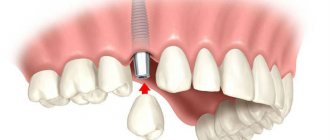
Dentist and dentist: what is the difference
Let's figure it out.
What is the difference between a dentist and a dentist? Dentist is a profession that requires secondary education. After graduating from medical school, the newly minted dentist specializes only in the treatment of hard dental tissues, namely dentin and enamel. Consequently, he will not be able to help a patient who comes with acute pain.
A dentist is a medical specialist who has 6 years of university education and a year of internship behind him. He is endowed with a wide medical specialization and is able to perform various manipulations in the oral cavity: treatment and extraction of teeth, insertion of dental implants, bite straightening and much more.
The difference between a dentist and a dentist is obvious and quite significant. In this case, the question arises: why is a dentist needed if his powers are not as broad as those of a dentist?
In dental clinics there is no profession of “dentist” as such. There are quite a few highly specialized dentists of various specialties there. In addition, the dentist cannot be left as an on-duty specialist, since if necessary, he will not be able to provide the necessary assistance to the patient.
Having found out the difference between a dentist and a dentist, the advantage of the second specialist becomes obvious. That is why oral health should be entrusted to a doctor with a full university education.
The difference between a dentist and a dentist is the level of training and the type of treatment they can perform.
The list of works provided for in the job description of a dentist includes:
- A dentist is a broad-spectrum
diagnostic specialist; - treatment of relatively simple diseases of teeth and gums - gingivitis, stomatitis, caries and some others;
- removal of teeth not complicated by periodontitis;
- treatment of simple maxillofacial injuries.
- carrying out physical procedures;
- consultation regarding the choice of oral hygiene products;
- cleaning teeth from plaque and tartar, and some others.
In case of more serious dental pathologies - malocclusion, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, lesions that have caused tooth destruction by more than 50%, and in other cases requiring the participation of a more trained specialist, the dentist gives the patient a referral to a dentist of the appropriate specialization.
A dentist is a general specialist. He has theoretical knowledge and practical skills sufficient to perform therapeutic, orthodontic, orthopedic and surgical operations.
Although, like a dentist, when faced with a particularly difficult case, he can refer the patient to a doctor of a narrow specialization.
Narrower specializations
This type of activity is multidisciplinary and covers a wide range of activities. Therefore, modern science has divided this branch of knowledge into a number of specialized specialties:
- Dentist-therapist. You can find out what this doctor does if a person has dental problems and pain. His responsibilities include a preliminary examination of the patient’s teeth and prescribing subsequent treatment. He also treats caries and inflammation in the oral cavity. After examination and diagnosis, the doctor refers you to specialized specialists.
- Prosthetist. If the therapist did not cope with the task, then people come to this doctor. He deals with prosthetics and offers different options to patients. Then he makes a description, impressions of the teeth and adjusts them to the particular structure of the patient’s mouth.
- Dental hygienist. Examines the oral cavity, removes plaque, polishes enamel and advises people on the prevention of dental diseases.
- Orthopedist. It is based on the removal of distortions in the bite and the installation of different types of orthopedic dentures - removable, fixed and combined, and also corrects the position of the teeth in the oral cavity.
- Surgeon. You cannot do without it, because there are cases when surgical intervention is necessary. The surgeon prepares the oral cavity for the upcoming procedure of inserting dentures. His competence includes jaw practice, treatment of wounds on the face and mouth, and jaw restoration.
- Maxillofacial surgeon. The specialty of these doctors was complex operations of various types using general anesthesia and correction of the jaw area.
- Pediatric dentist. In young children, baby teeth have certain characteristics, and working with them requires skills. In addition, the pediatrician must get along with children so that they are not afraid before the procedure.
- Orthodontist. Unlike an orthopedist, he deals primarily with exceptional cases, anomalies, and deviations in the development of the jaw.
- Periodontist. Specializes in the gums and soft tissues that support and surround teeth. Consults patients about bleeding gums, the appearance of tartar and plaque on teeth.
