From this article you will learn:
- how many baby teeth does a person have,
- How are temporary teeth different from permanent teeth?
- Scheme of loss of baby teeth in children.
Milk teeth are a set of twenty temporary teeth that begin to erupt in a child, usually at the age of 5-6 months (the central incisors of the lower jaw erupt first). The need for temporary teeth is evolutionarily determined by the small size of the jaws of newborns. Permanent teeth are much larger than milk teeth, and their number is 1.5 times greater, and therefore, if children immediately had permanent teeth, they simply would not be able to fit into small jaws.
Because of this, in small jaws, smaller temporary teeth (in a reduced number) erupt first, and only when the jaws reach the desired size does the child replace milk teeth with permanent ones. Therefore, the time when baby teeth fall out in children is integrally connected with the growth of the jaw bones and the development of the rudiments of permanent teeth. Typically, the loss of primary teeth begins in children at the age of 6 years, and in girls this process begins earlier and proceeds faster.
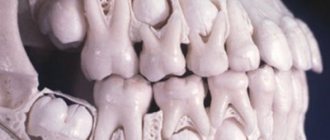
In Fig. 2 you can see how the change of baby teeth to permanent ones in children looks like on an x-ray. In this case, we see that the child has already erupted permanent central and lateral incisors, as well as the first permanent molars. But in the lateral sections of the jaws we also see still preserved milk teeth, between the roots of which the rudiments of permanent teeth are located.
How many baby teeth do children have?
So how many baby teeth do children lose? In a newborn, in the depths of the upper and lower jaws there are only 20 rudiments of temporary teeth - 10 follicles for each jaw. It should be noted that the formation of follicles begins already at 6-7 weeks of embryonic development, and when a child is born, the crowns of his baby teeth are already fully formed (although they have not yet erupted). But the formation of the roots of baby teeth continues to occur after the birth of the child.
Studies have shown that a baby tooth begins to erupt when its root is 25-50% formed. One of the theories of eruption says that the developing root, as it were, pushes the baby tooth out of the jaw. Normally, the process of teething in the primary occlusion begins at 5-6 months, and in completely healthy children it ends by 24 months (the last to erupt are the temporary fifth molars). In diagram No. 1 you can see how many baby teeth children should have depending on their age.
Scheme of teething in children without pathology (scheme No. 1) –
→ Eruption of baby and permanent teeth
In diagram No. 1 you can see the timing of the eruption of baby teeth - in completely healthy children who do not have any pathology. These data are taken from the National Guide to Pediatric Dentistry. But if there is (for example, any somatic pathology), the timing of the eruption and loss of baby teeth can shift by 3-5 months. Below in the article we will tell you at what time children’s baby teeth fall out and what leads to this.
What help can dentists provide?
If the baby tooth is stable and healthy, its presence does not lead to malocclusion, and a permanent one is not expected to appear in its place, then the doctor will try to extend its service life as much as possible.
If we are talking about incisors or canines, the dentist may suggest correcting them with veneers or lumineers, or performing a restoration with a composite so that they look aesthetically pleasing in the smile area and do not stand out from the rest with their small coronal part.
If we are talking about chewing molars and premolars, then the installation of a crown may be recommended. But it is important to remember that the patient himself needs to make every effort to preserve such a “special” tooth: he, like everyone else, needs careful daily hygiene, as well as enhanced protection. For example, to protect the enamel from bacterial attack, you can undergo fluoridation or remineralization procedures.
Baby teeth in children: loss pattern
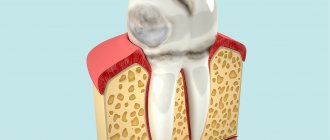
We have already said that the loss of baby teeth is associated with the growth of the jaws and the growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth. The rudiments of permanent teeth are located close to the roots of primary teeth, and therefore their development leads to pressure on the roots of temporary teeth (24stoma.ru). This pressure leads to resorption (resorption) of the roots of baby teeth, and as a result – to their mobility and loss. The exception is permanent molars (6-7 teeth), the eruption of which occurs without the loss of temporary teeth, and therefore parents often miss their appearance.
