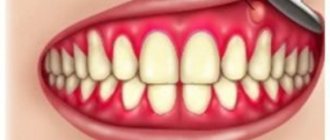
Among the many dental diseases, there are those that are only partially associated with dental diseases.
The oral cavity contains tissues whose abnormal changes are related to dental problems.
One such problem is fibromatous growth of gum tissue (fibromatosis).
Brief description of the disease
In addition to fibromatosis, this disease in dentistry is called hyperplasia or gingival hypertrophy.
It is characterized by the progressive, uncontrolled formation of new connective tissue cells in the gums and periodontium. From them fibril tissue is formed, which is a causative factor in the increase in the size of the gums.
According to statistical data, the disease is rare, its mechanism is not completely clear.
Types of gum hyperplasia
Periodontal tissues can grow in different ways, involving different areas of the gums. There are several types of hyperplasia:
- localized: the growth of new cells occurs in a limited area, next to one tooth or group of teeth (only on one or both sides);
- generalized: the gums grow over the entire surface on one or both jaws;
- papillary: new cells are formed only in the area of the gingival papilla, the pathology does not affect other gingival tissues;
- marginal: the gingival papilla and the area of the gingival margin grow;
- diffuse: growth of both marginal and attached gums occurs (an increase in periodontal tissue to the entire height from the gingival margin to the mucogingival border).
Hyperplasia may be limited. The increase in tissue in this case is similar to a tumor, strictly isolated, and has a wide base or pedicle. It looks like a growth or bump.
Forms
There are 2 forms of this pathology. They differ from each other only in the area of damage to the oral cavity.
Focal
The second name for this form of fibromatosis is limited. This is a fairly rare form of the disease that progresses slowly. With it, only those tissues that are localized in the area of the tubercle of the upper jaw grow.
In isolated cases, such growth appears on the lingual part of the (inner) gum near the lower jaw. They do not differ in color from healthy tissues and are painless.
Why is it so important to sanitize the oral cavity during pregnancy? We'll talk about this in our article. In the following review you can read about how to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
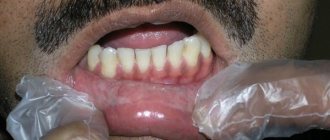
The areas that have increased in size have a rounded shape and a fairly smooth surface with a dense, uniform consistency. The formations are covered by a third of the crown of the teeth (less often completely).
They prevent the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. Pathology threatens the collapse of the partitions between the teeth and the development of osteoporosis.
Generalized
This form is characterized by the formation of several pathological areas at once. Gradually increasing in size, they unite into one large lesion. As a result, the crowns of the teeth are almost completely covered by overgrown tissue.
The generalized form is of 2 types:
- diffuse – tissue growth occurs uniformly;
- nodular - overgrown tissues have a large number of nodules.
The development of the disease occurs slowly. Having grown, the pathology becomes a serious obstacle to the correct implementation of oral hygiene procedures and interferes with normal nutrition, since these tissues interfere with biting and chewing food.
Over time, both forms of the disease turn into a serious cosmetic defect that affects the psychological state, developing depression.
Causes
The initial etiology of the development of the disease has not been precisely established. But it is known for sure that fibromatosis is caused by two causative factors: genetic predisposition and the influence of certain groups of drugs.
Genetic predisposition
The disease manifests itself in childhood (from 1 year) or during the period of the beginning of hormonal changes in the body (from 10-11 years) . Its development can be triggered by:
- changes in the body's reaction during the eruption of permanent (molar) teeth;
- changes in the functioning of the endocrine system during puberty.
Effect of medications
The second reason is a side effect from long-term use of certain groups of medications. The disease begins to manifest itself at an older age. Both men and women are equally susceptible to it.
The development of fibrosis is influenced by:
- Immunosuppressants – used after organ transplantation.
- Antiepileptics - prescribed to prevent epileptic attacks and reduce the frequency of their manifestations.
- Calcium channel blockers , prescribed for hypertension and pathology of the heart and blood vessels.
- Hormonal contraceptives containing estrogen.
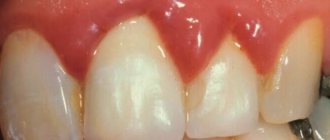
The disease begins with an increase (swelling) of the interdental papillae. Then the consistency changes: they become elastic and dense, the color changes to pink.
