Treatment of periodontitis
If during caries microbes are found in the hard tissues of the tooth, during pulpitis - in the tooth cavity (pulp chamber) and root canals, then during periodontitis - they extend beyond the boundaries of the tooth root.
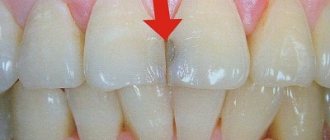
This complication is called periodontitis , i.e. periodontal inflammation. Periodontium - the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth - is the connective tissue that fills the narrow space between the tooth and the bone bed of the jaw (these are ligaments, nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels). The main functions of periodontal tissue are shock-absorbing and nutritional. When chewing food, the periodontium absorbs the load on the tooth and evenly redistributes it to the bones.
When a tooth remains untreated for a long time, there is a risk of a serious complication of caries - periodontitis. First, cariogenic microorganisms destroy hard tooth tissues (enamel and dentin), then penetrate into the pulp chamber, infecting the vessels and nerves located in it and causing pulpitis. When pulpitis is asymptomatic and is not treated for any reason, the inflammatory process deepens and, passing through the canals, extends beyond the root apex.
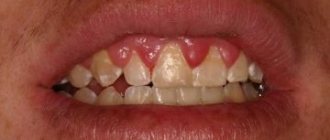
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissues surrounding the root tip. The periodontium itself is a complex of tissues located in the gap between the tooth root and the jaw bone. Behind the root, the infectious process creates a focus of increased pressure, which causes spontaneous pain in the tooth, which sharply intensifies when biting on it. Patients often complain of the feeling of a “grown tooth” or “lengthened root”. Sometimes on the gum, or less often on the skin near the causative tooth, a “swelling” occurs - a fistula, from which contents from the source of infection are periodically released. Under certain circumstances, periodontitis is asymptomatic, without causing pain or complaints; periodic exacerbations of the disease are possible. In any case, the infectious process causes rarefaction (loss) of the bone tissue behind the root, which ultimately leads to the formation of a large cavity in the bone tissue - a cyst.
- Penetration of infection from the root canal through the hole at the apex of the root: untimely treatment of caries or pulpitis;
- poor-quality root canal filling;
- incomplete elimination of foci of infection during the treatment of pulpitis;
According to the nature of the course, periodontitis is divided into acute and chronic.
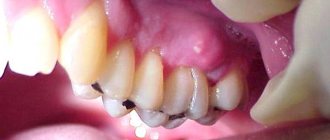
Acute periodontitis is manifested by sharp pain in the tooth area, aggravated by touching it. Swelling of the lips, cheeks, gums is enlarged, the tooth is mobile. Sometimes there is a hole in the gum from which pus flows. This is a fistula, i.e. a channel that has formed to drain contents from an infected cavity.
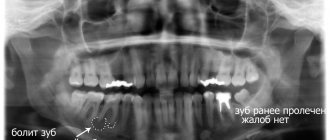
Chronic periodontitis can manifest itself in the form of unpleasant and mild pain (feeling of heaviness, fullness, awkwardness, pain when chewing load on this tooth). Chronic periodontitis may not manifest itself for a long time and may be discovered by chance on an x-ray during the treatment of neighboring teeth.
The first measure in the treatment of periodontitis is to release the impurities that have accumulated behind the roots. To do this, it is necessary to remove the softened carious tissues of the tooth and go through the entire length of the infected canal. Typically, the patient then experiences immediate pain relief. Next, it is necessary to expand the root canal, which contributes to the rapid drainage of infection and recovery of the tooth. Rinses are prescribed, and medicine is placed into the diseased canal. When the inflammatory process behind the root subsides, the tooth canals are filled, after which the coronal part can be restored with a filling.
The photographs can be used to trace the dynamics of bone tissue restoration behind the root of a chewing tooth after high-quality endodontic treatment of periodontitis.
Treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in dentistry
Osteoporosis is a systemic disease, which means its treatment and prevention must also be systemic. Dental treatment is auxiliary, local in nature, but also plays an important role in preserving teeth.
Systemic therapy
Treatment of osteoporosis:
- Physical activity. Dosed load is extremely important for bone tissue growth. For prevention purposes, you need to walk more and do regular exercise. For treatment, a specially developed exercise therapy complex is required.
- Saturation of the body with vitamin D and calcium . For prevention purposes, it is enough to adhere to proper nutrition, consuming about 800–1000 mg of calcium per day and 800 IU of vitamin D. For complex treatment, the addition of medications is necessary. The therapeutic dose of vitamin D ranges from 1000–2000 IU, and the maximum permissible daily dose is 4000 IU. Calcium needs 1200–1500 mg/day. Calcium supplements must be taken throughout the entire course of treatment.
- Drug therapy. It is impossible to do without it in the treatment of osteoporosis. Substances that prevent bone tissue destruction are usually used - bisphosphonates, but other drugs can also be used.
Dental treatment
There is no specialized program for the treatment of osteoporosis in dentistry. The goal of therapy is to slow down the process of demineralization of teeth and ensure their safety. For this purpose, remineralization and fluoridation are used.
