Dental periodontitis is an inflammation of an infectious nature that occurs at the membrane of the tooth root and affects the tissues of the oral cavity located next to it. Periodontitis is difficult to confuse with other dental diseases, because it has a clear symptom – severe and constantly increasing pain, which cannot be relieved by taking tablets from the pharmacy.
Treatment of periodontitis must be carried out urgently, because you risk not only losing a tooth, but also acquiring complications that are dangerous to the overall health of the body! How periodontitis occurs, what signs will help to identify the disease in a timely manner, how periodontitis is treated in dentistry, at what prices the service is offered in Moscow - we will talk about this in detail in this article.
Causes of dental periodontitis
Various reasons can lead to the appearance and development of dental periodontitis, but in the vast majority of cases the disease appears:
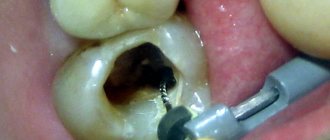
- Against the background of untreated dental caries and pulpitis;
- Due to poor quality treatment of tooth canals, or more precisely, mistakes made when filling the canals.
Less commonly, periodontitis occurs after injuries, incorrectly installed dental fillings, or violation of the dosage of dental medications.
Whatever the cause of periodontitis, its treatment cannot be delayed due to fear of dentists. It is important to understand that you will not stop the inflammation on your own, with pills or folk remedies, and the more it progresses, the less chance you have of saving the tooth. In addition, periodontitis can also affect neighboring healthy teeth.
How to identify periodontitis and not confuse it with caries or pulpitis? We already talked about the most striking symptom of the disease at the very beginning of the article, but the signs of periodontitis may vary depending on the form of the disease. Therefore, below we will consider the main types of dental periodontitis, as well as talk about their characteristic symptoms.
Take a short test and calculate the cost of treatment!
Take a short test
- Which teeth have caries?
- Visual assessment
- Reaction to stimuli
- Cost calculation
×
Manukyan Artavazd Genrikovich
Chief physician of the clinic
Why does periodontitis occur?
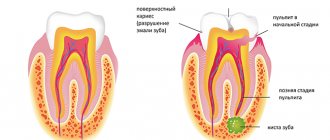
The main cause of periodontitis is a complication of caries or its improper treatment. The disease can also occur against the background of chronic pulpitis. In each case, the infection enters the periodontium through the openings of the root canals. Inflammation progresses and suppuration forms.
Over time, the disease leads to the destruction of periodontal tissues near the root apex. The ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth in the alveolus can no longer perform its functions. This means that the crown gradually loosens, causing discomfort when chewing solid food.
Local factors contributing to the development of inflammation:
- poor oral hygiene, accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- mechanical damage to the tooth;
- gross mistakes by the doctor during complex dental procedures;
- bad habits.
Common factors include various chronic ailments (diabetes mellitus, hormonal imbalances, diseases of the cardiovascular system). Doctors count about 30 somatic diseases that can cause periodontal inflammation.
Signs of acute periodontitis
Symptoms of acute periodontitis are always pronounced. Among them:
- Acute aching pain, the intensity of which is constantly increasing;
- Pain increases when trying to eat;
- If treatment for periodontitis was not started on time, attacks of pain will appear more and more often, and the intervals between them will become shorter and shorter;
Against the background of intense pain, a person cannot eat, speak, sleep, and may develop an elevated temperature. In the acute form of periodontitis, significant tumors and swelling often appear in the area of the diseased tooth. The cheek may also swell. This occurs due to the active accumulation of pus in the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
Professional dental care from Medline-Service
Our network of clinics provides treatment for dental periodontitis of varying complexity, combining traditional and modern technologies (including laser). We are ready to provide qualified dental care for any form and complexity of the disease. If you are interested in the treatment of acute, fibrous or other periodontitis in Moscow, make an appointment with us by phone or using online services.
Reviews
We took my mother to this clinic. She’s doing great with us, she goes to the dentist regularly, but her gums were repaired in a regular clinic. They said it was age, a chronic problem, and they couldn’t do anything. And we tried to change the clinic to a paid and normal one, and it turned out that it was not at all so hopeless, and it was too early for mom to turn into a completely old woman without teeth.
Sergey
Symptoms of chronic periodontitis
Chronic periodontitis is a very insidious form of the disease, since it can develop completely asymptomatically. It is extremely rare for a person to feel a slight pain when trying to bite something on a sore tooth; sometimes unpleasant sensations appear when consuming hot food and drinks.
Chronic periodontitis of the tooth is diagnosed with an x-ray, which clearly shows the process of bone destruction at the apex of the tooth root. This form of the disease has its own classification, according to which there are: fibrous, granulating and granulomatous periodontitis. With fibrous periodontitis, there is almost no pain, which is why it is most often recognized either in the acute phase or during an examination by a dentist and x-rays.
Treatment of this form of periodontitis is quite simple and is carried out in 1-2 visits to the doctor. Granulomatous chronic periodontitis most often develops asymptomatically, but under the influence of certain external factors it easily turns into an acute form. The disease has its own characteristic symptom, manifested in the formation of granulomas - capsules with pus, which separate tissues affected by inflammation from healthy ones. The treatment process for granulomatous periodontitis is long and complex, it can last for several months and even require surgical intervention!
