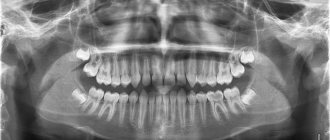
Sometimes people are in no hurry to visit the dentist even when the tooth hurts noticeably. They prefer to endure it by swallowing painkillers. This removes the symptom, but significantly aggravates the cause of the pain – inflammation. And the consequences of such an independent “cure” always lead to a sad and predictable result: destruction of the pulp and purulent processes on the tooth roots.
For what reasons can a tooth root become inflamed?
Despite the availability of many effective methods of therapeutic treatment of inflammation under the tooth root, it is often necessary to resort to the use of surgical treatment methods. This is indicated in the following cases:
- Root canal obstruction was detected
- there is a pin or stump tab that cannot be removed without damaging the root
- there are many cysts - perihilar or growing into the maxillary sinus
- there is a perforation (perforation) of the wall of the tooth root or its cavity
- The use of conservative methods of treating root inflammation does not help
Important:
Most often, periodontitis refers to inflammation in the area of the apex of the tooth root (apical, periapical periodontitis). The cause of tooth root inflammation is untimely treatment of caries and pulpitis. Another type of disease, marginal periodontitis, is classified as periodontology; in this case, the lesion spreads to the gums in the cervical part of the tooth.
Causes of the disease
The roots can become inflamed due to infection, as well as in its absence. The first option is the most common. The second is associated with a jaw injury.
Infection occurs in different ways:
- From the carious cavity, bacteria , bypassing the periodontal pocket, penetrate into the pulp. Then pulpitis develops. Inflammatory reactions spread further, moving to the periodontium and bone.
- With severe gum damage, a deep periodontal pocket forms between the soft tissues and the crown. It must be cleaned and closed. Otherwise, painful microorganisms will penetrate into deeper layers and cause damage to the roots. Severe inflammation will occur.
- Bacteria are able to enter healthy dental tissues through the bloodstream and lymph from an inflammatory focus located elsewhere in the body. In such a situation, doctors talk about the hematogenous and lymphogenous nature of the lesion.
Symptoms and treatment
Periodontitis can be chronic and worsen. The characteristic symptoms that are revealed during examination by a dentist and as a result of anamnesis vary depending on the stage of development of the disease.
Exacerbation of periodontitis is characterized by the following signs and complaints from the patient:
- Regardless of the time of day, you are constantly haunted by a monotonous, equally intense, aching toothache.
- When pressing on the tooth, the pain intensifies
- There is a feeling that the tooth has “grown” - it interferes and does not allow the jaws to connect, since any attempt to do this ends in a painful attack
- The accumulation of purulent contents provokes pulsating pain, radiating along the branches of the trigeminal nerve
- Feeling worse, weakness appears, temperature rises
- Submandibular lymph nodes may become enlarged
Exacerbation may be accompanied by serous and purulent discharge. In case of purulent periodontitis, the doctor is first faced with the task of getting rid of pus: the tooth cavity is cleaned, the canals are treated.
Symptoms of tooth root inflammation in chronic form are not so pronounced:
- The tooth does not hurt constantly, but when pressing, unpleasant pain occurs
- A fistula may occur with frequently exacerbating granulating periodontitis. In this case, under the influence of exudate, the tissues “melt” and the exudate exits through a hole in the gum located in the area of the root apex. In the remission stage, such a formation looks like a changed area of the mucous membrane
- The presence of bad breath (halitosis) is also a sign of chronic apical periodontitis. Microorganisms that cause caries contribute to the destruction of hard tooth tissues, enter its internal cavity and provoke tissue death in the pulp, which leads to the accumulation of necrotic masses, which are the main factor of halitosis.
The chronic form of tooth root inflammation is treated conservatively in most cases; only in the most advanced cases is surgery prescribed. Modern standards of all medicine and dentistry in particular consider any disease comprehensively, that is, they do not treat fistulas, cysts or granulomas separately. In the treatment of tooth root inflammation, antibiotics, painkillers and other medications are used.
Tooth structure
The tooth consists of two parts. 1 - The top part of the tooth - the crown, which is visible in the mouth and 2 - the root of the tooth, which extends into the jaw bone to support the tooth in the desired position.
Teeth also consist of:
- enamel - hard outer coating
- dentin - the softer material that supports the enamel and forms the majority of the tooth
- pulp is the soft tissue in the center of the tooth, consisting of nerves, blood vessels and lymphatic vessels.
