Flux in a child: causes and treatment
If a child complains of severe pain in the mouth, his cheek is asymmetrically swollen and his temperature has risen - these are signs of periostitis.
Periostitis is an inflammation of the periosteum, a dense connective plate that covers the surface of the jaw bone. The disease is better known as flux. In the article Stom-Firms.ru we will consider the causes of formation, possible complications and methods of treating childhood flux .
What you should never do - common mistakes
There are a number of important rules that parents should definitely follow when checking for signs of gumboil development in their child. Experts in the field of pediatric dentistry put forward the following categorical prohibitions in this regard:
- apply heat to the cheek from the side of the diseased tooth - such a compress can cause the infection to spread to the throat, ears and other parts of the body,
- giving a child antibiotics - the decision to prescribe such serious drug therapy can only be made by a professional doctor. Otherwise, potent drugs can negatively affect the health of the baby’s body,
- try to open the abscess yourself - again, only a doctor can do this correctly, in compliance with all the rules of asepsis, that is, without the risk of serious infection of internal organs and systems,
- overdo it with painkillers - if the child is really unwell, of course, before arriving at the dentist, you can give him half a painkiller tablet, but no more. Regarding the correct dosage and suitable remedy, you should consult your doctor, at least by phone.
You should not give your child antibiotics on your own.
During rinsing, make sure that the child does not swallow the solution - this can lead to infection entering the body. If after visiting the dentist the symptoms do not go away and the baby’s condition does not improve, it is better to consult a doctor again, and this should be done as soon as possible.
Features of flux in children
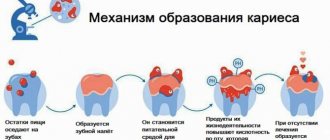
In adults, periostitis is less common; it develops more often in children. This is due to the structural features of baby teeth. They are more porous than indigenous ones. The pulp is located closer to the surface, and the root canals are wider. Because of this, pulp inflammation easily spreads to the periosteum.
Periostitis in a child develops very quickly. And it's not just about the structure of the teeth. The immune system is not yet developed enough, so it cannot effectively respond to infection. And due to the small area of soft tissue, inflammation can move from the tooth to the periosteum in just a few hours.
How are baby teeth different from molars?
Baby teeth appear at the age of six months. First, the central incisors erupt on the lower jaw, then on the upper jaw. By about 2.5 years old, the baby already has a full, white-toothed smile. His mouth contains 20 milk teeth, which will serve the child for several years.
After about six years, temporary teeth begin to be replaced by permanent teeth. When the baby brings the first “trophy” to his parents, it causes sincere joy and tenderness. And also the desire to carefully examine what the baby is holding in his fist. And while studying the tooth, parents can draw several wrong conclusions.
pixabay.co/
The first is that baby teeth have absolutely no roots. This impression is created because the root shoot of a fallen tooth is usually located on only one side, and sometimes it does not exist at all. In fact, primary incisors and molars, of course, have roots, but over time they become smaller.
This occurs in order to ensure a natural and painless process of changing the dentition. When the time comes to change the bite, the roots of the baby teeth gradually dissolve. And thanks to this, the indigenous ones “push out” their predecessors from the gums, taking their place.
The second incorrect conclusion may be related to the size of the tooth. It seems incredible that such a “baby” could have the same structure as an “adult” native.
“The structure of baby teeth is almost the same as permanent teeth,” comments Natalya Terentyeva. “They have roots, root and coronal pulp, root canals through which nerve fibers pass. Milk teeth differ from molars in that their enamel is weakly mineralized, which means it is more susceptible to destruction and the development of carious processes.”
Causes of baby flux
Pulpitis is the main, but not the only cause of periostitis in children. Let us list other factors influencing the development of the purulent process:
- It is difficult for a 2-4 year old child to fully brush their teeth. Food debris and plaque can accumulate in the gum pockets and cause inflammation.
- Children “taste” everything, this injures the gums and introduces bacteria into the oral cavity. Weak immunity and structural features of periodontal tissue lead to the fact that even a small wound on the gum can provoke the appearance of gumboil in a few hours.
