Have questions?
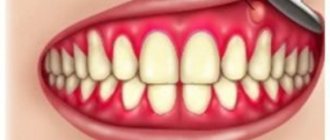
A tooth abscess is an acute inflammation in the root area, accompanied by copious discharge of pus.
People who do not take good care of their oral hygiene are susceptible to the disease. Microbes easily penetrate through defects in the tooth surface (cracks, chips, carious cavities) into its soft part - the pulp - and multiply, causing inflammation, accumulation of pus, and swelling of the gums. Since the pulp contains nerve endings, tooth inflammation is extremely painful. Most often, the process develops quickly (within 24 hours) and, if left untreated, can lead to damage to bone tissue, tooth loss, and the spread of infection in the body.
Tooth abscess: what is it - symptoms and treatment
A dental abscess is an acute infectious pathology characterized by a clearly limited accumulation of pus in the root area. The purulent process is often a dangerous complication of periodontitis, periostitis, and other dental diseases. The lack of timely treatment threatens with adverse consequences not only for the affected segment, but also for the entire body. In Moscow, dental services are provided by the Center for Aesthetic Dentistry near the Otradnoye metro station. Our doctors will quickly and efficiently help eliminate any problem with sore teeth and gums.
Possible complications
Undesirable consequences can develop even after treatment, which is why it is so important to strictly follow all instructions and prescriptions of the specialist. If you put off going to the doctor for too long, you may encounter serious complications:
- damage to the bone tissue of the jaw with the risk of further spread of infection throughout the body and the development of general intoxication of the body,
- pneumonia and other pathologies of the respiratory system,
- meningitis – develops against the background of a long course of the disease,
- formation of a fistula with constant discharge of pus, which is fraught with dangerous infectious complications,
- inflammation of the bone and brain, osteomyelitis in later stages.
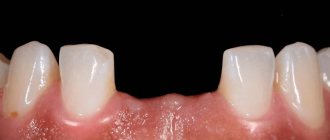
This is what a fistula on the gum looks like.
Tooth loss occurs in advanced stages of pathology. As a result, the risk of facial deformity, sepsis, and serious systemic diseases increases.
What is a tooth abscess
An abscess in dentistry is an inflammatory process accompanied by the formation of a cavity with pus near a segment or its root. The abscess on the root of the tooth is surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule, separating it from healthy tissue. Pyogenic bacteria penetrate into the unit through chips, cracks, and carious cavities.
During their life, microbes produce toxins that irritate the pulpal nerve receptors, which causes pain. In addition, toxic products of pathogenic flora increase vascular permeability, resulting in soft tissue swelling.
There are three main types of abscess:
- Periapical - pus accumulates at the root of the tooth (near its apex). A hilar abscess is formed due to an infectious lesion of the pulp. The etiological factor is untreated caries or periodontitis. The progressive inflammatory process spreads to the periosteum and surrounding soft tissue with the formation of a fistula and purulent lump on the gum.
- Periodontal - the focus is located inside the periodontal pockets. The cause is periodontitis. The pulp remains intact, and the infection is localized between the gum and the alveolar ridge.
- Desnevoy. Gum abscess is a purulent formation in the area of the gingival papillae between the segments.
Classification of pathology
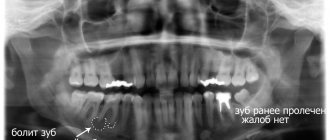
As part of the diagnosis, the doctor carefully examines the external manifestations of the disease and, if necessary, sends the patient for an X-ray examination. Before starting treatment, we need to find out what form of abscess we are dealing with. Below is the basic classification of the disease.
Gingival abscess
In this case, the lesion affects only the soft gingival tissue, but does not extend to the periodontal ligaments. When penetrating into deeper layers, the infection can provoke inflammation of the periosteum, and then flux develops, which is accompanied by the formation of a purulent lump on the gum. Among the most common causes of pathology are soft tissue injuries, for example, as a result of too intense brushing of teeth or damage from a fish bone. First, a limited area turns red and swells, and already on the second day the process of growth of the neoplasm begins with the possible release of pus when pressed.
