Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
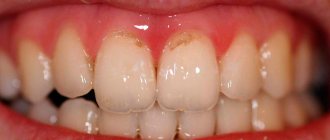
Depending on the nature of periodontal changes caused by inflammatory processes, several types of chronic periodontitis are distinguished. The most harmless and most asymptomatic of them is fibrous.
Among the most common causes of this form of periodontitis are the following:
- Sufficiently long-term infection of periodontal tissues.
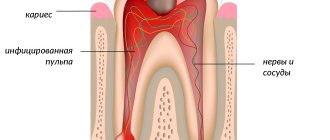
As a rule, in this case, pathogenic microflora that forms in the root canal during pulpitis or deep caries has a detrimental effect on them. If the harmless fibrous form is not treated in a timely manner, it can turn into more dangerous types of chronic periodontitis.
- Effective treatment of the granulating or granulomatous form of the disease.
In this case, the damaged tissues acquire a fibrous structure over time, which does not pose a particular danger to oral health and does not require medical intervention.
- Traumatic effects on the tooth
Fibrous periodontitis can be caused by prolonged excessive loads that the tooth is forced to experience due to poor-quality fillings that increase the height of the bite, poorly constructed removable or fixed dentures, or exposure to orthodontic structures. In this case, it is necessary to exclude traumatic effects and, if indicated, treat the roots of the tooth.
- Entry of foreign substances into the periodontium.
This could be an incorrectly inserted pin, excess filling material, or even a broken endodontic instrument. The decision to carry out treatment procedures is made individually in such cases.
Under the influence of any of these factors over a long period of time, a change in the structure of the periodontium occurs. Its ligaments thicken, and the cells are replaced by fibrous formations, as a result of which the tissues scar, become rough and thicken significantly.
Classification of periodontitis
There are several classifications of periodontitis, which have more similarities than differences. However, in our country, the classification of I. G. Lukomsky, which provides for the separation of acute (serous and purulent) and chronic (fibrous, granulating and granulomatous) apical periodontitis, as well as chronic aggravated periodontitis, has become most widespread.
Classification of periodontitis according to I. G. Lukomsky
Acute forms:
- Acute serous apical periodontitis.
- Acute purulent apical periodontitis.
Chronic forms:
- Chronic apical fibrous periodontitis.
- Chronic apical granulating periodontitis.
- Chronic apical granulomatous periodontitis.
- Aggravated chronic apical periodontitis.
- Root cyst.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis –
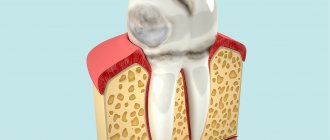
For the treatment of periodontitis - the price is indicated for 2021, based on an analysis of the price lists of economy-class dental clinics and mid-price segment clinics. The cost of treatment of chronic periodontitis will depend primarily on the number of root canals in the tooth (Fig. 4).
As a rule, all incisors and canines have only 1 root canal. The lower premolars (4-5 teeth from the center) have 1 canal, and the upper ones have 2 canals. The lower and upper molars (from 6 to - most often have 3 root canals (but the lower ones often have only 2, and the upper ones sometimes have all 4).
The lower premolars (4-5 teeth from the center) have 1 canal, and the upper ones have 2 canals. The lower and upper molars (from 6 to - most often have 3 root canals (but the lower ones often have only 2, and the upper ones sometimes have all 4).
Periodontitis: cost of treatment
- 1-channel periodontitis – from 5500 to 8000 rubles.
- 2-channel periodontitis – from 6500 to 9000 rubles.
- 3-channel periodontitis – price from 7,500 to 10,000 rubles.
This cost includes anesthesia, removal of the old filling, all manipulations in the root canals, including their mechanical and medicinal treatment, as well as their filling using the lateral condensation method of cold gutta-percha. Please note that the price only includes the installation of a temporary filling.
This price does not include permanent fillings or removal of the old artificial crown. If your tooth has already been treated before, and you need to unseal poorly filled root canals, as well as remove the anchor pin from the canal, then in this case the cost will increase by about 2000-4500 rubles (depending on the complexity of unsealing the canals and removing the pin).
