Periodontal disease is a non-inflammatory disease of the periodontal tissue (periodontal tissue). It occurs against the background of endocrine pathologies, chronic diseases of various organs and systems, metabolic disorders and the functioning of the circulatory system. The disease has a hereditary predisposition. In this material we will look at whether the disease is of a viral nature, whether it can be transmitted from one person to another, whether it is possible to become infected with periodontal disease through a kiss, and also find out what are the signs of the development of the disease, whether it is accompanied by pain, and when exactly when this occurs illness, you should consult a doctor. Let's consider whether the disease is contagious.
Diagnosis of periodontal disease
To identify signs of periodontal disease in adults, the following diagnostic procedures are usually performed:
- inspection;
- probing of the gingival sulcus;
- assessment of tooth mobility;
- X-ray examination (orthopantomography);
- biomicroscopy of the gums to determine the degree of microcirculation impairment.
The patient will also need observation from a general practitioner and endocrinologist to detect and treat general somatic pathology.
After a diagnosis of “dental disease periodontal disease” is made, further examination should be aimed at finding the causes of disturbances in the processes of cellular tissue nutrition, predicting the further development of the disease and the likelihood of inflammatory complications.
Symptoms of dental periodontal disease
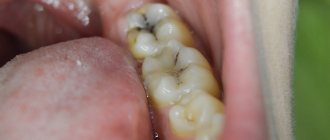
The main symptom of the disease is detected during x-ray diagnosis of periodontal disease. The image shows a uniform decrease in the height of the interdental septa with alternating foci of osteosclerosis and osteoporosis in the deep parts of the alveolar process and the body of the jaw, as well as in other bones of the skeleton. Traditionally, changes are accompanied by the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine systems and metabolic disorders.
There are other symptoms of severe periodontal disease that are more noticeable to the patient and others:
- gum retraction;
- exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth;
- pale gum color;
- lesions of teeth of non-carious origin (wedge-shaped defects, hyperesthesia).
How can stomatitis be transmitted?
Transmission routes:
- airborne droplets (at the time of communication);
- hematogenous route (through blood);
- contact or household route (unwashed hands, use of shared utensils or other personal hygiene devices);
- from mother to child (breastfeeding);
- interaction with other biological fluids (saliva during kissing, the entry of amniotic fluid into the baby’s oral cavity, sexual intercourse).
Since stomatitis of infectious etiology is contagious for any person, you should familiarize yourself with each type in detail and learn to distinguish them from non-infectious inflammation.
Viral
The viral form is one of the most contagious among other types. This disease is characterized by the presence of a specific pathogen that causes this condition. In this regard, the following are highlighted:
- herpetic;
- enterovirus;
- influenza and parainfluenza;
- associated with the causative agent of chickenpox;
- adenoviral.
Depending on the incubation period, which lasts 5–14 days, characteristic symptomatic manifestations appear. During this period of time, the patient is contagious to others, but danger threatens when symptoms appear (presence of ulcers with blisters, soreness, elevated body temperature). More often, stomatitis is transmitted by airborne droplets.
It is important not to confuse the clinical manifestations of infectious stomatitis with signs of tonsillitis (during examination, the mucous membrane of the tonsils is affected)
Bacterial
Bacterial stomatitis - manifests itself in children. This is due to a weak immune system and frequent injuries to the oral mucosa. Damaged tissue is an entry point for bacteria. In the area of implantation, local inflammation, swelling, and pain appear. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. When foreign microorganisms enter the blood, intoxication syndrome increases (body temperature rises, malaise, drowsiness, loss of appetite).
This species is as contagious as a viral one, and is most often transmitted through the air and through household contact.
Fungal
Fungal stomatitis in the mouth is contagious for healthy people if they use shared, poorly washed dishes, etc. The household route of transmission predominates here.
A characteristic feature of this type of stomatitis will be a white coating over the inflamed area of the mucous membrane. Intoxication syndrome is unlikely, since the fungal infection occurs only in the mucous (mucosal) layer.
Aphthous
Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa that is not associated with an infectious nature. It occurs most often against a background of stress or as a manifestation of a local allergic reaction.
Traumatic prosthetic stomatitis
Sores or ulcers often appear in the oral cavity due to damage from foreign bodies (solid food, dentures, toothbrush with coarse bristles, etc.). Since the dentures are not tightly fixed, their movement causes irritation and injury to the mucous membrane. At the site of unstable fixation, the tissue becomes inflamed.
