Electrotherapy is an extensive section of physiotherapy, which includes techniques such as galvanization and electrophoresis, diadynamic therapy and amplipulse therapy, interference therapy and faradization, darsonvalization and ultratonotherapy, electrosleep and electrical stimulation.
Currents vary in voltage, frequency, intensity and shape. They are prescribed by a doctor according to an individual program for each patient, taking into account factors such as the underlying disease, concomitant pathologies and complications. The choice of a specific technique depends on the patient’s age, individual skin sensitivity and many other factors.
One of the treatment methods is called fluctuarization, the basis of which is the use for therapeutic purposes of pulsed currents of a low frequency sinusoidal shape - from 40 to 2000 Hz - and an intensity from 1 to 40 mA.
Features of fluctuarization
According to the mechanism of therapeutic effects, fluctuarization is similar to such types of electrotherapy as amplipulse therapy (AMP) and diadynamic therapy (DDT). The difference is that when using fluctuarization, the likelihood of the skin becoming accustomed to the stimulus is reduced (due to its special characteristics - asynchrony, aperiodicity and randomness), this makes it possible not to increase the current strength during the procedure.
For some pathologies, this type of electrotherapy has shown greater effectiveness than diadynamic therapy and SMT therapy. In addition to the above, another distinctive feature of fluctuarization is the appearance of an analgesic effect already during the procedure due to the effect of asymmetric currents on the receptors.
How does the procedure work?
The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis in a physical therapy office.
At SM-Clinic, the Mustang Physio apparatus is used to perform fluctuarization.
The session is performed with the patient in a horizontal or sitting position. Electrodes are applied to the site of exposure and the device is turned on at minimum power. Then the current strength is gradually increased until the patient feels a slight tingling sensation at the points where the electrodes come into contact with the skin.
When carrying out the procedure, depending on the nature of the disease and the prescription of the attending physician, different methods of placing electrodes are used: transverse, longitudinal, paravertebral, as well as cavity electrodes and turundas.
The procedure lasts from 3 to 15 minutes, depending on the characteristics and severity of a particular disease. For the full impact of this physiotherapeutic method on the body, it is necessary to undergo from 5 to 15 sessions.
Indications
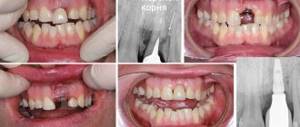
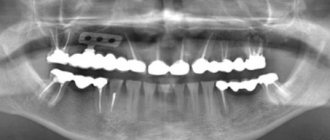
The fluctuarization method is widely used to treat dental diseases.
There are many indications for the use of fluctuarization, some of which are listed below.
- Osteochondrosis of the spine with radicular syndrome, radiculopathy and herniated intervertebral discs;
- Exacerbation of arthritis and arthrosis, including deforming arthrosis;
- Neuralgia;
- Chronic gynecological diseases outside the acute phase;
- Exacerbation of pulpitis, periodontitis, alveolitis, pain after filling teeth;
- Condition after surgery for acute purulent inflammatory processes.
Electrotherapy
Electrotherapy is a method of physiotherapy based on the use of dosed effects on the body of electric currents, electric, magnetic or electromagnetic fields.
In electrotherapy, electricity is used for therapeutic purposes, as an analgesic and sedative for diseases such as neuralgia, convulsions, paralysis, or stimulating and irritating the neuromuscular system, for muscular atrophy, rheumatism of the joints, some female diseases, neurasthenia, hysteria and other diseases .
Our center uses traditional effective
electrotherapy techniques using modern equipment.
Galvanization
Galvanization is the use for therapeutic purposes of exposure to a constant, unchanged low-voltage electric current (up to 80 V) at a low current strength (up to 50 mA). Currently, galvanization uses exclusively current obtained by rectifying and smoothing alternating mains current.
Passing through the skin, the galvanic current encounters great resistance from the epidermis. A significant part of the current energy is spent on overcoming this resistance, and it is here - at the place where the main amount of it is absorbed - that the most significant reactions during galvanization develop. First of all, this is hyperemia and a burning sensation with tingling under the electrodes, resulting from a current-induced change in the normal ratio of tissue ions, the pH of the environment, and the formation of heat. Along with this, the release of biochemically active substances, activation of enzymes and metabolic processes reflexively cause increased blood flow to the area of influence.
Therapeutic electrophoresis
Therapeutic electrophoresis is a combined (simultaneous) effect of direct current, often galvanic, and a small amount of a medicinal substance or a cocktail consisting of several drugs entering the body.
