Vital extirpation
Stage I. Anesthesia.
Before administering anesthesia, it is necessary to carefully collect a life history:
— whether anesthesia was previously performed, whether there are any allergies to food, other medications, etc.
The most serious complication is anaphylactic shock, which lasts 2-6 minutes. It is preferable to carry out the test in vitro (“in vitro”). During a routine appointment, a provocative test is often used: drop a drop of anesthetic under the tongue. Wait 10-15 minutes. In case of complications during anesthesia, provide emergency assistance and apply arsenic paste to the tooth for subsequent devital extirpation at the next visit.
Stage II. Preparation of a carious cavity.
When the cavity is localized in the cervical region of premolars and molars (Class V according to Black), in addition to preparing the carious cavity to access the root canals, trepanation of the tooth crown is required (access through the chewing surface of the tooth).
Stage III. Opening of the tooth cavity.
We remove the roof of the tooth cavity using a thin fissure bur in a circular motion (analogous to opening a tin can).
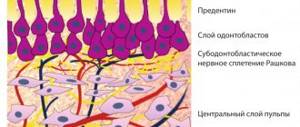
Stage IV. Amputation of coronal pulp.
We carry it out using a sharp excavator or a spherical bur corresponding to the diameter of the tooth cavity.
V stage. Expansion of the root canal mouth.
Small spherical bur, fissure bur, conical bur at low speeds.
Stage VI. Pulp extirpation.
We remove the root pulp using a pulp extractor, which we insert into the canal along the side wall until it stops, turn it 1-2 times around its axis and remove it. If the manipulation is carried out correctly, then a cone-shaped cord remains on the instrument, sometimes even with deltoid branches. But this is only in uncurved and wide channels. In curved canals, we use H-files, which are made by cutting, to remove root pulp. Therefore, with the H-file you can make reciprocating movements (back and forth), movements towards yourself, i.e. cut off the pulp. And if you carry out circular movements with the H-file, the tool will break off in the canal.
VII. Stopping bleeding (hemostasis).
We introduce a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, aminocaproic acid, and “Caprofen” into the root canal on a turunda (on a root needle). Hemostasis sometimes takes 20 minutes. If an attempt to stop the bleeding is unsuccessful, diathermocoagulation (electric shock) is used. Often, bleeding from the root canal during extirpation is associated with incomplete removal of the pulp. The use of 3% sodium hypochlorite solution for medical treatment of the canal, which dissolves the remaining pulp, leads to stopping the bleeding.
VIII. Instrumental and medicinal treatment of the canal.
The purpose of machining is to taper the channel as much as possible. Stepback technique for pulpitis. Medicinal treatment of the canal is carried out with 3% sodium hypochlorite solution (NaOCI), 2% chlorhexedine solution (R4 / Septodont/).
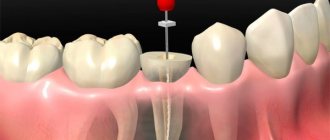
IX. Obturation of the root canal.
X. Insulating gasket, x-ray control.
XI. Seal.
Vital extirpation is carried out in one visit.
Vital pulpotomy
Typically, vital pulpotomy is performed on children, since the root part of the pulp will continue to grow and develop after the procedure. Adults undergo conservative treatment, which involves removing the entire infected pulp (even if it is still alive) followed by filling the root canal. It is considered irrational to preserve the root part of the pulp when root growth has already completed.
It is worth noting that this type of treatment is carried out not only on those teeth where the coronal and root parts of the pulp are clearly differentiated and have a pronounced boundary - these are molars and premolars. For those teeth where there is no clear transition point from the crown to the root, pulpotomy is performed along the cement-enamel boundary.
Devital extirpation
The devitalization paste contains arsenic anhydride. It is applied to the opened (!) pulp horn for 24 hours (one day) in incisors, canines and premolars, and for 48 hours (two days) in molars. Available in syringes and dispensers.
For delayed devitalization, paraformaldehyde paste is used, which is applied for 7-10 days. High concentrations of paraformaldehyde gas are released, which causes necrosis and mummification.
Indications: allergy to anesthetics, business travel. In pediatric practice (less toxic).
Mechanism of action of arsenic paste
Arsenic is a cellular (protoplasmic) poison.
1. Acts on the vascular wall, causing its paralysis. Exudation prevails, nerve endings are compressed and inflammation worsens.
2. As a protoplasmic poison, arsenic penetrates deep into the cell.
3. Causes granular breakdown of the myelin sheath of the nerve fiber.
4. Acts on SH thiol compounds, which, like a “stapler,” hold protein molecules together. Enzymes of tissue respiration are destroyed, which leads to hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the pulp.
5. Histamine and serotonin are released in large quantities, which leads to increased pain.
Therefore, it is necessary to warn the patient that in the first 2-4 hours after applying the arsenic paste, the pain will intensify. Prescribe painkillers.
By the time the pulp is removed (24 hours in single-rooted teeth and 48 hours in multi-rooted teeth), pulp suspended animation occurs.
We perform devital amputation in 2 visits.
First visit.
Stage 1. Partial preparation of a carious cavity (necrectomy).
Medical treatment. Identify and open the pulp horn (painful manipulation).
Remember. Arsenic paste is applied to the exposed pulp horn!
The amount of arsenic paste corresponds to the diameter of spherical bur No. 1 (the smallest bur). Place a loose cotton ball on top. Isolation is carried out with water-based dentin or dentin paste.
The patient should not eat for 2 hours until the dentin paste hardens. Otherwise, the seal of the temporary filling will be broken, and the arsenic paste may leak into the gingival papilla in the case of the cervical localization of the cavity or at the proximal contact. In this case, necrosis of the gingival papilla will occur.
II visit. Check the tightness of the temporary filling and remove it. Further, all stages are the same as for vital extirpation. It is more comfortable to work as there is no bleeding.
For obliterated root canals, a mummifying paste (based on resorcinol-formalin paste) is applied.
For severe mental disorders, they are treated with amputation.
Devital pulpotomy
The devital pulpotomy method is used in the case of elderly patients with already overgrown root canals or if the patient suffers from severe somatic pathology. To do this, open the pulp chamber and put a drug into the hole that kills the pulp. The dead pulp is then removed down to the border of the root canal. A product is applied that mummifies the root part, after which a special gasket is placed and the hole in the tooth is filled. In this case, pulpotomy is performed as a barrier method to prevent the inflammation process from spreading to periodontal tissue.
When pulp removal is inevitable
The list of indications that determine the need for pulp removal includes the following clinical situations:
- Development of acute inflammatory processes affecting the pulp chamber;
- Acute form of pulpitis that occurs against the background of infection of the cavity;
- The need to open the chamber due to mechanical damage;
- Failure to comply with the dental intervention protocol, causing complications;
- Preparation for prosthetics, which requires eliminating the risk of infection of supporting units.
The decision on devitalization is made based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis.
Prediction of treatment success
Vital pulpotomy is a fairly reliable procedure if the goal is to preserve at least part of the pulp functional. However, the success of such treatment largely depends on the dentist’s ability to determine how deep the infection has gone. In other words, the doctor is faced with the task of accurately establishing whether the pulpitis has affected only the coronal part or has spread to the root area of the pulp. Often, a dentist skilled in clinical research methods can confidently determine the boundaries of infection only in 50-60% of cases. Thus, pulpotomy cannot be considered an absolutely definitive treatment. And at the same time, as a method of temporary treatment, pulpotomy is still appropriate, especially since the chances that the pulp will remain at least partially viable are quite high. In the case of pulpitis treatment in children, the vital pulpotomy method is a priority, since the process of root formation is very important.
Symptoms of vital depression
In the state of health of patients with vital depression, the maximum of poor health occurs in the morning hours. In the first half of the day, the person is overcome by melancholy, despondency, and blues. A person makes desperate attempts to distract himself, but his efforts are in vain - the blues do not recede.
A patient with vital depression forces himself to perform elementary activities: his experiences are so strong that he has difficulty performing hygiene procedures, eating breakfast, and cleaning the apartment. It is especially difficult for a person to fulfill professional duties. A patient with vital depression continues to go to work, but he copes extremely poorly with the workload. A person gripped by all-consuming melancholy cannot concentrate on the task at hand and is often distracted by his internal experiences.
With vital depression, the subject ceases to be interested in events happening in the world, refuses to engage in hobbies, and does not enjoy pleasant news. The patient cannot explain what specific moments dissatisfy him and upset him. Even if, from an objective point of view, everything in a person’s life is smooth and stable, she still sees the world in gloomy tones.
In the afternoon, a person’s well-being improves somewhat, but the emotional status never reaches a state of normal mood. With vital depression, dejection and depression negatively affect the quality of sleep. The patient has difficulty going to sleep in the evening, often wakes up in the middle of the night, feeling a “stone on his soul,” and gets up very early in the morning.
Stages of devital amputation
Treatment of pulpitis in an advanced stage does not take place in one visit, with the exception of the dentist’s decision to remove the tooth.
When saving a tooth, devital pulp extirpation in children is carried out in three stages.
- Examination, teeth cleaning and consultation. Preparation of a crown at the site of a carious cavity. Cleaning the cavity and treating it with an antiseptic. Opening the pulp and “deadening” the nerve with paste. Application of a temporary filling.
- Removing fillings and pastes. Repeated preparation. Removal of part of the pulp. Washing and drying the cavity. Adding medicinal paste. Installation of a temporary filling.
- Removal of the old filling and installation of a permanent filling with accompanying manipulations for the restoration of the dental crown.
A professional dentist can perform devital pulp amputation quickly and without any consequences. The tooth is completely preserved and can even partially perform its functions.
Treatment of vital depression
The gold standard in the treatment of vital depression is a combination of medication and psychotherapy. After examination, at the initial stage the patient is prescribed antidepressants with a stimulating effect. The choice of a specific drug occurs on an individual basis, taking into account contraindications and possible side effects. To overcome vital depression, the course of treatment with antidepressants is at least three months. While taking antidepressants, drinking alcohol is prohibited.
Against the background of drug treatment, there is a gradual fading of the symptoms of vital depression and an improvement in the psycho-emotional state of a person. On average, two weeks after the start of antidepressant therapy, the patient’s motor activity is activated, cognitive abilities are improved, and melancholy and melancholy disappear.
Along with antidepressants, to overcome vital depression, the patient may be prescribed medications from the group of mood stabilizers - mood stabilizers. Long-term use of drugs of this class helps to overcome bad mood, eliminates depression and depression, and improves a person’s social adaptation in society.
After the severity of the symptoms of depression has been reduced, psychotherapy methods are included in the treatment. Individual psychotherapeutic techniques are focused on identifying and correcting the factors that gave rise to vital depression. The psychotherapist guides the patient to change the interpretation of the traumatic event. It helps to identify destructive thoughts in a person’s thinking and guides them to the formation of new creative and functional ideas. The doctor teaches the client methods of safely overcoming stressful situations, introduces methods of relieving nervous tension and relaxation.
Since with vital depression there is a high threat of relapse of the disease, the person is advised to reconsider his lifestyle. A person who has at least once encountered the symptoms of this affective disorder should change the work and rest schedule, avoid mental overload and psycho-emotional shocks, and do not forget about the benefits of physical exercise. If you are prone to vital depression, a person should include healthy natural foods in their diet, not abuse alcoholic beverages, and regularly take pharmacy vitamin complexes.