The photo shows a gingival abscess
Periapical form
With a periapical abscess, inflammatory processes develop in the dental pulp. The patient experiences dull, aching pain in one place, and bad breath may appear. Among other accompanying manifestations, experts identify a general loss of strength, chills, and increased body temperature. It is important to have time to perform an autopsy before serious damage to the nerve occurs - in this case, there is a chance to save the tooth.
Periapical form of abscess
Periodontal view
The infection gradually makes its way through the alveolar bone closer to the root of the tooth. As a result, a sharp acute pain appears when mechanical action is applied to the mucous membrane in the area of the lesion. Sensitivity to temperature changes also increases. In parallel with this, the concentration of purulent exudate occurs in the periodontal pocket. In advanced stages, pathological mobility of teeth may be observed. You need to act quickly to avoid undesirable consequences, including complete tooth loss.
Periodontal type of abscess
What treatment methods are used
Under no circumstances should you try to open the abscess yourself - such arrogance can lead to nerve injury, extensive infection and other serious problems. Pathology requires appropriate treatment, so it is impossible to do without the help of a specialist. If a focus of inflammation is detected, the purulent lump is first opened, exudate is removed and antiseptic treatment is performed. To prevent further development of infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. If the lesion has managed to reach the internal structures of the tooth, it may have to be removed. Next, let's talk about everything in order.
Opening an abscess, including tooth extraction - surgical intervention
A small incision is made on the gum in the area where pus accumulates, after which the contents of the lump are removed, the tissue is treated with antiseptic, and drainage is installed if necessary. However, if the inflammation has spread deeper and damaged the internal structures of the tooth, you will most likely have to remove the affected element and install an implant and crown instead. In such a situation, purification of the cavity from pus is usually carried out after tooth extraction.
This is what drainage looks like in dentistry
Antibiotic therapy
After surgery, a course of antibiotics is necessarily prescribed - this is necessary to prevent further development and spread of infection. Usually a broad spectrum of action is prescribed, for example, “Lincomycin” for children under 6 years of age or “Amoxicillin” for adult patients. The course takes about a week on average. If the rehabilitation process proceeds without complications, it takes about 5 days to restore the affected tissues.
Therapeutic rinses
After opening the abscess and fixing the drainage system, the specialist may prescribe antiseptic rinses. These are special pharmaceutical products that help stop inflammatory processes, provide antibacterial treatment and stimulate the process of restoration of damaged tissues. Instead of ready-made rinses, you can use infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs, but only after agreement with your doctor.
Gargling with medicinal herbs will help in treatment
Ways to eliminate pain
Taking painkillers is just an attempt to alleviate your condition, but not a solution to the problem. You can take one tablet to relieve an acute symptom until you visit a doctor. Painkillers are also prescribed in the postoperative period. Among the most popular drugs in this category, dental experts highlight the following:
- "Ibuprofen" - 3-4 tablets per day are allowed. The drug in tablet form is contraindicated for use in children under 6 years of age, and suppositories and suspensions are contraindicated for use in children under 3 months of age.
- "Analgin" - prescribed in a dosage of 0.5-2 tablets at a time, but not more than 8 per day. You can give the drug to a child only with the permission of a doctor. The drug in tablets is approved for children from 10 years of age, suppositories - from one year,
- "Paracetamol" - the maximum daily dosage corresponds to 8 tablets - from 12 years. Especially for young patients, children's "Paracetamol" is produced for children from 2 years old.
Before taking any medications, you should consult your doctor. You should not overuse painkillers immediately before going to the dentist, as this may distort the clinical picture.