The root canal system contains the pulp of the tooth and extends from the crown of the tooth to the end of the root, its apex. One tooth can have more than one root canal.
Relieve pain before going to the doctor
For any form of periodontitis, it is necessary to make an appointment with a doctor, but often the aching tooth “does not want” to wait for the appointed time and hurts unbearably. Taking a pain reliever will help relieve the condition. For toothache, experts advise taking medications that are most optimal for such cases. The pill will not cure, but it will relieve the pain. This does not mean that you can postpone a visit to the doctor - after the pill wears off, the pain will return, so a trip to the dentist should not be postponed or put off “for later”.
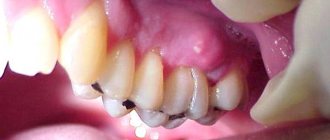
Abscess on the gum with periodontitis -
Gum suppuration can look completely different, but in any case, the formation of an abscess on the gum always occurs in the projection of the causative tooth. If the cause of suppuration is an infection in the root canals, then you will always see an old filling or crown on the causative tooth, or the tooth will be partially destroyed. In this case, infection in the root canals gradually leads to the development of a focus of chronic inflammation at the apex of the tooth root.
In dentistry, such inflammation of the tooth is called chronic periodontitis. From time to time, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation may occur, and in this case, pus begins to form at the apex of the tooth root, which comes out through the bone tissue and penetrates under the gum, forming an abscess there. Therefore, please note that with periodontitis, an abscess on the gum often forms not at the gingival edge, but closer to the projection of the apex of the root of the causative tooth.
Abscess on the gum with periodontitis: photo
Symptoms -
An abscess with periodontitis may look like a slight swelling of the gums in the area of 1 tooth or in the area of several teeth if a significant purulent abscess has formed - flux (Fig. 4). Typically, the appearance of gum swelling is preceded by pain when biting one of the teeth. The pain can be acute, but sometimes purulent inflammation can occur without pain. Sometimes, in the projection of gum suppuration, swelling of the soft tissues of the face appears.
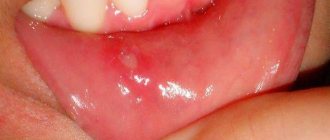
The abscess formed under the mucous membrane of the gums can burst with the formation of a fistula opening (Fig. 7-8). The fistula opening is connected through a fistulous tract to the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Therefore, gradual discharge of pus may be observed from the fistula openings. As soon as the acute inflammation at the root apex subsides and the process of pus formation stops, the fistula openings can close, but only until the process worsens again.
X-ray diagnostics -
If you have a fistula or a purulent sac on your gum, treatment is only possible at the dentist. Before starting treatment, you need to take an x-ray to confirm the presence of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (24stoma.ru). The image will also show the quality of root canal filling, if it was performed previously. It’s sad, but according to official statistics, dentists fill root canals poorly in as many as 60-70% of cases.
The most common mistake dentists make is not filling root canals up to the apex of the tooth root, as a result of which infection begins to multiply in the part of the root canal that is not filled with filling material. As a result, a focus of chronic inflammation develops at the apex of the tooth root, for example, in the form of a cyst or granuloma. Below you can see what cysts and granulomas look like on a diagram, an x-ray, and also on the apex of the root of an extracted tooth.
Treatment of gum suppuration during periodontitis -
If, against the background of an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, an abscess appears on the gum, then what to do will depend on the results of examining the tooth and analyzing the x-ray. In some cases, it may turn out that the tooth can no longer be treated, and then you will be referred to a surgeon for removal. However, in most cases, it is possible to cure such a tooth, and then the doctor’s algorithm for further actions will depend on whether root canal filling was previously performed in this tooth.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis with fistula
The inflammatory process can occur with complications, one of them is odontogenic fistula. More often it occurs with granulating periodontitis. These are holes in the mucous membrane, formed as a result of the proliferation of granulations and destruction of the tissues surrounding the tooth. Through the resulting fistula, pus is released, which is formed during inflammation under the root of the tooth.
To some extent, the resulting fistula helps to reduce the pain experienced by a person: the purulent contents do not linger in the tissues, but come out, easing the course of the disease. But you should not delay the examination by the dentist and the appointment of treatment - this is fraught with tooth loss.
The fistula will not disappear on its own; it is necessary to remove the cause that caused it – inflammation in the periodontal tissues. The treatment regimen for root inflammation is standard in all cases:
- thorough mechanical cleaning of the canals
- carrying out disinfection
- temporary filling with a drug until inflammation in the periodontium disappears
In particularly advanced cases, overgrown granulations are surgically removed.
