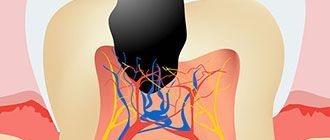
Author: Salatsky Dmitry Nikolaevich Chief physician, orthopedic dentist, gnathologist, maxillofacial prosthetist When treating most dental diseases, doctors do not limit themselves to simply removing the affected necrotic tissue, cleaning out the carious cavity. Very often, the dentist’s task becomes the need to remove the pulp, the neurovascular bundle located inside the tooth, and clean it with further filling of the tooth canals (endodontic treatment). In this case, the dentist must go through all the canals in the tooth without exception, since the anatomical space inside the dental unit remaining uncleaned and unsealed can lead to irreversible consequences due to which it will have to be removed.
When is tooth canal cleaning necessary?
Here are three common cases when a patient is required to have canal cleaning:
- Before installing the prosthesis on the tooth, the unit is depulped and ground down so that a crown can subsequently be installed on it;
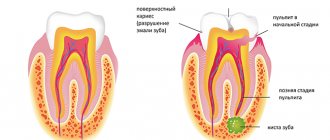
- When diagnosing pulpitis (inflammation of pulp tissue). Usually pulpitis is a consequence of advanced caries and infection. The problem is accompanied by acute pain; it is painful for the patient to chew on the side of the pathological tooth, which indicates severe inflammation inside the tooth;
- If a person has been diagnosed with periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues around the tooth. Usually the problem is a consequence of untreated caries and a dynamically spreading infection.
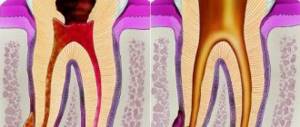
Internal tissues and pulp become inflamed due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. They can also get inside due to mechanical injuries (chipping off a piece of a tooth, splitting a crown due to a blow or fall, tooth dislocation), gum disease.
Note! Pain is not always the only signal to remove the pulp and clean the tubules of dead granules. Very often, cell death occurs without pronounced symptoms, when the tooth stops hurting, and the inflammatory process is already actively developing inside it. A visit to the dentist and a complete examination of the oral cavity will help you understand that there is a purulent-inflammatory process in the tooth.
It is important to thoroughly clean the canals from pulp residues, since pathogenic microflora will still provoke purulent-inflammatory processes. Therefore, it is advisable to remove inflamed tissue not only from the canals, but also from the crown part of the tooth.
In particularly complex and advanced cases, partial pulp resection is prescribed. If the dentist does not consider this method, unfortunately, the tooth is removed.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
Instrument fracture in the root canal
The risk of instrument fracture is very high in case of file deformation (bending, unwinding of turns) and most often occurs when passing and expanding narrow, curved, previously sealed canals (Fig. 8). The main reasons for this complication may be the lack of adequate access to the mouth of the root canal; violation of the sequence of use of endodontic instruments; use of instruments without taking into account indications; non-compliance with operating mode and rotation speed; application of significant force during manual or machine endodontic treatment; metal fatigue caused by repeated use of the tool.
Rice. 8a. Introduction of a curved file.
Rice. 8b. Broken instrument in the root canal.
Prevention of tool breakage consists in strict adherence to the operating mode and use of the tool according to indications. The sequence of use of tools must be taken into account. During machining, the use of endolubricants is recommended.
Incomplete and insufficient obturation of the root canal is mainly due to incorrect determination of the working length, incomplete passage of the canal (Fig. 9), the use of the technique of one gutta-percha or silver pin in canals that have an oval, dumbbell-shaped, slit-like (irregular) shape that does not correspond to the shape of the pin, and also using liquid-mixed paste for filling (using a channel filler). As a result, shrinkage is inevitable, as well as dissolution of the paste some time after filling.
Rice. 9a. Obturation of root canals: high quality.
Rice. 9b. Obturation of root canals: incomplete.
The removal of filling material beyond the apical foramen is often observed after excessive mechanical treatment of the root canal. The result is destruction of the physiological apical constriction. It can also be disrupted due to a chronic inflammatory process in the tissues of the apical periodontium. In addition, there is a real possibility of removing material beyond the apex when using a machine channel filler. The risk of complications increases sharply when filling a root canal without taking into account the working length (Fig. 10).
Rice. 10. Removal of a significant volume of sealer beyond the apex.
The removal of the filling material beyond the apical foramen is observed in the case of using a large amount of sealer, as well as as a result of excess pressure during the condensation of the filling material in the root canal.
Pushing the gutta-percha pin beyond the apex may be a consequence of incorrect determination of the working length and/or incorrect selection of the size of the main pin (Fig. 11).
Rice. 11. Removing the gutta-percha pin beyond the root apex.
