From this article you will learn:
- what is deep caries,
- its differences from other forms of caries,
- stages of treatment of deep caries.
Deep caries is a designation for a type of dental caries, the peculiarity of which is that between the dental pulp (neurovascular bundle) and the bottom of the carious cavity only a very thin layer of healthy hard dental tissue remains. In other words, this is an advanced type of caries, the lack of treatment of which in the near future will lead to the development of pulpitis and, accordingly, the need to remove the nerve and fill the root canals.
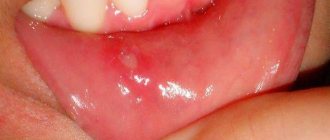
This form of caries is distinguished by the presence of a deep carious cavity, which is filled with decay of hard tooth tissue and food debris. Due to the fact that the nerve is separated from the carious cavity by only a thin strip of healthy dentin (Fig. 1), patients usually complain of pain from exposure to thermal irritants. Therapy for deep caries is somewhat different from the treatment of other forms of the caries process (for example, superficial and medium caries) - which we will describe in detail and show on video in our article.
Deep caries: photo
In the absence of immediate treatment, this can lead first to the development of pulpitis (inflammation of the dental pulp), and then periodontitis. With periodontitis, inflammation extends beyond the dental pulp, which is accompanied by the appearance of a purulent sac (periodontal abscess) at the apex of the tooth root.
Definition of the concept in dentistry
Deep caries is the last stage of the carious process occurring in the tooth, which is characterized by extensive damage not only to hard tissues, but also to the deep layers of dentin. In general, the concept of “deep caries” reflects the depth of the lesion.
Caries can be:
- primary - a consequence of untreated secondary caries;
- secondary (recurrent) - the occurrence of a carious process under a filling in a previously treated tooth.
Based on the sensation of pain and clinical examination, the disease is divided into 3 forms:
- Acute form. It is determined by the narrow entrance opening of the carious cavity and the wide base (during examination), as well as by descriptions of the patient’s sensations - reaction to food temperature and chemical irritants.
- Chronic form. It is characterized by a wide (funnel-shaped) inlet and a narrow base. The patient feels pain when the “hollow” is clogged with food and during examination with a probe by the dentist.
- Deep cervical caries. It is characterized by the development of demineralization of enamel tissue and the carious process in the cervical area of the tooth (near the gums).
According to the clinical course, caries is also divided into several forms:
- compensated,
- subcompensated,
- decompensated.
CLASSIFICATION OF CARIES
In our country, two clinical classifications of caries are used:
- Classification of caries according to I.G. Lukomsky (1949).
- Carious spot.
- Superficial caries.
- Average caries.
- Deep caries.
- According to the international classification of diseases (IBC-10 3rd edition WHO, 1997), caries is divided into:
- K02.0 enamel caries (stage of white [chalk] spot, initial caries);
- K02.1 dentin caries;
- K02.2 cement caries;
- K02.3 for suspended caries;
- K02.3 Odontoclasia;
- K02.8 Other dental caries;
- K02.9 Dental caries, unspecified
Despite the apparent differences, these classifications have much in common. Enamel caries, according to WHO, corresponds to caries in the spot stage and superficial caries. Dentin caries corresponds to medium and deep caries. It is important to note that dentine caries has two courses - the acute course of dentine caries and the chronic course of dentine caries.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, diagnostics are carried out, which include:
- external inspection using a mirror;
- instrumental examination using a probe;
- voicing symptoms (complaints) by the patient;
- thermal diagnostics (checking the reaction to cold and hot);
- electroodontic diagnostics (testing the reaction to exposure to current);
- radiography (performed if the presence of secondary deep caries is suspected or to exclude it).
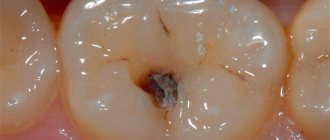
If upon examination significant damage (destruction) of the tooth crown is detected, expressed by the presence of a deep carious cavity and accompanied by pain during probing, then this confirms the presence of deep caries in the patient.
In the acute form, the carious cavity is filled with light, softened dentin. In chronic deep caries, the walls and bottom of the cavity are filled with a layer of dense pigmented dentin (from brown to black). Percussion of the tooth is not accompanied by pain.
Pain relief methods
Local anesthetics used in modern dentistry are divided into two types - ether and amide drugs.
