Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Periodontitis is one of the most common diseases of primary teeth. In its course, it has a number of very important differences from the disease of the same name, which affects the permanent teeth of adults. They are explained by anatomical features: in children's teeth, the process of root formation proceeds differently, which causes differences in the thickness and structure of the periodontium.
The constant change of dental tissues in childhood provokes the frequent development of inflammatory processes, and the unformed slit-like space leaves the periodontium unprotected.
Thinner enamel than in permanent teeth also plays a role in increasing the percentage of this disease among children. It causes the rapid development of caries and its incredibly rapid transition to pulpitis and periodontitis.
Among baby teeth, molars and, in very rare cases, incisors are susceptible to this disease.
How does periodontitis manifest?
If the child is already old, he usually tells his parents that his health has changed, pain and other unpleasant symptoms have appeared. And in order to identify inflammation in babies, attentive parents should pay attention to the following signs:
- the child loses his appetite, any meal, especially hot food, causes pain;
- the baby’s health condition deteriorates, he becomes lethargic;
- the child does not sleep well because unpleasant sensations torment him at night;
- Body temperature may rise to 38–39 °C;
- in some cases, the pain becomes throbbing, which indicates the accumulation of pus and requires immediate help.
However, it should be noted that sometimes the symptoms are unmanifested and hidden.
Prevention methods
Periodontitis, like most dental diseases, can be prevented by following generally accepted recommendations:
- caring for the baby’s health begins from the first days of pregnancy - the expectant mother must take care of her balanced, high-calorie diet, compensating for the lack of nutrients with vitamin and mineral complexes;
- carry out hygiene measures from the first weeks of a child’s life: you need to clean the oral cavity even before teething;
- after the first crowns appear, you need to choose a suitable baby paste and brush: the first should be with a high fluoride content and a low level of abrasiveness, and the second should have the correct head shape and soft bristles;
- accustom the baby to proper hygiene: constantly explain to the baby the importance of brushing his teeth, teach him to use a toothbrush and toothpaste first, and as he grows up - rinses and flosses;
- create a culture of proper nutrition: the child’s diet should be balanced, high in protein, calcium, fluorine, vitamins C and group B, sweets should be given in moderation, if possible replacing with healthy treats (dried fruits, candied fruits, honey, nuts, fruits and berries, curd desserts);
- Carry out regular dental examinations with x-ray diagnostics: due to the constantly changing periodontal disease, children should visit the doctor more often than adults - every 3-4 months.
Periodontitis in a child is more dangerous than it seems. If left untreated in time, the disease can lead to severe complications that affect the formation of a permanent bite and the health of the entire body. But even with timely diagnosis, there is a risk of unsuccessful therapy and serious consequences. Therefore, the key attention is paid to prevention.
Why does periodontitis develop?
The causes of periodontitis include:
- complications caused by the lack of timely treatment of caries;
- lack or overdose of medications that mummify the pulp;
- inadequate treatment of pulpitis;
- allergic reactions to drugs used in dental correction;
- gum injuries during caries treatment;
- malocclusion, causing mechanical overload of the teeth and microtraumatization of the apical part of the periodontium;
- dental injury due to falls, impacts;
- spread of infection by hematogenous or lymphogenous route in the presence of distant chronic foci in the body.
Diagnostics
The acute form of periodontitis is often detected at a doctor’s appointment and in rare cases requires detailed diagnosis. The chronic form of the disease in children occurs in several stages, including hardware tests.
Signs of periodontitis upon examination:
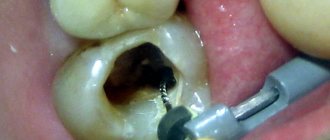
- the crown has a carious cavity;
- darkened tooth enamel;
- if there is a seal, its partial destruction;
- dull sound when tapped;
- no pain on percussion;
- The gums are swollen and red.
In advanced cases, there may be a fistula with discharged fluid, but the formation is not always present.