Removal of gutta-percha beyond the root apex is possible during the process of lateral condensation of gutta-percha (Fig. 12).
Rice. 12. Lateral condensation of pins.
Preventive measures: control of working length at all stages of endodontic treatment; competent formation of the root canal; maintaining the integrity of the anatomical (physiological) narrowing.
If removing a small amount of sealer beyond the apical foramen may not cause problems, since it is quickly resorbed, then gutta-percha removed beyond the apex, which itself is biologically inert, can maintain inflammation in the apical periodontal tissues for a long time, being a mechanical irritant.
Longitudinal root is possible during the process of lateral condensation of gutta-percha pins and is a consequence of excessive thinning of the walls of the root canal during mechanical treatment. In addition, a longitudinal root fracture can be observed with strong lateral pressure on the sprider during the condensation of gutta-percha pins.
Prevention measures include assessing the condition of the hard tissues of the tooth root, their thickness, as well as improving manual skills and applying adequate efforts in the process of condensation of gutta-percha pins.
Preparing for channel cleaning
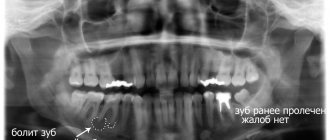
To assess the condition and structure of the root system, the patient is prescribed a preliminary diagnosis:
- CT scan;
- radiography;
- radiography;
After this, the dentist chooses a cleaning tactic and a special tool for the job.
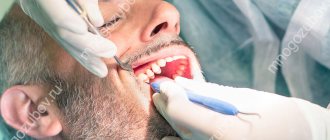
Before opening the coronal part, local anesthesia is administered, since in a state of inflammation, internal structures can provoke acute pain. In this case, the dentist administers the anesthetic using the following methods:
- point or infiltration, that is, when injections are made into the projection of the apexes. An injection into the cancellous bone using the same infiltration method will also numb the area well;
- The conduction technique involves anesthesia of the nerve branch that surrounds the neighboring units. Anesthesia also affects some of the soft tissues, so after the injection and treatment, the patient may continue to experience unpleasant sensations in the immobilized part of the mouth for a long time.
Symptoms of periodontitis
It is impossible not to notice the symptoms of periodontitis. These include:
- The occurrence of severe pain that is constant;
- The appearance of painful sensations when chewing or touching;
- A clear feeling of which tooth hurts, with a feeling of bursting from the inside;
- Discharge of a small amount of fluid from under the tooth, accumulation of pus in the gums;
- The pain may be throbbing and radiate to the temporal or ear region;
- Bad breath;
- Visible swelling and redness of the gums.
Will root canal cleaning save a tooth that is more than 50% destroyed?
Yes, quite, but instead of installing a composite filling, it is recommended to install a microprosthesis or a ceramic crown. The only difference is in the final stage of the operation.
Clinical case: the patient was diagnosed with advanced caries, which developed into pulpitis. The tooth is badly damaged, but the root is intact. The dentist removes necrotic tissue, qualitatively treats the canal passages, cleans them under a microscope, and then places a microprosthesis or a full-fledged crown.
Treatment of acute periodontitis
Any form of the disease requires immediate treatment. Surgical treatment of acute periodontitis involves opening the tooth for free access to the canals and mechanical cleaning using local anesthesia. It is also necessary to treat the canals with an antiseptic or administer antibiotics if necessary. Several treatment sessions may be required, during which the tooth is either left open or covered with a temporary filling. After the inflammation and pain are eliminated, a permanent filling is installed, after which an x-ray must be taken.
In some cases, periodontitis is treated surgically. If the nerve becomes inflamed, it must be removed. After completing treatment, it is useful to rinse your teeth with a soda solution for some time. Unpleasant sensations may occur for several weeks after treatment. But soon they will pass. If no repeated problems arise within six months, we can assume that the disease has been eliminated. Thanks to modern medicine, relapses of the disease occur in only 15% of cases.
The effect of treatment is short-lived
Wrong. Although nothing can completely replace a healthy tooth, quality root canal treatment followed by a suitable filling or crown can be very successful. In approximately 85% of cases, the effect of treatment is lifelong.
If a tooth becomes affected again several years after root canal treatment, it often needs to be re-treated. However, in some situations, such as a crack in the tooth, very severe tooth root decay, or severe loss of bone around the tooth, the dentist has no choice but to remove the affected tooth.
Need to take painkillers
Right. Relatively, this is true. The pain experienced after root canal treatment is usually caused by inflammation around the tooth and may only last for a limited period of time. This process can be successfully managed with the help of common anti-inflammatory drugs: ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), acetaminophen (Tylenol).
If severe pain continues for several months after the procedures, you should consult a dentist or endodontist to avoid possible complications.
