Causes
According to statistics, in most cases, periodontitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that arise due to insufficient oral hygiene or the presence of concomitant diseases. Let's consider a few more factors that can trigger the development of periodontitis:
- Irregular or improper brushing of teeth.
- Diseases that reduce the body's defenses (HIV, diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus).
- Violation of the integrity of the gums due to injury.
- The presence of concomitant diseases of the oral cavity (gingivitis, caries, tartar).
- Changes in hormonal levels.
- Periodontitis is often caused by smoking.
- Malocclusion.
- Hereditary factor.
Symptoms of periodontitis
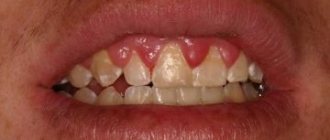
Signs of periodontitis can vary. Manifestations of the pathological process depend on the location of inflammation and the severity of the disease. The following clinical picture may be observed:
- Pain in the gums of various types (aching, throbbing, shooting).
- Gaps appear between the teeth.
- An unpleasant, putrid odor that does not disappear even after cleaning the mouth.
- Increased gum sensitivity.
- Exposure of the tooth root.
- Loose teeth.
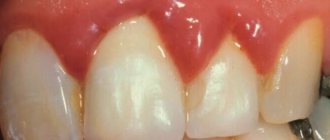
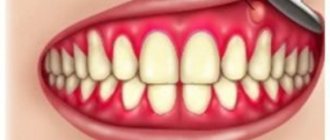
- Bleeding gums.
Complications
If periodontitis is not treated in a timely manner and the disease is left to take its course, the risk of developing serious complications increases. First, the patient’s body temperature rises, sometimes to critical levels (39-40 degrees). An increase in temperature indicates that the infection in the oral cavity has begun to actively multiply and spread to nearby tissues. The patient feels the taste of pus, the gaps between the teeth become visually noticeable.
The next stage is the loss of the tooth root from the socket. First, the gums begin to bleed terribly, and healthy teeth fall out. Periodontitis is dangerous because if left untreated, it transforms into a more dangerous disease - periodontal disease. In the presence of this pathological process, necrosis of bone tissue and alveolar processes occurs, and a gum abscess occurs.
To prevent the irreversible consequences of periodontitis and to avoid being left without teeth at a young age, periodontitis must be treated as soon as possible. To effectively cure the disease without relapse, it is recommended to consult a competent specialist who will select the necessary course of treatment, restore the healthy appearance of the oral cavity and leave unpleasant symptoms behind.
Call us right now at 8-495-668-1016 and make an appointment with the highly qualified dentists of Dr. Jacques' center to solve your problem as soon as possible.
What is the main feature of periodontitis treatment?
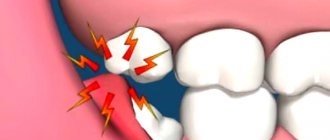
With periodontitis in the periodontal tissues, against the background of the inflammatory process, there is a gradual destruction of all the structures that hold the teeth. Also, with prolonged inflammation of gum areas and damage to deeper layers of tissue, the depth of periodontal pockets in the thickness of periodontal structures may increase, which are filled with the contents of dental plaque. As a result, purulent contents may be released from these pockets.
Also, all periodontal tissues are subject to destruction during a long course of the disease, the teeth in the sockets begin to loosen and in advanced cases may fall out. The main cause of this disease is the presence of a microbial factor, that is, foci of infection in the oral cavity. First of all, these are plaque and calculus, advanced dental caries or previously untreated gingivitis.
In addition to local factors, systemic diseases, endocrine system disorders or gastrointestinal pathologies can affect the course of periodontitis. The presence of deformations or anomalies of the dental system, bite pathologies, or incorrectly performed dental treatment previously can also aggravate periodontitis.
That is why, when drawing up a treatment plan for periodontitis, it is necessary to take into account all indicators of laboratory and diagnostic examinations, opinions from related specialists - therapists, pediatricians, family doctors, and data from the patient’s medical history. The correct sequence of patient examination includes:
- Examination by a periodontist and a conclusion about the condition of the teeth, their prognosis and the decision to preserve or remove teeth.