Oral diseases in which the roots become inflamed
Among the most common dental ailments that can destroy dental canals:
- Advanced caries, pulpitis. With a huge carious cavity, destruction and damage to bone structures can never be ruled out.
- Poor oral hygiene. If basic hygiene rules are violated, the gums become inflamed and the enamel becomes weak. This creates the preconditions for more serious problems.
- The presence of a granuloma or cyst at the base of the root. In the picture you can see a rounded neoplasm. There is liquid inside it. Therapy is carried out surgically. There is no other way to remove the cyst. As soon as the treatment is carried out, the inflammatory process in the remaining roots will subside.
- Poorly performed dental treatment. A filling that does not fit tightly to the walls, mediocre cleaning of the canals, cracks/fractures of the root - all these are factors that provoke inflammation.
- Recession of gingival tissues. With it, the neck of the tooth is exposed and ceases to be reliably protected. Then its sensitivity to the negative effects of bacteria increases.
With any of these diseases, there is an excellent chance of saving the tooth. The main thing is to start the fight for a healthy smile as early as possible.
Treatment methods
As already noted, in modern dentistry, preference is given to conservative treatment. However, it is often impossible to fully treat tooth root inflammation without surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment
This is a complex methodology that includes several types of activities:
- mechanical cleaning of channels
- disinfection of canals using medications
- Temporary filling with medication
Conservative therapy includes the prescription of antibiotics for inflammation of the tooth root.
Surgery
Involves the operation:
- removal of 1/3 of the root tip
- removal of part of the root (hemisection)
- removal of a tooth from the dental socket
Important: Doctors try to save teeth using all conservative treatment methods available today, since they are successful in 70-90% of cases.
Why gums fester: reasons
1) With exacerbation of chronic periodontitis -
infection in the root canals leads to the formation of a focus of purulent inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Depending on the type and size of such lesions, dentists call them by terms: granuloma, cyst or granulating periodontitis. You may not be aware of the presence of such foci for years, but sooner or later an exacerbation of chronic inflammation occurs, and then pus-filled abscesses form in the projection of these foci on the gums (Fig. 1-2).
2) Against the background of gum inflammation (periodontitis) -
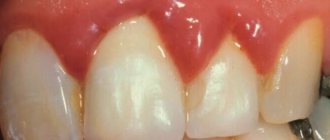
in slightly less than half of all cases when the patient’s gums near the tooth fester, the cause is a local or generalized form of periodontitis. Despite the fact that the causes of these two forms of periodontitis are different, the common thing is that the formation of a purulent abscess occurs in a deep periodontal pocket formed between the gum and the surface of the tooth root. Below you can see what an abscess on the gum looks like during periodontitis (Fig. 3).
The causes and treatment of an abscess on the gums will always be interconnected, and therefore, depending on the background of what disease (periodontitis or periodontitis) the suppuration occurred, either treatment of the root canals and the source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root will be indicated, or treatment of the periodontal pocket using anti-inflammatory therapy , curettage and other methods. Below we will discuss in detail the treatment of gum suppuration in both cases.
Stages of periodontitis treatment
How many times you will have to come to the doctor to treat inflammation at the root of the tooth depends directly on the form of the disease, in remission or during an exacerbation. The course of treatment is also influenced by the method chosen by the doctor. Often, therapy requires a course consisting of several stages of treatment and a visit to the dentist. Until the inflammatory process is eliminated, the tooth cannot be filled, so you will have to visit your doctor several times:
- Preparatory stage. Diagnosis of the condition of the tooth root using x-rays
- When removing the old filling, the tooth is drilled to open access to the canals and remove the nerve
- Channels are expanded to the required size
- Treating the canals with antiseptic drugs and applying medication
- A temporary filling is installed
- At the next visit, the temporary filling is removed and the canals are treated with antiseptic. This stage can last for weeks, or even months - the process will be repeated until the inflammatory focus is completely eliminated and the number of visits will depend on this
- A permanent filling is placed and x-rays are taken again for control.
In addition to the procedures performed in the clinic, the patient must undergo antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy. At home, he should do warm rinses with special antiseptic solutions (herbal, medicinal - as recommended by a doctor).
Diagnosing granuloma on a dental photograph
Since the nodule appears deep in the tissue near the root, it is very difficult to determine its presence in the early stages. At first, it will not appear externally as swelling or redness. You can see the symptoms only when the spread is strong enough, when purulent exudate begins to accumulate. It is best to recognize the presence of a problem at a stage when treatment can still be effectively carried out using x-rays or radiovisiography. In the photographs, the disease looks like a dark round spot. The tumor can have different sizes - from 0.1 to 1.2 cm.
