Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The appearance of a small bump on the gum
sometimes it confuses people. Meanwhile, this is a very common dental problem, although the reasons for its occurrence can be completely different. Let's try to figure it out: you have such a lump, what can it mean and how to cure it?
Causes and formation of compactions
The formation of lumps on the gums can have a variety of reasons, but the main one is poor quality oral care. Plaque after eating food can be deposited not only on tooth crowns, but also on gum tissue. The plaque accumulates pathogenic bacteria, which provoke the development of various ailments, for example, the formation of a fistula.
Most often, fistulas form on the upper jaw and cause great discomfort. A fistula manifests itself as a severe pain syndrome of a sharp and aching nature. In other cases, the neoplasm does not define itself in any way, however, the pathological process continues to develop. Sometimes a fistula may come and go.
There are two types of neoplasms of different nature:
- infectious;
- non-infectious.
An infectious growth provokes the proliferation of microbes that poison the human blood by releasing toxic waste in the implementation of their life cycle. A non-infectious fistula is formed as a result of a jaw injury or after taking medications. Trauma to the gum tissue can occur after the installation of dentures: a loose denture has a constant traumatic effect on the tissue, causing inflammatory processes.
A negative effect on tissue can be caused by poor-quality material for the manufacture of a denture/crown or poor-quality sanitation of the tooth before installing a crown. The result is a lump that is soft to the touch and hurts when pressed. Pain may also indicate flux developing in the tissues. If it is not removed in time, the purulent infection can enter the bloodstream and cause infection.
Symptoms of purulent inflammation in the mouth
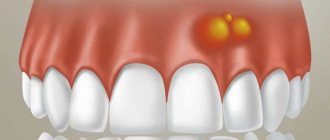
A periodontal abscess is similar to the pathogenesis of a boil or boil. The first symptoms of the pathology are expressed in red infiltration and swelling of surrounding tissues. Pain occurs when pressing on the site of infection. After some time, a white ball appears, containing pus inside. The person’s well-being deteriorates, signs of a cold are observed: hemicrania, general fatigue, chills.
Photo: this is what a gum with an abscess looks like
Pus on the gum appears above the tooth or between the tooth and gum, depending on the location of the infection. Further formation of an abscess can be recognized by the following signs:
- unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth;
- speech function disorder;
- feeling of discomfort during chewing and swallowing;
- blue discoloration of tooth enamel.
Where does pus come from in the gums?
Pus in the gums most often indicates one of three diseases:
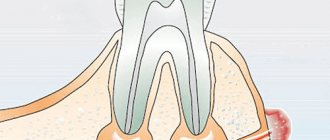
1. Periodontitis. It is characterized by inflammation of the gingival tissues, in which a periodontal pocket is formed at the site of inflammation. The pocket formed between the tooth and gum collects food debris, microbes, and dental deposits. Gradually, pathogenic microflora leads to the appearance of an abscess.
This is interesting: Symptoms and possible complications when a wisdom tooth is cut
2. Periodontitis. This is a disease, the main symptom of which is an inflammatory process that breaks out near the apex of the tooth root. The gums indicate acute inflammation in the area of the tooth root by redness and swelling, and the tooth by pain when pressed. Mostly, periodontitis appears after pulpitis - either uncured, or cured, but poorly.
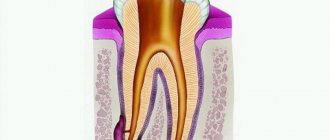
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the dental nerve. When germs enter a nerve, they infect it. In this case, the pulp must be removed from the dental canals, after which the canals must be sealed. Acute pulpitis brings the patient very severe pain, forcing him to see a dentist, while chronic pulpitis can be practically asymptomatic, which is why the chronic inflammatory process often goes unnoticed. In the meantime, microbes that have penetrated the pulp move along the dental canals and sooner or later reach a small hole at the top of the tooth root. From there they enter the tissue surrounding the tooth root - the periodontium, where a purulent formation occurs. Pus accumulates in the periodontium, there is little space for it, and a fistula forms on the gum, through which the pus exits the area of inflammation into the oral cavity. Purulent exudate periodically oozes from an abscess of this kind, but all the pus will not come out of the periodontal tissue until the doctor treats the problem.
If pulpitis has been diagnosed and treated, this does not guarantee that periodontitis will not develop on the treated tooth. After removing the pulp, the doctor must disinfect the tooth and seal the dental canals tightly and along the entire length with a special material. If the dentist does not kill all the microbes, does not notice a small canal in the tooth, or leaves voids in the canals, he leaves room for the proliferation of harmful microorganisms, and over time an inflammatory process begins near the root of the tooth, which can also be accompanied by the opening of a fistula tract.