Due to the very low speed of movement of ions, the high resistance of the epidermis, the limited time of the procedure and the current strength, during the procedure, ions of the drug substance are introduced only into the epidermis, forming a kind of depot in it. From it, the medicinal substance is gradually washed out by the blood and lymph flow and spreads throughout the body, and therefore one should not count on a quick effect of the medicinal substance during electrophoresis. And the amount of substance entering the skin depot is only 2-3% of that used during the procedure.
In the mechanism of the therapeutic effect of this method, the leading role belongs to the current, which simultaneously increases the sensitivity of tissues to the action of the drug.
Transcranial electrotherapy
Transcranial electrotherapy (TES) is a treatment method using non-invasive stimulation. TES selectively (selectively) activates the system of endogenous opioid peptides (EOP) of the brain, primarily b-endorphin, using pulsed electrical action supplied through head cutaneous electrodes.
To achieve the specified selectivity during TES therapy, it is necessary to comply with two basic principles: the direction of current application (frontomastoid processes) and its resonance characteristics in relation to the image intensifier. The image intensifier is the most important system of the body, regulating the activity of the neuro-immuno-endocrine system of the body.
The following main effects of TES therapy have been clinically confirmed:
- normalization of psychophysiological status: anti-stress and antidepressant effects:
- increased performance;
- normalization of sleep;
- reduction of fatigue;
- improved mood;
- improving the quality of life in general;
- reparative effect:
- acceleration of healing of damage of various origins of all types of tissues, including defects of the skin and mucous membranes;
- regeneration of hepatocytes, peripheral nerves, connective tissue;
- effective pain relief, even in cases where drug treatment of pain syndrome is ineffective: it is known that b-endorphin has an analgesic effect that is almost 30 times greater than the effect of morphine;
- normalization of autonomic regulation processes, normalization of vascular tone, normalization of blood pressure;
- stimulation of immunity;
- inhibition of tumor growth, improving the quality of life of cancer patients;
- relief of withdrawal syndromes, elimination of post-withdrawal affective disorders in the treatment of alcoholism, substance abuse and opiate drug addiction, elimination of pathological craving for alcohol and drugs;
- anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effects;
- increasing the effectiveness of other treatments, including medications.
TES therapy has broad indications for use, which determine its homeostatic orientation. In total, more than 100 indications for the use of TES therapy have been studied.
Diadynamic therapy
Diadynamic therapy is treatment with direct currents with half-sinusoidal pulses with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz. Mainly two types of diadynamic currents are used: single-phase continuous and two-phase continuous, as well as various modulations and combinations of these currents - intermittent rhythmic current, modulated by short or long periods, etc. The main features of the action of diadynamic currents in the body are the blocking of sensitive nerve endings and, in connection with this, an increase in the threshold of pain sensitivity, reaching almost complete anesthesia, as well as stimulation of trophic processes, tissue metabolism and resorption of perineural edema. Diadynamic currents normalize cortical neurodynamics, acting reflexively on the peripheral part of the pain analyzer; breaking the reflex arc of the vicious circle of pathological impulses is important. Due to irritation of vegetative formations, peripheral vessels dilate, trophism and blood supply to tissues improve, ion concentration and membrane permeability change. All this contributes to the disappearance of edema and the normalization of impaired functions.
Indications:
- acute pain syndromes with damage to the peripheral nervous system (neurological manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis, neuralgia, mono- and polyneuropathy, ganglionitis, plexitis);
- diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system (myositis, periarthritis, epicondylitis, arthrosis, stiffness in joints after injuries and surgical interventions, etc.);
- diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, colitis, biliary dyskinesia, pancreatitis, dumping syndrome);
- respiratory diseases (protracted pneumonia, bronchial asthma);
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages, algodismenorrhea;
- urinary retention and incontinence, enuresis;
- impotence;
- prostatitis;
- initial stages of hypertension and obliterating diseases of the vessels of the extremities;
- migraine;
- Quincke's edema;
- diseases of the ENT organs (laryngitis, otitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, vocal cord paresis);
- arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, periodontal disease;
- itchy dermatoses, keloid scars, etc.
Amplipulsetherapy
Amplipulse therapy is a method of electrotherapy in which the patient is exposed to alternating sinusoidal modulated currents (SMC) of low strength. They combine the advantages of high and low frequency currents.