- Essential drugs:
— Procaine (Novocaine) is the oldest anesthetic (synthesized in 1898) with a wide range of applications, capable of anesthetizing procedures for 30–60 minutes;
— Benzocaine (Anestezin) is a drug discovered in the same 1898, characterized by a short-term effect - up to 20 minutes.
- Amide drugs:
— Lidocaine (Xylocaine) is a more modern drug (invented in 1943), which has a strong anesthetic effect for 75 minutes or more;
— Articaine (Ultracaine) is a very popular drug in modern dentistry, discovered in 1978. It is characterized by a strong analgesic effect and acts immediately after administration for 1 to 5 hours.
When choosing an anesthetic, the patient should take into account the presence of chronic diseases and allergies. For example.
- If you have bronchial asthma or frequent allergy attacks, you should choose medications that do not contain preservatives.
- For diabetes mellitus or thyroid diseases, use medications without vasoconstrictor components.
- For cardiovascular diseases or high blood pressure - drugs with adrenaline (epinephrine).
Important! Before starting treatment, be sure to notify the dentist about the presence of diseases and allergies, so that the specialist has an idea of your health and chooses the right anesthesia.
Will it hurt when injected into the gum?
Very little. You will feel a slight pain when the soft tissue is punctured. To administer the injection, special carpule syringes with the finest needle are used, so the pain is minimal. Prepare for the fact that the drug will be administered for a relatively long time - within 1 minute. Slow administration of the anesthetic is necessary, which makes the procedure painless.
Can anesthesia be used for pregnant women and children?
Can! Modern drugs have an exclusively local effect, which does not extend to the fetus and does not harm the body as a whole. This has been proven by recent studies by European specialists and doctors of the American Dental Association.
Important! You should not delay caries treatment during pregnancy. An affected tooth is a source of serious infection. It can enter the mother's bloodstream and reach the fetus. Its spread can only be stopped by localizing the pathological process and proper treatment.
What are the differences from other forms of the disease?
Deep caries is very similar to some forms of the disease, but there are still visible and invisible differences.
Difference from pulpitis
Pulpitis is a complication of advanced caries. The forms of the disease can be distinguished from each other by their characteristic symptoms:
- Defeat. With pulpitis, the nerve is affected; with caries, the nerve remains unharmed.
- Feelings of pain. With pulpitis, pain can occur spontaneously, even without exposure to irritants on the tooth. With caries, pain disappears along with the disappearance of irritants.
- Night sleep. With pulpitis, sleep can be disturbed due to severe pain; with caries, the tooth does not hurt at night.
Difference from average caries
The similarity between the two forms of the disease is that the patient in both forms feels pain from cold, sour or sweet foods. However, with average caries they go away within 1-2 minutes, with deep caries they last longer.
Medium caries is characterized by the fact that in this form the carious lesion does not affect the tooth pulp and does not cause inflammation of the nerve, as in deep caries.
Why do we feel pain during caries?
Caries is insidious. Starting completely painlessly, it inevitably progresses. Penetrating deeper, it affects and destroys the hard tissues of the tooth, reaching the border of the pulp - loose connective tissue penetrated by blood vessels and nerves. The pulp has very good innervation and reacts to the slightest external stimuli - cold, heat, sour, salty, sweet, etc. And the deeper the caries penetrates, the thinner the border between the affected tissue and the pulp, which immediately reacts to the irritant with severe pain. It can be short-term, constant, throbbing, aching, and eventually become unbearable.
Important! Healthy teeth don't hurt. If you experience symptoms of pain, contact your dentist immediately. Don't expect the pain to go away on its own. You will simply waste precious time, risk your own health and may lose your tooth.
Stages of treatment
Treatment of deep caries is impossible without anesthesia (pain relief) and it takes place in several stages.
- Anesthesia. It is carried out using injection (infiltration or conduction) administration of an anesthetic substance.
- Drilling out a carious cavity using a drill. In this way, the specialist can reach and remove all affected areas of dentin, which is very important to prevent relapse under the filling.
- Treatment (disinfection) of the walls of the tooth and the bottom of the cavity.
- Installation of a therapeutic insulating pad and temporary or permanent filling.
- The final stage involves grinding and polishing the filling.
The following factors influence whether a filling will be installed - temporary or permanent:
- at what distance from the pulp is the carious cavity located;
- parameters of dentin, which separates the pulp from the tooth cavity;
- degree of pain.