Causes of acute periodontitis
Among the main reasons for the development of acute periodontitis are:
- acute inflammation of the pulp that occurs against the background of teeth affected by caries; pulp and periodontal tissues are closely related;
- the use of arsenic for pulp devitalization, which provokes inflammation of the pulp tissue due to the toxic effect of the drug penetrating the periodontium;
- the use of strong antiseptics and various cauterizing agents that are injected into the root canal, which provokes inflammation in nearby tissues;
- entry of a large amount of filling material into the periodontal space.
Causes of inflammation
Periodontitis is an acquired disease; it is caused by both health problems and mechanical damage.
The most common reasons include:
- untreated pulpitis (inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth due to an infection brought inside);
- caries;
- fillings and dentures installed poorly (not in size or not accurately).
In addition, periodontitis occurs in smokers, people with diseases (heart, digestive) and those who are susceptible to hormonal imbalances.
Age is not a barrier for the onset of periodontitis. In children, it occurs after injuries or bruises to the oral cavity. In adults, the formation of ulcers is caused, among other things, by trauma to the canals with surgical instruments and excessively large fillings that violate the integrity of the tooth.
In addition, in some cases, periodontitis is a consequence of the body’s individual reaction to certain medications or chemicals entering the tissue during treatment.
Do not heat the sore spot or use traditional medicine. The best thing is to see a doctor
Causes of chronic periodontitis
Approximately 1.5–2 weeks from the moment the first symptoms of the disease appear, it becomes chronic.
Factors that also contribute to the development of chronic periodontitis are:
- advanced form of caries;
- pulpitis;
- advanced acute periodontitis is the most common cause.
Also, chronic periodontitis can develop due to tissue overload due to traumatic occlusion or adentia.
Chronic periodontitis can be infectious or non-infectious.
Causes of infectious periodontitis
Chronic infectious periodontitis can occur due to the presence of many bacteria in the oral cavity: streptococci, staphylococci, porphyromonas, proteus, diphtheroids, yeast-like fungi, etc. Infectious agents enter the tissue through the dentinal tubules or root canal openings, as well as through the bone type of alveoli. The second way is extradental.
Among other causes of infectious periodontitis are chronic odontogenic infections, which include: periodontitis, osteomyelitis, pulpitis (ulcerative), pericoronitis. Often pathogenic organisms enter the oral cavity in the case of tonsillitis or scarlet fever.
Causes of non-infectious periodontitis
Periodontitis of non-infectious origin can occur as a result of trauma to a tooth with damaged periodontium of the intracanal pin. Thus, drug-induced chronic periodontitis develops as a response to the use of resorcinol-formalin or other drugs that provoke coagulative necrosis.
Chronic apical periodontitis –
Chronic periodontitis is most often the outcome of an acute process, but in some cases it can develop independently (especially with weak immunity). Chronic periodontitis occurs, as a rule, asymptomatically, or with slight pain when biting on the causative tooth.
Severe symptoms appear only during exacerbation of a chronic process, which can be triggered by hypothermia of the body, decreased immunity after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection. There are 3 forms of chronic periodontitis...
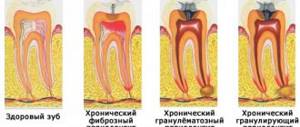
Chronic fibrous periodontitis –
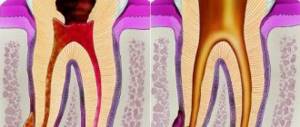
It is characterized by the fact that periodontal fibers (the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth that connects the tooth to the bone) are gradually replaced by connective fibrous tissue. Chronic fibrous periodontitis has extremely few symptoms, and pain may be completely absent.
Sometimes a diagnosis can only be made based on an x-ray. If on an x-ray the normal periodontium is defined as a narrow uniform strip between the tooth root on one side and the alveolus of the bone on the other, then with fibrous periodontitis there is sometimes a significant expansion of the periodontal fissure.
Chronic granulating periodontitis –
This is the most active form of chronic periodontitis. It is characterized by the appearance in the area of the root tips - granulation tissue, which visually looks like loose granular tissue of red color. Granulation tissue has the ability to grow rapidly, which leads to active bone destruction and its replacement with granulation tissue.