All these names, or rather, specialties, can be mastered at the Faculty of Dentistry of a medical university. The first 2-3 years are spent on general training, and then there will be training in a specific profession. It is for this that you need to pass the exam for the category.
The large number and complexity of pathologies of the dentofacial apparatus, the constant improvement of existing treatment technologies and the development of new ones require in-depth, specific knowledge and skills from dentists.
This feature has found its implementation in the concept of narrow specialization of dentists.
Depending on the type of work performed, the following specializations of dentists differ:
- therapist;
- orthodontist;
- surgeon;
- orthopedist;
- hygienist;
- pediatric dentist.
Dentists often combine several specializations at once.
Dental surgeon
The prerogative of the profession of a dental surgeon is the following operations:
- Dental surgeons often treat diseases that are within the competence of dentists of other specialties;
tooth extraction; - treatment of neoplasms in the PR;
- elimination of TMJ dysfunctions, diseases of the salivary glands and trigeminal nerve;
- primary treatment of wounds and injuries of the mouth, neck, face;
- plastic surgery and reconstruction of jaw bones;
- operations on periodontal tissues (gingivectomy, gum pocket removal, soft tissue transplantations, gingivoplasty, plastic surgery of the oral vestibule and frenulum);
- correction of tooth position anomalies.
- implantation.
Dental surgeons often treat diseases that are within the competence of dentists of other specialties: phlegmon, periodontitis, sinusitis, periostitis, abscesses, osteomyelitis.
They also diagnose specific diseases, the symptoms of which may appear in the PR - syphilis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis.
Dentist-therapist
Typically, patients who seek help from a dentist first see a therapist.
Dental therapist is the broadest specialization in dentistry.
Typically, patients who seek help from a dentist first see a therapist, who in most cases is able to deal with their problem alone.
The job description of a dental therapist provides for the following work:
- examination of the oral cavity;
- diagnosing;
- treatment of teeth (caries, pulpitis, etc.) and periodontal disease (gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease, periodontitis);
- preparation of PR for prosthetics, its sanitation;
- teeth whitening and PG;
- preventive examination and advice on caring for RP.
When pathologies are identified that urgently require the participation of a specialist doctor, the therapist refers the patient to them.
Orthopedist
An orthopedist is engaged in the restoration of teeth using prosthetics.
A doctor in this specialization is engaged in the restoration of dilapidated, missing or aesthetic teeth using prosthetics.
Orthopedist:
- takes impressions of teeth, from which the dental technician subsequently makes a prosthesis;
- tries on, adjusts and secures the prosthesis on the patient.
Prosthetic structures include crowns, bridges, inlays, veneers, and removable dentures.
Orthodontist
An orthodontist corrects the position of teeth using removable and non-removable orthodontic devices.
Orthodontics is a subsection of dentistry dedicated to dental anomalies.
The scope of practice of an orthodontist includes:
- prevention of deformations of individual teeth, dentition and jaws;
- normalization of occlusion;
- correction of jaw development;
- teeth straightening.
Correction of the position of teeth is carried out using removable and non-removable orthodontic devices - mouthguards, braces, braces.
Children's teeth at the stage of formation and growth are most successfully corrected. In adults, this process is much more difficult.
The specialty “General Dentistry” was introduced by orders of the Ministry of Health No. 553 and 112. This specialty is of particular importance for rural areas, where it is desirable to have a specialist who can provide assistance in several clinical areas.
However, until now, due to a number of organizational, educational and legal problems, general practice in dentistry has not received proper development.
Children's
Children and adolescents under the age of 17 are patients of the pediatric dentist. A child's teeth have many differences from adult teeth.
This includes the presence of baby teeth, the constant renewal and formation of the dentofacial apparatus, and the inability to use certain anesthetics for children.
And the reaction of children to the dental chair creates increased problems.
A dentist treating children must not only be able to distinguish pathology from the age norm, detect deviations in bite and tooth formation in time, but also be a bit of a psychologist.
Hygienist
The goal of a hygienist is the prevention of dental diseases.