How to alleviate the condition with folk remedies
In order to relieve acute manifestations of the pathological process at home, you first need to apply cold to the affected area. This will help relieve some of the swelling and soreness. As for therapy with folk remedies, it is allowed only with the permission of a doctor. You should not self-medicate under any circumstances, because otherwise you can provoke an increase in symptoms and the development of dangerous complications.
Cold may relieve the patient's condition
Important! A periodontal abscess should not be heated - warming compresses will only intensify the inflammation and contribute to its more rapid spread.
If the attending physician has given the go-ahead for the use of herbal remedies, you can prepare a decoction from the medicinal collection. To do this, just take a teaspoon each of oak bark, nettle, sage and calamus root, pour all the ingredients into 1 liter of boiling water and leave the decoction for a couple of hours. Next, the product is filtered and used for periodic rinsing of the mouth during the day.
Why does a tooth fester?
Let's look at why pus forms in teeth. The causes of the pathology can be:
- mechanical damage to the oral mucosa;
- dental diseases of an infectious nature (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, etc.);
- hematogenous spread of microbes from other foci of infection in the body (sinusitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adnexitis, etc.);
- maxillofacial injuries accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the segment;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- Iatrogenic causes associated with the introduction of bacteria during dental treatment.
There are risk factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of pathology: smoking, decreased body defenses, hypothermia, chronic stress. Timely treatment of tooth root periodontitis and other dental diseases reduces the likelihood of an abscess.
Causes
The most likely cause of a jaw abscess is mechanical damage , trauma , or periodontal pockets (cracks between the tooth and gum that can become infected). An abscess can be caused by any infection that enters the damaged area, either from the outside or through the body’s bloodstream. If a patient has chronic tonsillitis, the cause of inflammation may be streptococci and staphylococci, which constantly multiply in the hypertrophied palatine tonsils. In this case, the patient is recommended not only to treat the abscess itself and damaged soft tissues of the oral cavity, but also to remove the tonsils, if their treatment is not possible. Otherwise, infection may recur many times.
Symptoms of gum abscess
The main symptom of the disease is pain. It has a different character (aching, pulsating, acute), is constant or occurs periodically under the influence of stress factors (cold, heat, sour, sweet foods). The pain is often worse when chewing. It can be local or spread to neighboring teeth, ears, eyes. In addition, with an abscess there are other clinical manifestations:
- hyperemia of soft tissues around the affected segment;
- swelling of the inflammation zone;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- foul odor;
- mobility and change in the natural color of the segment;
- the presence of an ulcer on the gum with purulent discharge;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- facial deformation due to swelling;
- hyperthermia, lethargy, sleep disturbance.
Symptoms that occur with an abscess
- sharp and throbbing pain, which is localized in the area of one specific tooth, but most often it spreads throughout the entire jaw and persists for a long period of time,
- if you put pressure on a tooth, very painful sensations appear, the pain is also provoked by the chewing load,
- the reaction to external stimuli increases - hot and cold exposure,
- redness of the gum tissue occurs,
- pronounced swelling of both the gums and a certain part of the face,
- general malaise occurs, body temperature rises,
- the smell from the mouth is putrid in nature, which is caused by the accumulation of a large amount of pus,
- cervical lymph nodes enlarge.
What to do when you have an abscess
What to do if a tooth breaks: immediately seek help from a dentist. When a fistula forms and the purulent contents drain, the person’s well-being improves and the intensity of pain decreases. However, the pathological process, when the lesion is opened independently, continues to progress and can lead to complications: mediastinitis, thrombophlebitis, sepsis, meningitis, etc.
Therefore, it is important to promptly treat inflammatory diseases of teeth and periodontium. How much it costs to treat pulpitis and other pathologies at North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1 can be found on the corresponding page of the official website.