- Periostitis can develop after tooth extraction if there is a source of infection in the mouth. For example, gingivitis or tonsillitis. Bacteria from the source of inflammation quickly reach the periosteum through an open wound.
In some cases, the disease develops as a result of jaw injuries and after hypothermia.
Specific manifestations of the disease
Periostitis is easy to diagnose on your own due to specific symptoms, but do not be deceived - easy to diagnose, flux requires a professional approach to treat.
Self-medication in this case can result in serious complications.
The main symptoms of flux are:
- pronounced swelling of the tissues adjacent to the site of inflammation;
- elevated temperature;
- pain syndrome;
- hyperemia and swelling of the gums;
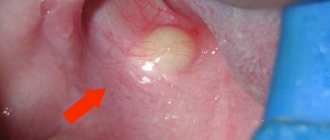
- the appearance of a clearly visible abscess on the gum.
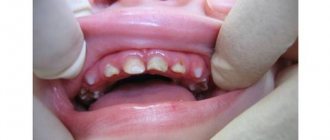
Swelling will be barely noticeable in the initial stages of the disease. But the further the inflammatory process develops, the more pronounced the asymmetry of the face becomes - the cheek on the side of the inflammation may become very swollen.
Depending on the location of the pathology, swelling sometimes spreads to the upper or lower cheekbones, goes towards the ear or under the eye.
At the onset of the disease, the child becomes more capricious due to a mild but already unpleasant pain syndrome.
Children often lose their appetite or try to chew on only one side of their mouth. When you press on a sore tooth, the discomfort will intensify.
Hyperemia develops already in the early stages of periostitis. A large amount of blood flows to the affected area, as a result of which the gums become a brighter, rich red color and swell over time.
The abscess does not appear immediately. The more pronounced it is, the more time the disease has developed. Sometimes the abscess can even break out on its own.
According to the nature of the course, acute and chronic periostitis are distinguished. The acute form of the disease in children is much more common than the chronic form, and it is more severe.
There are many types of periostitis, but most often children encounter:
- acute serous periostitis;
- acute purulent periostitis.
- chronic odontogenic periostitis;
- chronic nonodontogenic periostitis.
The result of neglected flux can even be the destruction of permanent teeth that are forming to replace milk teeth. Such a complication threatens that after the baby teeth fall out, the child’s permanent teeth will not erupt, and the baby will have to resort to prosthetics from childhood.
Why is flux dangerous in children?
Parents often underestimate the danger of periostitis. They try to treat the disease with folk remedies or leave it to chance. With this approach, serious complications may develop:
- An abscess is a purulent inflammation of the bone.
- Phlegmon is the transfer of suppuration to adjacent tissues. It can lead to blood poisoning - sepsis.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges.
- Inflammation can spread to the permanent tooth bud . In this case, the molar often does not grow or erupts with a delay.
If your baby has developed gumboil, you should not hesitate to contact the dentist. Warming up, compresses, self-prescribing aspirin, antibiotics or painkillers - all this leads to an exacerbation of the disease.
Features of the pathological process
Periostitis can occur in acute or chronic form. In the first case, a small patient exhibits all the signs of gum suppuration, severe swelling and acute pain in the causative tooth, which intensifies with mechanical action. Often the characteristic symptoms are accompanied by high temperature.
If appropriate medical care is not provided in time, you may face the risk of the pathological process becoming chronic. In such a situation, the disease becomes even more dangerous, even though the acute symptoms usually subside.
The mucous membrane turns red and swells within the pathological focus
In no case should they remain idle or try to correct the situation with improvised means without first visiting a doctor. The advice of traditional medicine really helps to relieve acute manifestations of the disease, but this does not mean that the pathology can be completely cured in this way. The infection will continue to spread through soft and even bone tissues, which can result in serious serious complications.
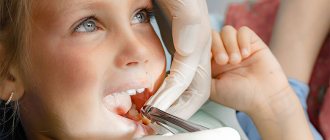
Flux treatment: surgery and recovery after it
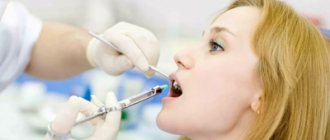
After the initial examination, the dentist administers local anesthesia to the child. Then he treats the oral cavity with an antiseptic solution and uses a scalpel to cut the problem area down to the bone. Removes suppuration and installs drainage, which removes remaining pus within 4 days.
