From this article you will learn:
- why does a fistula appear on the gum,
- features of treatment in adults,
- how to treat a fistula on the gum of a child with baby teeth.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
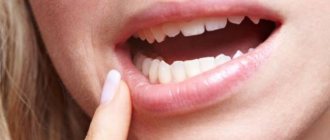
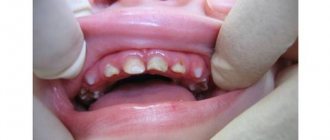
A fistula on the gum is always a symptom of purulent inflammation occurring in the root area of one of the teeth (Fig. 1-2). Most often, fistulas form against the background of exacerbation of apical periodontitis. This dental disease is most often a consequence of untreated caries and pulpitis, and when it occurs, a focus of chronic inflammation forms at the apex of the tooth root. Typically, such chronic inflammation is asymptomatic, but with hypothermia or decreased immunity, an exacerbation can occur - with the formation of pus at the site of inflammation.
The formation of pus in some cases leads to the formation of a fistula tract in the bone, which opens on the surface of the gum with a fistula opening. Accordingly, purulent exudate formed at the site of inflammation will be released from the fistula opening into the oral cavity. As a rule, the fistula opening is always located on the gum in the projection of the root of the causative tooth. In most patients, the appearance of a fistula is always preceded by pain when biting on one of the teeth. After the fistula has formed, the pain usually disappears immediately.
Fistula on the gum: photo
As we said above, a fistula on the gum is most often a companion to a focus of purulent inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. In dentistry, this disease is called “apical periodontitis.” The reasons for its development may be: 1) untreated caries and pulpitis in a timely manner, 2) poor-quality root canal filling, 3) trauma to the front teeth as a result of a blow or fall, which is more common in children. In the first two cases, you can always see caries, a filling or an artificial crown on the causative tooth (Fig. 1-2).
If the cause is an injury, you can usually see a chip on the tooth, or that the crown part of the tooth has acquired a bluish color. But a fistula can appear not only with periodontitis of the tooth. It can occur, for example, as a result of perforation, crack or fracture of the tooth root (allowed by the dentist during root canal treatment), and a fistula can also appear as a result of such gum disease as localized and generalized periodontitis.
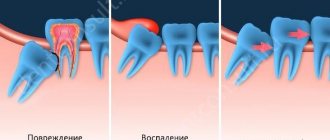
With periodontitis, periodontal pockets form along the surface of the roots of the teeth, from which purulent discharge drains during periods of exacerbation. If the periodontal pocket is very deep, then the outflow of pus from it may be impaired. In this case, an abscess forms in the projection of the periodontal pocket between the gum and the root of the tooth, which dentists call the term “periodontal abscess.” One of the outcomes of a periodontal abscess may be the formation of a fistula, through which pus will escape into the oral cavity (Fig. 3).
What does a fistula on the gum look like (video) –
Pay attention to video 1 - how the doctor inserts a thin gutta-percha pin into the fistula opening, used for filling root canals. Through the fistula tract, the pin can be advanced directly to the source of inflammation, i.e. get it right to the top of the tooth root. This clearly shows that the fistula tract connects the fistula opening on the gum - directly with the source of inflammation at the root of the tooth.
Types of anal fistula
Medical experts distinguish two types of fistulas. Among them:
- external entities;
- internal education;
Internal fistulas form in the rectum and emerge from the lumen of the anus, affecting the soft tissue of the perineum. In 90% of cases, this type is considered a complication that occurs at the acute stage. It is extremely rare that fistulas form after unsuccessful surgery performed by incompetent surgeons. Thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins also leads to the formation of fistulas.
Features of the recovery period
When a diagnosis of “vesico-vaginal fistula” is made, the patient, with consent, undergoes surgical intervention - fistuloplasty; in the presence of stones, surgical intervention is supplemented with cystolithotomy. When the expected results are achieved (restoration of adequate urodynamics of the lower and upper urinary tract), patients undergo rehabilitation measures. In case of unsatisfactory results of treatment, complications that have arisen are treated, or sanitation of the genitourinary organs is carried out and, if necessary, repeated surgical treatment. A follow-up examination is carried out 3 months after surgery, a year later and annually thereafter.
| Rehabilitation activities | Recommendations |
| Hygiene | Carefully monitor vaginal hygiene, using products that do not disturb its microflora |
| Diet | The diet should be balanced, without foods that can cause bloating and constipation. |
| Medicinal | The use of special tampons and ointment dressings for rapid healing and relief of pain and inflammatory symptoms in the postoperative period |
Symptoms of anal fistula
When fistulas form near the anus, certain symptoms are observed.