Diagnosis and characteristic symptoms
The process of development of pathology is usually accompanied by severe symptoms, so diagnosing the problem is not difficult. The presence of purulent inflammation in the oral cavity is indicated by the following accompanying symptoms:
- a dull nagging pain that can become pulsating. Acute pain manifests itself in attacks,
- bitter or metallic taste in the mouth,
- increased reaction of dental tissues to temperature and mechanical stimuli,
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck,
- swelling of the mucous membrane near the source of inflammation,
- loss of appetite, fever and chills, increased body temperature,
- headaches, insomnia, general loss of energy,
- redness of inflamed soft tissues,
- discharge of purulent exudate from the gums,
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
A dull, nagging pain in the tooth that can become pulsating.
Gradually, the intensity of the manifestation of the above symptoms weakens. However, this does not mean that the inflammation goes away without outside help. Most often this is due to the death of the nerve and root, against which the infection continues to progress, but without significant symptoms. In the worst case scenario, the infection will spread to the jawbone.
Also, improvement in the patient's condition may occur after the abscess breaks through. The swelling decreases, the swollen cheek decreases in size, chills and signs of the inflammatory process disappear. But the problem has not been solved - the pathology has become chronic, which can lead to relapse and the formation of a fistula1. In any case, it is necessary to consult a dentist and ensure proper prevention of the disease.
How to treat a tooth abscess
Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed at eliminating the infectious process and relieving pain. A comprehensive program may include the following activities:
- Opening and draining the lesion. An incision is made on the gum, a drainage is installed through which the pus can freely come out. The drainage system is installed for several days. During this period, the patient is prescribed rinses with antiseptics and saline solutions.
- Endodontic treatment. It involves removing the pulp, treating the root canals with medications and filling them.
- Excision of the root apex. Surgical intervention is performed when the source of infection is located in the periapical area. The surgeon cuts the gum and removes the abscess along with the affected part of the root. The segment itself is preserved.
- Removing a unit. The need for tooth extraction occurs when there is significant destruction of the tooth.
- Therapy with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Restoration of the coronal part with a filling or orthopedic construction.
Treatment of the disease
You should not try to cure a purulent “bump” on your own. Therapy should be carried out by an experienced dentist. First, the specialist carries out an examination and carries out the necessary diagnostic measures. Then he proceeds to opening the purulent formation. To do this, he uses a scalpel or laser beams. Since the drainage procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the patient does not feel pain.
The next step is to wash the wound and treat it with antiseptics, and apply antibacterial compounds. It also happens that drainage is installed in the affected area for several days to avoid re-accumulation of pus.
Afterwards, the tooth is treated or pulled out. In the first case, the nerve is removed. To do this, medicine is put into the unit and after a few days the dead nerve is removed. Afterwards, the canals are cleaned and sealed. Filling material or an individually made inlay is placed on top.
A tooth is pulled out only in advanced cases, when the roots have become unusable and cannot be treated. To prevent this, you need to see a doctor in a timely manner, and not hope that the disease will go away on its own.
If the patient complains of acute and pronounced pain, he is prescribed a painkiller. Most often these are tablets, but it is also possible to use a special anesthetic gel.
In order to achieve a guaranteed victory over inflammation and prevent recurrence of the abscess, the patient is also prescribed an antibiotic. The average course for the described diagnosis is from five to seven days. It is unacceptable to interrupt it in the middle because the condition has improved - the disease may return.
Local treatment, carried out at home after the dental surgeon has opened the abscess, consists of applying compresses with antibacterial compounds and performing therapeutic rinses. These procedures stimulate regeneration and accelerate tissue renewal.
Who treats an abscess
Only a dentist can cure a tooth abscess. If you suspect an abscess, you should contact your general practitioner. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, schedule a consultation with a dental surgeon.
Preventing a tooth abscess is easier than curing it. To do this, it is necessary to carefully observe oral hygiene, promptly eliminate inflammatory processes in the body, and visit the dentist twice a year. A balanced diet and vitamin-mineral complex products will help compensate for the lack of vitamins and minerals necessary for dental health.