3. Periostitis of the jaw. With periostitis (flux), the periosteum of the jaw becomes inflamed, which usually occurs due to chronic periodontitis. The pathological process begins with a slight swelling of the periodontal tissue, then the gums swell and begin to hurt. Afterwards, facial tissues swell in the area of inflammation. Like periodontal inflammation, inflammation of the periosteum can be accompanied by the opening of the fistula canal.
Purulent formations on gingival tissues can represent an independent pathology, in which the patient does not have periodontitis, periodontitis, or periostitis. Suppuration is provoked by such unfavorable factors:
- injury to the gums (filling, prosthesis, braces, any non-food object, blunt impact);
- hypothermia (local or general);
- chronic infectious diseases (local or general);
- poor local hygiene;
- smoking.
If the lump on the gum does not hurt
In what gum diseases does the lump not define itself as a pain syndrome? These include:
- fistula (white lump on the gum);
- epulis (pedunculated tumor);
- exostosis (bone protrusions);
- periodontitis (hard lump on the gum);
- hematoma during root removal.
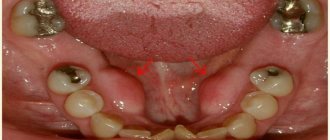
Fistula
A lump on the gum above (or under) a tooth with an opening for pus to escape is called a fistula. If suppuration flows freely from the hole, a person does not feel discomfort in the presence of this pathology. If the outlet is blocked by a compacted accumulation of pus, the person feels sharp pain.
The main reason for the formation of a fistula is considered to be a complicated form of periodontitis, in which the growth of gingival tissue begins (gingival hyperplasia). The overgrown form is a favorable environment for bacteria to live, the result of which is purulent discharge. A white lump on the gum of an adult (fistula) becomes chronic if left untreated.
A fistula on the gum can develop in two directions:
- acute illness;
- chronic fistula.
The acute form of the fistula is treated quickly, chronic fistulas are removed only by surgery.
Important! The fistula must be treated to save the tooth. The development of infection in the gums can cause even strong healthy teeth to fall out.
Exostosis
This pathology is a jaw anomaly in which the bones of the skull protrude slightly outward. In other words, they are bony protrusions in the mouth. Over time, this growth can increase in size and cause discomfort. With this anomaly, dental prosthetics is impossible: the prosthesis will constantly irritate the growth and create discomfort.
The following factors can cause the development of exostosis:
- jaw injuries;
- hereditary pathology;
- congenital anomalies;
- lump on the gum after tooth extraction.
The presence of exostosis can be determined using an x-ray and a visual examination by a dentist. To remove or not to remove exostosis if the lump above the tooth does not hurt? It is up to the patient to decide. However, this deviation can become malignant over time.
Epulis
This pathology is a mushroom-shaped growth (a ball on a stalk) of red or natural color. Most often, epulis affects the lower jaw and is common among women. Epulis can also affect the gums of children when teething for the first time.
The cause of the pathology is constant mechanical impact: too large a filling or formed tartar. Also, the reasons for the appearance of epulis include:
- jaw injury;
- malocclusion;
- hormonal disorders;
- poor quality denture material.
The symptoms of epulis and gingivitis are of a similar nature, therefore, when diagnosing, the dentist takes a differentiated approach that excludes the presence of gingivitis. The patient is prescribed an x-ray to determine the extent of bone tissue damage at the site of the pathology. A histological test is also performed.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis manifests itself as a dense lump on the surface of the gum, the cause of which is considered to be pulpitis or the presence of an open dental canal. An abscess forms at the apex of the tooth root, which, if left untreated, transforms into a root granuloma and cyst.
Hematoma
A hematoma appears after improper tooth extraction and is characterized by the formation of a watery tumor. Such a neoplasm is not dangerous and resolves on its own over time.
Symptoms that require attention
Mostly the bumps appear on the upper jaw and are visible to the naked eye if you open your mouth wide. Often a ball on the gum does not cause any discomfort, so due to the lack of pain it is simply forgotten about. If a lump or lump appears on the gum, there are a number of alarming symptoms, if detected, you should immediately contact your dentist:
- increase in size of the tubercle;
- a sharp “shooting”, “jerking” pain that appears when pressing, eating, or performing hygienic cleaning;
- ichor, pus, and blood are released from the growth;
- swelling spreading to the cheek, gum tissue, neck, with accompanying enlargement of the submandibular or postauricular lymph nodes and pain spreading to the ear, shoulder or arm on the side where the lump is inflated.
