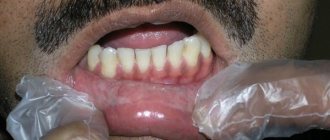
Often, dental patients visit the dentist because a hole appears in the gum near the tooth. Knowledge about the causes of holes in the periodontium and possible treatment methods will allow us to identify the disease at an early stage and cure the disease, preventing the development of complications.
You should know that the appearance of a hole in the periodontal tissue indicates the presence of a serious disease in the oral cavity, and ignoring an unpleasant symptom can lead to infection of the dental root.
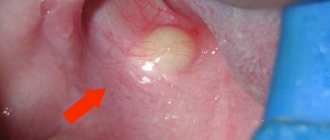
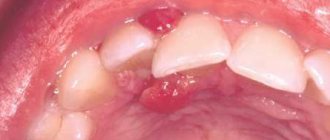
What is a fistula on the gum?
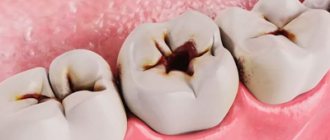
Externally, the pathology looks like a convex edematous formation up to 1 cm in diameter with a white spot or hole in the middle. Its presence indicates an active process with a large amount of pus. There are 2 possible forms of dental fistula:
- External – the classic location of the fistula with access to the gum surface.
- Internal - the exiting end of the fistula tube does not reach the surface of the gum, forming a hidden process that cannot be detected by visual inspection. This option requires an x-ray examination.
The fistula itself is not dangerous - on the contrary, it releases purulent contents from the source of infection, thereby relieving internal pressure on the tissue and, accordingly, reducing the affected area. However, the presence of a fistula indicates a serious purulent process in the maxillofacial region, which is fraught with various complications. The most dangerous of them:
- loss of teeth in the area of inflammation;
- destruction of bone tissue and associated fragility of the jaw bones;
- infection of adjacent structures of the body - sinuses, ears, brain, lymph nodes;
- penetration of infection into the general bloodstream with the development of sepsis.
What folk recipes can you use?
Traditional medicine is rich in a variety of effective ways to combat diseases of various types. If there is a fistula, traditional medicine recipes will not be able to ensure complete elimination of the hole, but will significantly speed up the recovery process. The most common and effective recipes include:
- Herbal infusions. St. John's wort, calendula and chamomile are taken in equal quantities (you can take one herb) - 40 grams - and pour 400 ml of hot water. Leave for 2 hours, filter. It is recommended to wash inflamed areas with the infusion or use it as a rinse 2-3 times a day.
- 10 well-crushed mummy tablets are mixed with chopped onion and a tablespoon of olive oil. The finished mixture is carefully laid out on a clean bandage, folded in several layers, and placed as an application on the inflamed area. The procedure is repeated 3 times a day and lasts 5 minutes. Before performing it, the diseased gum should be treated with disinfectants.
- Mouth rinse. Add a teaspoon of salt and a few drops of iodine to a glass of water. Rinse every day every two hours. The procedure is effective and kills all pathogenic microflora in the area of inflammation.
Symptoms
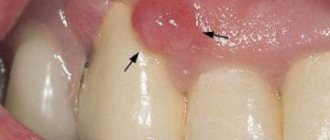
The main symptom of a dental fistula is determined visually and looks like a whitish tubercle or hole on the surface of the gum, through which purulent contents are released. Additional general signs of pathology:
- toothache - can be aching or shooting, worsens with pressure (chewing, brushing), weakens after partial discharge of the exudate;
- unpleasant putrid odor;
- mobility of the problematic tooth - it is provoked by the destruction of the retaining ligaments and purulent melting of the hard tissues of the periosteum;
- hyperemia and swelling of the soft tissues of the gums in the area of inflammation;
- deterioration of the general condition of the body with increased temperature, intoxication of the body, weakness;
- enlargement of adjacent lymph nodes.
Attention! Often, after the bulk of the pus has drained, the discomfort goes away, the fistula heals, and the patient believes that the problem has resolved itself. However, the aggravation of the process is a matter of time. The infection remains inside and at any moment can trigger the formation of a second abscess with an expansion of the affected area. Such relapses are especially difficult to treat.
Causes of a fistula on the gum
The main reason for the formation of a fistula is the presence of an infectious process in the root of the tooth or in the periodontal space. Among the factors contributing to this, several provoking reasons can be identified. Basic:
- Deep caries with pulpitis , its untimely or improper treatment. Without proper therapy, this pathology quickly develops into periodontitis and periostitis with the formation of a purulent infiltrate.
- Chronic form of periodontitis - inflammation from the pulp chamber through the root canals penetrates beyond the apex with the formation of a periapical abscess. The pus affects the bone tissue, grows and, under pressure, forms a sinus tract (fistula) in the direction of least resistance.
- Periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum) – typical for severe periodontitis, complicated eruption of “eights”, injury.
- Chronic periodontitis - in this case, the infection enters the periodontal area not through a carious cavity, but through periodontal pockets. Pathogenic microorganisms destroy the dentogingival ligaments, and accumulations of pus form a periodontal abscess, in the projection of which a fistulous tract is formed.
- Perforations of the root wall - various abnormal holes in the tooth wall can appear as a result of poor-quality endodontic treatment, deep caries, destruction of hard tooth tissues, trauma, etc.