Abscess before and after wisdom tooth extraction
Inflammation can begin to develop literally in any part of the jaw, and quite often it occurs in the area of the wisdom teeth. The destruction of the latter occurs very quickly, since the development of pathology is often facilitated by carious processes caused by poor oral hygiene.
“My wisdom tooth was coming out, along with an abscess. When a dull nagging pain appeared, I decided that it was just a figure eight climbing. But every day the pain intensified, and the gums swelled. I really didn’t want to go to the doctor about it, because I knew very well that I would have to remove it. In general, I went to the dentist only on the third day. They cut my gum, opened the abscess, and installed drainage. The extraction was scheduled in a week - it was necessary for the inflammation to go away. The operation itself was performed under sedation, so I didn’t feel or even remember anything. And with an abscess, the main thing is not to slow down and go to the doctor right away!”
Lyudmila K.N., Chelyabinsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
In most cases, the process of teething and growth of eights occurs incorrectly, which is why neighboring teeth suffer. Therefore, most often, when an abscess forms, removal of the figure eight is prescribed. And even after extraction, there remains a risk of further progression of the pathology, since the open wound becomes an ideal environment for the proliferation of bacteria. Therefore, after the procedure, the doctor must thoroughly disinfect the tissues and prescribe antibiotics.
Reasons for the formation of an abscess
An abscess can occur either due to poor personal hygiene (using someone else’s toothbrush, irregular teeth brushing), or after visiting a dental office, for example, after treatment or removal of a wisdom tooth.
The cause of the appearance of an abscess is bacteria that are found on the surface of the teeth and in the oral cavity. They can appear in the patient’s body during dental surgery if the rules of asepsis (use of non-sterile medical materials) and antiseptics (insufficient anti-infective treatment) are violated.
At risk are not only patients with a pathologically weakened immune system (patients with diabetes and cancer), but also people who have dental problems:
- carious damage, chips, cracks;
- periodontal disease;
- gingivitis.
With chronic tonsillitis, there is also a high risk of developing an abscess, since foci of infection are constantly present in the body.
Abscess after tooth extraction
After an operation to remove a tooth, a purulent abscess may begin in the injured areas of the tissues of the oral cavity, gums and cheeks. An unhealed wound is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria, therefore, in its place or in the depths of a tooth pocket, suppuration quickly forms, which, in the absence of appropriate treatment, can “spill” into the soft tissues.
The cause of an abscess after tooth extraction is most often the patient’s negligent attitude to the doctor’s recommendations. The procedures prescribed by him must be strictly followed, otherwise repeated surgery cannot be avoided.
If you start the process, even strong antibiotics will not help. Therapeutic measures aimed at removing purulent formations consist of opening and cleansing the abscess cavity, followed by anti-inflammatory therapy.
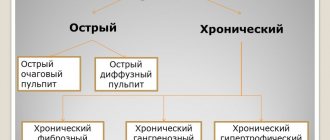
Classification
Depending on the characteristics of the course, there are two types of periodontal abscesses.
- Spicy. They have distinct symptoms. The pain increases sharply. Deep periodontal pockets and tooth mobility are obvious to the dentist. It can reach grade 3. The patient also has a high fever and signs of intoxication.
- Chronic. They are much less common. They have erased signs. Patients complain of bleeding and sore gums. On examination, the dentist sees swollen mucous membranes of a bluish tint, exposed roots, and periodontal pockets with pus. Periodically, chronic abscesses worsen.
Depending on the area of formation, abscesses are distinguished:
- in the apical part or in the middle of the root,
- near the neck of the tooth.
Diagnosis of an abscess
The process of diagnosing an abscess is quite simple. The doctor conducts an examination, during which the strength of hard tissues, the stability of the dental crown, and the presence of dental diseases are checked. At the same time, attention is paid to the patient’s reaction, the location and size of the suppuration.
To obtain a more accurate idea of the course of the inflammatory process, radiography is prescribed. This diagnostic method allows you to eliminate errors when making a diagnosis and establish the depth and extent of the abscess.