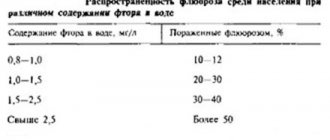
Reasons for the appearance of a fistula on the gums of a child (+photo)
The etiology of phlegmon is based on various dental pathologies, which are a constant source of infection. Among them, experts identify the following pathologies:
| Name | Description |
| Cyst | These are hollow neoplasms that form in the soft tissues of the oral mucosa and gums, including. Their cavity is gradually filled with pathological fluid and purulent exudate, which precedes the fistula. A characteristic feature of this pathology is its hidden and latent course. When characteristic symptoms appear, the infection is already very widespread. |
| Periodontitis | With the development of pathology, inflammation and deformation of the periodontal soft tissues occur. As a result, hollow pockets are formed that are filled with replacement connective tissue. Its surface becomes granular and porous, which is a favorable environment for the appearance of channels through which pathological exudate flows out. This provokes the formation of a fistula. |
| Osteomyelitis | This is a pathological process that is associated with inflammation, which provokes the decomposition of the jaw bone tissue. The occurrence of pathology is facilitated by advanced inflammation of the gums and teeth. Weakened children's immunity provokes the rapid development of pathology, the main symptom of which is fistulas. |
| Maxillary sinusitis | It can be a complication of various pathologies of dental etiology, one of the main signs of which are fistulas located in the area of the affected tooth. |
| Retracted primary/molar tooth | When they erupt, children develop cysts in which inflammation rapidly occurs. They are easily infected, which contributes to the formation of a fistula. |
| Injury | Injury to the mucous membrane of the gums allows bacteria to quickly penetrate into the affected area. This provokes the rapid development of purulent inflammation, which contributes to the appearance of a fistula tract. |
Important! Any source of development of a fistula on the gum of a child indicates the occurrence of an infectious or inflammatory dental disease. Therefore, it is necessary to seek qualified assistance from a specialist as soon as possible.
Causes of pathology
Most often, a dental fistula is a consequence of dental diseases.
- Pulpitis
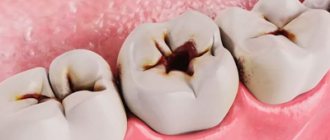
is a decay process that progresses in the oral cavity and can affect the pulp, the connective tissue of the dental cavity. Further, the infection often spreads to the soft tissues surrounding the tooth and into the jaw bones. - Caries
- the action of bacteria causes the tooth to rot, and a cavity forms inside it. Advanced caries can cause pulpitis.
- Gum cyst
- a purulent sac that appears most often due to advanced pulpitis. When the cyst is filled with pus, a fistula often appears on the gum. The photo can be viewed on the Internet.
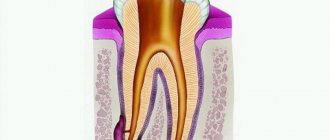
- Periodontitis
- inflammation of the gums at the root of the tooth.
- Granuloma
- a round nodular formation with clear contours, most often located at the apex of the root. Formed during advanced periodontitis.
In most cases, a fistula forms in the tissues of the oral cavity when it contains pathogenic microorganisms, as well as:
- after tooth extraction;
- when soft tissues and roots are damaged;
- when the dental canals are filled incorrectly with a filling substance.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a fistula at the beginning of the disease do not manifest themselves in any way. Then, depending on the degree of development of the disease, characteristic signs appear:
- At an early stage, pain develops in the area of the tooth, which intensifies when touching the formation on the gum or when eating food.
- At a later stage - redness of the gums, swelling of the mucous membrane, discharge of purulent contents from the fistula opening, causing loose teeth and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity.
- In a complicated course against a background of weakened immunity, osteomyelitis may develop in infants. With the progressive form of the fistula, hyperthermia, enlarged lymph nodes, and facial asymmetry due to swelling of the upper lip and neck are noted.
- There is difficulty breathing due to inflammatory manifestations and an increase in the amount of pus, leading to blockage of the nasal passage.
- Swelling of the eyelids and corners of the eyes is possible.
- Symptoms of a fistula , the predecessor of which was the chronic form of single-genus sinusitis. They are different and depend on the age of the child. Infants and young children experience redness of the upper jaw and signs identical to those of osteomyelitis. In adolescents, inflammation spreads to many facial sinuses.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- Heat.
- Migraine.
- Respiratory dysfunction.
- Swelling of facial muscle tissue.
- Acute pain in the trigeminal nerve area.
- Painful palpation of the fang pit and gums.
- The skin and mucous membrane of the nostrils and upper lip have changes in color.
Attention! If you notice one or another symptom in a child that is characteristic of a fistula on the gum, you should contact a dental clinic and receive qualified medical care.
What are the differences from adults?