Causes
The causes of this disease can be divided into three etymological groups: traumatic, infectious and allergic. The main factors contributing to the occurrence of periodontitis are as follows:
- Acute or chronic inflammation of the dental pulp;
- Residual root pulpitis;
- Pulp damage of gangrenous type;
- Damage to the periodontium due to pushing of the filling material during filling;
- Periodontal damage due to dental canal treatment;
- Spread of infection from the affected canals to the periodontium;
- Infection enters the periodontium through the blood and lymphatic routes;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth due to maxillofacial trauma;
- Allergy of periodontal tissues to medications or toxins that arise in areas of inflammation of the oral cavity;
- Malocclusion.
Mild but prolonged pain after treatment is normal
Wrong. It is not normal to experience constant pain for up to several months after root canal treatment. Causes of pain include hidden canals that were not cleaned during the procedure, or a crack in the tooth.
In these rare cases where pain persists, patients should be referred to an endodontist who specializes in root canal treatment for a diagnosis and appropriate treatment. In cases where the root or tooth is destroyed and no treatment method is suitable, the dentist has no choice but to remove the tooth.
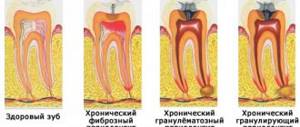
Treatment of chronic periodontitis
Before starting treatment for chronic periodontitis, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination of the patient. To do this, probe and x-ray of the affected area of the jaw are performed. Based on the results, an effective treatment method is prescribed.
Periodontitis is treated in two ways.
- Treatment of the disease with a therapeutic method involves the use of antibacterial medications that have a wide spectrum of action, localize inflammation and relieve symptoms. Periodontal canals inside the tooth are treated with antiseptics, and general strengthening drugs are also used to accelerate tissue regeneration. It is also possible to use laser processing. Treatment lasts up to six months. The dynamics are monitored using x-rays.
- The surgical method is used if therapeutic treatment does not produce the desired results. It consists of removing the affected tissue, resection of the apex of the tooth, or its complete removal. If there is a large amount of pus, installation of elastic drainage is required. After the procedure, the patient must take medications prescribed by the doctor to avoid infection and to accelerate tissue regeneration.
Root canal treatment is a very painful procedure.
This is not true. Root canal treatment does not cause pain. In fact, root canal treatment is performed to relieve pain from inflammation of the pulp chamber (where the nerve is located) or a dental abscess. The myth that root canal treatment causes severe pain is becoming a thing of the past. With the use of modern anesthesia methods, this procedure is no more painful than installing a filling.
If there is a serious abscess process, anesthesia may not work, and your doctor will prescribe antibiotics before root canal manipulation. If a root canal is difficult to access, your dentist may refer you to an endodontist, a doctor who specializes in treating dental cavities and root canals.
Root canal treatment is expensive
Right. Although root canal treatment is expensive, it allows you to preserve the tooth, as well as its functionality and chewing functions. If you have a root canal and install a crown on the tooth, the cost of treatment will be less than if you remove the tooth and replace it with a bridge or dental implant.
The cost of treatment will depend on how many root canals the tooth has, whether it is the first time it has been treated, and on the qualifications of the dentist (general dentist or specialist).
How long can you walk without a filling and what to do if it falls out?
You need to make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible. This is especially true if the tooth hurts after the filling has fallen out. If you still cannot visit the office, you should follow a number of simple rules before doing so. This will help minimize harm and avoid complications.
- Do not put pressure on the tooth or chew hard foods on it.
- It is better not to chew on a damaged tooth at all.
- The oral cavity can be rinsed with chamomile decoction, soda and saline solutions at a comfortable temperature.
- Be extremely careful when brushing your teeth, do not put a toothpick or other sharp objects into the hole.
During the examination, the dentist will determine the cause of the problem and will be able to eliminate the problem as quickly as possible.
Root canal treatment is a lengthy process that requires several visits to the doctor.
Wrong. Today, root canal treatment can take one to two hours if there are no complications. The number of visits to the dentist often depends on the condition of the tooth and the number of canals in it.
In cases where the damage is severe, your dentist or endodontist may place medication inside the canal to prepare (disinfect) the inside of the tooth and then finish treatment after a few days. But if there are no lesions or complications, all procedures can be performed in one visit.
Teeth that have undergone root canal treatment often require a crown.
Right. Often, teeth undergoing root canal treatment have severe caries or large fillings. A tooth with a large filling is at high risk of destruction. For this reason, your dentist may recommend that you get a post and crown after root canal procedures.
Some dentists place a post and filling on the tooth immediately after the root canal has been treated. Although a post adds more strength than a filling alone, a crown is also recommended to improve strength characteristics.