A dental hygienist is a relatively new specialization in dentistry.
Its goal is the prevention of dental diseases, its field of activity is dental hygiene, proper dental care.
A dental hygienist performs the following work:
- diagnosing RP diseases;
- professional teeth cleaning;
- disease prevention;
- training in proper dental care skills;
- educational activities (inspections in kindergartens, schools, institutions, organizations, enterprises).
Order of the meeting
Certification is scheduled no later than three months from the date of receipt of data about the specialist by the committee. If the data does not match the requirements for the latter, the documentation will be refused (no later than 2 weeks from the date of receipt). The secretary of the committee agrees with the chairman of the expert group of the required specialization on the date of the examination.
Members of the expert group review the certification works of doctors for the category, completing a review for each of them, displaying the following data:
- level of practical skills of a specialist;
- participation in social projects related to the medical field;
- availability of published materials;
- self-education of the certified person;
- compliance of knowledge and skills with the declared category of doctors.
The examination must take place within two weeks from the date of receipt of the report. The result of the review is an indicator of the possible outcome of the certification. The secretary informs the specialist of the date of the meeting, which includes an interview and testing. More than 70% of correct answers allow you to consider the test passed. The interview takes place by questioning the person being certified according to theory and practice, the knowledge of which must correspond to the requested qualification.
The meeting is accompanied by the preparation of a protocol, which is signed by the members of the expert group and the chairman. The final decision is noted on the qualification sheet. A specialist receives the right to retake the exam only after a year. Within 7 days, the certified person receives a document confirming the promotion, reduction or refusal to assign a category.
Dentist profession
A dentist has more authority regarding the conduct of medical procedures. Specialty training lasts 6 years, during which doctors master several important disciplines. Upon completion of training, the specialist is asked to choose one of the areas: therapist, surgeon, orthodontist, orthopedist or hygienist.
Comprehensive training is necessary in order to know the structure of the human body and be able to establish the relationship of one organ with another. The doctor also has to master the basics of psychology, since some patients come to the office in a depressed state, which aggravates the therapy.
Each category in dentistry should be considered in more detail.
Therapist
The doctor treats the diseased tooth and installs a filling. The dentist also copes with these responsibilities. Both specialists can also examine the patient’s oral cavity and diagnose the disease. The difference between a dentist and a dentist is that a dentist solves minor problems (gum inflammation, mild caries).
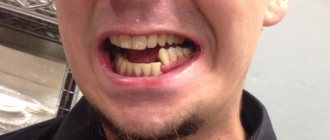
In the photo, pulpitis is one of the complications of caries that requires dental care.
Caries is caused by the gradual destruction of the enamel elements. If treatment is not timely, the pathological process spreads to dentin and pulp. The problem arises under the influence of negative external factors: taking certain types of medications, consuming carbohydrate-containing foods, and lack of proper oral care.
One of the complications of caries is pulpitis, in which the nerve endings of the tooth are involved in the pathological process. The main symptom of the disorder is acute severe pain, which is difficult to relieve even with potent drugs. Pulpitis requires immediate treatment from a dentist.
Periodontitis develops as a result of bacterial infection of the jaw bones. The condition can cause complete or partial edentia (loss of teeth).
Another problem that the dentist deals with is periostitis (flux). The disease is accompanied by severe swelling of the soft tissues of the mouth and intense pain.
The competence of the general practitioner also includes solving non-carious problems:
- demineralization of enamel;
- fluorosis;
- wedge-shaped defects;
- enamel abrasion;
- necrosis of bone tissue.
- increased sensitivity of teeth;
- diseases of the mucous membranes of the mouth (stomatitis, periodontitis, gingivitis).
There is no difference between a dentist and a dental therapist. Both specialists deal with general problems and provide referrals to specialist doctors if necessary.
Some private clinics provide services to restore the aesthetics of a smile. They include enamel whitening, elimination of bad breath, and dental restoration with reflective composites. All of the above types of services are provided by dental therapists.