Despite the safe form of the disease in this category of people, the question arises whether it is possible to become infected with traumatic stomatitis in general or not.
With ordinary prosthetic stomatitis, there is no danger to others, but if complications are detected after infection, the patient becomes infected.
Stages of periodontal disease
In modern dentistry, there are three degrees of severity of periodontal disease.
Mild degree
How does periodontal disease begin? In the early stages, the disease occurs without pronounced symptoms with gradual atrophy of the gum edge and bone tissue. With periodontal disease of the anterior teeth, a slight exposure of the dental necks occurs; in some cases, patients experience increased sensitivity of teeth to food irritants (hot and cold, sweet and sour). On X-ray images, the onset of periodontal disease is indicated by the first signs of bone tissue atrophy.
Average degree
With an exacerbation of periodontal disease, not only the necks, but also the roots of the teeth are exposed - by 2 - 3 millimeters. X-ray images show destruction of bone tissue along half the length of the root and the presence of foci of sclerosis.
Severe degree
With severe periodontal disease, exposure of the roots of the teeth reaches 4–5 millimeters, bone tissue atrophy on X-ray photographs covers two-thirds of the root.
Signs of disease development
In the early stages, periodontal disease is usually asymptomatic in humans. It is accompanied only by a slight change in the color of the gums. Painful sensations and any other manifestations are not inherent in it, which is why patients in the first months of the development of the pathology do not pay attention to it and do not come to the doctor in a timely manner.
In the later stages, the development of periodontal disease in a person can be recognized by a number of characteristic symptoms. These include:
- Change in gum color. With periodontal disease they become pale. Inflammatory processes, suppuration, and bleeding are rarely observed with this disease.
- Reduction of alveolar processes in size. This symptom leads to exposure of the neck of the tooth. At the same time, the teeth themselves do not become loose and remain firmly in place.
- Itching that periodically occurs on the gums.
- Minimum amount of plaque and tartar on the teeth. In some cases, they may be completely absent in patients.
Also, with periodontal disease, a person may experience non-carious lesions of tooth tissue. These include abrasion of enamel, erosion, and wedge-shaped defect. Such pathologies require additional diagnostics and usually indicate the presence of concomitant diseases in the body, including pathologies of metabolic processes.
In the later stages of the disease, the patient may experience inflammation of the gums, tooth loss and the formation of ulcers. As a rule, at least 15-20 years pass between the onset of pathology and this stage.
Pain due to periodontal disease
With periodontal disease, patients may experience pain. The reason for its appearance is the exposure of the necks of the teeth. Because of this, their sensitivity to cold and hot foods increases. When contacting such products, an acute short-term pain usually appears, which disappears after the end of exposure to the irritant on the neck of the tooth.
With periodontal disease, patients do not have gum pain. If this symptom is present, there may be some additional damage (for example, cuts to the gums) or other diseases that complicate the underlying disease. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor for additional advice.
Oral thrush, one of the most common forms of thrush, is a fungal infection caused by the yeast Candida that affects the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Candida is a genus of yeast. There are about 150 different species of Candida that can cause serious yeast infections. The most common cause of thrush is Candida albicans.
Typically, infectious fungi are a natural component of the skin, oral cavity, and intestinal flora. They do not cause discomfort as long as their reproduction is limited by the balance of other microorganisms and the immune system. Problems only arise when fungi overgrow or break through the natural barriers of the skin and mucous membranes, causing thrush.
Periodontal disease – what to do?
At the initial stage of periodontal disease, you should consult a periodontist. No folk remedies will help get rid of the disease. Only a specialist will be able to carry out the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribe, based on the identified symptoms of periodontal disease, treatment aimed at slowing down degeneration in periodontal tissues and preventing inflammatory complications. It is also necessary to eliminate non-carious dental lesions and undergo a thorough examination by a therapist to diagnose and treat common diseases that provoke the development of periodontal disease.
Complex therapy of periodontal disease involves the following measures:
- Timely removal of dental plaque.
- Normalization of occlusal relationships (grinding teeth, prosthetics, splinting).