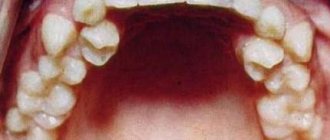
But sometimes permanent teeth erupt incorrectly, and this leads to the fact that the roots of temporary teeth may not undergo resorption for a long time. This situation is especially common in the area of eruption of permanent premolars (4-5 teeth), less often in the area of incisors and canines. In diagram No. 2 you can see the average time frame for when baby teeth change in children. An interesting fact is that in girls, tooth loss begins earlier and progresses faster (compared to boys).
When baby teeth fall out in children: scheme No. 2
Do all baby teeth fall out in children? Please note that temporary teeth can remain in the oral cavity for a much longer time. The main factor causing the loss of a baby tooth is the pressure of the permanent tooth germ on the roots of the baby tooth. Therefore, in the absence of a permanent tooth germ, or its death due to inflammation at the roots of a baby tooth, temporary teeth can remain in the oral cavity much longer than normal. In this case, milk teeth can sometimes be found even in 30-year-old people.
Summary: at what age do baby teeth fall out - loss begins with the central incisors of the lower jaw at 6-7 years of age (in girls, reliably from 6 years of age). Then, at the age of 7-8 years, the central incisors of the upper jaw and the lateral incisors of the lower jaw fall out (and in girls this process reliably begins at the age of 7). If we talk about the age at which milk teeth fall out, then usually this process ends at 12-13 years with the loss of the last milk teeth (second temporary molars).
When you compare the tables for the loss of baby teeth and the eruption of permanent teeth, confusion may arise in your head regarding the name of the teeth. For example, first and second temporary molars and first and second permanent molars. Please note that in place of the fallen first and second temporary molars, permanent premolars (4-5 permanent dentition teeth) will erupt.
What problems can pathology cause?
The main problems may be related to aesthetics (small crown size) and supporting function (short roots). But this is not all the complications that the presence of milk units in the permanent dentition can lead to: they can interfere with the growth of the permanent ones, cause malocclusion, and provoke incorrect placement of “neighbors.” This situation can cause you a lot of inconvenience, ranging from the inability to fully eat and chew food, ending with aesthetic defects, impaired sound pronunciation, difficulty in hygienic care, and, as a result, the appearance of various dental diseases.
Anatomical differences between primary and permanent teeth
As we said above, temporary teeth differ from permanent teeth in a smaller number, as well as in significantly smaller sizes (they are 2 times smaller than permanent teeth).
At the same time, the shape of the crowns of primary teeth is always more spherical, and in the area of the neck of the primary tooth there will always be a noticeably more pronounced narrowing. In addition, temporary teeth are whiter than permanent teeth and often have a bluish tint. Differences between temporary and permanent teeth (description below) –
Anatomical differences:
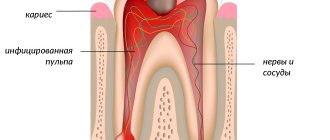
- Tooth enamel – the enamel of temporary teeth is much less mineralized (saturated with minerals, primarily calcium and phosphates). Therefore, with insufficient oral hygiene, children develop caries almost instantly. In addition, the thickness of the enamel of temporary teeth is approximately 2 times less than that of permanent teeth - this circumstance leads to a very rapid transition of caries to pulpitis. There are also many microcracks and pores on the surface of the enamel of temporary teeth.
- Dentin of the tooth - the dentin layer is located under the layer of tooth enamel, and its thickness is also 2 times less (than that of permanent teeth). The dentin of temporary teeth is lighter, it is less mineralized, softer, and therefore it is much easier to prepare with a drill than the dentin of permanent teeth. Due to the fact that dentin is less mineralized and softer, the carious process in dentin spreads deeper faster, which leads to the rapid development of pulpitis in baby teeth.
- Pulp (neurovascular bundle) - some parents ask: “Are there nerves in baby teeth?” Of course, they exist, but due to the thinner layers of enamel and dentin, the pulp in baby teeth is located much closer to the surface of the tooth. The pulp chamber (tooth cavity), in which the pulp is located, is always larger in primary teeth, and therefore the pulp occupies a relatively large volume in the tooth. And besides, in baby teeth the “pulp horns” (processes) are more pronounced, which creates an additional danger of injury to the pulp during the treatment of caries.