Orthodontist
The main task of the doctor is to perform prosthetics. The doctor restores the chewing function of the jaw in the absence of one or more elements in the oral cavity. In addition, with the help of orthodontic structures, the aesthetics of a smile is restored, thanks to which a person ceases to be embarrassed by others.
Another name for an orthodontist is a prosthetist. First, all patients see a therapist, who issues a referral to an orthodontist.
The differences between the specialist in question and the dentist are obvious: the first is engaged in restoring the shape and aesthetics of the tooth, the second is in treatment.
Today, orthodontists are in increasing demand. They can offer patients modern prosthetic options to solve various occlusion problems. Orthodontic structures differ in purpose, cost and installation time. In each specific case, the doctor selects the best option for the patient.
Surgeon
If the tooth enamel or pulp of the element is severely destroyed, then the only way out is tooth extraction. What kind of doctor removes teeth? This function is performed by a dental surgeon. The doctor is also involved in other activities:
- performs maxillofacial surgeries;
- prepares the oral cavity for implant installation;
- corrects dental anomalies;
- gives advice on correcting malocclusions.
The surgeon performs a list of rather complex tasks that a dentist-therapist cannot cope with. After extraction of the problematic unit, the surgeon gives advice on caring for the oral cavity to minimize complications and speed up wound regeneration.
Orthopedist
What does an orthopedic doctor treat? The specialist is engaged in the restoration and correction of defects of the entire musculoskeletal system. He, like an orthodontist, can save a unit whose coronal part is destroyed but the root is intact. The differences between the specialists in the profile under consideration are that an orthodontist deals only with dental problems, while an orthopedist solves a wider range of problems related to joint damage, etc. Orthopedics also provides for dental implantation and prosthetics if there are problems with bite.
Orthopedic structures to normalize the bite
Pediatric dentist
The structure of the jaw in children has some differences, so separate specialists deal with the elimination of dental diseases in children. The doctor knows what filling materials and anesthetic agents can be offered to young patients.
The opinion that children do not need to have their baby teeth treated is wrong. Carious processes can spread to the pulp, nerve endings of the element, as well as periodontal tissue, which in the future will create problems in the formation of a permanent bite. To treat children, the doctor will have to use not only other drugs, but also instruments. In addition, the pediatric dentist must have the skills of a psychologist to prepare the patient for the upcoming procedures.
Hygienist
This profession is considered relatively new in dentistry. The main goal of the specialist is to properly care for the patient’s teeth and teach the patient hygiene skills. The list of services provided by the doctor includes:
- diagnosis of oral diseases;
- professional enamel cleaning;
- prevention of caries;
- medical examinations in various institutions (kindergartens, workplaces, schools).
The dentist deals exclusively with simple manipulations in the field of dental treatment. He does not have the right to provide more complex types of dental services.
1. Examines the oral cavity and assesses the condition of the teeth.
2. Determines the cause of concern.
3. Treats gum diseases.
4. Engaged in filling small areas of damaged dental tissue.
5. Explains the rules of proper oral hygiene.
6. Consults on the choice of dental accessories, selects them based on the condition of the teeth.
7. If serious problems with the condition of the teeth are identified, refer the patient to an appointment with a competent specialist.
From the list of responsibilities, the need for the profession of a dentist is obvious, which makes it relevant.
However, this profession also has its downside: the lack of career prospects. Unfortunately, a dentist is not appointed to the position of head of the department.
The very first mentions of dental therapy are found in the history of Ancient Egypt. Tools similar to modern analogues have been found more than once in tombs. Many more Egyptian skulls with crowns on their teeth were also discovered there, and these were not only rich people. Judging therefore, it can be said that some types of dentistry were developed in Egypt. In addition, the first toothpaste was mentioned at the same time. It included:
- ashes of the burnt entrails of a bull;
- ground eggshell;
- myrrh;
- crushed pumice.
Then in the IV-V centuries. BC, the great Hippocrates became interested in this science. He recommended eliminating pain with a hot iron. At that time, many people suffered from toothache and did not understand how to deal with it. Fatalities from common flux were common, and during the time of Hippocrates, dentistry advanced several steps forward.
