Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Doctors consider any burns on any part of the body to be the most painful injuries. With such damage, large areas of the skin are affected and nerve endings are damaged. Burns have a long recovery period and very unpleasant symptoms. And gum burns are especially painful. We will talk about what to do if you receive such an injury and, importantly, how to avoid it, in this article.
Why are gum burns dangerous?
Despite all the external harmlessness, any gum burn can lead to serious consequences. Firstly, after an injury it is easy to introduce an infection into the soft tissues and cause complications. Secondly, with severe burns and significant lesions, necrosis of the mucous membrane occurs, which requires immediate intervention by a specialist. It is important to remove dead tissue as soon as possible to prevent necrosis from spreading further.
Do not forget that the thin layer of epithelium in the mouth is a huge number of capillaries. It is the gums that ensure the correct and strong fastening of the teeth; it is the gums that keep our smiles beautiful and even for many years.
If the gums are swollen due to periodontitis -
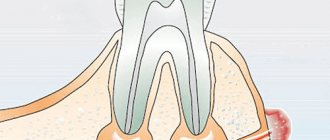
No less often, complaints that the gums around the tooth are swollen are associated with the patient having an inflammatory gum disease, which is called periodontitis. With periodontitis, there is destruction of the attachment of the gingival margin to the necks of the teeth, destruction of the bone tissue around the teeth, as well as periodontal fibers, due to which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue. As a result of these processes, periodontal pockets are formed between the gum and tooth (Fig. 14).
There are a lot of pathogenic bacteria in such pockets, and therefore serous-purulent exudate is always released from them. When the pocket becomes deep enough (more than 4 mm), the drainage of exudate from the gum pocket may be disrupted, which leads to the formation of a purulent abscess in the depths of the pocket. Dentists usually use the term periodontal abscess in this case (Fig. 15-16).
Swelling of the gums in the projection of the periodontal pocket –
Why gums swell during periodontitis: reasons
Periodontitis can be local and generalized. Local periodontitis differs in that it occurs only in one or several teeth exposed to a traumatic factor. For example, the formation of a periodontal pocket can be caused by trauma to the gums due to the overhanging edge of a filling in the interdental space, or by an incorrectly made crown or removable denture. Also very often the cause is traumatic occlusion, when some teeth are subjected to increased chewing load (for example, due to the loss of part of the chewing teeth).
If the teeth that have swelling on the gums do not have fillings or crowns, and you do not have long-term chronic inflammation of the gums, then you can immediately say that the reason is the presence of premature closure of the teeth in this area of the dentition. As a result, an increased mechanical load is placed on the tooth, which leads to the onset of destruction of the bone around the tooth and the formation of a periodontal pocket (24stoma.ru).
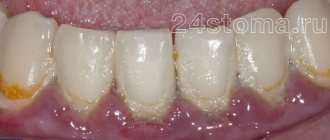
But in chronic generalized periodontitis, the causes of gum swelling are completely different. You can immediately suspect this form of periodontitis if you periodically experience bleeding when brushing your teeth, there is constant low-grade inflammation of the gingival margin in the area of all teeth (which is accompanied by swelling of the gingival papillae, their redness or cyanosis). The cause of this form of periodontitis is the accumulation of soft microbial plaque on the teeth, as well as hard dental deposits.
Microbial plaque and tartar bacteria produce toxins that destroy the dental-gingival attachment and bone tissue around the teeth, and also destroy the periodontal attachment of the tooth to the bone. With this form of periodontitis, periodontal pockets can be found in almost all teeth, and not 1-2 teeth as in the local form of periodontitis. When the discharge of serous-purulent discharge in one of the pockets is disrupted, a periodontal abscess is formed in the projection of the pocket.
Symptoms - if periodontitis, swelling of the gums occurs mainly in the projection of the apex of the tooth root or the bone interradicular septum, then with periodontitis the gums always swell in the projection of the formed periodontal pocket. Sometimes you may notice that thick pus spontaneously secretes from under the gums in the area of swelling, or it may appear when you gently press on the swelling (such symptoms clearly indicate that the cause is periodontitis, not periodontitis).
