Content:
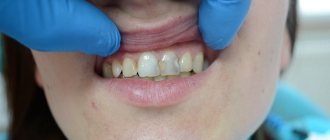
Around each tooth there is a small gingival fold, tightly adjacent to its cervical part, which is called a physiological periodontal (gum) pocket.
With poor dental care or due to hereditary factors, soft plaque accumulates on the teeth, which, under the influence of microflora, turns into hard dental deposits - stones.
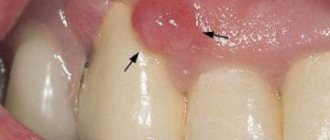
Tartar, accumulating on the tooth wall, pushes back the gingival fold, forming a pathological gingival pocket, which causes gum inflammation and bleeding. As a result of inflammation, bone tissue is destroyed, gums swell, bad breath appears, ligaments around the teeth are destroyed, teeth lose support, begin to loosen and eventually fall out.
Alternative methods of performing the procedure
Removal of hard dental deposits in the pocket cavity can be done in various ways. A significant part of them can be classified as a closed type of operation, because their use does not involve any incisions in the gums.
Vacuum curettage in dentistry
The periodontal cavity is cleaned here with special curettes, which are connected to a vacuum suction device for separated particles from the treatment area. Fewer injuries and instant removal of tissue particles and plaque reduce the risk of complications and shorten the rehabilitation period.
Chemical
This technique uses various chemicals (particularly citric acid) to soften and then remove hard plaque particles. The solution has not only a cleansing and softening effect, but also an antiseptic, making it easier and with less damage to remove all excess from the gum pocket, while simultaneously disinfecting the cavity and reducing the likelihood of infection.
Ultrasonic
The method of destroying hard dental deposits using ultrasound requires the use of special equipment, for example, the Vector apparatus. Using ultrasound, as well as a water-air jet under pressure, it allows you to successfully remove hard plaque, although ordinary hand tools are also used for curettage.
Cryo method
The use of liquid nitrogen to remove various deposits and affected tissues is also practiced when treating periodontal pockets. Freezing also kills pathogens, reduces the risk of complications and makes the entire operation completely bloodless.
Laser
Laser curettage is one of the most modern methods of cleaning gum pockets. The laser beam heats the area of action to a high temperature, instantly burning out foreign inclusions and bacteria, while simultaneously closing the blood capillaries, preventing bleeding. This method causes less tissue trauma, does not require sutures, and shortens the recovery period.
Curettage of periodontal pocket
Curettage is an outpatient dental operation - gum cleaning, which involves removing pathological gum pockets from tartar and soft bleeding tissues that grow during chronic inflammation of the gums around the neck of the tooth.
At the first signs of gum inflammation, you should contact a dentist, who, depending on the severity of the situation, will offer either professional teeth cleaning or surgical intervention: - closed curettage of the gums; — open curettage of periodontal pockets; - flap surgery.
If the patient comes in on time, before deep changes have occurred in the gum pockets and the integrity of the sockets is not compromised, professional teeth cleaning to remove tartar is sufficient to improve the health of the gums. The doctor will remove hard and soft dental plaque using manual instruments or using an ultrasound or laser device.
When the depth of pathological pockets reaches 2 mm, superficial cleaning turns out to be ineffective, because without curettage it is impossible to qualitatively clean them from pathologically changed tissues, since curettage allows you to clean not only pathological pockets, but also tooth roots, and therefore stop the development of inflammatory processes.
How to care for your teeth and gums if you have gum pockets
Problematic gums require special care, even after basic treatment procedures. You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day; it would be a good idea to use antiseptic rinses.
It is advisable to purchase a special device for more thorough teeth cleaning - an irrigator. It not only helps remove plaque, but also has a massage effect, causing blood flow to the gums. This promotes rapid tissue regeneration after surgery.
Treatment of periodontal pockets
Indications and contraindications for curettage
Curettage of periodontal pockets is necessary if:
— gingival crevices more than 2 mm deep; - gums are inflamed and bleeding; - abundant tartar fills the gum pockets; — the bone tissue around the roots of the teeth is destroyed and replaced with granulation tissue.
Contraindications for curettage are:
— acute infectious diseases; - infectious processes in the oral cavity and pharynx, such as stomatitis and sore throat; - suppuration from under the gums; - fibromatous growths of the gums; - thinning of the gum mucosa; — anomalies in the position of teeth in the dentition; - underdevelopment of the jaw; — tooth mobility III-IV degree; - blood clotting disorder.