The specialist recognizes the presence of the disease at the initial stage when healing adjacent incisors, canines or molars.
At a more advanced stage, you can find out how dental granuloma is treated by diagnosing the following symptoms:
- Acute pain, especially when pressed. Painful sensations also worsen when suffering from infections.
- Swelling, redness and hyperemia of the mucous membranes.
- Pus that flows out when you press on an area of the gum.
- The enamel takes on a darker shade.
- Dizziness begins.
- Enlarged lymph nodes - this does not happen often.
However, symptoms may indicate several other dental diseases. Therefore, the doctor is able to determine the formation of a purulent root node solely by x-ray.
Prevention
- Preventing any disease is easier than treating it afterwards. This is a true statement, so regular dental checkups should become a good habit. If you live in St. Petersburg, Krasnodar, Novorossiysk or Moscow, then you can contact any of the branches of the INTAN dental network for the best qualified help
- Also, timely treatment of caries and pulpitis will help to avoid periodontitis and its attendant complications. The cost of treating them will be higher and more time will be required.
- In case of acute inflammation at the root of the tooth, a quick visit to the doctor and timely treatment will relieve complications and prevent the process from becoming chronic.
- If caries is detected at any stage, you need to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible, undergo an examination and prescribed treatment (remove damaged tooth tissue, filling)
- Compliance with hygiene rules (brush your teeth twice a day with a properly selected brush and toothpaste, use dental floss)
- Diet is important. Dairy products and protein-rich foods, fresh vegetables and fruits should always be on the table. Minimize the consumption of sugar-containing foods and sweet carbonated water.
- Visit your doctor every six months for a check-up and professional teeth cleaning
Following simple rules for oral care will help you avoid inflammation of the tooth root and all the troubles associated with it.
Diagnosis of pathology
For any manifestations of pain and discomfort, you should contact a specialist as soon as possible. Only a qualified doctor can correctly diagnose and identify the exact cause of the problem. If a patient comes with a complaint of aching pain in the teeth, a number of standard diagnostic procedures are first performed:
- visual examination of the oral cavity using a probe;
- tracking reactions to temperature stimuli;
- X-ray examination, which can reveal the presence of hidden problems and complications (granulomas, cysts, etc.).
If the pain and aches in the teeth are not directly related to dentistry, the attending physician refers the patient to other specialists. Most often this is a neurologist and maxillofacial surgeon. The localization of pain also helps to determine the root cause.
- Local.
Aching pain covers one or more teeth. This is usually associated with injuries and dental diseases. In some cases, this is a consequence of infectious diseases. - Generalized.
The entire dentition “aches.” The reasons why all teeth ache are usually associated with pathologies and diseases of the enamel.
The teeth of the lower jaw often ache more (especially the front incisors). In many people, they react more strongly to temperature changes, chemical irritants and inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, when pain responds in the anterior part of the lower jaw. On the other hand, the answer to the question why the lower teeth ache is exactly the same as in the case of the upper teeth: there are no separate reasons.
How to rinse your mouth if you have a tooth pulled out -
As you already understood, antiseptic mouth rinses are not mandatory. If the tooth was removed in the absence of purulent inflammation, if you have good oral hygiene and there are no untreated carious teeth, you can do without them altogether, simply rinsing your mouth with clean water after eating. Or, if you wish, you can rinse your mouth with regular herbal mouth rinses or fluoride solutions, because. they also have a weak antiseptic effect.
But if the tooth was removed due to inflammation, or you had a complex tooth extraction involving an incision in the gums and sutures, stronger rinses are needed. We will discuss in detail what to rinse after tooth extraction in these cases in the description of the following medications.
1) Chlorhexidine solution 0.05% (instructions) –
This drug has a fairly good antiseptic effect, is sold without a prescription, and its cost is only about 30 rubles. Has a slightly bitter aftertaste. After tooth extraction, rinsing with chlorhexidine should be done 3 times a day (each time the solution should be kept in the mouth for about 1 minute). And we remember that you cannot do active rinsing movements, only weak rinses and baths.
There is also another popular antiseptic, Miramistin, which costs many times more and is slightly inferior in antiseptic effect to chlorhexidine. The only advantage of Miramistin is its antiviral activity, which is important for stomatitis, but not after tooth extraction. In addition, after rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine, a thin indelible film of chlorhexidine bigluconate is formed on the surface of the oral mucosa, which will continue to exert its antiseptic effect for another 2-3 hours.