- Explaining to the patient all possible treatment options and manipulations to save teeth
- Agreeing on a treatment plan with the patient
- Determining the stages of use of selected treatment methods and drug prescriptions, taking into account a given clinical case
This scheme allows each doctor to correctly begin to resolve the issue of how to treat periodontitis in each clinical case.
Classification of periodontitis
Depending on the course of the pathological process, periodontitis occurs:
- Spicy. Characterized by rapid development. Without the necessary therapy, literally in 2 months the pathological process can lead to tooth loss.
- Chronic. The disease occurs in a latent form, tissue destruction occurs slowly, but still, after a certain time it leads to serious complications.
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, the following are distinguished:
- Generalized periodontitis. The inflammatory process affects the periodontium completely; the cause of development is often low immunity.
- Localized periodontitis. It can be treated more quickly and often occurs due to injury to the gums.
Depending on the severity there are:
- Easy. It goes unnoticed. Signs include bleeding. The gaps between the teeth do not exceed 2 mm.
- Average. Pain in the gums appears, the teeth gradually become unsteady and gaps between the teeth of up to 4 mm appear.
- Heavy. This stage of periodontitis is characterized by destruction of bone tissue and deformation of the interdental septa. Gaps from 5 to 10 mm. Partial or complete loss of teeth is observed.
How is periodontitis treated?
To make sure of the diagnosis, you need to visit a competent dentist, who will visually determine the primary diagnosis. In order to finally verify the presence of periodontitis, it is recommended to undergo general blood and urine tests to identify the inflammatory process in the body, as well as undergo panoramic radiography of the teeth.
Dentists at the Dr. Jacques Center offer periodontitis treatment in the following ways:
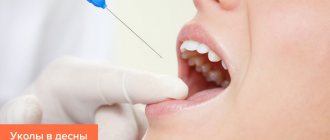
- If you consult a doctor at the initial stage, the patient will be prescribed drug therapy, physiotherapy, and, if necessary, orthopedic correction.
- When diagnosing moderate periodontitis, experts suggest performing minimally invasive interventions, such as cleaning dental pockets, antiseptic procedures for tooth roots, splinting or clasp prosthetics, which will prevent tooth loss.
- In more complex cases, full-scale surgical intervention cannot be avoided: bone augmentation or flap surgery. The purpose of the manipulation is to strengthen the gums and hide the tooth roots. The procedures are performed under anesthesia, so patients will not feel any discomfort.
Detailed video about what periodontitis is and how it is treated
Causes and methods of treating periodontitis
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Prevention
Periodontitis is inflammation of the periodontium, i.e. all tissues surrounding the tooth root. These include the gums, periodontium (ligaments connecting the root to the bone), alveolar processes (those parts of the jaw bone in which the teeth are attached). The concepts of periodontitis and periodontal disease are often confused. Let us remember that with periodontal disease, the periodontal tissues do not become inflamed, but atrophy, causing periodontal dystrophy; infection has nothing to do with it2.
Causes of periodontitis
This disease often becomes a logical continuation of gingivitis (gum inflammation), but can develop simultaneously with it. The reasons for their occurrence are similar1,2,3.
- 1 Tartar, poor oral hygiene (including due to malocclusion, in the presence of braces, dentures).
- 2 Chronic periodontal injuries (inconvenient edge of a denture, filling or crown, gnawing on nuts, bones, the absence of a large number of teeth, their early removal in children, etc.).
- 3 Smoking.
- 4 Piercing of soft tissues of the mouth, cheeks, habit of biting the lip or cheek.
- 5 Genetic predisposition.
- 6 Viscous saliva.
- 7 Hormonal disorders (during pregnancy, diabetes, etc.).
- 8 Stress, frequent travel.
The key point is the formation of tartar. Whatever the underlying cause, it all starts with plaque on the teeth.
Symptoms of periodontitis
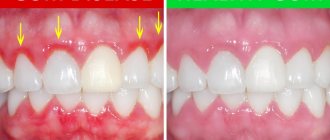
Bleeding gums are a sign that cannot be ignored. Typically, a person decides that they are pressing too hard on the brush when brushing, eases the pressure, or changes to a softer brush. If blood appears occasionally during cleansing, for example, once every six months, then, obviously, the person is right. But if this happens every week, it makes sense to think about it. Regular bleeding or change in gum color to a darker one is a reason to urgently contact a periodontist2,3. Signs that the condition is worsening and periodontitis is developing:
- Bad breath
- Exposing the tooth root, receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Destruction of the alveolar processes of the jaw, tooth loss
To identify periodontitis at an early stage, distinguish it from gingivitis and decide how to treat periodontitis, the doctor performs probing of the depth of periodontal pockets and radiography.