Gum cancer
Lump on the gum above the tooth
Occurs in the background:
- caries, pulpitis, gum inflammation (gingivitis, periodontitis), periodontitis or their poor-quality treatment;
- the presence of stomatitis or herpes;
- teething;
- reduced immunity;
- formation of cysts, fistulas, epulis, exostosis.
A ball over a child's tooth
Lump on the gum under the tooth
Reasons for the appearance of a lump:
- The occurrence of a fistula, hematoma, cyst on the upper or lower jaw.
- Development of periodontitis or gumboil.
- In a child of primary school age, during the replacement of primary molars with permanent teeth, when the first ones do not fall out on their own. In such situations, the surgical method of removing the interfering tooth is practiced. The same method is used to eliminate a tumor in an adult that has arisen due to the abnormal location of the wisdom tooth root.
Does it hurt or not?
If the formed lump above the gum hurts when pressed, eating, or hygiene, this indicates the development of:
- Periostitis. Flux is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, severe pain, enlarged lymph nodes, and swelling of the soft tissues in the mouth.
- Gingivitis. The main symptoms are bleeding gums and the formation of red balls on their surface.
- Periodontitis. Its advanced form causes loosening of the teeth due to the looseness of the gum tissue. On the latter, white bumps appear with bacteria actively multiplying inside, provoking purulent-inflammatory processes;
- Granulating form of chronic periodontitis. It is manifested by the formation of an infiltrate near the root that is painful to the touch, paroxysmal pain, slight loosening of the teeth, redness, looseness and swelling of the gums, and enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes on the side of the diseased area. It is possible that fistulas may develop through which pus flows out, leading to the cessation of pain. The lack of adequate therapy can lead to complications - abscesses, soft tissue phlegmon, the development of gumboil or osteomyelitis of the jaw (purulent inflammation of the bone), sepsis, odontogenic sinusitis.
When teething, painful sensations are also possible.
When a soft or hard lump on the gum does not hurt, this is a sign of hematoma, the development of exostosis, epulis, periodontitis, and fistulas.
Pus ball on the gum
If a compaction with pus has formed between the cheek and gum, this is a typical consequence of intense inflammation during perio- and periodontitis, prolonged trauma to the gingival tissue under poorly installed veneers, crowns, fillings or implants.
Purulent bumps on the gums mainly appear in the form of fistulas, through which the contents leak out, or gumboil, in which the contents remain inside, stimulating the development of inflammation, and the surrounding soft tissues “swell” and swell.
Growth on the upper gum
Red or white ball
The color of the swelling is also a diagnostic sign, allowing the dentist to identify the nature of the disease. The inflammatory process is indicated by blood globules and redness of the mucous membrane (gingivitis, gumboil, epulis).
A white lump on the gum is formed during purulent inflammation (periodontitis) or indicates exostosis, accompanied by the proliferation of bone tissue. A growth that matches the color of the rest of the gum is a sign of the initial stages of periostitis, epulis, and the development of a malignant tumor.
If the lump hurts
This pathology includes the following diseases:
- periostitis (flux);
- periodontitis (white balls)
- gingivitis (red ball on the gum).
Periostitis (flux) is a process of inflammation of bone tissue. A distinctive feature of this pathology is hyperthermia with acute pain, swelling of the mucous tissues of the oral cavity and swelling of the lymph nodes.
Gingivitis is characterized by bleeding of the soft tissue of the gums and the formation of small red balls. Gingivitis is the initial stage of the development of pathological periodontitis.
The development of periodontitis leads to loosening of the gum tissue and loosening of the teeth. Advanced periodontitis is a collection of white balls on the gums in which pyogenic bacteria multiply.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can determine the causes of white spots on the gums. The patient needs to talk about his feelings and events that preceded the appearance of this formation. Doctors usually visually identify the disease. But to clarify the diagnosis, you may need:
- blood analysis;
- X-ray.
The appearance of white spots on the oral mucosa may not necessarily indicate a dental disease. The patient should visit an otolaryngologist to exclude or confirm an ENT disease.
Baby's bumps
The reasons for the appearance of tumors in a child are of a different nature. Let's look at the main problems:
- A white bump on the gum of an infant appears before the eruption of a baby tooth. To alleviate the baby's suffering, special drops are used.