Symptoms – patients complain of aching pain, which periodically worsens. Biting on a tooth and tapping it causes a moderate pain reaction. There may be a fistula on the gum in the projection of the causative tooth, from which scanty purulent discharge will be released.
On an x-ray – chronic granulating periodontitis is very clearly visible on x-rays. In the projection of the apex of the tooth root, an irregularly shaped darkening with flame-like outlines is determined. This darkening indicates that the bone tissue in this area has collapsed and has been replaced by granulation tissue.
Chronic granulomatous periodontitis –
Chronic granulomatous periodontitis is characterized by the formation of something like a purulent sac at the apex of the root. Depending on the size of this formation, it is customary to distinguish the following 3 types of this form of periodontitis: granuloma, cystogranuloma and radicular cyst. They have the same structure, are filled with pus, and differ only in size...
- Granuloma - differs in that it measures up to 0.5 cm in diameter. Treatment for granuloma is relatively simple, unlike larger lesions.
- Cystogranuloma – has dimensions from 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter.
- Cyst - a formation at the apex of the root is called a cyst when its diameter exceeds 1 cm. Cysts can reach 5-6 cm in diameter, and even completely fill, for example, the maxillary sinus of the upper jaw. For cysts measuring 1-1.5 cm, conservative treatment is possible, and for larger ones, surgical removal is recommended.
Granuloma and cyst on x-ray –
An x-ray shows a darkening with clear, even, rounded contours in the area of the apex of the tooth root. This darkening indicates that bone tissue has resolved in this area. The even, clear contours of such darkening indicate that the formation (cystogranuloma or cyst) has a dense capsule that is not connected to the surrounding bone tissue.
Due to what growth occurs - the growth of these formations and their transformation into each other - occurs due to a constant increase in the amount of pus inside the formation, which leads to an increase in the pressure of the formation on the surrounding bone tissue. The bone is dissolved under pressure. As a result, education occupies a new space, and then everything starts all over again. As the granuloma grows, it turns into a cystogranuloma, and the latter into a cyst.
Symptoms of granulomatous periodontitis - this form of periodontitis, in terms of the nature of its course, occupies an intermediate place between the sluggish fibrous form of periodontitis and the aggressive course of granulating periodontitis. At the beginning of its development, chronic granulomatous periodontitis has very poor symptoms, and biting on a tooth or tapping on it does not always cause pain. However, at a later date, the symptoms intensify (24stoma.ru).
What does cystogranuloma look like at the apex of the root of an extracted tooth: video
Symptoms of periodontitis
Symptoms of acute periodontitis are:
- acute pain in the teeth, intensifying at the time of percussion;
- swelling of the lips and cheeks;
- swelling of the gums;
- tooth mobility;
- low-grade fever (37.2-37.7 C);
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Chronic periodontitis is characterized by:
- pain when eating (especially hot);
- sharp pain when biting;
- swelling of the mucous tissues near the affected tooth;
- hyperemia of the oral mucosa;
- the appearance of submucosal, subcutaneous granuloma.
During an exacerbation, a fistulous tract may appear next to the affected tooth, from which pus is released. Often the opening of the fistula tract is localized in the area of the cheeks, cheekbones and chin. Serous-purulent fluid may ooze from the wound. Alternatively, granulation tissue may swell. After an exacerbation, closure of the fistula is observed with the formation of a scar in its place.
Chronic type of granulomatous periodontitis
often asymptomatic. As a result, a greatly enlarged granuloma changes into a cyst, which is characterized by the following clinical manifestations:
- swelling of the gums;
- severe pain in the tooth;
- changes in enamel color;
- hyperemia;
- flux.
If the cyst increases critically in size, even a jaw fracture is likely.
Fibrous chronic periodontitis
characterized by mild symptoms. With this form of the disease there may even be no pain at all. This form of periodontitis is the least dangerous. But in case of exacerbation, the pain can instantly intensify, swelling of the soft tissues of the collateral type is observed, loose teeth and enlarged lymph nodes appear.
Complications of chronic periodontitis include abscess of the soft tissues of the neck and face, meningitis, osteomyelitis of the jaws, periostitis, brain abscess, purulent sinusitis and blood poisoning.