The first toothbrushes appeared in the Middle East in 500 AD. And in the 4th century AD. e. found forceps used to pull out bad teeth. And also powerful drugs that relieve pain appeared: arsenic and opium. Therefore, people began to understand that there is no need to rush to remove teeth, but that they can be treated. So, in 659 the first fillings appeared.
This specialization developed, and already in Russia, during the reign of Peter I, the profession of dentist officially arose, and rapidly became popular among men and women. In 1881, the first educational institution appeared in St. Petersburg, which trained future dentists. Then such institutions began to open throughout Russia.
Categories of dentists
Dentists are required to confirm their qualifications every 5 years.
Each dentist has a certain qualification category, which is an indicator of the level of his theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
The procedure for assigning a qualification category is determined by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Dentists are required to confirm their qualifications every 5 years.
Those who wish to improve their qualifications themselves must wait 3 years from the date of the last certification.
Regulatory documents provide for three types of categories in ascending order:
- second (is basic);
- first;
- highest.
| Category | Requirements |
| Second | Work experience in the specialty for at least 3 years. Successful completion of certification. |
| First | Work experience in the specialty for at least 7 years. For a specialist with secondary education – at least 5 years. Successful completion of certification. |
| Higher | Work experience in the specialty for at least 10 years. For a specialist with secondary education – at least 7 years. Successful completion of certification. |
Dental diseases, their names and photos
- Second. Awarded to people whose work experience is more than 3 years after certification. To obtain a category, a doctor must be savvy in both theoretical and practical skills.
- First. Given to dentists who have worked in their specialty for more than 7 years. In this case, he needs to study related disciplines related to prosthetics, dental work, etc.
- Highest. Issued to doctors whose work experience exceeds 10 years. Doctors of this level of training have advanced theoretical and practical knowledge and skills.
Not only the doctor’s knowledge, but also his salary depends on the category. Some dentists only treat children. They can eliminate small cavities caused by a child's excessive consumption of sweets or poor oral hygiene.
In some cases, the dentist is unable to provide assistance to a small patient. This is due to several factors:
- A child's jaw is different in structure and structure from an adult's.
- The dentist does not have special equipment and devices for treating pulpitis or complicated caries.
- Lack of drugs necessary for therapy.
- Inability to find an approach to the child.
If one of the listed problems is present, the child is referred for treatment to a pediatric dentist. In most cases, a dentist can also cope with simple caries in a baby. The dentist also conducts preventive examinations of children 2 times a year.
Uncomplicated caries in a child
To improve his specialization, after a certain amount of time, the dentist must upgrade his category.
The category depends on the length of work in the specialty, starting from the moment it was received. They are changed after completing advanced training courses.
1. Doctor of the second category - awarded to a doctor whose work experience is more than 3 years, after receiving certification. The specialist must be well-versed both theoretically and in terms of practice.
2. Doctor of the first category - work experience of at least 7 years. A specialist must increase knowledge in his field, as well as study related disciplines.
3. The highest category implies at least 10 years of work experience in the specialty. This category corresponds to advanced theoretical and practical training.
A doctor’s category affects not only his professionalism, but also his salary.
Documentation
Four months before recertification, the specialist must submit an application for confirmation or obtaining a higher qualification. Passport details, existing category and date of receipt, personal signature are indicated here.
A certification sheet and a report on the work done over the past few years, approved by the chief physician of the health care facility and the human resources department where the certified person works, are also filled out. Copies of documents on education, work history and assignment of current qualifications are also sent to the commission.
Rubric “Question and answer”
Who is a dentist?
The concept was used in the 20th century and is now considered obsolete. Previously, the term was used to describe dentists who did not have a special higher education. In foreign countries, a dentist is a dentist who has received secondary education in his specialty. This term can be used to describe a dental laboratory specialist, a dentist, or a paramedic.
The answer to the question will be negative, since the dentist does not have the necessary skills and knowledge to carry out the procedures that are the responsibility of a dental therapist.