- A lump on the gum under a tooth in a school-age child appears when baby molars are replaced with permanent ones: if the baby tooth does not fall out, it must be removed.
- A ball of pus near a baby tooth requires immediate removal to avoid the spread of infection: the tooth is removed.
- A purulent lump on a child’s gum near a molar requires opening and rinsing with antiseptic medical solutions.
Preventive actions
A number of rules apply to the prevention of bumps on the gums:
- Careful oral hygiene.
- Avoiding strong coffee and tea.
- Refusal of high carbohydrate foods.
- Professional oral hygiene once every 4–6 months.
- Annual visit to the dentist for the prevention of dental diseases.
- Timely treatment of carious lesions and inflammatory gum diseases.
Bibliography
- Yakovleva V.I. – Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of dental diseases, Minsk 1994.
- Gaurav, Solanki and Renu Solanki - Dental Plaque Forming Bacteria's Characterization and Stress Responses - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2012.
- Ivanov V.S., Urbanovich L.I., Berezhnoy V.P. — Inflammation of the dental pulp, M., Medicine, 1990.
- Laura Mitchell - An Introduction to Orthodontics - Oxford University Press, USA - 2007
- Muravyannikova Zh.G. — Dental diseases and their prevention, Rostov-on-Don, 2007.
- L. V. Kharkov, L. N. Yakovenko - Directory of a dental surgeon: diagnosis, clinic, principles of surgical and drug treatment (in children and adults), M.: Book Plus, 2008.
- Afanasyev V.V. — Surgical dentistry: textbook, M.: Geotar—Media, 2011
- Doni L. Bird - Modern Dental Assisting - Saunders - 2011
- Tarchenko A.I. – Pharmacotherapy in dentistry, Kyiv, 1986.
Find a clinic
Treatment
Therapeutic procedures are prescribed depending on the location of the tumors, their nature and developmental characteristics.
When a fistula appears, the mouth is sanitized with a soda solution, which helps eliminate purulent discharge. The procedures are carried out continuously until the tumor is completely reabsorbed. The more often you rinse your mouth, the sooner the fistula will resolve.
In case of periodontitis, the sealed canal is opened and the wound is sanitized with antiseptic solutions. Then a temporary filling is placed in place of the open canal and a course of antibiotics is prescribed. After healing, the tooth is filled with a permanent filling.
Gingivitis can be treated independently using dental gels and medicated rinses. Prevention of gingivitis is thorough sanitation of the oral cavity.
Periodontitis requires outpatient treatment - washing the inflamed tooth pockets with a medicinal solution. After the rinsing procedure, the dentist prescribes a course of antibiotics.
Epulis is removed by curettage. If the pathology is irreversible, the dentist removes the teeth. Teeth that cause the growth of pathological tissue must be removed.
Flux requires careful surgical intervention: the neoplasm is opened, the cavity is cleared of residual pus. If the diseased tooth is covered with a crown, it is removed and treatment procedures are carried out. Sometimes it is necessary to carry out joint surgical and therapeutic procedures.
Method No. 2. Electrophoresis
Doctors have no clear opinion regarding this method. Some consider it effective, others argue that it is outdated and does not provide a 100% guarantee that the problem will be solved without a trace. However, if you want to do without surgery, it’s still worth a try.
Indications for electrophoresis include:
- the presence of purulent inflammation in the mouth,
- small cysts and granulomas,
- alveolitis,
- periodontitis1.
Electrophoresis can also be prescribed for treatment.
The essence of the procedure is the introduction of drugs into the area of infection. In order for medications to have the maximum effect and be able to eliminate the source of infection, they are administered using weak current pulses. However, treatment in this way is long-term, in order to get results, you need to perform up to 10–20 electrophoresis procedures.
Household folk remedies
A common folk method of combating formations in the mucous membrane is rinsing with a saline solution. In a liter of boiled, cooled water, dilute 4 tablespoons of table/sea/iodized salt and leave to infuse. After 50 minutes, the mouth is sanitized by slightly heating the solution. The saline solution also goes well with herbal infusions with antiseptic characteristics: calendula, eucalyptus, yarrow and chamomile flowers.
To eliminate tumors, alcohol-containing medicinal solutions are also used. Rinsing the cavity with regular vodka helps a lot. Medicinal herbal tinctures are prepared using alcohol/vodka/cognac.
Herbal infusions are also used separately. Herbs soothe irritated mucous membranes, eliminate foci of inflammation, have an antibacterial effect, and resolve tumors. To brew the infusion, you need to pour 4 tbsp of herbs with a liter of boiling water. After half an hour, the infusion is ready - strain and rinse your mouth.