Prevention of periodontitis
The following can be recommended as preventive measures to prevent periodontitis:
- regular dental examination every six months;
- timely and high-quality treatment of caries and pulpitis;
- restoration of the dentition to reduce and properly distribute the load on other teeth when chewing;
- Carrying out all treatment and preventive procedures only in well-established dental clinics.
Are you worried about discomfort in your teeth and gums? There is no point in wasting precious time experiencing discomfort! Experienced medical doctors will quickly and professionally determine the cause of your ailment, and also help save teeth with chronic inflammation.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of periodontitis is carried out on the basis of a clinical examination, including:
- interviewing the patient,
- visual examination of the oral cavity,
- probing the entrance to the tooth cavity,
- determination of the degree of tooth mobility.
To accurately establish a diagnosis in dentistry, the following is used:
- X-ray examination;
- radiovisiography;
- transillumination;
- electroodontodiagnostics.
In case of acute inflammation, an X-ray image will not yet show any changes in the periodontium, but in the chronic course of the disease, an X-ray is simply necessary. With its help you can determine the form of chronic periodontitis:
- with fibrous periodontitis,
the image will show uneven changes in the lumen of the periodontal fissure; sometimes there is thickening of the root in the apical region. In some cases, sclerosis of the alveolar bone tissue is observed around the source of inflammation. - with granulating periodontitis,
more or less extensive granulations (growths) appear in the periodontium, usually round in shape with unclear boundaries. The image also shows a pronounced deformation of the periodontal fissure and reduced bone density. - with granulomatous periodontitis
, it is clear that the growing granuloma (round in shape with clear boundaries) gradually destroys the bone tissue of the alveoli, developing into a cystogranuloma, and then into a cyst, which begins to grow from the apex of the tooth towards the bone tissue. Such a pathological process usually requires surgical intervention.
Price for treatment of periodontitis: how it is formed, what it depends on
Without examination and diagnosis, it is impossible to give an exact price for the treatment of periodontitis. Because periodontitis therapy may include a different set of procedures and be carried out using different methods. For example, conservative therapy may be chosen, and sometimes periodontitis can only be cured through surgery. In addition, as we wrote above, the cost of periodontitis treatment will depend on the number of tooth canals.
If you want to find out the exact cost of periodontitis treatment, you need to contact your dentist.
In our dental clinic in Moscow - “Firadent”, periodontitis treatment is carried out using the most modern technologies, allowing us to perform all the necessary procedures with impeccable quality and without pain and discomfort for the patient. We use a dental microscope to treat dental canals, and we can also treat dental periodontitis under sedation - light medicated sleep. Treatment of periodontitis under sedation is especially indicated for patients experiencing panic fear of dentists.
Treatment of periodontitis
The treatment regimen for the disease is determined by the stage of its progression and the specific clinical picture. The doctor pays special attention to finding out the cause that provoked periodontitis.
The traditional method of treating the disease includes: the use of pastes that promote the resorption of granulomas and cysts, as well as drugs that activate the restoration of bone tissue. Resection of the apex of the tooth root is prescribed only if therapeutic methods do not bring the expected result. In any case, the doctor strives to preserve the integrity of the tooth as much as possible.
The most important thing in treatment is pain relief and elimination of the source of inflammation in order to spread the infection to other areas of the maxillofacial area. In case of mild infectious periodontitis, it is enough to clean the root canals using an antiseptic.
Treatment of acute periodontitis
In case of acute periodontitis, it is necessary to drain the exudate from the canal through the root or gingival canal or the hole remaining after tooth extraction. Then the doctor prescribes antibiotics (sulfonamide medications). If the pain is severe, then analgesics are also prescribed.
After the acute inflammation has been relieved, the doctor begins cleaning the root canal and administering medications. If there is no discharge from the root canals and no pain, the canals are sealed. If exudate is released, then drainage of the canal cavity will follow.
If periodontitis has developed as a result of the action of strong drugs, then treatment begins with eliminating the cause that provoked the disease. First, you should reduce the intoxication of periodontitis by reducing exudation and draining the contents from the root canal. This can be done through mechanical treatment or antidotes that reduce the release of exudate.