- Blood and ichor are released from the anus, an unpleasant pungent odor, purulent and mucous discharge appear.
- The patient notices pain in the affected area.
- Inflammation develops, the epidermis becomes irritated and swells.
- Purulent compactions form near the fistula, which bleed when pressed.
- The patient loses his appetite and sleep is disturbed. The patient becomes irritable, nervous, and quickly gets tired.
- The process of bowel movements and urination is disrupted.
- Blood clots, pus and mucus are found in the stool. When defecating, the patient strains, which causes spasms and pain in the intestines.
- With a complex fistula, serious local processes develop. The shape of the anus changes, anal fissures and scars appear. Wounds form on muscle structures that bleed regularly.
A common complication is sphincter pathology, which, if left untreated, leads to the appearance of malignant tumors.
When an anal fistula forms, pectenosis develops in parallel. Scars appear on the walls of the anus, after which the canals are injured and tightened.
What can a doctor do?
Therapy for patients with external fistulas is based on:
- local treatment;
- general therapeutic;
- operational.
Local therapy refers to the treatment of the resulting wound, as well as the protection of surrounding tissues from the effects of fluid that is released from the canal. For example, if the fistula is on the leg, abdomen, etc., then the purulent area is treated with various means (ointments, pastes and powders). They are applied at the external opening of the canal, thereby preventing the skin from coming into contact with pus, mucus, etc.
In addition, chemical agents can be used that prevent irritation of external tissues by neutralizing secretions from the fistula passage. For this, it is recommended to use inhibitors of proteolytic enzymes (for example, Gordox, Contrikal, etc.).
Mechanical methods of protecting the skin are aimed, first of all, at reducing or completely stopping discharge from the canal using special devices.
For the general treatment of purulent and other fistulas, they are constantly washed with an antiseptic solution.
Tubular granulating passages quite often close on their own after eliminating the causes of their occurrence (for example, removal of bone sequestration, ligature, etc.). But labiform fistulas never go away on their own. To treat such deviations, only surgical intervention is used to excise them, suturing the external holes, or resection of the affected organ.
It should also be noted that in some cases, surgeons create fistulas artificially specifically so that the patient can eat, or in order to remove accumulated secretions from any internal organ. These channels can be either permanent or temporary. After the patient's condition improves, the temporary canals are closed surgically.
In addition to external ones, internal fistulas (interorgan) are also created artificially. As a rule, they are imposed either for a long time or for life.
Causes of rectal fistula
In 90% of cases, fistulas and fistulas are formed in the absence of treatment during an infectious disease. Soft tissues are affected, an infection spreads in the body, which penetrates the walls of the rectum and connective tissue. A perirectal abscess appears, and a purulent fistula forms in parallel.
According to medical statistics, fistulas are often the result of injury or surgery. When removing affected soft tissue or rectum, surgeons may damage healthy epithelium, thereby provoking the growth of a fistula. In the female half, the pathology is diagnosed after childbirth. During labor, a woman strains strongly, the walls of the anus are stretched and deformed. Fistulas between the intestines and the vagina are formed during prolonged labor, when the birth canal ruptures, or when the fetus is specifically laid down.
A fistula occurs after gynecological surgery. The infection spreads in the body if the surgeon used unsterile instruments and did not follow hygiene rules. Also, the formation of a rectal fistula appears in people who suffer from Crohn's disease and intestinal pathology.
If a patient has been diagnosed with fecal fistulas, then we are talking about cancer of the rectum, tuberculosis of the affected area. The likelihood of developing actinomycosis increases. Neoplasms often appear with AIDS, syphilis, chlamydia and other infectious diseases.
Anal fistula, treatment
How to treat fistulas in the anus? In most cases, removal of the anal fistula is used. Surgical treatment will help avoid complications and relapse. Conservative treatment is used only in the initial stages of the disease. The patient is treated at home and regularly attends consultations with a proctologist.