For garlic tincture, take 4 garlic heads, 5 medium lemons and 700 grams of alcohol. Peeled, chopped lemons and crushed garlic are poured and left for 5 days. The oral cavity is treated every fourth hour until the tumor is reabsorbed.
Horseradish tincture with alcohol has an antiseptic effect and eliminates inflammatory foci in the mucous membrane. It is enough to grate 300 grams of root vegetables and pour half a liter of vodka. The mixture is infused for 3 days. Sometimes, to enhance the medicinal properties, horseradish is sprinkled with salt (a little). Rinse your mouth every fourth hour until the tumor disappears. After 4-5 days the swelling subsides.
Freshly squeezed juice of Kalanchoe leaves has a healing effect on inflamed gum tissue. To use, squeeze out the juice (through a meat grinder or crush the leaves in a mortar) and rub into the inflamed area. To disinfect the oral cavity, you can chew the leaves, freed from the film.
Honey with salt has an amazing effect in counteracting inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa. Salt actively removes pus, and honey soothes irritated mucous membranes and has an antibacterial effect. The mixture is prepared at the rate of 2 tablespoons of liquid honey per spoon of salt.
What can you do at home?
Treatment can be performed at home, but only after consultation with a doctor. The patient receives a regimen to follow. What can you do before visiting a doctor? There are several recommendations that make the situation easier:
- Whatever the reason for the appearance of white spots, rinsing with an antiseptic solution will improve the condition. It is sold in pharmacies - “Chlorhexidine”, “Furacilin Eludril”, “Etonium”. But you can cook everything yourself. Add salt or soda (1 tsp) to warm water (1 glass). Everything gets mixed up. Rinse procedures can be performed every 2 hours. These measures stop the action of pathological microflora, reduce swelling, itching, and pain.
- You can make an infusion of beneficial herbs. Plants with anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, regenerating effects are needed. Sage, chamomile, calendula, and oak bark are suitable for this. The plants are suitable for brewing either separately or together. To prepare a healing solution, you need crushed herbs (2 tablespoons), which are poured with boiling water. The product is infused for several hours, after which it can be filtered and used for rinsing.
- Propolis has a powerful antibacterial and regenerating effect. For diseases of the mucous membrane, it is allowed to be taken. You can buy the tincture ready-made or make it yourself. To do this, 20 g of the product should be filled with alcohol (70%). After 3 days the product will be ready. Store it for a long time in the refrigerator. To prepare a solution for rinsing, you need to add the prepared tincture (2 tsp) to water (1 glass). The procedure is performed at least 5 times a day.
Experts believe that if white spots on the gums do not disappear on their own within a few days, then you should not self-medicate. Especially if other unpleasant phenomena occur with these symptoms.
Prevention
Preventing the development of pathology is better than treating it. What methods can be used to improve the health of the oral mucosa? Among the effective remedies, the following recipes have gained popularity:
- Massaging the gums with the juice of crushed cranberries prevents inflammation in the gums and bleeding: cranberries are an excellent prevention of periodontal disease.
- Agave (aloe) juice is used to prevent and treat gingivitis: it strengthens the mucous membrane and saturates the body with vitamins if you rinse your mouth with a 1:4 mixture of juice and water.
- To prevent gingivitis and strengthen mucous tissue, rinse with an infusion of sorrel leaves: brew 1.5 tbsp of finely chopped fresh leaves with a glass of boiling water and leave for an hour.
- Calamus root (1 tbsp/l) is pounded into powder in a mortar and steamed with boiling water (1 cup) for an hour. Rinse your mouth with the strained infusion.
- Fir oil helps a lot if you apply gauze soaked in it to your gums.
Traditional recipes can be combined with medications, after consulting with your dentist in advance. Combined treatment gives a good effect. In addition to sanitizing the oral cavity, natural remedies strengthen the structure of the gums and tooth enamel.
Sources used:
- V. Zijnge, M. B. M. van Leeuwen, J. E. Degener, F. Abbas, T. Thurnheer, R. Gmür, H. J. M. Harmsen, Oral Biofilm Architecture on Natural Teeth
- Muller H. P. Periodontology. - Lvov: GalDent Publishing House, 2004.
- Wagner, F; Dvorak, G; Nemec, S; Pietschmann, P; Figl, M; Seemann, R (January 2017). "A principal components analysis: how pneumatization and edentulism contribute to maxillary atrophy." Oral diseases.