Mesial occlusion or progenia: what is it?
Several centuries ago, people with mesial occlusion were considered mentally retarded.
A similar defect was present in the composer Richard Wagner and Emperor Charles V, but such great people could not achieve great success with mental disabilities, so the theory was not confirmed. Since with a mesial bite the lower jaw is pushed forward, the face takes on a menacing and angry appearance.
That is why pathology contributes to the formation of not only aesthetic, but also psychological problems: a person feels uncomfortable with such a defect. Problems of the dental system also develop. Incomplete closure of the teeth and the resulting gap between the jaws contribute to the accelerated proliferation of pathogenic microflora, which leads to various diseases of the oral cavity. Treatment of mesial occlusion is important not only for restoring facial aesthetics, but also for preventing various dental diseases.
Causes of mesial bite
There are three main factors associated with malocclusion that cause its development: genetic, congenital, acquired. According to statistics, in 13 people with mesial bite the cause is a genetic predisposition. The anomaly can form during fetal development as a result of various maternal diseases provoked by viral infections. Also, mesial bite can result from:
- birth injuries;
- adenoids, which interfere with nasal breathing;
- incomplete upper dentition;
- adentia (partial or multiple);
- enlarged tonsils, cleft palate;
- rickets, bone hypoplasia, osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- microdentia, macroglossia;
- short frenulum of the tongue.
Malocclusion is caused by artificial feeding, a deviated nasal septum, untimely teething, and uneven wear of milk teeth. Bad oral habits of children also influence the formation of malocclusions.
Diagnostics
To decide how to correct a mesial occlusion, it is necessary to collect important information, patient complaints, visual signs and test results. A preliminary conclusion is made by the doctor after an external examination of the person. This happens according to the following scheme:
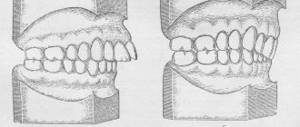
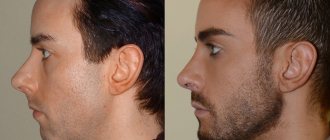
- The face is assessed. If the front and profile are concave, then ⅓ of the skull inevitably “goes” back, especially when viewed from the side. The chin is protruded forward, looks massive and disproportionate. The lower lip is thick, as if swollen, and the upper lip is thin and undeveloped. The image is angry, dissatisfied and gloomy.
- Another sign is posture. The maxillotemporal joint is directly connected to the spinal column. Imbalance of the body when standing or raising arms, as well as visual curvature may indicate pathology. The child's mesial bite shows a slight backward deviation of the figure. If you draw a line from head to toe in the middle, the skull will be tilted and the pelvic bones will be pushed out. The normal correct state does not allow deviation, there is no pronounced asymmetry of parts of the body.
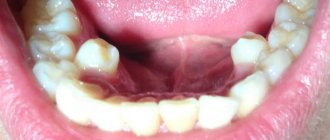
- The last factor in the external examination of an orthodontist is the oral cavity. If the lower incisor occupies the convex position of the upper dental arch, then this is called reverse dental overlap. This fixes the problem of single or multiple progeny. When the dentist notices that the tonsils are rapidly increasing in size and the frenulum looks somehow elongated, then additional diagnostics are necessary to decide how it is possible to correct the mesial bite.
If the doctor determines the situation of primary or adult malocclusion, then he gives a referral for other orthodontic procedures, namely:
- Cone-beam 3D computed tomography of the skull provides the specialist with an accurate idea of the anatomical location of the jaw and the condition of the temporomygomatic joint. Based on the results of the data obtained, an implantation plan is drawn up, and the feasibility of using surgical techniques is studied.
- Determination of the closure relationship and position of the lateral molars using casts.
- A detailed photo of the anatomy of the head is taken to formulate a therapeutic program and subsequently monitor positive dynamics.
- Electromyography of the cervical and facial muscles to identify their dysfunction.
- X-rays reveal previous injuries and bone pathology disorders.
- The use of an orthopantomograph allows you to study the structure of teeth.
Sometimes, research involves a neurologist, otolaryngologist, speech therapist, physiotherapist, ophthalmologist or surgeon. This is necessary to clarify the complete etymological picture.