A fistula on the gum in adults occurs in the same way as in children. It is usually preceded by inflammation, which provokes the accumulation of pus at the root. A fistula is formed, through which the exudate breaks to the surface. The main difference is in the root causes. In adults, the process is facilitated by:
- caries;
- poor-quality filling of canals;
- pulpitis;
- periodontitis;
- gum injury when installing dentures;
- granuloma;
- cyst in the apical part of the root.
A purulent papule on the gums is diagnosed less frequently in children than in adults. But if a fistula occurs, it develops quickly, since the child’s immune defense is not sufficiently developed.
Fistula in children develops many times faster than in adults
Diagnostics
Diagnosis will require a visual examination and x-rays.
If a fistula appears in the gum area, the child must be taken to see a dentist. It is possible to see and find out the real source of a purulent formation only with a standard examination and examination.
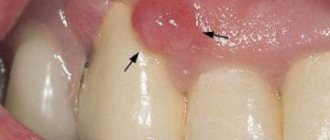
A fistula is a tubercle on the surface of the gum mucosa, which is very clearly visible upon visual inspection. It is often located near the root teeth and differs in color from the gums.
For a complete diagnosis, the dentist prescribes an x-ray of the jaw. This is the most effective and informative examination method. It allows you to determine the degree of damage and the type of pathological condition. Thanks to an X-ray image and a detailed visual examination of the gums, the dentist will differentiate the diagnosis and prescribe a competent course of treatment.
Symptoms and signs
At first, the child does not experience serious discomfort. Upon careful examination, you may notice swelling of the gums and redness of the mucous membrane. Vivid symptoms appear a few days after the onset of the disease. The child complains about:
- discomfort when chewing food;
- aching pain when pressing on the gum;
- mobility of baby teeth;
- headache;
- nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- temperature increase.
Upon visual examination, redness, swelling, and a white-pink bump in the affected area are observed. When the seal bursts, the purulent contents penetrate the body, causing intoxication.
At the beginning of the development of complications, you may notice swelling of the gums and its redness.
Basic therapy methods
Taking into account the severity of the disease, the dentist selects the appropriate therapeutic course, which may include the following components:
- Tooth extraction is performed only in the most extreme cases.
Drug therapy for a fistula on the gums of a child is prescribed at the beginning of its development. For these purposes, antibacterial drugs are used in tablets or injections. Antihistamines are prescribed. The local use of ointments and gels to relieve inflammatory manifestations on the gums is also effective. A prerequisite is the use of antiseptics in the form of solutions for rinsing the mouth.
- Medical (dental) manipulations. In later stages, to cure the disease, a therapeutic method is used, which consists of cleaning the dental canals, removing plaque and purulent deposits on the teeth and gums. Then the dentist performs professional hygiene and fills the affected tooth.
- Surgical intervention. If there is a large area of damage and when it is no longer possible to save the tooth, it is removed and gum therapy is performed.
- Alternative methods. You can cope with the problem of fistula with the help of alternative medicine, which is one of the effective and safe methods. To irrigate the oral cavity and treat the gums, use: A decoction of chamomile or oak bark for three days.
- Rinse the soda solution pure or with the addition of sea salt or two drops of iodine at least four times a day.
- Infusion of herbs: calendula, sage, St. John's wort.
- Lotions on the gums with the juice of Kalanchoe or agave leaves.
- Chew a small pea of propolis for 5 days in a row, twice a day for 7 minutes.
- Applications are made using sea buckthorn oil with medicinal herbs ground into powder.
Reference! All methods of treating a fistula are aimed at relieving the symptoms of inflammation, maintaining asepsis of the oral cavity and speeding recovery. Achieving rapid recovery dynamics is only possible with strict adherence to all doctor’s prescriptions and recommendations.
How to treat a fistula?
It is pointless to treat a fistula without paying attention to eliminating the cause of its appearance. First of all, it is necessary to cure the diseased tooth, which has become a stimulus for the spread of inflammation. The dentist thoroughly cleans the canals of the problematic tooth, removes pus and removes all caries deposits. After that, he disinfects the tooth and fills it.
The consequences are worse when the cause of the fistula is poor treatment of caries. In this case, the dental canals are first cleared of the filling, then filled with anti-inflammatory agents. And only when the dentist is convinced that there is no infection, he fills the tooth again.
Next, the patient is prescribed a rehabilitation course. The gums are irradiated with ultrasound or treated with a laser. After this, the fistula sometimes needs to be cauterized with a diametric current. The inflammatory process is blocked with antibacterial drugs. The patient is prescribed salt baths and is recommended to rinse the mouth with wound-healing solutions. If necessary, the patient is prescribed antiallergic drugs and special toothpastes, which will help prevent secondary infection. If a complication does occur and the inflammatory process spreads, for example, to the periosteum, the fistula is removed by surgery.
What complications may arise?
The resulting disease is quite dangerous! If you ignore the development of a fistula on the gum and do not seek medical help from a doctor, complications may arise in the form of:
- Flux
Flux – inflammation of the periosteum.