If there is a high probability of inflammation developing in the pulp area, the dentist will place a temporary filling. And only if there are no complaints of pain and discomfort for several days, the patient will have the temporary filling replaced with a permanent one.
TREATMENT OF MIDDLE DENTIN CARIES
For the treatment of middle dentin caries, the following scheme can be used - a treatment plan, omitting the collection of complaints and anamnesis, diagnosis and differential diagnosis:
- Choosing the color of the future restoration and the material from which it will be made
- Anesthesia;
- Tooth isolation;
- Preparation using a turbine tip and micromotor, air-water cooling, intermittent movements to prevent overheating and thermal burn of the pulp;
- Antiseptic treatment of the bottom of the tooth cavity;
- Preparing the tooth cavity for packaging the selected material.
- Placing a filling;
- Occlusion check;
- Grinding, polishing.
- Recommendations for the patient.
For the treatment of dentin caries, depending, of course, on the location of the cavity, on the condition of the patient’s oral cavity, his wishes and financial capabilities, the following filling materials can be used:
- Amalgamma;
- Glass ionomer cement;
- Chemically cured composite materials;
- Composite materials are photocurable;
- Dual-curing composite materials;
- Compomers;
- Ormokers.
Deep caries of the front teeth. What are the differences in treatment?
Deep caries of the front teeth should be treated as carefully as possible so as not to burn the pulp. The main difficulty in treatment is:
- minimum thickness of all tooth tissues;
- inconvenient location of the cavity, if we are talking about caries located in the interdental space.
When infection penetrates into the pulp, pulpitis develops rapidly. A few hours is enough. The disease is accompanied by increasing pain. It needs to be treated immediately.
Tooth structure and types of carious lesions
A tooth consists of several parts. On top it is covered with hard mineralized enamel, underneath there is dentin, and even deeper - the root of the tooth and pulp. Caries is a pathological process that is accompanied by demineralization and softening of hard dental tissues with the subsequent formation of a carious cavity. The process can affect any part of the tooth; depending on this, caries of enamel, dentin or cement is distinguished.
Carious lesions of the enamel are characterized by symptoms such as softening, the appearance of a white or brown spot, roughness, and sometimes the carious cavity is located in the enamel. If the lesion affects the bone tissue of the tooth, which makes up its bulk, in this case we speak of dentin caries. This form of lesion is characterized by the formation of a carious cavity directly in the dentin.
Cement caries affects the root of the tooth and contributes to its exposure. It often occurs with gum disease, when there is no close contact between the tooth and the gum.
Is it possible to treat deep caries of a wisdom tooth?
The patient can make the decision to remove a wisdom tooth if pain occurs on his own. But only a highly qualified dentist can make a verdict on its treatment.
Treatment of a carious "eight" is considered rational if it has a partial covering in the form of a hood of gum, as well as an antagonist - the third molar located on the opposite side.
Removal shown:
- with a horizontal tooth position;
- presence or absence of 1st and 2nd molars;
- impossibility of treatment due to incomplete opening of the mouth;
- displacement of teeth in a row due to wisdom teeth.
What symptoms should you consult a doctor for?
A visit to the dentist is a mandatory event that should be carried out annually - 1 - 2 times a year. If you notice the following signs, you should contact the clinic immediately.
- The presence of light or dark spots on the surface of the tooth.
- The appearance of sensitivity to cold, hot, sour, sweet, salty.
- Tooth pain when biting food.
- Minor or severe pain in the tooth.
Important! If caries is detected, do not refuse treatment - this risks the development of serious complications and tooth loss. After it is done, try to follow all the dentist’s recommendations.
Will it hurt when I get an injection in the gum?
To administer the anesthetic, special carpule syringes with a very thin needle are used, which minimizes discomfort during the injection. The drug is administered quite slowly, over 40-45 seconds.
In most clinics, before the injection, so-called topical anesthesia is performed using a special anesthetic gel or septic tank. In this case, the specific area of the mucous membrane to which the composition was applied is anesthetized. In this case, the needle entry will be painless.
Complications
Teeth do not heal on their own. In any case, you will have to see a doctor, but it is better to do this as soon as possible. If it so happens that for some reason you have delayed this process, be prepared for the fact that caries will turn into pulpitis or periodontitis.
The pain in such cases becomes unbearable - throbbing, pulling, almost incessant. At a certain point, the patient will not even be able to tell which tooth hurts, since the pain can take over the entire jaw and radiate to the eye, ear, and temple.
