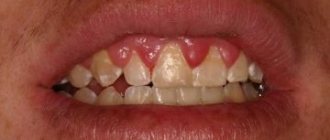
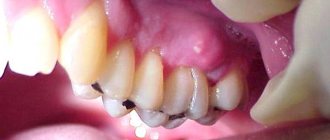
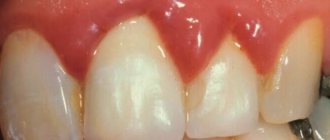
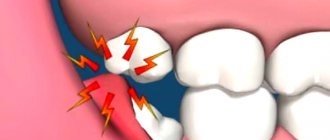
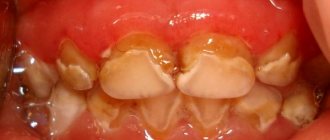
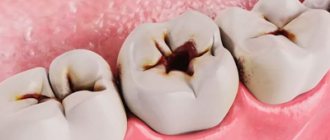
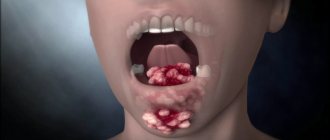
What is a gum abscess, definition of the disease
Let us consider in more detail what an abscess on the gum is and the mechanism of its occurrence. A purulent focus occurs as a result of long-term untreated inflammation of periodontal tissues. The pathogenesis of the disease is associated with the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms (mainly Bacteroides forsythus and Porphyromonas gingivalis) into the periodontal tissues. Possible routes of penetration of microbes:
- from the outside: through a carious cavity, chips, cracks on the surface of the segment;
- from the inside (hematogenously, lymphogenously): in the presence of other septic foci in the body.
During their life, bacteria produce toxic substances that lyse tissue cells, resulting in the formation of a cavity filled with pus. The abscess under the tooth is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, which separates it from the intact periodontal tissues.
Microbial metabolic products have a neurotoxic effect on nerve receptors located in the pulp of the segment, which causes pain. In addition, they increase the permeability of the capillary walls, resulting in swelling of the surrounding tissues.
METROGYL DENTA® for periodontal abscess
METROGYL DENTA® has antibacterial activity and helps relieve inflammation caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The gel can be used to treat periodontal abscess in the postoperative period. Before using the drug, you must brush your teeth. Then a small amount of gel is carefully applied to the affected area of the gum using a cotton swab. The duration of action of the drug is 30 minutes; during this period you should refrain from drinking and eating. The duration of treatment is on average 7-10 days. Before using METROGYL DENTA®, we recommend consulting with your dentist.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Causes of gum abscess
The human oral cavity contains about 30 strains of microorganisms, represented by more than 700 species of bacteria. Under normal conditions, microbiocenosis does not harm its owner. A dental abscess occurs only in the presence of certain factors:
- traumatic disruption of the periodontal junction;
- infectious dentogingival pathologies;
- transmission of microorganisms through the bloodstream from other infectious foci (meningitis, pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc.);
- gum damage during segment therapy;
- trauma to the crown or root of the unit;
- peri-implantitis (inflammation around the implanted tooth root).
The likelihood of developing the disease increases with poor oral care, hypothermia, accumulation of tartar inside deep periodontal pockets, and smoking. Professional hygiene and gum treatment in Moscow is carried out by doctors of the North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1. A timely visit to the clinic will reduce the risk of the formation of a purulent formation.
Kinds
Spicy.
This periodontal abscess is accompanied by severe pain in the area of one or more adjacent teeth. Unpleasant sensations can be sharp and intense, pulsating, recurring or constant. Due to inflammation, a person’s chewing function is impaired, the teeth become mobile, and when they are closed, the pain intensifies.
Chronic.
Such a periodontal abscess is accompanied by periodic formation of purulent contents in the area of the inflamed gum. With this form of the disease, a person develops a fistulous tract along the root of the tooth. Often a chronic abscess is asymptomatic. In this case, the diagnosis can be made based on X-ray data. A chronic abscess from time to time turns into an acute form with all its clinical manifestations (severe pain, mobility of teeth, etc.).
Up to contents
Symptoms of gum abscess
Gingival abscess manifests itself in two types of symptoms: local and general clinical. Local symptoms are caused by reactive manifestations in the area of inflammation. The appearance of general symptoms is associated with intoxication of the body. The main symptomatic manifestations of the disease:
| Local inflammatory reaction | Symptoms of intoxication |
| pain when pressing on the affected unit; hyperemia of the gums over the area of inflammation; swelling of the tissue around the abscess; smell of rot from the mouth; violation of facial configuration; formation of a tubercle with purulent contents near the tooth; increased mobility of the diseased unit; darkening of tooth enamel; enlargement of nearby lymph nodes. | hyperthermia; dyspnea; cranialgia; violation of orientation in space; tachycardia; aching joints; lethargy; drowsiness; irritability. |
The leading symptom of an abscess is pain. It can be fixed only at the point of inflammation, but more often the discomfort radiates to the head, auricle, eye socket, neck, and neighboring segments. Soreness has different intensity, character (sharp, shooting, dull), occurs periodically in response to stress factors, or is constantly present.
Stages of development and classification of gum abscess
A gum abscess most often has an acute course, characterized by a clear clinical picture with increasing pain and swelling. Sometimes, in the absence of treatment, the process may subside, the clinic becomes weakly expressed and erased. This means that the abscess has become chronic.
