Approximately every fifth child under one year of age periodically develops thrush in the oral cavity, and the development of the disease at an older age cannot be ruled out. Parents of children should know what oral candidiasis looks like and what treatment is necessary to prevent the progression of the disease.
Principles of treatment
How to treat thrush in a child’s mouth must be decided immediately after its first signs appear. Untimely or incorrectly selected treatment becomes the main reason for the pathology to become chronic, in which serious complications may develop. If candidiasis in a child’s mouth is detected at the earliest stage of its appearance, then to eliminate it it will be enough to treat the oral cavity with disinfectants and antifungals for several days. But parents must understand that the problem may return if the influence of all factors that provoke the growth of fungi is not eliminated.
To do this you need:
- improve hygienic care of the child and the equipment used for feeding;
- a nursing woman should review her diet and wash her breasts before breastfeeding;
- find out if relatives living in the same apartment have an exacerbation of thrush.
You also need to pay attention to the functioning of the child’s digestive system. Very often, oral candidiasis is combined with intestinal dysbiosis. To get rid of concomitant pathologies, it will be necessary to take a course of medications with probiotics; they are prescribed for an infant by a doctor.
In cases where thrush is detected already in the second or third stages of development, external treatment does not always completely help normalize the microflora. The pediatrician prescribes systemic antifungal agents, which parents must give to the child according to a certain schedule.
Symptoms and external manifestations
Thrush can be recognized by examining the oral cavity; the child’s behavior also changes.
General signs:
- refusal to breastfeed or eat;
- weight loss;
- sleep disturbance;
- frequent regurgitation;
- complaints of pain, burning, itching in the mouth, sensation of a lump in the throat.
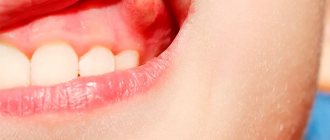
During infection, the condition of the mucous membrane changes, it becomes red and swollen, and areas of unnatural color appear.
Don't confuse plaque from breast milk with thrush!
Rules for treating thrush in children
Treatment of thrush should first of all be safe for newborns and children in the first months of life. To do this you need:
- use only age-appropriate medications or traditional methods;
- treat the oral cavity before feeding, since exposure to the tongue can cause vomiting;
- when removing plaque, do not put too much pressure on the mucous membranes;
- do not allow gauze swabs used for treatment to get into the throat.
When prescribing special antifungal agents, the course of therapy must be completed to the end. The disappearance of white plaque does not indicate that the disease has been completely eliminated.
Antimycotic drugs often cause side effects, so their help is resorted to in extreme cases.
If a temperature appears against the background of thrush, it is necessary for the child to be examined by a doctor. Thrush may be accompanied by a viral infection, in which case antifungal therapy is combined with the use of antiviral, antipyretic and other medications.
Skin candidiasis
The disease in infants is often mistaken for allergic dermatitis. The disease occurs with a frequency of 10 to 24% and usually manifests itself at 2 to 3 weeks of a child’s life. Its distinctive feature is the predominance of the erythematous form of inflammation.
Skin candidiasis in children can be congenital or acquired. It occurs in erythematous or vesicular forms. It has several variants of the course - damage to large folds and candidiasis diaper dermatitis.
Congenital candidal dermatitis in children appears more often on the second day of life. With cephalic presentation, the skin of the upper part of the body is affected: face, head, upper back. The mucous membranes are not affected.
Acquired candidal dermatitis in children begins with large folds and always occurs with thrush in the mouth. In the absence of adequate treatment, the infectious process spreads to the smooth skin of the thighs, abdomen and back. In advanced cases, the entire skin is affected. The disease should be distinguished from bacterial diaper rash, which is characterized by weeping, which is not characteristic of skin candidiasis and the absence of peripheral foci of screening and other dermatomycosis in newborns.
Diagnosis of mycosis is based on the detection of pseudomycelium and budding candida cells by microscopy and/or isolation of pathogen cultures.
The vesicular form is characterized by the appearance of a significant number of flabby and small bubbles against the background of hyperemia.
The erythematous variant of inflammation is characterized by the appearance on the skin of smooth, shiny, moist, tense areas of a dark red color. Dark red color of the lesions, distinct borders, scalloped edges, varnish shine, a moist rather than weeping surface, a narrow border of desquamated epithelium along the periphery, the presence of dropout foci (erosions and fresh blisters) along the periphery, absence of dryness and itching even in cases of widespread lesions are the distinctive features of skin candidiasis in children.
Rice. 12. Erythematous form of skin candidiasis in infants (diaper dermatitis).