- Infection of the body with bacterial flora , which provokes the development of kidney pathology, intestinal problems, and diseases of the digestive system.
- The occurrence of tonsillitis and other diseases of the respiratory system due to the ingress of purulent contents onto the tonsils.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw. The chronic form provokes the formation of an abscess in the nasal cavity, on the eyelids, and in the area of the inner corners of the eyes.
- An untreated fistula destroys the periodontal tissue. It grows in them and manifests itself as a serious cosmetic defect in the facial part of the skull. This occurs due to the penetration of the fistula through the cheek to the outside. In this case, pus and bloody liquid are released.
- If the fistula is not treated, it has a destructive effect on the bone tissue, which leads to tooth loss.
Important! Self-treatment of a fistula or a later visit to the dentist allows microorganisms and the products of their activity to penetrate the bloodstream and lymph, having a negative impact on the functioning of internal organs and tissues.
Treatment methods
Treatment of dental diseases in which damage to the gum mucosa is observed directly depends on the causes and nature of the pathology.
For stomatitis, local treatment with agents that are active against certain types of pathogens, with an anti-inflammatory effect or other actions is recommended. In addition, immunostimulating, antihistamines and other drugs for oral administration may be prescribed.
When a fistula forms, the doctor first identifies the pathological focus - the source of infection. For this purpose, an X-ray examination or an otropantomogram may be prescribed.
After this, the causative disease is treated (periodontitis, granulomas , dental cysts , periodontal abscess, etc.).
A drainage system can be installed in the fistula tract to ensure unimpeded outflow of pus and prevent its release into nearby structures (maxillary sinuses, periosteum, etc.)
Prevention for baby's primary and molar teeth
One of the main aspects of treatment for a fistula in the gum area is compliance with the prevention requirement:
- Proper oral hygiene is the basis of prevention.
Keep your mouth clean by carefully performing hygiene procedures.
- Brush your teeth from early childhood, choosing the right toothpastes and special brushes.
- Carry out the procedure of rinsing your mouth after every meal.
- Treat dental ailments in a timely manner.
- Be sure to visit the dentist twice a year for timely detection and treatment of caries. Often, caries is the source of the development of fistula.
- Immediately show your child to a specialist if a purulent lump appears on the gum.
- Maintain food intake
- The diet should be balanced, rich in vitamins and calcium.
- Eat plenty of vegetables, fruits and solid foods.
By taking all precautions, the formation of a fistula and other dental pathologies can be avoided.
Popular questions
- Why did a child develop a fistula between his teeth?
Mainly, the formation of a fistula on the gum of a baby tooth develops against the background of long-term caries.
Usually, the initial stages of the disease are asymptomatic and often parents do not notice these symptoms. The only sign is the presence of white bumps formed between the teeth. Against the background of a violation of the integrity of the enamel and an unbalanced diet, caries quickly develops on the child’s healthy teeth.
- How to provide first aid?
Self-medication of a fistula in a child is unacceptable. Providing first aid consists of relieving the characteristic symptoms and making the child feel better. For these purposes, the oral cavity should be rinsed with an antiseptic, and the fistula should be treated with dental gel, which is used for teething. If necessary, give the child an antipyretic and antihistamine. Then he will immediately go to the dental clinic.
- There is something sharp on the child’s gum – what is it?
Inflammation of the gums involves thickening and swelling.
In such areas, the boundaries of purulent neoplasms are more clearly visible. On palpation, you can feel a hard lump with a sharp tip. What could it be? First of all, when a fistula is formed, a rod is formed. As the inflammatory process progresses in the soft tissues, the purulent secretion puts additional pressure on the rod.
As a result, it can push itself to the surface of the gum on its own. The rod does not always have sufficient density to disrupt the integrity of the thin periodontal film. Therefore, resting against the gum, it takes on a sharp shape.
Causes
A fistula is a signal that there is a pathogenic microflora in the mouth. There are several common causes of the disease.
- Thin and weak children's enamel. Baby teeth quickly decay. In the carious cavities, inflammation begins, leading to suppuration and hardening of the gums.
- Untreated caries that promotes the growth of granulosa tissue. Because of this, periodontitis develops, stimulating the accumulation of pus at the root.
- Osteomyelitis. Infectious lesion of the skeletal system, provoked by bacteria and weakened immunity.
- Injuries that compromise the integrity of the gums. They become a trigger for inflammation.
During the examination, the dentist must take into account the age of the child. A fistula in children under 2 years of age may indicate congenital abnormalities of the jaw or improper teething. Children 7-10 years old are susceptible to the disease during the period of replacement of milk teeth with molars.
In the vast majority of cases, fistula is a consequence of untreated caries
The formation of a fistula canal is facilitated by a passion for sweets, superficial oral hygiene, sudden hypothermia, and improper filling of teeth. In preschoolers, the cause is the habit of sucking fingers and putting toys in their mouth.