Types of damage
Before you find out how caries on the front teeth is treated, you need to understand to what extent it has developed. There are several types of the disease based on the scale of spread:
- Superficial (shallow damage to tooth enamel). Usually at this stage the patient does not yet experience discomfort.
- Average. Slightly affecting contacts and causing aching pain when sugar enters.
- Deep. At this stage, the dentin (the main part of the incisor) is damaged.
- Radical. Here, the carious formation is already difficult to eliminate without complete removal.
- Atypical. It first affects the cutting edge as a result of heredity, smoking or poor nutrition.
Before understanding how to treat cervical caries on the front teeth and whether it hurts, the doctor needs to determine at what stage the disease is.
If the dentist does not do this and only carries out superficial work without completely cleaning the canals, then in the future a cyst may form in the jaw. And it will already be necessary to remove it with the help of surgical intervention, until the pathology has grown to the brain. The sooner treatment begins, the less pain the patient will feel, so it is better not to put off going to the doctor until tomorrow.
Is it possible to determine the onset of the disease yourself?
In most cases, it is not possible to notice the problem at an early stage of its development. Most often, caries occurs in hard-to-reach places (between the teeth or on their back surface).
But sometimes they show specific signals that there is trouble with the incisors:
- when there is a sharp change in temperature, short-term pain occurs;
- sometimes the uneven edges of a carious cavity can be felt tactilely, using the tongue;
- a specific odor appears from the mouth, especially in the morning before meals;
- a dark spot becomes noticeable.
It is important to understand that such signs are not always present, and only a doctor can determine the onset of the disease. It has all the necessary tools and devices for high-quality diagnostics. Therefore, you should not neglect a visit to the doctor and check in time whether everything is in order.
Description of the pathological process
Its occurrence is provoked by cariogenic microorganisms, streptococci and lactobacilli (some types of them), which appear due to insufficient oral hygiene. Typically, bacteria begin to multiply in plaque, which is difficult to clean with a brush (most often on the back surface of the incisors). The carious area is difficult to notice on your own, especially in the early stages, since darkening begins to appear only when the area is already very widespread. That's why regular checkups with a dentist are so necessary - only he can carefully examine the entire oral cavity using a small mirror or take an x-ray.
Sometimes people wonder: “can children have caries on their front teeth?” Unfortunately, yes, it is also called “bottle” or “carob”.
It occurs in a small child if he often eats sweets (baby formula, cotton candy, candy, etc.). Such products contain a large amount of carbohydrates, which quickly destroy fragile tissues.
You also need to be careful with breast and cow's milk. It often sticks to the teeth in the upper jaw when children accidentally fall asleep with a bottle in their mouth. This product also contains sugar (albeit natural), and it quickly oxidizes and destroys the enamel. During sleep, this is especially dangerous due to the fact that the intensity of salivation, which is created for self-cleaning of the oral cavity, decreases. You can see the result of the defeat in the photo.
Ultracaine
French drug, available in 1.7 ml carpules in three forms:
- Ultracaine DS forte
– containing 1:100,000 epinephrine. A highly effective anesthetic for operations and treatment of pulpy teeth. Not recommended for patients with thyroid diseases and cardiovascular pathologies. - Ultracaine DS
- with an epinephrine concentration of 1:200,000. Ideal for pain relief in pregnant and lactating women and patients with compensated cardiovascular diseases. - Ultracaine D
– without adrenaline/epinephrine. Used when there is a high risk of allergic manifestations. Can be used by patients with bronchial asthma, cardiovascular pathologies, and thyroid diseases.
The drug can be used starting from the age of four.
Caries in the spot stage
Initial stage of caries. Characterized by the appearance of spots on the enamel. In the demineralized area, damage to the enamel structure is observed. As a rule, patients cannot detect it themselves.
The spot may be white or pigmented. If a brown or black stain is easy to notice, then a coated stain can only be diagnosed using an aqueous solution of methylene blue.
Important. With timely treatment, remineralization therapy can be carried out and tissue can be restored. This is why experts recommend visiting the dentist once every six months - in order to take timely measures and prevent caries from developing.
The carious spot is treated with solutions of sodium fluoride and calcium fluoride. The patient is prescribed vitamins, calcium and phosphorus supplements, and brushing teeth with fluoridated toothpaste is recommended. Your doctor may also recommend a special diet that includes foods high in calcium and certain proteins.