Classification of mesial occlusion
Progeny is of the following types:
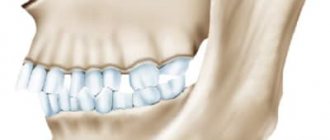
- True. With this type of bite, an increase in most parameters of the lower jaw is observed. The pathology is characterized by severe symptoms and an overdeveloped lower jaw. This mesial bite is facilitated by a genetic factor and problems with bearing a fetus. The pathology of this form is noticeable from early childhood, so treatment should begin at the age of 3-4 years.
- False. The mesial bite of this type is characterized by normal dimensions of the lower jaw. Pathology is formed as a result of underdevelopment of the upper jaw or its incorrect position. It can also be caused by chronic ENT diseases, problems with nasal breathing, early change of teeth, short frenulum of the tongue. Also associated with a false mesial bite is the habit of thumb sucking or prolonged pacifier sucking.
- Combined. Combines signs of true and false progeny. Such malocclusion requires a long period of treatment. It is compiled individually, most often requiring both surgical intervention and the subsequent use of orthodontic structures.
Each of the listed abnormal bites can be of three degrees of severity. They are determined by the size of the gap that is formed between the incisors of both jaws and the angle of the lower jaw.
Retention period
Like any orthodontic treatment, correction of mesial occlusion requires retention, that is, consolidation of the result. To prevent the teeth from moving apart, a permanent retainer is installed on the back of them, which is a thin and almost invisible wire. Removable mouthguards or bite formers, which can be worn at night or worn during the day, help keep the jaws in the correct position. After creating the correct closure, it is also necessary to improve the functioning of the muscles - for this, patients are prescribed a course of gymnastic exercises.
Forms of mesial occlusion
When diagnosing malocclusions, three main forms are distinguished: dentoalveolar, gnathic (skeletal), and mixed. The first includes progeny, characterized by incorrect position of the teeth. For therapy, you can use a brace system. The second type of abnormal bites is accompanied by a violation of the size of the jaw bones. This is a complex form that often requires surgery to treat. With a mesial occlusion of a mixed form, a combination of skeletal and dentoalveolar signs is observed - abnormal jaw sizes and incorrectly formed dentition.
Preparing for surgery
After a comprehensive examination of the whole body for the presence of contraindications, the oral cavity, and the structure of the skull bones, the doctor begins the preparatory period for the operation:
- Using casts of the jaw, a model is made using high-tech equipment, which will be a sketch of the postoperative jaw apparatus.
- The orthodontist prepares the teeth for surgery by installing braces to pre-align them. This stage is the longest and takes from six months to 1.5 years (possibly longer in the presence of a serious anomaly). While wearing braces, it is important to follow the recommendations of doctors and visit regularly to adjust the braces and evaluate the current result of treatment.
The clinic has the latest equipment, which allows us to conduct any examination of teeth and jaw bones, thanks to which the diagnostic accuracy is at the highest level. And, as you know, a correct diagnosis is half the success of treatment.
Symptoms of mesial occlusion
The most clearly degenerate sign of malocclusion is a strongly protruded jaw. Symptoms can be facial and intraoral and are associated with the following disorders:
- gaping of the mouth;
- angry face in profile;
- chin pushed forward;
- development of speech defects, problems with chewing;
- in some cases, dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint develops;
- reverse incisal overlap;
development of periodontal disease due to improper distribution of load on the teeth.
If, due to an incorrect bite, the teeth have a twisted position, gingivitis, caries, and tartar can form. The patient has a violation of chewing function, and difficulties with prosthetics arise. Also, with mesial occlusion, a characteristic clicking of the jaw often occurs during meals.
Complications without treatment
In case of malocclusion, treatment is always necessary, since the pathology is not only accompanied by cosmetic defects, but can also cause various complications, which include:
- improper chewing load leads to rapid wear of tooth enamel, which causes increased sensitivity and the risk of premature loss;
- development of periodontal disease against the background of increased periodontal wear;
- problems with the digestive system due to poorly chewed food;
- underdevelopment of individual facial muscles and the appearance of painful sensations in them;
- premature tooth loss;
- difficulties associated with treatment - prosthetics and implantation.