- Inflammation of a granuloma or dental cyst - the pathology can “sleep” for a long time without manifesting itself. All major troubles begin with a weakened immune system.
- Poor quality filling - especially if the filling is not installed hermetically, in violation of the technology, with the presence of pathological cavities in the root apex, etc. The probability of such an error in some clinics reaches 65%.
- Inflammation of tissues during severe eruption of wisdom teeth - develops when injured gum walls become infected with the formation of a purulent abscess.
- Poor fit of the crown or bridge prosthesis - the gap between the tissues and the prosthesis becomes a reservoir for bacterial infection.
- Tooth injuries (cracks and fractures) allow bacteria access to the pulp chamber.
- Oncological diseases in the jaw area, as well as treatment with radio irradiation and chemotherapy - in this case, fistulas can be multiple.
- Violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during dental operations.
A number of additional factors enhance the influence of the main causes. Among them:
- pathologies of the immune system;
- poor oral hygiene;
- severe and constant stress;
- physical and mental overload;
- lack of nutrition, unbalanced diet with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- abuse of sweet and high-carbon foods;
- smoking;
- some malocclusions.
On a note! In rare cases, a fistula may result from an error during implant installation. Poor design, unaccounted for allergies, untreated infections, and poor sanitation can cause pathology.
Perforation of the tooth root
Root perforation is a non-physiological hole that occurs in most cases due to a dentist’s mistake. During treatment, the doctor makes an extra hole in the patient’s mouth, and then forgets to close it with special medical material. Most often, errors of this nature occur when filling canals or inserting pins during prosthetics.
Symptoms of the inflammatory process in the hole made do not appear immediately, but over time they become more acute and provoke a periodontal abscess, leading to the formation of a fistula.
How to treat a fistula on the gum?
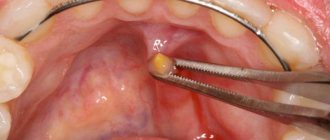
The main treatment is surgical. In addition, a set of conservative techniques is widely used - endodontic, medicinal, physiotherapeutic. Their composition and procedure for use depend on the depth, size, and cause of fistula formation and are selected individually in each specific case.
Surgery
With purulent abscesses, the presence of a fistula alleviates the patient's condition. However, this only creates the appearance of recovery. To completely stop the process, it is necessary to promptly open the purulent cavity, clean out its contents and install drainage for the outflow of pus.
In addition, surgery is used to eliminate some causes of purulent inflammation. In particular, for truncation of the root apex, removal of cysts and granulomas, removal of wisdom teeth, suturing of periodontal pockets and more complex maxillofacial operations.
Endodontic treatment
The procedure for performing the procedure using the example of deep caries:
- the tooth is prepared, access to the pulp chamber is opened;
- open the chamber and root canals, remove the nerves;
- treat the cavities with an antiseptic, prepare the walls for filling;
- completely eliminate the inflammatory process by installing temporary fillings with antibacterial and regenerating compounds;
- obturation of the canals with pins is carried out, permanent fillings are placed under X-ray control;
- restore the coronal part.
Drug treatment
It is used at all stages of conservative and surgical treatment. List of drugs:
- antibiotics – mainly broad-spectrum drugs;
- local antiseptics and painkillers in the form of gels, ointments, injections;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- antihistamines - to eliminate swelling and tissue hyperemia.
Physiotherapy
A set of physiotherapy procedures is an addition to other types of therapeutic interventions. They increase the effectiveness of treatment and have an additional anti-inflammatory, restorative, restorative effect. Basic techniques:
- electro- and ultraphonophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- UHF therapy;
- darsonvalization;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound.
Problems during wisdom tooth eruption
A hole in the gum near the wisdom tooth is often accompanied by the appearance of unpleasant symptoms and the formation of fistulas in the oral cavity. Often, patients begin teething either too late, or the tooth goes in the wrong direction.
An acute process of inflammation begins, and the gums increase in size. The diseased area is additionally damaged by pieces of food and teeth when biting, which as a result leads to infections and increased inflammation. After some time, the inflammation intensifies, reaches the root of the tooth and provokes the formation of a fistula. A photo of a hole in the gum near a wisdom tooth is shown below.
How to prevent fistula?
Basic preventive measures:
- carefully observe the rules of hygiene;
- undergo regular preventive examinations with your dentist;
- treat oral diseases in a timely manner;
- monitor the condition of the body in the presence of chronic pathologies;
- Follow the rules of a healthy diet and lead a healthy lifestyle - this will strengthen the immune system and maintain a high level of regenerative processes.
Remember: the presence of a fistula is evidence of severe inflammation, often chronic. Preventing its occurrence is much easier and simpler than subsequently curing it.
Prevention
Among the preventive measures against the occurrence of periodontitis and gingival fistula, the following should be highlighted:
- improving the quality of individual oral hygiene;
- regular visits to the dental office;
- conducting professional oral hygiene procedures every six months;
- proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
The fistula completes the chain of caries-pulpitis-periodontitis and the next step after it will be tooth loss. Although, even if surgery is indicated, doctors try to do everything possible to preserve it. We must remember that, by and large, a lot depends on ourselves - on whether we sought help from a dentist in a timely manner and how carefully we monitor the health of our oral cavity in the future.