Rice. 13. Vesicular form of skin candidiasis in a child (diaper dermatitis).
Candidal dermatitis of large folds
Damage to the skin of large folds begins with redness and swelling, against which small blisters and pockets of screening appear along the periphery. Candidal dermatitis is often mistaken for diaper rash. Clear lesions with scalloped edges, a tense, smooth and shiny surface and the presence of desquamated epithelium (epidermal corolla) along the edge of the white border are its distinctive features.
Rice. 14. Erythematous form of diaper dermatitis.
Candidiasis diaper dermatitis
The disease develops in children who carry candidiasis in the intestines. On the skin, as a result of massive fusion of vesicles and lesions, erythematous plaques with a fringed, clearly defined edge appear, along the periphery there are foci of screening.
Typically, the infectious process involves the perianal area, inguinal folds, perineum and lower abdominal wall. In boys, the skin of the penis and scrotum is affected, in girls - the vagina and labia.
Rice. 15. Erythematous form of the disease in infants.
Treatment of skin candidiasis in children
To treat the disease in newborns, antifungal drugs are used in the form of creams and ointments: Ketoconazole, Isoconazole, Clotrimazole, Econazole, Sertaconazole. At the same time, oral thrush and intestinal candidiasis are treated. For congenital candidiasis and severe condition of the newborn, fluconazole is used orally or intravenously. If there is no effect, Amphotericin is prescribed.
Rice. 16. Skin candidiasis in a child (inflammation of the periungual ridges).
Folk remedies
The fight against thrush with folk remedies is most effective at the early stage of the onset of the pathology. Use:
- Soda
. A teaspoon of dry powder is poured into a glass of warm boiled water, stirred, the finger is wrapped in gauze, moistened in the resulting product and carefully wiped the tongue, gums, and inner surfaces of the baby’s lips. Treatment with soda is carried out up to 6 times a day. - Honey
. Liquefied honey is diluted in a 1:2 ratio with water, and the resulting solution is used to wipe the oral cavity in the same way as when using soda. Honey is used only if the baby is definitely not allergic to it. - A decoction of sage or calendula flowers
. One or two spoons of herbal raw materials are poured into glasses of boiling water and filtered after cooling. The solution is used to treat the oral cavity up to 6 times a day.
Oak bark, St. John's wort, and eucalyptus leaves also have antifungal properties. It must be taken into account that all means used to combat thrush must be used for at least two more days after the disappearance of the curdled coating.
The lack of effect in the treatment of candidiasis with folk remedies is an indication for the use of antifungal agents.
It is not forbidden to combine folk remedies with the use of pharmaceutical medications. You definitely need to pay attention to the diet; children over one year old should receive less sweet foods and more lactic acid products. Plant fruits have a positive effect on the body - eating fresh berries, fruits and vegetables enhances the body's defenses.
Preventive measures
Don't forget to thoroughly clean pacifiers, bottles and other devices!
Thrush in the mouth often occurs in children, especially between the ages of 1 and 5 years. The pathology is highly treatable if detected early. But in order to protect your child from taking medications and unpleasant procedures, you need to constantly engage in disease prevention.
How to prevent the development of a fungal infection:
- do not allow the child to put fingers or any objects into his mouth, especially while walking on the street;
- You cannot kiss a child on the lips and prohibit other relatives from doing this;
- carry out wet cleaning daily, wipe off dust, treat toys, ventilate and moisten the room;
- thoroughly boil pacifiers, bottles, teethers;
- teach your child to wash their hands after going outside and going to the toilet, before eating, and to properly care for their teeth;
- take your child to the dentist twice a year, even if nothing bothers you;
- The diet should contain fresh fruits and vegetables - they have a beneficial effect on the immune system;
- the child should know that it is forbidden to use other people’s towels and toothbrushes;
- to avoid intrauterine infection, a woman needs to cure vaginal candidiasis before conception, and during pregnancy try to avoid factors that can provoke the development of a fungal infection;
- A nursing mother needs to properly care for her breasts, rinse the mammary glands with warm water before feeding, and treat the nipples with a soda solution after feeding.
A strong immune system protects not only from thrush, but also other diseases. To strengthen protective functions, the child must move more, be sure to walk in the fresh air, and follow a daily routine.