In general, coloproctologists welcome radical excision of the fistula, since taking medications does not guarantee that the source of the disease will be eliminated. During surgery, the abscess is opened, after which the purulent contents are removed. During the rehabilitation period, the patient takes antibiotics, attends physical therapy, electrophoresis, ultraviolet radiation and other procedures.
The treatment process is selected individually for each patient. When fistulas are formed, the fistula is dissected or excised into the lumen of the rectum. The affected areas of the anus are opened and cleaned of pus and contents. The sphincter is sutured. To block the internal fistula canal, the mucous flap is also removed.
The treatment method depends on the location of the fistula tract and fistula. The presence of infiltrates and purulent pockets in the pararectal area is taken into account. With timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment, in 90% of cases the disease is eliminated in a short time. If surgical intervention is not performed on time, anal sphincter insufficiency is observed, the fistula recurs, and the mucous membrane becomes inflamed. The most dangerous complication is the appearance of malignant neoplasms. The rehabilitation period takes on average fourteen days. The patient must observe the rules of personal hygiene, change the diet and listen to the recommendations of the attending physician.
How to avoid fistula tracts
The question of how to avoid the appearance of abnormal canals in the genitourinary system is relevant for many men and women who are concerned about their health. You can avoid the occurrence of fistula tracts:
- avoiding infectious diseases during the postpartum and postoperative period;
- if there are injuries, consult a doctor immediately and undergo a course of treatment;
- after surgery, observe all restrictions: diet (foods that will not cause constipation and bloating), lack of physical activity, etc.
Treatment without surgery at home
Surgery is not always used. In the early stages of proctological disease, laser therapy is also performed. There is no discomfort or pain during the procedure. The recovery period is significantly reduced. The risk of relapse and complications is reduced. After laser excision, tissue structures heal quickly, inflammation disappears.
Sitz baths have an effective effect. The patient makes baths at home with sea or iodized salt, with medicinal herbs and infusions. To prepare the contents, use a tablespoon of salt and baking soda. These components are added to five liters of filtered water and filtered. The patient takes a bath in a sitting position for twenty minutes. The course of treatment is fourteen days.
Sea and iodized salt affect the discharge of purulent masses, eliminate the inflammatory and infectious process in the body. Quite often, medicinal herbs are used for anal fistula. Proctologists advise preparing a decoction of calendula, chicory, oak bark and chamomile. The above components are mixed with a liter of filtered water. The water is infused with herbs and then filtered. The contents are diluted with five liters of warm water.
The bath is done in a sitting position for ten minutes. The course of treatment averages ten days, depending on the patient’s condition. You should not start treatment without consulting a proctologist and your attending physician. Make an appointment with a coloproctologist at the private proctology clinic “Proctologist 81”.
A medical specialist will conduct an initial examination and, using palpation, determine the location, size and structure of the fistula. After this, each patient is sent for testing. It is necessary to take a general blood, urine and stool test. In some cases, a blood glucose test will be required. The patient attends various diagnostic tests that will help establish an accurate diagnosis. These include radiography, ultrasound diagnostics, and magnetic resonance imaging.
Folk remedies
After treatment, to speed up the healing of damaged tissues, reduce inflammation and relieve pain, doctors recommend using safe folk remedies - herbal infusions and decoctions.
To prepare the infusion, you need to pour a tablespoon of plant material into a glass of boiling water, leave, and strain. The decoction is prepared a little differently: a tablespoon of raw material is poured into a glass of water, heated in a water bath for 15 minutes, then infused and filtered.
Prepared medicinal solutions are used to rinse the mouth. Procedures are carried out every hour. Rinse duration is at least 4 minutes. As a rule, after treating a fistula, a pregnant woman is recommended to use:
- Infusion of St. John's wort with honey (the infusion is prepared in the usual way, then honey is added to the solution at the rate of a teaspoon per 100 ml of liquid).
- A decoction of chamomile or calendula, as well as a collection of these herbs.
- An infusion or decoction of chamomile, oak bark, sage (the herbs are mixed in equal proportions).
- Propolis infusion. The product has a pronounced healing and anti-inflammatory effect, but is contraindicated for women who are allergic to bee products.