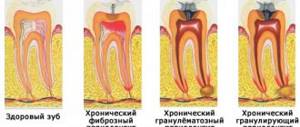
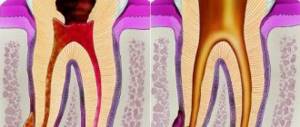
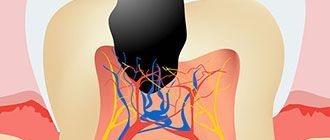
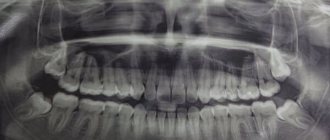
Additionally, an X-ray of the tooth is performed to clarify the clinical picture. The dentist can evaluate the condition of the periodontium from the image. With granulating periodontitis, the lesion of the bone tissue and cortical plate is clearly identified. The affected area always has a clear oval or round shape. In the fibrous form, a clear sign is considered to be expansion of the target in the apical region.
How does periodontitis occur in childhood and adolescence?
The main cause of inflammation is pathogenic bacteria. They cause destruction of enamel and affect the pulp and periodontal ligaments. Often bacteria, affecting almost all structural elements of the periodontium, interfere with the normal development of permanent teeth. In childhood, due to the continuous restructuring of soft connective tissues and the lack of clear anatomical delineation, the pathological process is much more complex than in adults. This is why it is so important to begin treatment for periodontitis as soon as possible in order to save baby or permanent teeth.
Causes of periodontitis in children
Dental periodontitis in children can occur due to a number of reasons:
- as a complication of caries that was not treated;
- as a consequence of improper treatment of caries complicated by pulpitis;
- due to chemical damage to the periodontium using canal sterilization agents;
- due to injuries to soft tissues and teeth during falls or accidents.
What is periodontitis like?
- Based on the localization of inflammation, apical and marginal periodontitis is distinguished. In the first case, the disease affects the periodontium in contact with the apex of the tooth. In the second, periodontal fibers covering the dental neck are affected.
- According to the course of the disease, there are acute and chronic periodontitis. In the first case, the child may complain of pain in the gum area (this is a consequence of serous or purulent inflammation). Chronic periodontitis often develops from an acute form, but sometimes it still forms against the background of chronic pulpitis.
- Depending on the type of lesion, periodontitis occurs in primary or permanent teeth. In the first case, the disease quickly moves from the serous to the purulent form and becomes the cause of the development of severe complications (abscess, sepsis, osteomyelitis). In such a situation, the child complains of constant pain, which intensifies when pressing on the tooth, and swelling develops in the gum area. In addition, body temperature rises, weakness, nausea, vomiting appear, and regional lymph nodes become enlarged. Chronic periodontitis is characterized by a more sluggish course with periods of exacerbations. If the disease develops in a granulating form, a fistula may appear on the mucous membrane of the gums, in the cheek area or under the lower jaw. The child feels weak, drowsy, and gets tired quickly.
Features of the treatment of periodontitis in primary teeth
Before proceeding directly to treatment, the doctor will definitely send the baby for an x-ray. Only by using it can one confirm the diagnosis and see the true picture of the course of the disease.
Based on X-ray data, the dentist decides whether to preserve the tooth. The balance may tip towards removal in cases where:
- there is severe damage to the root;
- tooth mobility is noted;
- the approach of permanent teeth is noticeable.
In all other situations, doctors try to do everything possible to save the tooth.
The choice of methods and means of treatment largely depends on how extensive the inflammation is, how many teeth it affects, as well as on the general health of the child. If the body is severely intoxicated, the tooth is removed at any age of the child, regardless of any additional factors.
If the doctor decides to leave the tooth, then its treatment is in many ways similar to that recommended for permanent teeth. The only difference is the use of special medications. It is especially important to choose the filling material correctly.
In the acute stage of the disease, the best treatment for baby teeth is a special paste that can dissolve over time without harming the baby’s health. In addition, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed and bed rest is prescribed.
When the symptoms characteristic of the acute form subside, they move on to the treatment regimen characteristic of chronic periodontitis. It includes:
- thorough removal of infected tissues and decay products;
- antiseptic treatment of root canals and tooth cavity;
- filling with paste;
- installation of a permanent filling.