Pharmaceutical preparations for external use
It is sometimes quite difficult to cure thrush in children without the use of special medications. For mild to moderate severity of candidiasis, medications intended for external application to the affected mucous membranes are used, these are:
- Candide solution
. A few drops of the drug should be placed on a cotton swab and used to treat the oral cavity. Use the medicine three times a day before feeding. At the same time, the mother should lubricate the nipples with the solution. - Miramistin
. When treating newborn children, it is better to use a solution; the mucous membrane of the mouth of a one-year-old child can already be irrigated with a spray. Miramistinam treatment is carried out after preliminary removal of plaque using a soda solution. - Nystatin
. A tablet of the drug in 250 thousand units. should be diluted in a glass of water. A cotton swab is moistened in the resulting solution, after which the mucous membranes in the mouth are treated. If ulcers appear, you can use nystatin ointment. - Potassium permanganate
. Make a 5% solution of potassium permanganate, the color turns out purple. Lubricate the internal surfaces of the oral cavity with potassium permanganate up to 5 times a day. Just be sure to carefully dilute the permanganate, since the remaining grains can cause a burn to the mucous membrane.
When using pharmaceutical antifungal agents, you must take into account all contraindications to their use.
Diagnostics
You can recognize oral candidiasis on your own; the disease has a number of characteristic symptoms. But only a specialist can confirm or refute the diagnosis after an examination.
Independent
You can identify thrush yourself by examining the oral cavity.
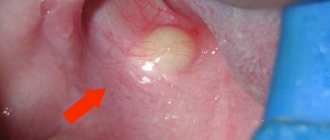
A characteristic symptom is a white, yellowish, pale gray coating on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks. Plaque from oral candidiasis is difficult to remove; after removal, bleeding ulcers and red spots appear. Sometimes, during infection, the mucous membrane becomes smooth, shiny, with small white grains on the surface.
Precursors to the development of thrush in infants are worsening appetite and sleep, constant crying for no apparent reason, and irritability. Older children begin to complain of discomfort in the mouth while eating, although there may be no visible damage to the mucous membrane.
Important! One of the characteristic signs of thrush is the appearance of a sour odor from the mouth.
Professional
Diagnosis and treatment of oral candidiasis is carried out by a pediatrician or adolescent doctor, dentist, or ENT specialist.
After the examination, the doctor will prescribe the necessary tests and, based on the examination results, select safe medications. Diagnostic methods:
- clinical blood and urine analysis;
- bacteria culture of plaque;
- test to determine the sensitivity of the fungus to drugs;
- indirect laryngoscopy - allows you to see the severity of damage to the mucous membranes;
- tests to determine immune status;
- test to determine blood glucose levels.
General treatment of thrush
Systemic antifungals
for thrush in the mouth of a month-old baby and young children are prescribed only if the infection is severe. The dosage of such drugs and the total duration of their use should be selected by a specialist. Failure to comply with the rules for taking antifungal medications increases the likelihood of severe adverse reactions.
In most cases, children are prescribed medications such as:
- Griseofulvin
. A package of 20 tablets costs around 300 rubles. - Terbinafine
. The cost of a package of 10 tablets is 200-250 rubles. - Ampholip
. Sold as a concentrate intended for the preparation of a solution for injection. One ampoule of the medicine costs 2900-3200 rubles. - Ketoconazole
. The price for a package of ten tablets starts at 90 rubles.
The popular drug Fluconazole is prescribed if the child is already 4 years old. It is advisable to give the diluted medicine from a spoon, so that part of the antifungal agent will immediately reach the mucous membranes.
When using systemic antimycotics, we must not forget about external treatment; the child also needs to treat the oral cavity with pharmaceutical or folk remedies.
Antimicrobial drugs are used either alone or in combination with a number of other medications.
These could be probiotics, immunomodulatory drugs, vitamins. The infection should be treated until the normal ratio of opportunistic organisms is restored, which is determined by analysis.
Reasons for the appearance of a child
Candidal stomatitis
The main reasons for the development of fungal infections in children are non-compliance with dental care rules, the presence of carious teeth and other dental diseases, and decreased immunity.
Causes of candidal stomatitis:
- Taking antibiotics. Weakening of the immune system and active growth begins if antibacterial drugs are given to the child, or if a nursing mother takes potent medications - the active substances penetrate into breast milk.
- Violations of feeding techniques, pathologies of the nervous and digestive systems, which provoke frequent regurgitation in children. Leftover food is an excellent environment for the active growth of fungal spores.
- Improper care of nipples and bottles - yeast-like fungi often live on the surface of these objects.
- Frequent injury to the mucous membrane of the tongue, cheeks, and gums.
- The habit of constantly putting hands and toys into the mouth.
- Failure to comply with drinking regime, excessively dry air in the room. The amount of saliva, which has an antimicrobial effect, decreases.