An important role in the occurrence of the disease is played by inflammation, which is caused by bacteria living in abundant dental plaque.
Symptoms
The pathology may not manifest itself in any way for some time: there will be no changes in the tissues and mucous membrane of the gums, or pain. It is important to always pay attention to the condition of the mucous membrane in the mouth and its color.
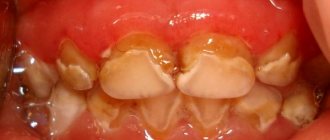
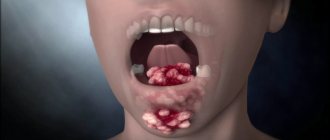
The first and main manifestation of the disease is a significant increase in the size of the tissue on the gums. The process of development of fibromatosis is usually divided into 3 degrees. Each of them has its own characteristics:
- I degree - the edges of the gums and interdental papillae begin to grow.
A thickening forms that resembles a roller in appearance. It grows throughout the affected area and reaches 1/3 of the height of the tooth crowns. Clinical signs of inflammation and pain are completely absent. - II degree - the thickening continues to increase in size and covers ½ of the height of the teeth.
Performing all hygienic procedures and eating solid food provoke bleeding from swollen affected areas. - III degree - the crowns of the teeth are almost completely covered by an overgrown thickening.
In advanced forms of the disease, the cutting edges and chewing surface of the teeth can completely overlap. Granulations form on top of the affected areas.
The enlarged affected areas are divided into segments corresponding to the original shape of the gum. Outwardly, they look like a bunch of rollers.
In isolated cases, such areas look papillomous, that is, they consist of several small growths.
What it is
Hyperplasia is a random rapid increase in gum tissue cells. Hyperplasia is not a tumor; it is benign changes in cell tissues, in which the cells themselves continue to perform their functions without changes. With hyperplasia, unlike oncological diseases, cells do not grow into surrounding tissues and do not metastasize. Many doctors are inclined to believe that it is not always a pathology, but only an experienced doctor can decide on a treatment method.
Gingival hyperplasia is manifested by excessive growth of tissue that can partially or completely cover the entire crown of the tooth. With this disease, only the gum tissue grows; the cheek and tongue tissues are not affected by changes. Hyperplasia is not an inflammatory process, so there is no drug treatment for it. In addition, it is necessary to correctly carry out differential diagnosis of the disease, being able to distinguish it from cysts and other tumor neoplasms. And only an experienced dentist can do this. Therefore, if you find that your gums are growing by leaps and bounds, consult a doctor immediately.
Gum hyperplasia is also accompanied by increased blood supply to the gums, so when brushing your teeth, the gums often bleed. Often patients mistake this disease for gingivitis or periodontitis and self-medicate, which does not bring any effect. In order not to waste time and not to advance the disease to such a stage when the tooth is completely under the gum, you must immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
A visual examination alone will not be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. Fibromatosis is a benign tumor disease.
When diagnosing, it is important to differentiate it from other tumor diseases. A histological study of the structure will help to accurately determine the type of tumor. This study is carried out on material taken from a biopsy.
Differential diagnosis of fibromatosis is carried out with symmetric fibromas, osteomyelitis, periodontitis, hypertrophic gingivitis. This is done due to their clinical similarity of manifestations.
X-rays are used to evaluate the condition of the entire bone structure. Additionally, an orthopantomogram is prescribed, which will help clearly identify destructive areas of the alveolar process.
How is the treatment carried out?
There are 2 types of treatment:
- Cancel the medications used if they caused the growth.
- Surgery (in all other cases).
Drug treatment
Therapy involves the complete abolition of drugs that provoked the development of the disease. In case of emergency, discontinued drugs are replaced with others.
Canceling medications in most cases leads to a gradual restoration of the original condition of the gums.
If recovery does not occur or the fibrous tissue has decreased slightly, it is excised surgically.
What treatment can be prescribed during pregnancy if your gums bleed. Read about this in our next article. By clicking on this link: you can find out the features of tongue tapping therapy at home.
In the next review, we will tell you how much it costs to take a panoramic photograph of your teeth and what the price depends on in different clinics.