If periodontitis is caused by injury, then treatment will be aimed at eliminating it. For example, it may be necessary to grind off a filling that injures the gums. If the damage has led to tooth displacement or damage to a bundle of blood vessels, then it is necessary to check the tooth for electrical excitability. This examination will help identify a possible tooth root fracture.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis
Treatment of chronic periodontitis is similar to treatment of the purulent type. In this case, the canal is drained to drain the exudate. Next, using an X-ray image, the location of the source of inflammation is clarified, in particular, it is clarified which of the canals should be cleaned first. After relief of inflammation, antimicrobial and instrumental treatment of the root canals is carried out, often using impregnation or physical methods of therapy.
It is worth understanding that after periodontitis, a relapse may occur if the patient soon froze in the cold or suffered another injury. The latter will inevitably lead to tooth extraction and implantation.
Treatment of the tooth and its canals in the treatment of periodontitis
- Anesthesia of the area of the diseased tooth. It is impossible to do without the use of anesthetics in the treatment of periodontitis, since the inflammation has gone deep into the tooth and affected the nerve endings. Without local anesthesia, the process of treating periodontitis will be very unpleasant and painful for the patient.
- When the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor will begin working with the diseased tooth. Treatment of periodontitis involves the removal of all destroyed dental tissues, depulpation of the tooth, as well as treatment of the dental canals.
- Treatment of canals for periodontitis involves their expansion and washing with antiseptic solutions. In order to eliminate inflammation and destroy infection, the dentist will place an antibacterial drug in the cavity of the canals.
- The drilled tooth is covered with a temporary filling and after that a break is taken in the treatment of periodontitis. The doctor sends the patient home, but before that he prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, and provides detailed advice on the care of his teeth and oral cavity. You must follow all the dentist’s recommendations exactly, otherwise the treatment of periodontitis will either take longer or, what is much worse, be completely ineffective.
Next time you will need to see the doctor in 3-4 days to continue treatment of periodontitis.
Treatment of acute periodontitis (or exacerbation of chronic) –
These forms of periodontitis are characterized by pronounced symptoms: severe aching or shooting pain, which intensifies when biting on a diseased tooth, and sooner or later swelling and swelling of the gums and sometimes the soft tissues of the face occur. Such symptoms require first of all first aid, which will allow the pus to drain and reduce pain, swelling, temperature...
1) Emergency assistance –
Emergency assistance will consist primarily of opening the tooth, the purpose of which is to create an outflow of pus from the apexes of the tooth roots through the root canals (video 1). But often this is not enough, for example, in situations where there is already a pronounced swelling on the gum or there is swelling of the soft tissues of the face - in this case, you need to make an incision in the gum for periodontitis (video 2).
Important: the patient will have to walk with the tooth/root canal open for approximately 2-4 days, after which he will have to come for a second appointment. It is very important that all this time the patient covers the open tooth (during meals) - using a thick cotton ball. This is important because if food debris gets clogged into the root canals, the outflow of pus through the canals will be disrupted and there will be a new outbreak of inflammation. After eating and rinsing the mouth, the cotton ball should be removed from the tooth cavity.
The cost of emergency care (tooth opening + incision) will cost about 1500-2500 rubles in a private clinic. And in the clinic at your place of residence, if you have an insurance policy and passport, it’s free.
Doctor's orders after the first visit –
- Antibiotics for periodontitis are the most important prescription; a broad-spectrum antibiotic is needed here, for example, “Ciprofloxacin” (Tsiprolet) or “Amoxiclav” (this is Amoxicillin + clavulanic acid). Keep in mind that Lincomycin 0.25 capsules, traditionally prescribed by dentists, are not suitable here, because... this antibiotic has a narrow spectrum of antimicrobial activity.
- Antiseptic rinses with Chlorhexidine solution.
- A strong analgesic for pain relief.
- An antihistamine, for example, Suprastin.
2) Second visit (after 2-4 days) –
First, the root canals are washed repeatedly with antiseptic solutions, after which “turundas” with an antiseptic agent (for example, cresophen) are placed in each root canal, after which a temporary filling is placed on the tooth. The patient is warned that if a tooth hurts, he should immediately consult a doctor.