For amplipulse therapy, alternating sinusoidal currents with a frequency of 2000-10000 Hz, modulated by low-frequency sinusoidal oscillations (within 10 - 150 Hz), are used. Unlike low-frequency currents, which have a pronounced stimulating effect on the neuromuscular and vascular systems, high-frequency current does not encounter much resistance from the skin, penetrates deeply into the tissue, and does not cause noticeable irritation of skin receptors. It is well tolerated by patients and has a stimulating effect on deep-lying tissues. As a result of the increased outflow of metabolic products from the pathological focus, swelling, one of the causes of pain, decreases. The cessation of pain helps to reduce spasm of blood vessels, they expand, and tissue nutrition improves.
Indications:
- injuries and diseases of the peripheral nervous system with reflex-tonic and pain syndromes;
- diseases of the autonomic nervous system with neurotrophic and vascular disorders;
- diseases of the nervous system with motor disorders in the form of central, peripheral and mixed paresis and paralysis;
- hypertension stage I-II;
- IHD;
- atherosclerotic obliteration of vessels of the extremities;
- chronic lymphostasis;
- diseases of the digestive system (chronic gastritis with secretory insufficiency, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase and incomplete remission, reflux esophagitis, hypotonic and hypokinetic disorders of the biliary tract and gall bladder in the absence of stones, etc.);
- disorders of fat metabolism of an exogenous-constitutional nature;
- diabetes;
- respiratory diseases (prolonged exacerbations of chronic pneumonia, chronic bronchitis and bronchiectasis beyond the acute stage, mild and moderate bronchial asthma);
- rheumatoid arthritis with minimal and moderate degree of process activity, arthrosis, periarthritis;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- functional male impotence;
- chronic prostatitis, cystalgia, bedwetting in children, urolithiasis (for the purpose of expelling ureteral stones);
- inflammatory and dystrophic diseases of the anterior and posterior parts of the eyes.
Considering the ability of sinusoidal modulated currents to penetrate deeply into tissues without causing discomfort or burns, amplipulse therapy is preferred (over diadynamic therapy) in pediatric practice when affecting mucous membranes.
Fluctuarization
Fluctuarization is the use for therapeutic purposes of alternating, partially or fully rectified low voltage current (up to 100 V) with chaotically varying (up to 2000 Hz) frequency and amplitude (up to 3 mA/cm2). A peculiarity of the effect of fluctuating currents on the body is that, due to the random change in their parameters throughout the entire duration of exposure, adaptation phenomena do not develop in the tissues. Fluctuating currents intensely irritate proprio- and interoreceptors, which is accompanied by painless synchronous contraction of myofibrils. At the same time, there is a slight increase in tissue temperature, hyperemia appears, which in turn activates tissue trophism, phagocytosis, enzymatic activity and the processes of resorption of toxic substances from the source of inflammation, and enhances cellular immunogenesis. When exposed to a purulent inflammatory focus, fluctuarization causes a limitation in the spread of the process and its reverse development. Postoperative application of currents promotes rapid rejection of necrotic tissue, wound cleansing, and accelerated regeneration. The formation of granulation tissue and epithelization of the wound surface occur faster. Thus, fluctuating currents can be used as a means of treating acute, including purulent, inflammatory processes.
Fluctuarization is used primarily in dentistry to relieve pain due to exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, alveolitis, pulpitis, arthritis of the temporomandibular joint, glossalgia, in acute and aggravated chronic inflammatory processes, including purulent (abscess, phlegmon, periodontal disease, etc.), actinomycosis. In addition, these currents can be used to treat pain syndromes caused by damage to the peripheral nervous system (neuritis, neuralgia, radiculitis, ganglionitis, etc.), as well as in the complex treatment of certain gynecological diseases of inflammatory origin.
Interference therapy
Interference therapy is the therapeutic use of low-frequency (1-100 Hz) “beats”, the frequency of which can be constant during the procedure or periodically change within a selected limit. “Beats”, which are a series of mid-frequency current oscillations, are formed inside the tissues of the body as a result of the interference (addition) of two initial currents of mid-frequency, supplied to the surface of the body through two separate circuits and differing in frequency.
The leading role in the mechanism of therapeutic action of interference therapy belongs to the improvement of peripheral circulation. It is manifested by normalization of the pathologically altered tone of the main arteries and capillary beds, an increase in the number of active collaterals, and improvement of microcirculation. In the mechanism of dilatation of peripheral vessels, the main significance is the inhibition of the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system by interference currents and the increased release of vasoactive substances during the procedure. In addition, the currents cause muscle contractions and have a kind of massaging effect, which may result in improved peripheral blood circulation and lymphatic drainage.
