia with direct electric current
The analgesic effect of direct electric current is used when opening a tooth cavity, in the treatment of pulpitis, during injections, when treating a tooth for a crown. For electrical anesthesia, direct current is used from the positive pole, but it is also possible from the negative pole. The cathode anesthetizes better than the anode (Rubin L.R., 1967). It is necessary to select a current strength that can block the pain impulse. The optimal current parameters for direct action on the nerve receptor are from 109 to 20 µA. For different groups of teeth, an electric current of a certain strength is selected: in the front teeth the average is 5-10 µA, in molars - 10-16 µA. An electric current of more than 30 μA leads to pulp damage and subsequent necrosis.
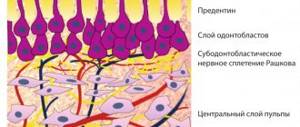
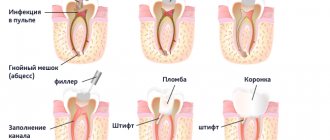
Physiotherapy of diseases of hard tissues of temporary and permanent teeth
Physical methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention are used at various stages of the carious process. For caries in the stain stage, remineralization of tooth tissue is used using calcium and fluoride electrophoresis. For children, use a 5% solution of calcium gluconate, for adults, a 10% solution of calcium gluconate. The exposure time is 10-15 minutes, then an application is carried out with a 2% sodium fluoride solution for 2-3 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 sessions. The procedure is carried out every day. Simultaneously with electrophoresis of microelements, general irradiation with UV rays is prescribed for multiple caries. They recommend 2-3 courses of UV irradiation, 20 procedures every other day. For superficial, medium and deep caries, electrical anesthesia and electroodontodiagnosis can be used during preparation.
Physioprophylaxis of dental caries
Physioprophylaxis of dental caries occupies a prominent place among other methods of preventing dental caries. Prevention of caries in children begins from the prenatal period of the child's development. For this purpose, the pregnant woman is prescribed general UV irradiation, aimed at strengthening the woman’s body and stimulating phosphorus-calcium metabolism, improving the formation and absorption of vitamins. Aeronization can be prescribed to normalize the autonomic nervous system. During the neonatal period (up to 1 month), daily walks and exposure of the child to reflected sunlight are important. In the summer, children should be exposed to sunlight for sufficient time. In the northern regions, children need to undergo artificial general irradiation with ultraviolet rays.
To prevent caries in children, irradiation of the gums and oral mucosa can be carried out, starting with l/3 biodoses and increasing by 1/3 biodoses, the duration of each subsequent irradiation, bringing up to 2-3 biodoses. There are 2 courses of radiation per year, preferably in winter and spring. The same procedures can be performed on adults prone to dental caries.
Non-carious lesions of teeth (before eruption)
Enamel hypoplasia
In the treatment of enamel hypoplasia with pronounced forms and large foci of impaired mineralization, which is accompanied by hyperesthesia, medicinal electrophoresis of calcium, phosphorus, fluorine and B vitamins is used in combination with novocaine. To do this, calcium electrophoresis is carried out from a 2.5% solution of glycerophosphate or a 2-4% solution of calcium chloride in alternation with vitamins B and a 6% solution with 2% novocaine. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures, 20 minutes each. To treat systemic enamel hypoplasia, UV irradiation is prescribed according to the generally accepted method during the period of low insolation of the body (November-April). You can apply galvanization of the cervical sympathetic nodes - 10-15 procedures.
Endemic fluorosis
It is recommended to carry out local saturation of tooth tissues with calcium, phosphorus, vitamins C, P, PP, group B. A 10% solution of calcium gluconate is used for electrophoresis and a 6% solution of novocaine. A course of treatment requires 10 procedures with calcium and 10 procedures with vitamin B1. Calcium electrophoresis in a course of 10-12 is prescribed after bleaching pigmented areas of enamel with a 30% solution of hydrochloric acid - 5 minutes and 33% solution of hydrogen peroxide - 10 minutes.
Expected Result
Physiotherapeutic methods in dentistry have a number of advantages. They have shown excellent results in combination with other methods of treating oral diseases.
When using one of the methods as independent therapy, only temporary relief is observed.
Among the advantages, patients note the complete absence of side effects.
Sources:
- https://www.drclinics.ru/nashi-uslugi/med-uslugi/stomatologiya/terapevticheskaya-stomatologiya/lazernaya-fizeoprotsedura_1/
- https://physiatrics.ru/1000378-fizioterapiya-v-stomatologii/
- https://dr-zubov.ru/lechenie/zuby/primenenie-fizioterapii.html
- https://stom.32top.ru/stat/308/
- https://phisioterapia.ru/lechenie/fizioterapiya-v-stomatologii/
- https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/fizioterapiya.html