Maybe, if the process is not complicated by other diseases or periodontal pathologies.
Points for promotion
Each specialist receives points that are used in making decisions about qualifications. They are awarded for attending conferences, including international congresses, giving lectures to colleagues or nursing staff, distance learning with a final certificate, and taking courses.
Additional points are awarded for the following achievements:
- publishing of textbooks, manuals, monographs;
- publication of an article;
- obtaining a patent for an invention;
- presentation at symposiums with a report;
- speaking in institutions and the media;
- obtaining a title;
- defense of the thesis;
- awards by public authorities.
Children's doctor
A pediatric dentist treats simple dental problems that arise in children. As a rule, this is caries that develops in young patients due to a sweet tooth.
• Problems in the treatment of children's teeth due to the differences that a child's jaw has compared to an adult's.
• Dental treatment may require special equipment and a different approach that the dentist does not have.
• Lack of drugs suitable for children.
• Inability to find an approach to a small patient.
If the pediatric dentist is unable to provide the necessary care to the child, you must make an appointment with the pediatric dentist.
In most cases, a pediatric dentist is able to help a small patient, since the oral cavity of children is more often susceptible to ordinary caries, which requires simple treatment. Also, do not forget to take your child for a preventive examination twice a year.
Composition of the commission
The commission consists of a committee, whose work takes place during breaks between meetings, and a narrowly focused expert group, which directly conducts certification of a specialist (exam, testing). Both the committee and the expert group consist of persons holding the following positions:
- The chairman, who oversees the work and divides responsibilities between the members of the commission.
- The deputy chairman performs the functions of the chairman in full in his absence.
- The secretary is responsible for registering incoming documents, preparing materials for the work of the commission, and recording decisions.
- The deputy secretary replaces the secretary and performs his duties during absence.
Each expert group includes specialists from related specialties. For example, the category of dentist and its receipt/confirmation requires being in the group of a periodontist, orthodontist, pediatric dentist, or therapist.
Dental surgeon
• Removal of diseased teeth that cannot be restored.
• Removal of healthy teeth that are interfering with the growth of adjacent units.
• Implantation, prosthetics.
• Correction of the dentition.
• Carrying out a number of operations, for example, incision of the gums, resection of tooth roots.
The difference between a dentist and a dentist is worth knowing for those who have decided to devote themselves to this profession.
A dentist, endowed with a minimum set of medical powers, still remains a sought-after specialist. It is especially in demand in small provincial towns or villages, where, in the absence of dentists, the dentist copes with the treatment of various diseases.
The difference between a dentist and a dentist
In the field of dentistry, there is another concept - dentist. How is he different from a dentist and a dentist?
Essentially, a dentist is a dentist (corresponding to a medical assistant). This concept applies to dental professionals working abroad. It has not taken root in our country. And many people have heard the word “dentist” only in foreign films; in everyday life it is “unheard of.”
Since a dentist is the same as a dentist, dentists are therefore mid-level doctors, that is, without a full higher education and with a limited range of services provided.
So, having figured out who a dentist and a dentist are and realizing that these are specialists in the same medical specialization, but with different tasks, you can easily contact a dental clinic for help if the need arises.
It is worth considering that there is also a difference between a dentist and a dentist in the prices for services. Dentists' prices will be significantly higher than the price for dentists' work.
Now we know who a dentist is. We also looked at what it does and its relevance, so you can safely contact any clinic, having the right concepts about dentists and dentists.
A dentist is a dentist who is a paramedic. This concept is more commonly used abroad; in some countries it simply has not taken root.
This profession differs in the type of education. You can study at a medical school, college and get a secondary education to become a dentist, but dentists only need a higher education. Accordingly, their specialization will be different.
Responsibilities of a dentist:
- examination of the patient, making a primary diagnosis;
- gum treatment;
- installation of seals;
- oral hygiene instructions;
- provision of pre-medical care and referral to specialists;
- assistance in choosing toothpaste and brush.