2) Soda-salt baths –
It is preferable to do rinses and baths with soda or salt only if, in addition to tooth extraction, you have had a gumboil (purulent gum abscess) opened. After making the incision, the doctor additionally inserts a glove rubber drain into it so that the edges of the incision do not stick together and purulent exudate flows out of the wound. Soda-salt baths will allow you to better draw out purulent exudate from the wound. They can be done 4-5 times a day.
But keep in mind that if you have drainage, you still shouldn’t do active rinsing movements, because... in addition to the loss of a blood clot from the socket of an extracted tooth, this can also lead to the loss of drainage from the wound. In addition to salt baths, in this case it is also recommended to periodically rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine solution 2-3 times a day.
3) Rinse aid “Parodontax Extra 0.2%” –
This rinse contains a higher concentration of the antiseptic Chlorhexidine - 0.2%, which will mean a significantly more pronounced antiseptic effect than regular chlorhexidine with a 0.05% concentration. This drug makes sense to use if you had a traumatic, complex removal with sutures or additionally opened a purulent abscess on the gum.
Rinses (baths) with this drug are carried out only 2 times a day, and it can be used for no more than 10 days. Although after a simple simple removal, antiseptic rinses are usually necessary for only 3-4 days, and after a complex removal - for 7-8 days. The cost of the drug is from 230 rubles per 300 ml bottle.
4) Rinse aid “PRESIDENT Antibacterial” –
This rinse also contains 0.2% chlorhexidine, but in addition it has high concentrations of anti-inflammatory components (mallow, chamomile and echinacea extracts). Accordingly, this drug will be good after a difficult removal with sutures or after opening a gum abscess. It will quickly relieve inflammation and speed up wound healing. A 250 ml bottle costs from 200 rubles.
5) “Stomatofit” (in the form of a solution) –
This is a concentrated solution of medicinal plants, which is diluted with water before use. It contains a high concentration of extracts of chamomile, sage leaves, oak bark, calamus root, common thyme, peppermint, and arnica. It has a good anti-inflammatory and weak antiseptic effect. Will speed up healing.
Pus in the gums with periodontitis -
Very often, the patient’s complaints that his gums near the tooth are festering are not associated with inflammation at the apex of the tooth root during periodontitis, but with the formation of periodontal pockets in local or generalized forms of periodontitis. With periodontitis, there is destruction of the attachment of the gingival margin to the necks of the teeth, destruction of the alveolar bone around the teeth, as well as periodontal fibers, with the help of which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue.
All this leads to the formation of so-called periodontal pockets between the gum and the surface of the roots of the teeth (Fig. 14). They create good conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the development of chronic inflammation. When one of the periodontal pockets becomes too deep, this can lead to disruption of the discharge of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate through the lumen of the pocket. As a result, an abscess forms in the projection of the periodontal pocket on the gum, which dentists call the term “periodontal abscess” (Fig. 15-16).
You can immediately suspect that gum swelling is associated with periodontitis, and not with periodontitis, if the tooth is completely intact (i.e., externally healthy and does not have a filling, crown or caries), if it has mobility, and mobility was present in this tooth and before the gums become suppurated, and also if, with slight gentle pressure on the abscess, pus comes out from under the gums (as in Fig. 16).
Differences between local and generalized periodontitis -
they are caused by completely different reasons and, accordingly, the treatment will also differ. With local periodontitis, the inflammatory process occurs only in the area of 1-2 teeth - due to exposure to a traumatic factor. For example, a pocket may appear as a result of trauma to the gum margin by the overhanging edge of a filling or crown. The cause may also be the premature closure of several teeth, which leads to chewing overload and destruction of the bone tissue around them.
But with chronic generalized periodontitis, gum suppuration occurs for other reasons. You can immediately suspect this form of periodontitis if you have symptoms of bleeding and pain when brushing your teeth, swelling, redness or bluishness of the gum margins in the area of most teeth. The cause of generalized periodontitis is soft microbial plaque and hard tartar that accumulate on the teeth as a result of insufficient oral hygiene.
Bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins and various pathogens that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. With prolonged inflammation, first the dental-gingival attachment is destroyed, and then the periodontal fibers and bone tissue around the teeth are destroyed. With this form of periodontitis, pockets are found in almost all teeth, and not just in 1-2 (as with local periodontitis). When the outflow of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate in one of the pockets is disrupted, a periodontal abscess forms in the gums.