Closed gum curettage
The procedure is called closed because it is performed blindly with minimal access to the problem area. Closed curettage of periodontal pockets is carried out when the gum pocket has a depth of 2 to 5 mm and the inflammation has not affected the bone tissue.
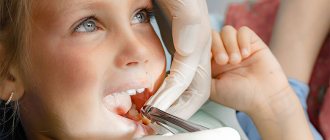
When performing a closed curettage, the doctor, under local anesthesia, uses special instruments to clean the walls of the teeth from hard plaque and thoroughly scrape out soft tissue from granulations.
Then the periodontal pockets are washed with a warm antiseptic solution using a syringe, and small grains of stone and granulation are washed out of them.
A protective dressing containing zinc oxide, oil and other healing ingredients is applied to the gums. In order for the bandage to perform its protective function longer, the patient is prohibited from eating for three hours.
Subsequently, for several days, the person who has undergone curettage carries out regular antiseptic mouth rinses. If necessary, painkillers are prescribed.
Possible complications
Complications can be caused by the individual characteristics of the body or violation of the doctor’s requirements. Increased tooth sensitivity can last up to two months. In order to speed up its regression, you will need to use special pastes and gels prescribed by your doctor. Swelling and hematoma at the surgical site may persist for up to 14 days. This is not dangerous and goes away on its own. In some cases, tightness and difficulty opening the mouth may occur, but this problem usually disappears within a few days. Teeth can remain mobile for up to 3 weeks. You must wait until the end of this period before returning to solid foods.
Open gum curettage
Open curettage is performed if there are pathological gum pockets deeper than 5 mm, as well as if periodontitis occurs, a disease in which deep damage to bone tissue develops with loosening of teeth. This is a full-fledged surgical operation.
Open curettage is preceded by mandatory anti-inflammatory measures, suppuration is eliminated.
Sometimes, before surgery, preliminary splinting of mobile teeth is performed.
The doctor performs open curettage of periodontal pockets in 2-3 visits, in the area of no more than 4-6 teeth at a time. First, using special graduated dental probes, the doctor measures the depth of each pathological pocket and makes a mark on the gum. Next, under local anesthesia, he makes a horizontal incision in the gum with a scalpel, removes the cut flap of the mucous membrane and gains free access to the granulations, scrapes out the exposed walls of the socket and tooth with curettes and then grinds them with cutters.
After antiseptic treatment, drugs that stimulate osteosynthesis are applied to the wound surface. Sutures are placed on the mucous membrane in each interdental space. The top of the seams is covered with a protective bandage.
In this case, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers, as well as rinses or other auxiliary procedures carried out at home.
After ten days, if healing is normal, the sutures are removed.
Good postoperative care under the supervision of a dentist will prevent the development of complications such as inflammation of the gums, suppuration of the postoperative wound, and loosening of teeth.
Complete restoration of bone tissue occurs 2-3 months after curettage.
What tools are used
Doctors usually use special hand instruments. In modern dental clinics, treatment of the subgingival area and root polishing is carried out with the additional use of ultrasound or laser. The use of such technologies allows us to achieve better and more durable results, as well as reduce the risks of complications.
As for hand tools, today specialists have a fairly wide range of different designs at their disposal, most of which, however, have a similar structure: handle, working area and shoulder. Tools can be made of metal, plastic or Teflon, or have diamond coating. Each modification is designed for use in a specific clinical case, and the choice here largely depends on the stage of the pathology and the age of the patient.
Dentists have many different instruments in their arsenal for the procedure.
Tools made of Teflon and plastic are suitable for removing soft plaque from children and adults. But to clean the implant under the crown, special plastic products are used - implacers. The diamond-coated option is relevant for cases where gum excision is required - this instrument has a semicircular working area and a slightly curved arm.
Curettage of gums in Krasnodar
In Krasnodar, you can undergo the gum curettage procedure at our Symmetry dental clinic. Our specialists have extensive experience and high qualifications, confirmed by many specialized diplomas and positive reviews from our patients. We have all the necessary modern, high-quality dental equipment.
Recommendations after the procedure
Recommendations after curettage in dentistry are always individual. In some cases, for the first time you just need to give up solid food and brush your teeth with a hard brush. In others, you have to comply with more stringent requirements, see a dentist and remove stitches after the damage has healed. It is important to listen carefully to the doctor’s advice and try to follow all instructions as accurately as possible - then the curettage procedure will bring maximum benefit and periodontitis will not bother you for a long time.