A dentist is trained to work with simpler cases than a dentist, so his income will be different.
Attestation report
The introduction includes information about the identity of the doctor and the medical institution where he holds a position. The characteristics of the department, its equipment and staff structure, and the performance indicators of the department in the form of statistical data are described.
The main part consists of the following points:
- characteristics of the population undergoing treatment in the department;
- possibility of carrying out diagnostic measures;
- carried out medical work with the indicated results for specialized diseases;
- deaths over the past 3 years and their analysis;
- implementation of innovations.
The conclusion of the report consists of summarizing the results, indicating possible problems and examples of their solutions, and opportunities for improvement. If published materials are available, a copy is attached. A list of literature used and studied over the past few years is indicated.
Job Responsibilities
Even at the institute, immediately after admission, the student is prepared for future work and clearly delineates what will become his vocation.
Job responsibilities of a dentist include:
- carrying out diagnostics and providing all types of dental services to the patient;
- treatment of teeth, oral cavity and maxillofacial area;
- preparation of dental and orthopedic instruments and their correct use for their intended purpose, adhering to safety precautions;
- collection of biomaterial for analysis;
- carrying out prevention, diagnosis and treatment of all types of caries;
- correct removal, prosthetics and installation of fillings;
- registration of medical documentation established by law;
- compliance with job instructions.
These are mandatory items that require strict implementation.
As mentioned earlier, the profession is in demand and profitable. Therefore, dentists have a wide choice of places to work:
- public and private clinics;
- dental offices;
- sanatoriums and children's institutions.
Factors that affect wages are length of service, qualifications and region.
Salaries in the specialty range from 30,000 to 100,000 rubles, and in large cities you can earn much more. As practice shows, in private clinics the income is much different compared to public clinics. On average, it is 45,000 rubles.
Requirements for a dentist
In addition to the clearly limited responsibilities that define the work of a doctor, there are also qualification indicators that are used to guide the employment of specialists.
People who:
- have a diploma with higher medical education, a certificate of a certain specialization;
- passed a medical examination and received a medical certificate;
- have experience in this field;
- have computer skills;
- presence of responsibility, sociability, attentiveness and accuracy.
Personal qualities and skills are no less important for this profession. These include:
- the presence of excellent coordination of movements, hand motor skills, excellent vision;
- knowledge of human anatomy and physiology;
- understanding the effects of medications used in dentistry;
- ability to use specialized instruments, as well as an X-ray machine and interpret images.
Legislation:
- Federal Law of November 21, 2011 No. 323-FZ “On the fundamentals of protecting the health of citizens in the Russian Federation,
- orders of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated July 23, 2010 No. 541n “On approval of a unified qualification reference book for positions of managers, specialists and employees,
- section “Qualification characteristics of positions of workers in the field of healthcare”, dated 07.07.2009 No. 415n “On approval of qualification requirements for specialists with higher and postgraduate medical and pharmaceutical education in the field of healthcare”
- and dated July 25, 2011 No. 808n “On the procedure for obtaining qualification categories for medical and pharmaceutical workers.”
- Order No. 274
Categories are awarded to dentists in the following sequence: second –> first –> highest.
Requirements for dentists when awarding the category:
What documents must a dentist provide to obtain a category?
- an application from a specialist addressed to the chairman of the certification commission, which indicates the qualification category for which he is applying, the presence or absence of a previously assigned qualification category, the date of its assignment, the specialist’s personal signature and date (Appendix No. 2);
- a completed printed qualification sheet certified by the HR department (Appendix No. 3);
- a report on the professional activities of a specialist, agreed upon with the head of the organization and certified by its seal, and including an analysis of professional activities over the past three years with a personal signature (Appendix No. 4).
Resume sample
To find a job faster, you need a resume that can be sent to several companies at once. You need to know how to compose it correctly.
The resume must include:
- Full Name;
- Date of Birth;
- contact details: phone, email;
- citizenship;
- experience;
- basic and additional education;
- professional skills;
- knowledge of languages;
- personal qualities.