Teeth in the area of gumboil are usually removed. But for patients under 4 years of age, the surgeon tries, if possible, to preserve the temporary tooth for the correct formation of the bite.
Treatment of the disease is not limited to surgery. The doctor prescribes antibiotics and antiseptic rinses that will avoid re-inflammation. If the periostitis was advanced, the doctor sends the child to the hospital for 10 days.
As a result of successful treatment, the temperature subsides, the swelling on the cheek goes away and the pain subsides. If the pain and fever do not go away, you need to go to the hospital again.
In the postoperative period, children are advised to drink a lot, rest and eat properly. The diet should contain a sufficient amount of protein, vitamins and minerals - calcium, magnesium, iron.
Prevention methods
To avoid the appearance of flux, it is enough to carry out preventive measures:
- monitor how the child maintains oral hygiene;
- use high-quality toothpastes in accordance with the baby’s age;
- bring the child to the dentist for examinations every six months;
- promptly treat carious lesions;
- strengthen the immune system.
Introduce healthy foods into your diet, minimize the amount of carbonated drinks and confectionery products.
How to avoid complications with periostitis?
To cure flux in a child and prevent complications, it is important to promptly consult a doctor. The infection can reach the brain through the lymph flow in a short time, because the jaws are close to it. The possibility of sepsis cannot be ruled out. The inflammatory process spreads faster the younger the baby.
Many paid medical centers and dentist offices are open on weekends and at night. If flux forms late in the evening, you need to immediately call an ambulance.
These sections will be useful to you
- Children's dentistry
- Removing a baby tooth
- Treatment of pulpitis in children
References used for the article:
- Fomenko I.V., Kasatkina A.L., Shishkina V.I., Firsova E.P. "Analysis of the causes of the development of odontogenic periostitis of the jaw bones in children." Volgograd scientific and medical journal. 2021. No. 1 (49). pp. 54-55.
- Kulakov A.A., Robustova T.G., Nerobeev A.I. “Surgical dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. National leadership" // M.: "GEOTAR-Media", 2010. - 928 p.
- Zhelezny P.A., Kolybelkin M.V., Izyumov A.O., et al. “Structure and nature of inflammatory processes in the maxillofacial area in children.” Medical science and education of the Urals. 2021. T. 18. No. 2 (90). pp. 91-94.
Expert editor: Katerina Aleksandrovna Melnikova
Pediatric dentist with 4 years of experience.
Preventing inflammation in the mouth
Preventive measures include careful oral hygiene and avoidance of bad habits that provoke the formation of tartar. These include smoking, uncontrolled consumption of coffee and strong tea
In addition, it is extremely important to comply with the following rules:
- visit the dentist regularly and get rid of caries on time;
- try to include solid foods in your diet - raw vegetables, fruits with hard skin;
- at the slightest suspicion of an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, immediately go to the doctor without starting the problem.
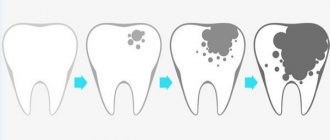
The development of this pathological process occurs as follows:
- At first, the child feels pain in the gums and blood on their surface. This is the first symptom of progressive gingivitis (an inflammatory process in the gums without a direct disruption of the connection between the teeth and gums).
- If the necessary treatment is not applied, the pathological process progresses to the next stage – periodontitis. With periodontitis, the periodontal junction is damaged. Due to the violations, peculiar “tooth pockets” are formed, into which food debris gets trapped.
- The last stage is filling the “pockets” with pus. It is at this stage that the child develops hard lumps on his gums.
Treatment process
If such bumps appear, the baby should be urgently taken to a periodontist for advice.
Using an x-ray, the doctor will assess how damaged the bone tissue is and determine a further treatment plan.
The therapy involves the direct elimination of deposits on the surface of the teeth and in the “pockets” that have appeared. After this, medications are added.