During the treatment process, which requires several visits to the clinic, the doctor constantly monitors the patient’s general condition and changes in symptoms. In cases where there is no improvement, the tooth is usually removed to avoid complications.
If periodontal inflammation provokes the development of purulent periostitis, surgical intervention becomes necessary. In this case, the gum is cut in order to ensure the free outflow of purulent and serous masses. The tooth is left in this form for up to 10 days.
The effectiveness of treatment is largely influenced by the professionalism of the dentist. The doctor must know the subtleties of the structure of baby teeth and have the skills to work with them, and also have the ability to win over the baby, ensuring the patient’s psychological state is favorable for work.
Treatment
Treatment of acute periodontitis is carried out in accordance with the location and type of damage to the soft tissue of the gums. In some cases, young children with periodontitis in primary teeth may require general anesthesia. However, the final decision remains with the attending physician. To avoid further complications, baby teeth are usually not removed. Exceptions are possible in the case of resorption (resorption) of roots by 2/3 or more, the development of chronic granulating osteitis and a high risk of spreading infection. At the first visit, young patients are prescribed systemic antibacterial therapy. Treatment of periodontitis in permanent teeth is carried out taking into account the degree of maturity of the tooth root. Conservative dental correction can be carried out in one or several visits. During treatment, the cavity and vault of the pulp chamber are prepared and necrotic tissue is carefully removed from the coronal part and root canals. After treatment, special medicinal mixtures are placed into teeth with multi-root canals, and only after they are removed and re-cleaned, a filling is installed. Single-root canals are filled immediately.
Surgical intervention
Surgery for periodontitis in children is performed in the following cases:
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- spread of infection to the permanent tooth germ;
- The baby tooth will soon fall out (the root is being reabsorbed).
Surgery is also necessary if an abscess has formed. Then it is opened and the cavity is cleaned. Most manipulations are performed under anesthesia, which is completely safe and does not harm the child. However, parents should warn the doctor if the baby has a history of allergies, chronic systemic illnesses, or central nervous system diseases.
Preventive measures
How to choose a clinic
When choosing a dental center, you should focus not only on the cost of procedures. It is very important to pay attention to the reputation of the institution, the experience of specialists, the ability to immediately undergo the required examination, and the scope of services provided. Children's dental clinic "MARTINKA" offers qualified care for acute and chronic diseases of the oral cavity and many other conditions. Our specialists will carefully conduct the necessary examination, identify indications and possible contraindications, and prescribe treatment. We practice an individual approach and do everything to ensure that your child feels as comfortable and calm as possible. Thanks to the care of our specialists, the baby will not be afraid of the environment or the upcoming procedure. In order to make an appointment with a doctor, just contact our consultants by phone listed in the “Contacts” section.
Preventive measures
To avoid the development of periodontitis in primary teeth, parents should bring their children to the dentist annually for a preventive examination. This will help to promptly identify and eliminate the inflammatory or destructive process that has begun. In addition, you should adhere to the following rules:
- provide the child with proper nutrition - fresh fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, dairy products;
- monitor oral hygiene - brush your teeth regularly; for children under one year of age, parents clean their teeth with gauze wrapped around their finger or with a silicone nozzle;
- strengthening the immune system - long walks in the fresh air, active games, swimming.
You should also protect your baby from facial injuries (use special reins, put special pads on the corners of furniture). All existing chronic diseases should be kept in remission. At the first sign of darkening of the enamel or pain, consult a doctor.
0
Complications
A slight aching pain after treatment is a normal reaction of the body. Normally, it lasts no more than a day. If the pain increases, swelling occurs, or the child’s general condition worsens, go to the doctor.
Perhaps the reason is individual intolerance to antiseptic drugs, which caused irritation of the periodontal tissues. In this case, physiotherapy is performed.
If the x-ray shows that the root filling was installed incorrectly, repeated mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canals is performed. This will neutralize and prevent secondary inflammation.