Stimulation of blood circulation leads to a local increase in temperature, improved oxygen supply to tissues and elimination of anoxemia, rapid elimination of toxic metabolic products, and activation of the reticuloendothelial system. With interference therapy, tissue pH shifts to the alkaline side, which has a beneficial effect on the course of the inflammatory process. Interference current, according to some authors, has bactericidal or bacteriostatic properties. It also has a trophic-regenerative effect.
Indications:
- diseases of the nervous system (neuritis, neuralgia, neurological manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis, causalgia, phantom pain, bedwetting, etc.);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (stages I and II hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia, atherosclerotic occlusion of the vessels of the extremities, varicose veins, consequences of thrombophlebitis, etc.);
- injuries of the musculoskeletal system, arthritis, arthrosis, joint contractures, osteochondropathy;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with a predominance of motility disorders;
- inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages; some skin diseases, etc.
Contraindications
As with any type of treatment, fluctuarization has a number of contraindications in which you should refrain from using this type of physiotherapy. These include:
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Meniere's syndrome;
- Decompensation of chronic pathologies of the cardiovascular system, mental illnesses;
- Tendency to bleeding;
- Active tuberculosis;
- Fever;
- The presence of foreign metal bodies and a pacemaker in the body;
- Impaired sensitivity of the skin;
- Individual intolerance to the method;
- Severe cachexia and general serious condition of the patient.
Therapeutic effect of the procedure
Fluctuarization has an effect on the body in the form of relieving inflammation, swelling, pain relief, and a resolving effect.
Blood circulation processes and the functioning of the lymphatic system improve. The procedure also has a pronounced neurotrophic effect, promoting the development and activity of neurons. Under the influence of fluctuating currents, muscle tone and contractility increase, processes in peripheral nerves are normalized.
All this together leads to significant relief of both the patient’s general condition and the symptoms of a specific disease.
To get details about the fluctuarization procedure at SM-Clinic and to make an appointment with a specialist, call.
Prices for fluctuarization at SM-Clinic
| Name of service | Price, rub.)* |
| Darsonvalization (1 field) | 790 rub. |
| Darsonvalization (2 fields or more) | 1,050 rub. |
We accept bank cards VISA, MASTERCARD, MAESTRO for payment
The full price list can be found at the reception or by phone.
* The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to check the cost of services at the reception or in the contact center by phone
+7 (495) 292-39-72
.
The posted price is not an offer. Medical services are provided on the basis of a contract.
Current forms during fluctuarization
There are three forms of current used in this type of electrotherapy:
- Alternating symmetrical current. This is a bipolar fluctuating current, the pulses of which change spontaneously in amplitude and frequency in both positive and negative polarity. This type of therapy has a pronounced effect on deep tissues - internal organs, lymphatic and blood vessels, muscles and subcutaneous fat.
- Bipolar asymmetric current is a partially rectified current, in which asymmetric oscillations also change asynchronously in frequency and amplitude, but are predominantly ejected in negative polarity, with each “positive” emission corresponding to 2-3 “negative” ones (in polarity).
- Unipolar rectified current, in which all the same spontaneous currents, chaotically varying in frequency and amplitude, are exclusively in negative polarity. According to its characteristics, this form of current is similar to galvanic current; it is a constant pulsating current. Due to the unipolarity of this type of current, it is possible to combine electrotherapy with the administration of certain medications.
Equipment
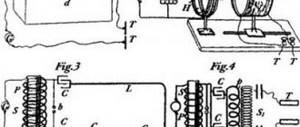
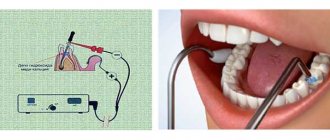
Various forms of fluctuating currents are obtained using a desktop pain relief apparatus ASB-2-1 (Fig. 2.12) and a portable “Dental Fluctuarization Apparatus” FS-100-4.
Rice. 2.12. Apparatus for fluctuating currents ASB-2-1: 1 - signal lamp; 2 - milliammeter; 3 — current regulator knob; keys for obtaining currents of different shapes: 4 - bipolar symmetrical; 5 - bipolar asymmetrical; 6 - unipolar.
Fluctuarization in cervical osteochondrosis
The method is successfully used, for example, if the patient is bothered by cervical osteochondrosis. The essence of the procedure is as follows. One electrode is placed on the back of the neck, the other in the upper third of the sternum. The current is bipolar symmetrical (first form), its density is average. Procedure time 10-15 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures, daily or every other day.
Types of rehabilitation: physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage: textbook. allowance / T.Yu. Bykovskaya [and others]; under general ed. B.V. Kabarukhina. - Rostov n/d: Phoenix, 2010. - 557, [1] p.: ill. - (Medicine). pp. 52-55.