Also, the fact that the cause was local or generalized periodontitis can be indicated by the presence of mobility of the causative tooth, especially if mobility was present even before the swelling appeared. Let's now figure out what to do if the gums are swollen due to periodontitis... Treatment of the local and generalized forms of this disease will differ, because their development is caused by various reasons.
Treatment of local periodontitis –
When you see a doctor, the doctor, based on an examination and analysis of an x-ray, will determine the presence of a periodontal abscess and the amount of tissue destruction around the tooth (the depth of the periodontal pocket). Treatment immediately begins with eliminating the traumatic factor - removing the overhanging edge of the filling, grinding the contacts on the chewing surface of the causative tooth. At the same time, under anesthesia, the periodontal abscess is opened to allow the pus to drain out.
Next, the pocket is washed with antiseptics, systemic antibiotic therapy is prescribed, as well as a home course of anti-inflammatory therapy, consisting of antiseptic rinses and treatment of the gums with an anti-inflammatory gel. At the same time, the issue of the need to depulpate the tooth can be resolved, i.e. removal of the nerve and filling of the root canals (this is necessary if the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches more than 1/2 the length of the tooth root).
Removal of the nerve in such a situation is required because infection from a deep pocket can penetrate through the bloodstream into the tooth pulp (through the apexes of the roots). And then in this case, the tooth pulp itself becomes a source of infection. But this is all just basic treatment! The main treatment will be an open curettage operation of the periodontal pocket, which will remove the inflammatory granulation tissue from under the gums that has formed at the site of the destroyed bone, as well as fill the pocket with special bone material, which will partially restore the level of inert tissue.
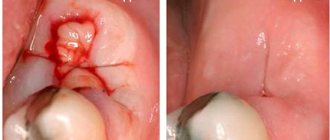
Progress of open curettage operation –
Please note that in the first stage of the operation, the gums are peeled off from several teeth to create good access to the periodontal pocket. In the photo above you can see a deep periodontal pocket between the canine and lateral incisor (at this point all inflammatory granulations have already been cleared from the pocket). Next, the pocket is filled with bone material, which can also be covered on top with a special membrane, after which the gum is returned to its place and sutures are applied. Please note that an x-ray 5 months after the operation shows an increase in bone tissue level of about 2.5-3 mm.
In addition, if a tooth is mobile, it may be necessary to splint it with adjacent teeth using fiberglass and filling material. You can read more about these treatment methods in the articles linked below:
→ Open gum curettage operation, → Teeth splinting technique
Treatment of generalized periodontitis –
In the generalized form of periodontitis, periodontal pockets occur not in just a few teeth, but in almost all teeth. Such periodontitis usually has a chronic course with sluggish symptoms, usually manifested by bleeding and soreness of the gums when brushing, and swelling of the gingival margin. Periodically, an exacerbation of inflammation may occur, and then abscess formation may occur in the area of one or more periodontal pockets (i.e., the formation of a purulent periodontal abscess).
Treatment of the generalized form of periodontitis is very complex, and therefore a separate article is devoted to this problem on our website, which you can read at the link above. But the main stages of treatment in this case will be removal of dental plaque and anti-inflammatory therapy, after which splinting of mobile teeth and/or gum curettage can be additionally applied.
Thermal burns
The most common injuries to the oral cavity are household thermal burns of the gums and mucous membranes. Each of us has received similar damage at least once in our lives: a careless sip of too hot coffee, and now we are suffering from unpleasant symptoms:
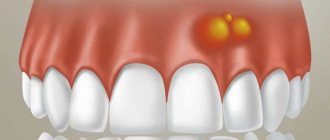
- blisters and bubbles filled with liquid appear on the gums;
- the gum surface becomes rough;
- bothered by continuous aching pain, which intensifies when touching and eating food;
Contrary to common misconceptions, severe thermal burns are very dangerous for gums and can lead to disastrous consequences. Dentists distinguish several stages of development of a thermal burn:
- The gums turn slightly red and recover quickly. The patient feels almost no pain and, if desired, can quickly cure such a gum burn at home.
- Blood rushes to the gums, the tissues begin to darken, swell, some areas become white, and become very hot. Blisters appear on the surface of the gums.