- Frequent colds, weakened immunity due to chronic pathologies, radiation or chemotherapy sessions, and taking hormonal medications.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules by parents.
- Vitamin deficiency - thrush often develops when the body receives insufficient vitamins B, PP, and ascorbic acid.
- Consuming large quantities of sweets, raw milk, poorly cooked meat, dirty vegetables and fruits.
- Dysbacteriosis, diabetes and other pathologies of the endocrine or digestive system.
- Allergic dermatitis, rickets, anemia.
Thrush is diagnosed in 20% of children under 1 year of age. This is due to the fact that the microflora in the mouth is constantly changing, the epithelium of the mucous membrane is not yet fully formed. All these factors contribute to the active growth and reproduction of yeast-like fungi.
Important! Oral candidiasis may be the first manifestation of blood cancer, a dangerous immunodeficiency condition.
Mechanism of occurrence
Fungi of the genus Candida are an opportunistic microorganism; 50-90% of people are carriers.
Under normal conditions, there are no symptoms of candidiasis; fungi begin to actively grow in the presence of certain factors. Then signs of infectious pathology appear.
Factors leading to the development of the disease
Various factors can provoke the active growth of fungi in the mouth of children.
Why thrush develops:
- Infants have poor nutrition from the mother. If a nursing woman’s diet is dominated by sweets, canned food and semi-finished products, and fast food, the risk of developing oral candidiasis in the baby increases several times.
- In young children - poor hygiene and teething, feeding with formulas high in sugar, and the habit of sleeping with a pacifier in the mouth.
- Older children have an unbalanced diet, improper tooth growth, caries and other dental diseases, wearing braces and plates to correct the bite.
- In adolescents, oral candidiasis often develops against the background of hormonal changes in the body, smoking, drinking alcohol or drugs, and hypothermia.
There is a high probability of developing oral candidiasis in premature babies and in bottle-fed children. Thrush is often diagnosed in newborns whose mothers have tuberculosis or HIV.
But the main provoking factors are considered to be improper oral care, decreased immunity, an acidic environment in the body, and constant exposure to a hot room with dry air.
Causes of thrush in a child’s mouth and methods of its treatment:
Routes of infection
Candida fungus
Thrush is an infectious disease that is transmitted from sick people to healthy people. Children most often become infected from their parents or from other children in kindergarten.
Main routes of infection:
- Intrauterine. Candida fungi penetrate the placenta, and the child is born with congenital candidiasis.
- During passage through the birth canal, if the woman has not treated genital candidiasis in time.
- Breasts can become infected during feeding if the fungus lives on the skin of the mammary glands.
- Contact. Infections are transmitted through handshakes, toys, and household items.
- The fungal infection is transmitted from young domestic animals and birds.
But even fungal infection does not always cause the development of an infectious process. It all depends on the state of the immune system and the presence of chronic diseases in the child.
External pain relievers
Thrush causes pain that prevents the child from eating well. While the disease passes, you can use drugs that will anesthetize the mucous membrane and, accordingly, their use will have a positive effect on the baby’s appetite. Such drugs include:
- Gel Cholisal
. Apply a thin layer of it to the affected surface; it is advisable to do this 10-15 minutes before feeding and after treatment with an antiseptic. The analgesic effect of Cholisal begins to develop within 3 minutes and lasts up to 6-8 hours. Do not use the gel more than three times a day. - Baby doctor
. The drug is intended to facilitate teething; it contains only natural ingredients. If thrush develops, the gel can also be applied to the mucous membranes of the cheeks and the inner surface of the lips. - Kalgel
. The drug is endowed with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties, which not only relieves pain in the oral cavity, but also helps stop the growth of fungi.
Medicines should not be used without specific indications. If thrush is detected in a timely manner, it can be dealt with in a few days using simple, non-toxic external means.
How to properly treat your baby's mouth
Children under 3-4 years old cannot rinse their mouths, so if they have oral candidiasis, parents need to constantly rinse their mouths with it.
Step-by-step instruction:
- Wash your hands thoroughly and treat with antiseptic.
- Wrap a small piece of gauze, always sterile, around your index finger.
- Dip your finger and gauze in warm water.
- Gently, without pressure, remove plaque from the tongue and cheeks.
- Throw away the gauze and wrap a new piece. Dip your finger into a solution of soda or Miramistin and treat the problem areas again.
You need to remove plaque up to 7 times a day, always after every meal, before bed, and in the morning immediately after waking up.
Quick treatment for thrush:
Diet
Fungal infection of the oral cavity goes away faster if you follow certain nutritional rules.