How to treat periodontitis?
It is quite difficult to cure chronic periodontitis completely; experts prefer to talk about long-term remission (improvement of the condition). Usually they try to eliminate the cause and then restore the periodontium.
The localized form is caused by local causes, most often dentures, fillings or crowns, bite, poor cleaning, etc. It is quite possible to eliminate these reasons, although sometimes it is necessary to redo prostheses and crowns.
The generalized form is associated with smoking, genetics, hormones, stress, etc. Here it can be quite difficult to deal with the cause. Usually you have to surgically remove the “pocket” between the tooth and the gum, clean it of stone, and polish the root. Antiseptics, vitamins, tissue biosynthesis stimulants, herbal infusions, and antibiotics are used for therapy. In any case, treatment of periodontitis is a long process, and special oral care selected by a doctor is lifelong2,3.
Prevention
- 1 Brush your teeth properly every day, using appropriate toothpastes, dental floss, and mouthwash.
- 2 Have a hygienic cleaning at the dentist once a year or more often if plaque and plaque form rapidly.
- 3 Eat a balanced diet, consuming protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- 4 Eat enough solid food, which must be chewed thoroughly on both sides of the mouth1.
As a preventive measure and additional protection of the oral cavity from inflammation, immunostimulating drugs, such as Imudon®, are used. This topical agent enhances the production and increases the content of interferon, lysozyme, secretory IgA in saliva, activates phagocytosis, thereby helping the body reduce the risk of inflammation and infection. Lactobacilli contained in the drug relieve inflammation and promote healing and restoration of the oral mucosa5.
The article was prepared based on materials:
1. Orekhova L.Yu. Periodontal diseases., Moscow, Poly Media Press", 2004, 432 p. 2. Dmitrieva L.A. Therapeutic dentistry, Moscow, Medpress-inform, 2003, 894 p. 3. Ivanov V.S. Periodontal diseases, Medical Information Agency, Moscow, 2001, 300 p. 4. INSTRUCTIONS FOR MEDICAL USE OF THE MEDICINE Imudon® dated 07/02/2018. 5. Shumsky A.V. Imudon® in the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa. Scientific and practical journal "Dentistry", 2000, No. 6, volume 79, p. 53-54.
The material was developed with the support of Abbott to improve patient health awareness. The information in the material does not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. Contact your doctor
RUIMD192278 from 11/12/2019
To learn more
Prevention of periodontitis
After successful treatment of periodontitis or in order to avoid this disease, specialists at the Dr. Jacques Dental Center recommend observing certain nuances:
- Carry out oral hygiene twice a day.
- To avoid injury to your gums, choose a brush of medium hardness.
- Stop smoking.
- Visit the dentist once every six months.
- In every possible way to increase the body's defenses.
The main preventive measure for the development of periodontitis is a timely visit to specialists in the presence of concomitant diseases of the oral cavity. To avoid trouble and not lose your teeth, contact your dentist at the first signs of illness.
Treatment of periodontitis at the dentist
The first stage of periodontitis treatment is the complete removal of dental plaque and stones, which are a favorable environment for the development of infection and prevent the gums from recovering. For successful treatment, it is necessary to clean the teeth and periodontal pockets as thoroughly as possible; special devices, such as dental lasers, can be used for this. After cleaning your teeth from deposits, you need to remove gum inflammation. For this purpose, antiseptics are used to kill the infection and agents that relieve inflammation and swelling of the gums.
If necessary, in advanced cases when the infection has deeply affected the bone tissue, surgical intervention may be performed. The gums are opened, deep pockets are washed with antiseptic agents, and stone is removed. Surgeries may be performed to partially restore the appearance of the gums and teeth. In some cases, surgical treatment of periodontitis involves regenerative measures to ensure the restoration of the supporting function of the tooth.
To prevent the possible return of the disease, after professional teeth cleaning, it is necessary to scrupulously monitor hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day with high-quality toothpaste and a brush, use a mouth rinse after meals, and visit the dentist once every six months for a check-up.