- Roots of teeth – some parents ask: “Do baby teeth have roots?” Of course, they have roots, but they are thinner and widely spaced (at the same time, the root canals and apical openings in baby teeth are wider than in permanent teeth). But the development and growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth leads to the formation of constant pressure on the roots of primary teeth, which leads to their gradual resorption and loss. We hope that our article: Scheme of loss of baby teeth in children was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dentist, 3. The European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry (EU), 4. National Library of Medicine (USA), 5. “Pediatric therapeutic dentistry. National leadership" (Leontyev).
Is chewing gum good for you?
The cult of chewing gum and whitening toothpaste at a young age does not add health to your teeth. Not only do teenagers chew gum for more than 15 minutes (this process can take several hours), but they also use it repeatedly. Chewing gum really cleans the mouth. However, only in the first minutes. Afterwards, it becomes a breeding ground for bacteria and plaque on thin enamel. Within a few hours in the mouth, 2 cubes of chewy sweetness can cause caries.
Striving for a stellar smile can lead to complete destruction of the enamel. Therefore, when at the age of 30 you want to show off your white teeth, you will have to spend a lot on replacing them. To prevent this from happening, you should contact a dental clinic, where they will select a program for gentle enamel cleaning. to become the owner of a “ Hollywood smile ”. Firstly, thanks to professional teeth cleaning to remove plaque and tartar. The dentist, using a sand-saline solution and an ultrasound machine, literally removes plaque from the teeth. This method can lighten the enamel by a tone or two, but not lighter than the natural color. This procedure is necessary in youth. It is not only possible, but also must be carried out every six months. Thanks to which your teeth will be healthier and cleaner.
Sometimes doctors offer gel teeth whitening. This is a long-lasting and invisible way to whiten and make your teeth lighter. Its advantage: safety for health and a very stable result. And lastly, clinics often use whitening strips. They contain peroxide and work many times better than any other method. However, due to the acid content, teenagers should avoid it.
Delete or leave
If there is a pronounced aesthetic defect, and there are also difficulties with the eruption of the permanent unit, removal is prescribed. But first, the dentist will conduct a thorough examination to make a final decision.
Assessing the state of a persistent unit
The tooth is left if it is well preserved and does not interfere with the rest, if the rudiment of a permanent element is missing or if it lies too deep, but the roots remain intact. To determine this, the patient undergoes X-ray diagnostics and, if necessary, computed tomography. The picture will show whether there are prerequisites for eruption, and will also help to assess the current state of the root system.
Identification of the rudiments of permanent units
If the rudiments are clearly visible in the picture, this is not yet a reason for removal. The decision is made based on the individual characteristics of the clinical picture. It largely depends on the age of the patient and the depth of occurrence. Sometimes removal followed by traction is prescribed, and in other cases everything is left as is. If there are no rudiments, the milk element is restored to give it an aesthetic appearance. For this purpose, veneers or lumineers can be installed, or prosthetics with a crown can be performed.
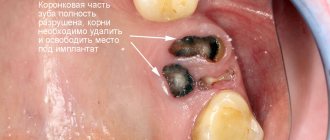
The photo shows the extraction of a permanent tooth.
Indications for removal
It’s another matter if the causative element hurts. What to do in this case and how to treat it? In such a situation, specialists usually prescribe removal. Here are some more compelling reasons for such a radical solution:
- grade 3 or 4 mobility is noted,
- aesthetic defect in the absence of rudiments,
- there is not enough space for the correct arrangement of neighboring elements if the rudiment is missing or is too deep,
- the presence of a developed permanent tooth, which is prevented from erupting by a temporary unit,
- damage caused by caries, inflammatory processes or trauma.
Most often, such a tooth has to be removed.
Problems with aesthetics due to discrepancies in the size of the crowns are not a direct indication for removal. If there is no other reason for extraction, the appearance of the crown can be restored using light composites, veneers or lumineers. Many people are concerned about whether it is painful to remove persistent units. There is no need to worry about this - modern anesthetics are highly effective, so there will be no pain during the procedure.