Depending on the location of the purulent focus, several types of pathology are distinguished:
- Periodontal abscess. Localized inside the hypertrophied periodontal pocket (between the alveolar process and the gum). The cause of the pathology is subgingival deposits, which are a breeding ground for the proliferation of bacteria.
- Periapical (root). The leading cause of occurrence is inadequate root canal treatment, leading to periodontal inflammation. Granulations form near the root apex. Progressive inflammation spreads to the periosteum and periodontal tissue. A connective tissue capsule with purulent contents is formed. Over time, a fistula forms with pus coming to the surface in the form of a lump.
- Desnevoy. The purulent cavity is located near the papillae between the segments. A possible cause is an injection into the gum.
Causes of development of purulent periodontal inflammation
Ignoring brushing and rinsing your teeth after eating only contributes to the development of pathological microflora, which subsequently leads to the appearance of periodontal disease, gingivitis, and periodontitis. Next, a gum pocket is formed, which is filled with pus and an abscess is formed.
Important!
By contacting the dentist at the first sign of gum disease (bleeding, redness, sensitivity) you will save time and money. By postponing a visit to the doctor, you are dooming yourself to unnecessary expenses and dooming your teeth to decay, which can be stopped with timely treatment.
In addition to poor hygiene, the development of periodontal abscess is facilitated by:
- mechanical periodontal injuries (a bone from a fruit or fish, a scratch with a fork);
- burn. We are not talking about “swallowing fire”; a hot drink is enough for an abscess to begin to develop on the weakened mucosal tissue;
- the habit of “grinding” your teeth, closing them tightly;
- crooked bite and deformed teeth.
To be fair, we note that 1% of the development of purulent inflammation of the subgingival pocket is the fault of unprofessional dentists. During mechanical cleaning or treatment of the tooth, the affected surface of the mucous membrane was not disinfected.
Stages of development of gum abscess
| Disease stage | Description |
| Initial | The beginning of inflammation. If the immune system is functioning well, the process may stop on its own. Symptoms are absent or mild. If the immune defense is insufficient, bone or soft tissue begins to melt. Hyperemia of the mucous membrane and discomfort appear. |
| Subacute | The inflammatory process intensifies. Pus accumulates in the pathological area (near the root, inside the periodontal pocket, near the gingival papilla). The pain intensifies. The tooth reacts to irritation. |
| Acute | Progression leads to abscess formation: a cavity with pus forms in the central zone of infiltration. The clinical picture is clearly expressed: the pain is constant, sharp, swelling appears. A lump appears on the surface of the gum, inside of which there is purulent exudate. Inflammation spreads to the submandibular lymph nodes. |
| Chronic | The abscess on the gum spontaneously opens and the contents of the cavity come out. Signs of acute inflammation subside. |
Complications that a gum abscess can cause
Without treatment of the disease and inadequate medical care, complications may develop. Adverse consequences arise due to the spread of inflammation to neighboring organs and tissues, as well as the spread of infection throughout the body with the formation of secondary septic foci. The most common pathological conditions that occur are:
- lymphadenitis - infection of the lymph nodes;
- sinusitis - infection in the maxillary sinuses;
- periostitis of the jaw (inflammation of the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis of the jaw bones (destruction of bone tissue due to purulent-necrotic melting of osteocytes);
- phlegmon - diffuse odontogenic inflammation of soft tissues, accompanied by progressive swelling of the face;
- destruction of the alveolar processes with significant loosening of teeth or their loss;
- peri-implantitis with implant rejection;
- sepsis.
Purulent lesions of soft periodontal tissues are always accompanied by general intoxication of the body. The temperature rises and chills appear. There is a headache, tachycardia, and the pulse quickens. Pain relief with medications brings short-term relief, but symptoms return after the medication wears off.
Treatment of gum abscess
Treatment of the disease is aimed at solving two main problems:
| Type of treatment | Methods |
| Symptomatic treatment of inflammation and pain syndrome | removal of an abscess on the gum (dissection, installation of drainage for the outflow of pus); antibiotic therapy (penicillins, fluoroquinolones, macrolides). Prescribed to stop the infectious process; NSAIDs (Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, etc.). Eliminate pain and inflammation; antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin). Used in the form of rinses and gum baths for antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. |
| Etiotropic treatment (elimination of the cause of pathology) | tooth extraction. Carry out when it is impossible to implement tooth-preserving measures; repeated endodontic treatment (opening of canals and their refilling); professional teeth cleaning to remove mineral and soft plaque; removal of the artificial root (for peri-implantitis). |
An abscess on the gum is a serious dental pathology. If treatment is not started in time, the process continues to develop and leads to adverse consequences. To avoid complications, at the first signs of inflammation you should make an appointment with the dentist. ]dentistry in Otradnoye[/anchor] offers assistance in eliminating problems with diseased teeth and periodontal disease.
Periodontal abscess – Prices
| Service | Price |
| In-canal whitening (first visit) | 1500 rub. |
| Whitening Opalescence BOOST | 12000 rub. |
| Professional home whitening Day White | 7000 rub. |
| Whitening Zoom 3 | 17,000 rub. |
| Making a mouth guard for whitening/fluoridation, for 1 jaw | 2000 rub. |