Remineralization
Dental remineralization of teeth is a procedure for saturating enamel with mineral elements. Usually these are calcium and fluoride. A mono-procedure is possible when calcium alone is used, but together with fluoride the effect of therapy is higher.
Remineralization can be performed manually, when the doctor sequentially applies solutions of calcium and fluoride to the surface of the teeth, as well as physiotherapy - in this case, the enamel is saturated with calcium and fluoride ions using electrophoresis or phonophoresis.
Fluoridation is a similar procedure, but fluoride acts as a remineralizing agent. Although the percentage of fluorine in human enamel is small compared to calcium, it plays an important role in metabolic processes and the formation of its structure, as well as the absorption of other elements, including calcium.
Fluoridation can be simple or deep, both are performed manually.
Simple fluoridation involves applying a fluoride-containing composition to the surface of the teeth using a brush or a custom-made tray. These are inexpensive and simple procedures, but they only act on the surface of the enamel.
Deep fluoridation is a more complex and expensive technique, but it gives the best effect, since fluoride penetrates into the deep layers of the enamel.
Hygiene procedures
Oral hygiene is very important for the preservation of enamel, and with osteoporosis it becomes especially important. The enamel becomes thinner, which means it is more likely to be destroyed by acids produced by bacteria.
Therefore, it is necessary not only to thoroughly brush your teeth with a brush and floss, but also to professionally clean the tooth surface from hard plaque - tartar, since the enamel underneath softens much faster.
A properly selected set of systemic and local treatment will help stop the development of osteoporosis and maintain dental health.
Treatment result
The inflammation behind the root has been eliminated, the tooth is not bothered, the fistula tract has been healed, tooth mobility has disappeared, chewing has been restored.
During initial root canal intervention, after the cessation of anesthesia, there may be minor discomfort of a short duration, and, if necessary, relieved with mild painkillers. After a permanent root canal, the tooth may be sensitive when eating very hard foods. This phenomenon does not cause much discomfort and goes away after a few days.
Be healthy!
The information was prepared by dentist Smirnov E.S.
The cost will depend on the chosen treatment method, the complexity of the work and the number of canals of the diseased tooth.
The following services may be required to treat periodontitis:
- Anesthesia 300 rub.
- Processing 100 – 300 rub.
- X-ray 250 rub.
- Unsealing the canal 400 – 800 rubles
- Canal filling 800 – 1000 rub.
- Drug therapy of the canal 250 rub.
- Ultrasonic treatment of the canal 250 rub.
- Temporary filling 150 rub.
Total : the average cost of treating periodontitis of a single-canal tooth will be 2100 rubles
See also:
Loss of bone tissue in the hip joint. Mechanical properties of skin and bone tissue. Is it possible to return bone tissue? Increased androgen levels in women are treated with folk remedies. What does bone tissue consist of?
Only with us: Enter promotional code bonus2021 in the coupon field when placing an order until March 31, 2021 and receive a 25% discount on everything!
Diagnosis of osteoporosis
To measure bone density, the densitometry method is used, which is carried out using the following methods:
- X-ray. Allows you to diagnose osteoporosis when up to 30% of the tissue has already been lost. Although it is also used, but more for diagnosing pathological fractures.
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry DXA. Allows you to identify bone loss at the stage of osteopenia, when bone mass has decreased, but there is no osteoporosis yet. The most applicable method.
- Ultrasound diagnostics. Ultrasound waves travel differently through media of different densities, allowing bone density to be diagnosed. The sensitivity of modern ultrasound machines makes it possible to detect a loss of 2–5% of bone mass.
- Quantitative CT or MRI.
Who needs to be tested
A clear indication for examination is pathological fractures, which occur if a person is slightly hurt or falls from a small height.
People from risk groups are also subject to control:
- Women during menopause.
- People 70+ of both sexes.
- Women breastfeeding.
- People with anorexia – a combination of lack of nutrition and low weight leads to an increased risk of the disease.
- Patients chronically taking corticosteroids.
- People with liver, kidney, blood, systemic diseases.
- Persons who were forced to remain in a state of immobilization (immobility) for a long time.
Drinking large quantities of coffee, smoking and alcoholism also lead to osteoporosis.
Bone atrophy - what is it?
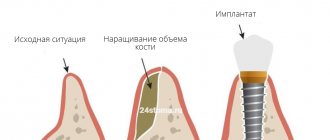
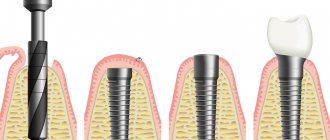
Bone atrophy is the process of a gradual decrease in the hard tissue of the jaw bone, while the size of the alveolar ridge is significantly reduced, pronounced nasolabial folds appear, the jaw decreases in size, and a “drooping” of the face occurs. Bone resorption (loss) occurs most often after surgical removal of the root, but a person can be born with this pathology.
Clinical case: a person’s tooth and root were removed a long time ago, and an implant and prosthesis were not installed in their place. Over the course of a year, bone tissue atrophies by approximately 25%.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment