How does a tooth root cyst appear?
The causes of cysts are varied, and among them it is impossible to single out the prevailing ones. So, this may be the result of physical trauma to the maxillofacial bones, or a rare but common medical error, in which the tightness of the root canal was broken, which became the basis for the emergence of a source of infection. A similar situation occurs when a dental crown is installed incorrectly. But the reasons for cyst formation are not limited to this. Untreated infectious diseases (in particular, sinusitis or periodontitis) are no less a provoking factor.
Antibiotics after tooth extraction with a cyst or complex figure eight extraction
After surgery, doctors often prescribe antibacterial and antibiotic drugs. Not in all cases, taking pills is justified, but if there is even the slightest possibility of infection of the wound, then you cannot refuse to take the medication.
Antibiotics are necessary to prevent cyst formation after wisdom tooth removal. It is difficult to remove the figure eight, since the root system is powerful and located deep in the jaw. To extract it, you need to cut the gum, cut off part of the bone, and saw the roots into fragments. With such a complex procedure, tissue is severely damaged and even an experienced surgeon can make a mistake.
Classification of dental cysts
There are not many types of cysts, so understanding them is not difficult. Four main types are distinguished by location:
- wisdom tooth cyst;
— a cyst due to an illiterate (unprofessional) installed dental crown;
- a cyst that arose as a result of the influence of a third-party infectious disease (sinusitis);
- a cyst localized in the area of the front teeth.
At the same time, a classification is used based on previous circumstances preceding the occurrence of the cyst:
- a disease caused by poor-quality removal of one or more teeth;
— periodontal type cyst, provoked by an inflammatory process in the gums;
- a cyst caused by the growth of a wisdom tooth (retromolar or paradental);
- a cyst that occurs in children, first during the period of the appearance of milk (follicular) teeth, and then molars (eruption cyst);
— a cyst that arose as a complication of periodontitis (radicular);
— a situation is also possible in which the tissue forming the tooth degenerates (keratocyst).
Diagnosis of symptoms of tooth root cyst
The appearance of a cyst implies the formation of a cavity, which gradually grows while simultaneously filling with pus. This condition can last for a long time, and the patient does not experience pain. A sign suggesting the presence of a cyst is slight pain that occurs when pressing on the gum. Such a symptom only in rare cases becomes a reason to visit a dentist. Basically, it occurs in later stages, when the pain intensifies and becomes nagging, continuous, cannot be relieved with analgesics, and inflammation begins to additionally manifest itself in the form of swelling and swelling of the gums in combination with a persistent unpleasant odor in the oral cavity. Finally, a situation cannot be ruled out in which a fistula occurs - that is, a channel through which the contents of the cavity independently come out.
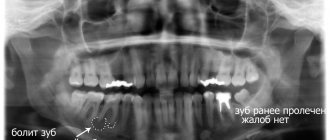
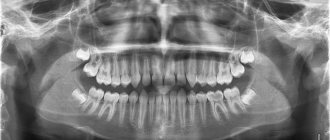
An effective way to detect a cyst in a timely manner is to conduct an X-ray examination followed by its opening and removal.
It should be noted that at the very beginning the disease poses minimal danger to surrounding tissues, since the cavity itself is reliably isolated by thick walls. However, as pus accumulates, the pressure on the walls increases, creating the possibility of a breakthrough, which can lead to blood poisoning and, in the long term, damage to the structure of the jaw bones. At the same time, the dynamics of cyst development are unpredictable and strictly individual. However, in the presence of other inflammatory processes or infections, in a weakened body the transition to the acute stage can occur quickly.
Particular attention should be paid to early diagnosis of the disease in pregnant women. This is due to the complexity of treatment: during pregnancy, only stabilization of the cyst is possible. If the inflammatory process worsens, the choice of treatment methods is strictly limited. That is why, at the planning stage of pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by a dentist.
What will happen if left untreated?
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease leads to dangerous consequences for health. Thus, the patient may encounter:
- destruction of roots, their strong loosening;
- jaw fracture;
- tumor formation;
- purulent abscess;
- periostat;
- osteomyelitis.
The disease can cause the development of sepsis. This is a very serious condition in which the infection enters the blood and quickly spreads throughout the body.
Tooth root cyst in children
The disease has features and varieties that are characteristic strictly for children. First of all, we are talking about formations that arise and go away on their own, without complications: in the form of a rash that appears on the gums, as well as the so-called “Epstein’s pearl”. Both varieties do not pose a danger due to the absence of purulent masses, which means that the cavity is infected. In addition, they may not occur at all, being only some of the phenomena accompanying the development of the child.
The situation is different with the appearance of a cyst during the growth of teeth (both milk and molars). In this case, the resulting cavities are infected, and given the previously described asymptomatic nature of the disease in the early stages, the most reliable method of determining its presence is regular visits to the doctor. This allows for successful treatment at the very beginning of the development of the cyst, saving the tooth in almost 100 percent of cases.
What is a cyst on the gum?
We have already said above that there is such a disease as apical periodontitis, in which a focus of inflammation forms at the apex of the tooth root. Most often, periodontitis has a sluggish chronic course (often almost asymptomatic), and only against the background of decreased immunity or hypothermia does inflammation worsen. With such an exacerbation, pus begins to actively form at the apex of the tooth root, i.e. A purulent abscess forms in the bone around the apex of the tooth root.
The pressure in the focus of purulent inflammation is increased, so the pus seeks a way out, spreading through the bone tissue. It first penetrates under the periosteum located on the surface of the jaw, and during this period there is only limited, extremely painful swelling on the gum. The next stage is when the pus penetrates through the periosteum under the mucous membrane of the gums. Those. gum cyst – is essentially a purulent abscess formed between the periosteum of the jaw and the mucous membrane of the gums. Because The mucous membrane is elastic, it really looks like a bag filled with pus, soft to the touch.
It should be noted that such a purulent sac can form on the gum not only on the front side of the alveolar process of the jaw (i.e. in front of the teeth), but also, for example, on the side of the palate. Moreover, if this is an ordinary leak of pus under the mucous membrane against the background of apical periodontitis, such a purulent abscess will still look like a small limited swelling, soft to the touch. But occasionally you can encounter other situations when a soft-to-touch swelling deforms a significant area of the gum.
What else can a cyst on the gum look like?
Such deformation of the palate as in the photo above is associated in this case with the formation of a very large root cyst in one of the upper incisors. Such cysts form at the apex of the tooth root in the absence of timely treatment of apical periodontitis. A cyst is a cavity in the bone tissue of the jaw, lined from the inside with a dense fibrous membrane and filled with pus. Cysts grow slowly, and when the growing cyst reaches the oral mucosa, it displaces the gum mucosa.
Variants of the outcome of inflammation - in most cases, purulent melting of the mucous membrane occurs, and pus exits through the formed fistula opening. In this case, after some time, the fistula may close, which will indicate a temporary subsidence of the inflammatory process at the apex of the tooth root, or purulent discharge may leak from the fistula into the oral cavity for a long time. As for the outcome with a root cyst, in this case there cannot be a breakthrough of pus through the mucous membrane, because root cysts have their own fibrous membrane.
Methods for treating dental cysts
As mentioned earlier, the only reliable and error-free method for diagnosing a cyst on the root of a tooth is an x-ray. In most cases, one x-ray is sufficient; however, due to individual tooth growth patterns, an additional x-ray of the root portion may be required.
Based on the analysis of X-ray data, the dentist determines and prescribes the type of treatment. Due to the difficulty of accessing the cavity, the process of getting rid of the cyst can take several sessions - however, only this method allows you to eliminate the pathology while keeping the tooth itself healthy.
There are two main directions of treatment: therapeutic and surgical.
— the sequence of actions during therapeutic treatment is as follows: the dentist gains access to the intradental canals (to do this, the tooth tissue is opened), expands them, cleans the cavity from pus, then disinfects it and installs a temporary filling. In the absence of relapse and a favorable outcome, the temporary filling is replaced with a permanent one. An alternative option may be the depophoresis method. Its difference is that the cleaning of the canals occurs due to the sequential introduction of a special substance into them, which, under the influence of an electric current, disinfects them. The common property of both methods is their applicability in the early stages of the disease;
— surgical intervention is used in most cases due to its reliability and high efficiency. There are three types of surgical treatment: cystectomy, hemisection and cystotomy. The first option involves opening the gum from the side and removing the cyst, followed by suturing. Rehabilitation takes place while taking antibiotics. Hemisection requires additional removal of the affected tooth root and crown fragment. If a cystotomy is prescribed, penetration into the cavity is carried out through the near wall. This method has a significant rehabilitation period.
In addition to the above methods, laser therapy is used. Its principle of operation is to insert a thin tube into the cyst, allowing complete disinfection using a laser, followed by vacuum cleaning. This progressive method is painless and effective, since it is guaranteed to preserve the tooth and protect against recurrence of pathology.
Surgery
Most often, a cystectomy procedure is performed to surgically remove a tumor. It involves removing the cyst and damaged root tip. The advantage of this method is its high efficiency. Its disadvantages include the fact that cystectomy is a rather complex operation, and not every surgeon decides to perform it.
A more complex method is hemisection. This operation is performed when one of the roots is completely destroyed. During surgery, the doctor removes the disease-causing capsule, damaged root and part of the tooth crown. The defect resulting from surgical resection is eliminated using composite materials or a crown.
Much depends on at what stage the capsule was discovered. Treatment can be accompanied by tooth extraction only if it is entirely located in the capsule of the cyst or its tissues are almost completely destroyed.
Rehabilitation period and prevention of dental cysts
Due to the fact that the cyst is an inflammatory infectious process, drug therapy necessarily includes taking antibiotics, which are selected by the attending physician. Vitamin complexes and immunomodulators act as compensating medications. Treatment of dental cysts with medications is carried out simultaneously with removal of the cyst.
The main ways to avoid the disease are to regularly visit the dentist and carefully monitor oral hygiene. For preventive purposes, you can periodically rinse with infusions and decoctions - for example, aloe, calendula, sage. Combined with strict adherence to the dentist’s recommendations and timely relief from chronic nasopharyngeal diseases, this will ensure dental health for years to come.
You also need to clearly understand that a cyst on the root of a tooth is one of the serious and complex diseases, the treatment of which requires time and highly qualified surgeons. Only this guarantees the absence of complications: re-infection, the occurrence of an abscess, pulpitis or fistula, damage to adjacent tissues and teeth.
Why does it occur
Among the main causes of pathology:
- advanced caries;
- jaw injuries;
- illiterate root canal treatment;
- overload of individual units as a result of poorly performed prosthetics;
- congenital anomalies of the upper/lower jaw;
- infections of the nasopharynx and oral cavity.
Regardless of the characteristics of the provoking factor, a gum cyst should be treated under the supervision of a dentist. Self-medication for this diagnosis is unacceptable.