The diet must be followed by nursing mothers and those children who, for the most part, eat from the adult table.
| Authorized Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
The diet must be followed throughout the entire treatment period. In the future, the child should receive as many vitamins as possible from food, this will improve the functioning of his immune system.
Caring for a child with thrush
A sick baby needs additional care. Required:
- sterilize used bottles and nipples;
- limit the amount of time you suck on pacifiers;
- ventilate the room periodically.
When a baby develops thrush, he refuses to eat, largely due to painful sensations when sucking. So that the child does not remain hungry, you can give him an artificial mixture a little from a syringe or from a spoon. Expressed milk is also given.
Candidiasis of the intestines and other digestive organs
After Candida damage to the skin and visible mucous membranes, candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract in infants ranks third. Carriage of microorganisms is quite common when the pathogens do not cause disease. Good immunity inhibits the development of the infectious process. But under certain circumstances, weakened children may develop candidal esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), gastroduodenitis (inflammation of the stomach and duodenum), enteritis (inflammation of the small intestine), enterocolitis (inflammation of the small and large intestines).
Factors contributing to the development of gastrointestinal candidiasis
The following factors contribute to the development of intestinal candidiasis:
- An imbalance between Candida colonization in the intestines and defense mechanisms that prevent excessive growth of microorganisms.
- The presence of physiological intestinal dysbiosis.
- Features of the structure of the mucous membrane in newborns. Failure of its protective and secretory functions.
- Long-term antibiotic therapy leads to the death of “good” bacteria and excessive growth of opportunistic flora, including fungi.
Signs and symptoms of candidal esophagitis
The disease may be asymptomatic or have nonspecific manifestations. Classic typical manifestations of candidal esophagitis are recorded extremely rarely. The infectious process develops in children born to mothers with vaginal candidiasis on the second day of life. Lack of appetite, refusal to breastfeed, excessive regurgitation containing whitish lumps, vomiting and rapid increase in dehydration are the main symptoms of the disease. Toxicosis is slightly expressed.
The basis of diagnosis is fibroesophagogastroscopy and culture of vomit on nutritional media in order to identify fungi of the genus Candida.
Rice. 10. Microscopy reveals pseudomycelium of Candida b and budding cells (photo on the left); when inoculating the vomit, an increase in colonies of pathogens is noted (photo on the right).
Signs and symptoms of intestinal candidiasis
Intestinal candidiasis in children occurs with symptoms such as lack of appetite (sometimes infants completely refuse to eat), regurgitation and vomiting, pain, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, and loose stools. The vomit contains greenish or whitish mucus, and the stool contains yellowish-greenish mucus and white lumps. The smell of stool is normal. Symptoms of toxicosis are mild or absent. Microscopy of vomit and feces reveals fungal mycelium and budding pathogen cells. Candida is isolated from feces in crops in quantities of more than 10 4–5 CFU/ml.
In more than half of infants, intestinal candidiasis is combined with lesions of the skin around the anus, buttocks and visible mucous membranes.
Rice. 11. Often in infants, intestinal candidiasis affects the skin around the anus and buttocks.
Treatment of candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract
In the non-invasive form of candidiasis, fungal cells do not form pseudomycelium and do not germinate the intestinal mucous layer. They multiply intensively in the lumen of the organ, disrupting cavity and parietal digestion. Treatment in this case is carried out with antifungal drugs that are not absorbed from the intestinal lumen - Nystatin.
In the invasive form of intestinal candidiasis, candida germinates the epithelial layer and penetrates beyond the basement membrane. The pathogens then enter the lymphatic system and bloodstream and spread throughout the body. In this case, Flucanazole, Ketoconazole and Intraconazole are effective.
The drugs are completely absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
If treatment is ineffective in children in intensive care units, Amphotericin B is used intravenously to treat candidiasis. For intestinal candidiasis in newborns, the drug is rarely used due to its high toxicity.
To correct the composition of intestinal microflora, probiotics are used. Immunocorrectors are used according to indications.
Possible complications
Affecting most of the oral cavity in children, candidiasis causes pain, but the disease with mild and moderately severe manifestations does not lead to complications. In severe cases of thrush, there is a possibility that a fungal infection will spread to internal organs, which significantly increases the risk of an unfavorable outcome.
To prevent this from happening, you should consult your doctor immediately if your baby:
- fever;
- difficulty swallowing and breathing.
- there are signs of dehydration;
- high temperature is recorded.
Before being examined by a doctor, you should continue to treat thrush with the chosen means. For fever, an age-appropriate antipyretic should be given. It is necessary for the child to drink as much as possible, this can avoid dehydration of the body.