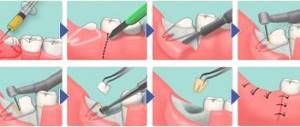
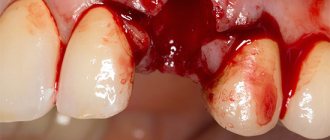
Tooth extraction procedure for periodontitis
An anesthetic injection is administered, which will relieve you of severe pain and allow the surgeon to calmly and correctly perform his work. It is worth paying attention to the choice of anesthesia. Before administering it, it is better to take a test to determine an allergic reaction. It is worth noting modern anesthesia using adrenaline. If your blood pressure is unstable, it is better to avoid this type of pain relief.
After the anesthesia has taken effect, the tooth is removed. If the tooth is multi-rooted, then it is divided into fragments. Next, a thorough inspection of the gums is performed. The hole is treated with an antiseptic, the remains of the tooth roots are removed, the pathological pocket is cleaned and the purulent fluid is completely removed. After the periodontitis tooth extraction procedure, special attention should be paid to food intake. Under no circumstances should there be leftover food in the hole that is still open! Otherwise, this may lead to the formation of a purulent process. In some cases, it is advisable to drain the hole for several days to avoid residual purulent fluid. Until the hole is completely regenerated, it should be periodically treated with an antiseptic.
Periodontitis can be a chronic disease, so if you encounter such a problem and eliminate it once, it is worth visiting your doctor periodically. Since your body may be pathologically predisposed to such a disease.
Category: Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog
How does the acute phase of chronic periodontitis manifest?
When exacerbated, chronic periodontitis of the tooth expresses itself with the same symptoms as the acute form of the disease. That is, there is a strong, aching pain, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek. Typically, chronic periodontitis enters the acute phase when the immune system is weakened, the flu, ARVI, or simply severe hypothermia are present. If, during an exacerbation of the chronic form, a fistula appears in the gum area, pus will flow from the area of inflammation and the pain in the tooth will gradually subside.
But this does not mean that periodontitis has gone away on its own; the inflammatory process will continue to develop and will manifest itself again under favorable external factors, which we discussed just above. Based on the type of periodontitis, a treatment regimen is selected. The price of the service depends on the regimen chosen for treating the disease. We will tell you below about all the stages of treatment of dental periodontitis in different forms and prices for procedures. But no matter in what form periodontitis develops, its treatment always begins with diagnosis.
Diagnosis of periodontitis involves examination of the oral cavity, x-rays, and examination of patient complaints. All this together helps to accurately diagnose the form of periodontitis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
Causes of the disease
Acute or chronic periodontal inflammation can occur for various reasons. Based on its origin, this dental disease can be of the following types:
- infectious. Inflammation occurs as a reaction of the body to damage to connective tissue by pathogenic microorganisms. For example, fusobacteria, streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, spirochetes or fungi. Sources of tooth periodontal infection can be a carious cavity, rhinitis, periodontitis, sinusitis, periostitis;
- traumatic. The cause of acute periodontitis can be a bruise, blow or biting a hard object. It often results from damage to the tooth with instruments during root canal treatment. Also, periodontal inflammation develops from chronic microtrauma caused by an artificial crown or filling;
- medicinal. It occurs under the influence of aggressive chemical components on the peri-apical tissues of the tooth, including drugs used to treat other dental diseases. This can be formaldehyde, iodine, chlorhexidine, phenol, eugenol and other strong substances.
Cost of periodontitis treatment
The price of periodontitis treatment mainly depends on the severity of the specific clinical case, i.e., on the form of the disease. The following factors also play an important role in pricing:
- diagnostic procedures;
- number of roots to be treated;
- chosen treatment strategy;
In any case, the calculation of the cost of activities carried out as part of the treatment of periodontitis at the “Smile” clinic in Moscow is transparent for each patient. We maintain strict control over the pricing of our services.
The doctor will name the approximate cost of treatment for periodontitis only after an initial examination of the patient. You can make an appointment with a dentist by calling the number listed at the top of this page, or by filling out the electronic appointment form on the main page of our website.
Come to our clinic, we can cure periodontitis of any complexity!
Chronic periodontitis and its symptoms
As a rule, after 1 – 2 weeks, acute periodontitis, if left untreated, becomes chronic. It has a specific feature - symptoms are almost completely absent, there is only slight pain when biting. This aggravates the severity of possible consequences due to delayed treatment. Therefore, regular visits to our clinic for preventive examinations are a sure way to protect yourself from possible health problems.
The chronic course of the disease is fraught with frequent exacerbations when a person’s immune status decreases. Even slight hypothermia can cause severe pain in the tooth and swelling of the gums.
Chronic periodontitis is classified into several subtypes depending on the nature of the development of the inflammatory process:
- fibrous – the periodontal gap increases;
- granulating - growths (granulations) of a round shape with unclear boundaries appear in the periodontium;
- granulomatous - the growth that appears (granuloma, which is a sac less than 5 mm filled with pus) has a clear boundary and, increasing in size, develops into a cystogranuloma (5 - 10 mm), and then into a cyst (more than 10 mm) with a growth vector in jaw bone tissue.