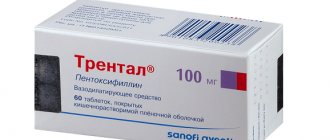
- The use of vitamins and agents that improve microcirculation (nicotinic acid, aloe extract, heparin).
Causes
An advanced form of periodontal disease is characterized by the development of dystrophic processes in the dental system, which leads to the occurrence of osteoporosis of bone tissue. In the absence of quality treatment, the pathology begins to worsen: teeth become weak, become very loose and fall out. The main causes of pathology include genetic predisposition, local metabolic disorders and mechanical damage.
Poor circulation in periodontal tissues
Disruption of local blood microcirculation occurs under the influence of the proliferation of pathogenic microflora, which contributes to the development of the inflammatory process. Ignoring inflammation of periodontal tissues leads to damage to vascular walls and capillaries, an increase in blood clots and disruption of the transport system.
Insufficient nutrition of periodontal tissues
A disruption of the local blood supply causes the periodontal system to lack useful components and minerals. Under the influence of nutritional deficiency, the teeth and mucous membrane in the oral cavity weaken, which is a favorable circumstance for the development of periodontal disease.
Metabolic disorders
Metabolism consists of chemical reactions aimed at cleansing, nourishing and restoring the body's cells. The main participants in the metabolic process include proteins, fats and carbohydrates, each of which performs its own function.
A balanced amount of fats and carbohydrates ensures the restoration of energy, and proteins act as building materials necessary to strengthen the body's cells. Under the influence of provoking factors - climate, intoxication, poor nutrition - a metabolic failure occurs.
Osteoporosis
The main reason for the development of osteoporosis is considered to be an insufficient amount of calcium, which is necessary to strengthen bones and chewing units. Experiencing a deficiency of a useful mineral, the bone structure becomes thinner and weaker, which leads to its gradual destruction.
The development of osteoporosis negatively affects the condition of the patient’s hair, nails, and teeth. The pathological process contributes to the thinning of the enamel coating, as a result of which the sensitivity of the chewing units increases, caries occurs and the processes of destruction of hard tissues are activated.
Jaw injuries
Mechanical damage to the dental system occurs as a result of an impact, a fall from a height, or a strong collision of facial tissues with a hard surface. The first signs of injury are severe pain, which intensifies when applied to the jaw, as well as severe swelling of the affected soft tissues.
Other reasons
Factors contributing to the development of periodontal disease include:
- the presence of malocclusion and severe curvature of chewing units;
- negative impact of orthopedic devices on periodontal tissues;
- deficiency of beneficial vitamins and minerals necessary to strengthen the body’s immune system;
- disruption of the endocrine system, which contributes to hormonal imbalance;
- development of diabetes mellitus.
Genetic factor
The most common cause of periodontal disease is considered to be a hereditary predisposition: the risk of developing pathology increases if immediate older relatives suffered from weak bone tissue.
Treatment methods
Methods and procedures used to treat periodontal disease in dentistry:
- exposure to high pressure oxygen in hyperbaric chambers;
- electrophoresis;
- diadynamic currents;
- amplipulse therapy;
- darsonvalization of gums;
- UHF therapy;
- gum massage;
- local hypo- and hyperthermia;
- ultrasound therapy.
Psychosomatics of periodontal disease
Based on the results of many years of research, American scientists have come to the conclusion that dental diseases such as periodontal disease are directly related to high anxiety, depression and an acute sense of loneliness. This is explained by the fact that increased levels of the stress hormone - cortisol - in the blood negatively affect the condition of the gums and jaw bones. In addition, during periods of nervous tension, people begin to pay less attention to oral hygiene and increase the doses of alcoholic beverages, nicotine and medications, which also contributes to the development of various diseases.
Hereditary factor
If the older generation suffers from this disease, it is worth worrying whether periodontal disease is transmitted in a particular family. The situation is worsened by problems with the cardiovascular and endocrine systems, as well as the presence of diabetes.
Shiyka Oksana
Dentist-therapist
Important! If someone in your family suffers from periodontal disease, you should pay increased attention to the condition of your gums - sensitivity, bleeding.
If you have a genetic predisposition, it is worth having your teeth professionally cleaned to remove plaque and tartar in a timely manner – as needed. A child can learn from his parents:
- structure and density of teeth;
- amount of antimicrobial substances;
- hereditary diseases that can impair blood supply to the gums.