- The mucous membrane is significantly (sometimes almost completely) hidden under blisters and is severely damaged. The pain becomes unbearable. Immediate medical intervention is required.
- The gums bleed profusely and become covered with flaps extending from the bone. The patient's jaw base is exposed, and there is a high risk of developing necrosis.
In more than 90% of cases, gum burns received in domestic conditions are first and second stage injuries. In such cases, fortunately, hospitalization is not required, and the discomfort can be relieved with pharmaceutical products.
Chemical burns
Another common type of injury to the oral cavity is a chemical burn to the gums, which occurs as a result of taking various medications and reagents.
Dental burns
A common type of chemical burn is injury to the gums during whitening with special compounds and polymers and dental treatment. Inattentive doctors can violate the application technique, and then drops of solutions and compositions will fall on the gums and burn the delicate mucous membrane when treating tissues with a UV lamp.
Dental chemical burns to the gums are particularly dangerous injuries. Such injuries are characterized by rapid development of deep wounds and death of soft tissue.
Work injuries
Employees of hazardous industries or finishing workers also suffer from chemical burns to the gums. Injury can occur both through contact with acids, metal salts and alkalis, and through their careless use.
Domestic injuries
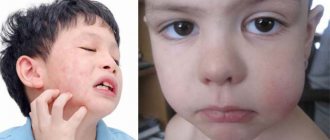
Unfortunately, most often children who suffer from chemical burns to their gums are drawn to taste household chemicals. Some adults also suffer chemical injuries when they decide to try unlicensed gum supplements, medications, soothing agents, or toothpastes from unknown manufacturers.
Symptoms of chemical burns
Chemical burns to the gums do not manifest themselves in exactly the same way as thermal burns. This type of injury is characterized by the following manifestations:
- voluminous blisters on the gums;
- swollen tissue;
- severe pain, itching.
How to treat burns?
Gum burns are very unpleasant injuries. A person immediately feels a sharp pain, which can spread to the roots of the teeth and temples. It becomes difficult not only to eat food, but also to swallow saliva. The tongue constantly probes the rough surface and swollen areas. Many people note an unpleasant metallic taste in their mouth.
First aid
First aid depends on the type of gum burn. In case of domestic injuries, you must act according to the following scheme:
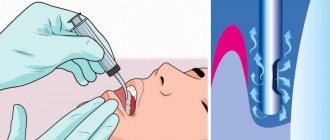
- First, rinse your mouth thoroughly with clean water. Thus, the patient removes food debris and reduces the temperature. There is no need to swallow the water; a new portion should be taken after a minute. Some patients are helped by “freezing” the nerve receptors with pieces of ice.
- Then the mouth can be rinsed with antiseptic preparations. An excellent healing agent for household injuries, including burns of the gums, is Asepta Active oral skewer. This remedy combines a combination of the anti-inflammatory, analgesic component benzydamine and the antimicrobial component chlorhexidine. This complex provides the antiseptic effect of the skewer while simultaneously relieving inflammation and pain, which increases the effectiveness and quality of tissue treatment.
- If desired, the burned area can be treated with sea buckthorn oil and rinsed with furatsilin solution or chamomile decoction several times a day.
Treatment of chemical burns to the gums should be entrusted to a dentist. Such injuries require maximum care and caution. Substances can react even with ordinary water and cause inflammation.
For chemical burns of the gums, self-therapy is strictly not recommended. If the treatment is incorrectly selected, the patient may develop a fever and experience throbbing pain in the burn area. In advanced cases, people experience swelling in the throat and swallowing becomes difficult.
In each specific case, the dentist develops individual therapy:
- For acid burns of the gums, rinsing with alkaline solutions (for example, water with 1-3 drops of ammonia, apple cider vinegar or a pinch of baking soda) is prescribed.
- If the burn is caused by phenol, doctors prescribe ethyl alcohol and castor oil dissolved 1:1 with water as treatment.