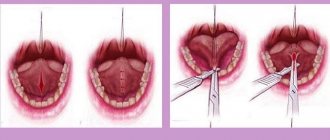
Surgical intervention
This method of treatment is the only way to get rid of the proliferation of fibromatous tissue today. The duration of the operation is 30-40 minutes.
The total duration of surgical treatment is about 30 days. The operation takes place in stages:
- Local anesthesia is administered: infiltrative or conduction anesthesia is used.
- Fibromatous growth is excised with the periosteum.
- All mobile (loose) teeth on one jaw are removed.
- Hemostasis is carried out with antiseptic treatment of the operated area of the alveolar bone.
- Using scissors, a silicone membrane is shaped to form the surface of the affected area and covered with it.
- The edges of the membrane and mucosa are fixed with a suture (fastening is performed by a combination of continuous and interrupted sutures).
- When fixing, the shape and position of the membrane is constantly adjusted with scissors. Its transparency allows the dentist to then monitor the progress of healing.
- If necessary, antibacterial, keratopdastic, and hemostatic drugs are introduced under the membrane.
The membrane is removed after the formation of granular tissue by removing all sutures. Further restoration and formation of the epithelium usually occurs without complications in the open oral cavity.
If fibromatous tissue has grown on baby teeth, they are removed during surgery.
A favorable outcome of the first operation allows the second operation to be performed on the other jaw after 8-10 days.
In some dental clinics, instead of conventional surgical instruments, a laser is used for dissection, which has a number of advantages: sterility, absence of postoperative swelling, minimal blood loss, and high precision of excision. The following video shows how this operation is performed:
It is important to remember that the use of folk remedies will not give the expected positive result. Refusal to undergo treatment and self-medication can lead to serious health consequences. Their elimination will be more difficult and longer than the treatment of fibromatosis.
Laser gum trimming video
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
gum disease
Expert “The specificity of the disease requires only surgical intervention. Since the process is not inflammatory, there is no drug treatment for hyperplasia. An experienced dentist will first send the patient for an x-ray to rule out malignancy. After all the details are clarified, the operation is scheduled.”
Therapist, periodontist, surgeon Elina Olegovna Tsorieva
Consulting specialist
Ivleva Eleonora Vasilievna
Doctor rating: 9.3 out of 10 (4) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 23 years
If left untreated
In almost all cases, the disease leads to the appearance of associated problems, which are considered complications in dentistry. Enlargements of the interdental papillae and gum margins lead to the formation of deep periodontal pockets.
Food debris can accumulate in them and bacteria can grow. It is impossible to empty the pockets yourself.
Such a complication very quickly degenerates into tartar, which causes inflammation of all tissues. Sometimes they detach from the tooth, which causes trauma.
The disease at stages II and III leads to bone atrophy in the affected areas of the upper jaw, osteoporosis, and destruction of the partitions between the teeth.
Loosening of the teeth, decay of the alveolar processes are observed, and dystopia develops (displacement of the teeth towards the tongue, cheeks, or rotation around its axis).
If the disease progresses in children, then there may be a delay in the change of bite and germination of permanent (molar) teeth, which in the future will adversely affect the development of the dental system.
What symptoms can be used to identify hypertrophy?
You can see the increased size of the gums visually. Hyperplasia is a non-inflammatory disease that can occur in both adults and children.
The first and most important symptom is the growth of gums, which seem to be on the tooth. This can be observed in the area of one tooth, between dental units, or throughout the entire jaw. In this case, the mucous membrane may not change its color, but may become bright red, and even turn a little blue. Patients with hypertrophy speak not only about the aesthetic disadvantage of the periodontium, but also about the occurrence of difficulties when chewing food, and pain when pressing on the gums.
Pathology can occur not only in humans, but also in cats and dogs. However, hyperplasia in animals is not contagious and is caused by other reasons.
Prevention
Since it is impossible to completely exclude the genetic factor in the manifestation of the disease, additional classical methods of dental prevention should be used.
Preventive measures to help prevent the development of the disease are:
- Correct and regular implementation of oral hygiene procedures.
- Professional dental cleaning by a dentist.
- Timely removal of deposits on teeth.
- Do not injure the gums with rough and hard food.
- Regular visits to the dentist to examine teeth and treat patients.
It is important to be careful and cautious when taking medications that can trigger the disease.