Also, with an abnormal bite, problems with diction, jaw joints, and the rapid occurrence of infections in the oral cavity may occur. With timely and proper treatment, such complications can be completely eliminated.
Treatment of mesial occlusion
Before you begin to correct mesial progeny, it is important to correctly determine its degree and shape. The specifics of treatment also depend on the age of the patient. In children, bite correction is carried out according to a scheme that differs from the method used for adults. Their correction process takes less time. If you or your child is experiencing mesial malocclusion, contact iOrtho Clinic. The clinic uses innovative Invisalign aligners to cope with malocclusions.
Methods of treating pathology in adults
Correction of incorrect jaw position in adults is performed in a comprehensive manner. The most commonly used braces are systems that can be used to change the position of teeth. For severe mesial malocclusion, braces are used in combination with other treatment methods or as a final stage. An alternative to braces can be veneers or aligners.
Also, as a method of correcting a forward jaw, myogymnastics is used, which consists of a set of therapeutic and preventive exercises. They are performed to correct disorders of the dental system. This method is used in adults in combination with other treatment options, and in children it can be used as an independent method when it comes to correcting a primary malocclusion.
As practice shows, mesial occlusion often requires surgical intervention, which involves increasing or decreasing the area of the lower jaw bone. After its completion, rehabilitation is required for a month, compliance with the rules established by a specialist. After surgery, the patient is required to wear braces.
Methods for correcting bites in children
If a child has a mesial bite, the cause of its development must be determined. If the pathology is not congenital, it can be corrected by straightening the length of baby teeth. In other cases, the use of the following orthodontic structures is required:
- double-jaw devices - removable structures that consist of upper and lower plates connected by wires or base material;
- Dilyar's face mask is a device consisting of a metal frame, two supporting pads of soft material, a transverse frame and palatal beams that provide fixation of the jaw;
- twin-block - a device with two removable orthodontic plates, which allows you to change the relationship of the jaws and the shape of the dental arches;
- extraoral devices – tight pressure bandage on the upper lip, face arches, chin sling;
- cervical traction is a type of face bow that affects the dentition.
For malocclusion in children, surgical intervention is extremely rarely required.
Features of surgery to correct incorrect mesial occlusion
The operation is performed on the lower jaw, changing its position in relation to the upper jaw and changing its size by removing or growing part of the bone.
The surgical intervention takes place under general anesthesia, after which the patient remains under observation in the hospital for some time.
Rehabilitation takes from 1 to 3 months, and a person can return to normal life activities (work, study, etc.) within two weeks after the operation, but with some restrictions regarding physical activity and food intake.
After surgery, the orthodontist recommends wearing a special corrective orthodontic system (braces or aligners) to create the optimal position of the teeth.
Prognosis and prevention
The most effective results in correcting malocclusion are achieved during the mixed or primary dentition. If you choose the right treatment method, it is possible to achieve high-quality jaw alignment in adulthood, but it will take more time.
The formation of the bite in infancy plays an important role. It is important to monitor the correctness of breastfeeding, the position of the child during sleep, and prevent the formation of bad oral habits. Timely treatment of disorders that slow down or impair the growth of jaw bones and dental correction is also required.
How to prevent jaw closure anomalies?
Measures to prevent the problem apply especially to children with “risky” heredity. If at least one of the parents has such an anomaly, the following measures must be taken from birth:
- prevent infants from prolonged sucking of thumbs, toys and other objects;
- in preschool and primary school age, eradicate the habit of chewing a pencil or pen;
- monitor the child’s posture;
- strictly monitor the specifics of breathing. Healthy breathing is nasal breathing. If the child is mouth breathing, this is a warning sign of a developing problem that the occlusion may be compromised;
- in children of the first year of life, it is necessary to prevent rickets by taking vitamin D;
- ensure the prevention of carious lesions in primary teeth;
- Visit the dentist’s office at least 2 times a year in order to prevent minimal and global dental problems.
If you or your relatives experience the listed symptoms and manifestations, do not waste your time - contact a trusted orthodontist. The dentist specializes in such dental abnormalities, offers comprehensive treatment, expert advice and assistance from the beginning of treatment until the patient’s actual recovery.