Help with gum disease at home
Before visiting a doctor, to slow down inflammation and relieve pain, you can rinse with boiled water and antiseptic solutions. However, it is not recommended to use alcohol-based formulations too often. They can dry out the mucous membranes, worsening their condition. You can use dental antiseptic gels. Do not heat or cool the inflamed area. Teeth brushing is done carefully so as not to injure the mucous membranes. Chew solid food carefully, on the other side (do not put stress on the inflamed part of the gum).
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component oral skewers ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component skewers - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Consumer Reviews
Natasha (vseotzyvy.ru)
“Mouth rinse Vertex JSC Asepta mouth rinse is sold in pharmacies, that’s why I bought it, it has more medicinal properties than just a cosmetic product, and indeed this rinse perfectly removes bad breath, disinfects gums, menthol gives freshness for almost a day perfectly helps smokers."
Dilya09 (otzovik.com)
“Hello to all readers of my review! I wanted to tell you my story about how I started using the Asepta oral brush.
It all started with the fact that I had an implant installed instead of an extracted tooth and was given strict instructions to rinse my mouth with chlogrexidine and, preferably, an oral scavenger. At the pharmacy, my choice fell on the Asepta drug, despite the price, because after the implantation procedure I had the feeling that now I would brush my teeth after every meal and rinse my mouth (it was just creepy). The price of this skimmer in pharmacies is above 160 rubles.
It doesn’t taste very nasty like some skimmers; after rinsing, it freshens your breath due to the “Lime” and “Mint” flavors. By the way, I don’t use it regularly anymore, I often forget to rinse my mouth, but, nevertheless, it is always present in the bathroom.
Of course, over the years, the memories of implantation have become dull, much has been forgotten, but Asepta and I are now friends. I take not only the skimmer, but also toothpaste. In general, not only is the skipper good, but the whole series is good. I recommend it to everyone who uses oral skewers.”
How to avoid complications?
In order not to aggravate the situation when treating gum burns, it is important to be attentive to yourself until the injury passes.
- For any type of gum burns, dentists do not recommend eating spicy, sour, or salty foods until the tissues are completely restored. Strong flavors irritate the affected tissues and can significantly prolong the healing process.
- You should not eat too hot foods - both during treatment and in the future, when the gums recover after the burn.
- All medicines, household chemicals, paints, solvents, and building materials must be stored in specially designated areas out of the reach of children.
If the pain from a burn becomes excruciating, we can take painkillers or use light anesthetic gels with analgin or benzocaine.
Complex gum burns, in which soft tissue dies, can only be treated surgically. The doctor in the hospital removes dead pieces of tissue and covers the damaged areas with donor parts. Such a “jewelry” operation often requires repetitions and additions. After treatment, the surgeon must prescribe antibiotics to the patient so that bacteria and microbes do not appear in the wounds and dangerous suppuration does not begin.
We hope that all of the above tips on caring for burnt gums will be for informational purposes only. Be careful and attentive to yourself, and accidents will bypass you.
Sources:
- The problem of treating inflammatory periodontal diseases in patients suffering from type 2 diabetes mellitus E.A. KHROMOVA* Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department I.V. KULIK* Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Department N.A. UDALTSOVA**, ***candidate of medical sciences, associate professor of the department; Deputy Chief Physician for Organizational and Methodological Work A.K. IORDANISHVILI****,*****Dr.Med.Sci., Professor, Professor of the Department *Department of General Dentistry, North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia; ** St. Petersburg State Budgetary Healthcare Institution “Dental Clinic No. 29”, Frunzensky District, St. Petersburg; ***Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "St. Petersburg State University" of the Government of Russia ****Department of Orthopedic Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov" of the Ministry of Health of Russia; *****Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical Dentistry of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education "Military Medical Academy named after S.M. Kirov" of the Russian Ministry of Defense;
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- The role of hygiene products in the treatment of periodontal diseases (S.B. Ulitovsky Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist StAR Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences, Department of Preventive Dentistry of Pavlov Pavlov State Medical University, St. Petersburg) S.B. Ulitovsky - Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Honored Dentist of StAR, Prof., Doctor of Medical Sciences; E.S. Alekseeva - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; A.A. Vasyanina - associate professor, candidate of medical sciences; V.A. Grigoriev - Associate Professor, Ph.D.