If your parents or family have had periodontal disease, it is important to pay attention to the health of your child’s teeth. Will help:
- formation of correct bite;
- the presence in the body of a sufficient amount of calcium and vitamin D for tooth enamel;
- eliminating bad habits;
- timely visits to the dentist.
The disease does not necessarily manifest itself. It is impossible to cure inherited teeth, but it is worth noticing the signs of the disease in time for a timely response.
Consequences of periodontal disease - why is it dangerous?
- Firstly, due to the absence of pronounced symptoms, this disease can progress unnoticed over many years and lead to total destruction of the teeth and jawbone - and then teeth fall out with periodontal disease.
- Secondly, the destruction of bone tissue leads to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract with the subsequent occurrence of diseases of the digestive system.
- Thirdly, advanced periodontal disease can provoke periodontitis - acute inflammation of the tissue and tooth loss.
In addition to the above consequences, generalized periodontal disease in an advanced stage causes another dangerous disease - osteomyelitis, that is, purulent bone damage.
Transmission routes
Each type of this disease has its own characteristics, symptoms and routes of transmission. Having knowledge characterizing the disease, we can conclude that it is necessary to visit a doctor.
Viral
Viral stomatitis is contagious. It is easy to recognize: watery blisters appear in the mouth, which burst and form ulcers. Body temperature rises to 40 degrees, severe pain occurs in areas of inflammation.
The causes are associated diseases:
- herpes;
- chickenpox;
- flu;
- adenovirus;
- enterovirus.
If you have these symptoms, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Infection occurs through personal items, as well as through airborne droplets.
Bacterial
The causes of the disease are bacteria - streptococci and staphylococci.
Symptoms:
- reddened, loose and swollen mucous membrane;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- lethargy, nausea;
- temperature rise is possible.
The bacterial species is contagious, but not as scary as the viral one. It is more dangerous for children, since their body’s defenses have not yet strengthened.
It is also transmitted by airborne droplets, through personal items and through contact with a patient.
Fungal
The cause of the fungal disease is a fungus from the Candida series. It often appears after taking broad-spectrum antibiotics, when the balance in the body is disturbed and many bacteria die.
A white coating appears on the tongue, cracks and ulcers form on the mucous membrane. The disease is not transmitted through droplets, but through personal items it can be transmitted.
Aphthous
Aphthous stomatitis is not a type, but rather its manifestations. Aphthae are round sores with a white or yellowish coating in the mouth. You can get them by brushing your teeth, cracking seeds, at a dentist's appointment, or chemically. Even hot drinks can burn, causing sores in your mouth.
It is important to know: any infectious type can become aphthous. And vice versa - viruses or bacteria get into a harmless wound, and it becomes infectious
If aphthous stomatitis develops as a result of injury to the mucous membrane, then it is not contagious. If, in addition to ulcers, there are signs of a viral infection (redness of the tonsils, for example), then there is a risk of infection. Aphthae alone do not indicate contagiousness.
Periodontal disease - contagious or not?
To the questions “Is periodontal disease contagious?” or “Is periodontal disease transmitted by airborne droplets?” Doctors answer unequivocally in the negative. Therefore, you should not believe various dubious articles on the Internet about how periodontal disease is transmitted. The disease is associated with metabolic disorders, and not with the spread of bacteria. Therefore, those who believe that periodontal disease can be contracted or that the disease is transmitted through a kiss are deeply mistaken. However, despite this, we must not forget about the rules of daily oral hygiene in order to prevent the occurrence of other problems with teeth and gums.
What is periodontitis? Causes and symptoms
With contagious periodontitis, the periodontal structures become inflamed, the periodontal junction is destroyed, and periodontal pockets are formed. Pathogenic bacteria accumulate in them.
The reasons for the development of an infectious condition are the accumulation of dental plaque, contagious gingivitis, and improper or insufficient oral hygiene. The contagious disease itself is infectious in nature.
Symptoms of periodontitis:
- redness and bleeding of the gums;
- bad breath;
- exposure of the necks of the teeth;
- loose teeth.
Is the disease contagious? Is periodontitis transmitted through kissing?
Periodontitis is infectious in nature because it is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. May accompany periodontal disease.
When kissing, the pathogen is transmitted, and there is a risk of infection and the development of periodontitis.