What causes dental caries?
Caries is a progressive disease that destroys the hard tissues of the tooth. Cariogenic bacteria live in the oral cavity; they form a biological film on the surface of the teeth - dental plaque. They feed on carbohydrates that enter our bodies through food and drinks. Bacteria process sugars and produce organic acids. Those, in turn, corrode tooth enamel and deep tooth tissues. This is how caries develops.
In this article
- What causes dental caries?
- How does caries progress?
- A dangerous complication of caries is pulpitis.
- How is pulpitis treated?
- Periodontitis as a dangerous consequence of caries
- How is periodontitis treated?
- What is the danger of caries for the gastrointestinal tract?
- ENT diseases as consequences of caries
- Why is caries dangerous for the heart and blood vessels?
- Risk of death from dental caries
- Conclusion
Although bacteria living in the oral cavity play an important role in the development of carious lesions, a complex of unfavorable factors is important for tooth decay:
- an abundance of “fast” carbohydrates in the diet (sweets, flour);
- poor dental and oral hygiene;
- lack of calcium, fluorine, phosphorus, vitamin D in the body;
- weakened immunity.
Reasons for how quickly advanced forms of caries develop
The main reasons for the development of complications due to caries are:
- lack of treatment;
- lack of protein, vitamins, minerals, phosphorus in the body;
- weakened immune system, stressful condition;
- violation of diet;
- past illnesses, including rickets, tuberculosis;
- unfavorable environment.
Complications usually develop within 1-4 years from the moment the first signs of tissue damage appear. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, negative consequences can be avoided. But in a neglected state, tooth decay occurs in just a couple of months, that is, the disease becomes acute. The main signs of the development of the problem are increased sensitivity, increasing pain, and unpleasant odor. In some cases, the lesion is not very noticeable externally, but inside the tissue is almost completely destroyed.
Complicated dental caries leads to the following consequences:
- death of the nerve, dentin darkens, becomes fragile, and quickly collapses;
- penetration of infection into surrounding tissues;
- development of diseases of the mucous membrane, suppression of the immune system, damage to the cardiovascular and other systems.
How does caries progress?
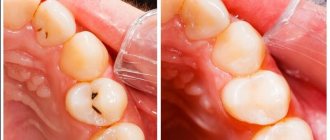
There is a myth that caries is necessarily a hole in the tooth, but in reality, dental disease begins with the loss of mineral substances in the tooth enamel and gradually progresses. Caries goes through four stages in its development. Let's look at them below.
- Spot stage.
There is no hole in the tooth yet, but a whitish spot is noticeable on the surface. A change in the color and structure of the enamel means that it is losing minerals in this area. At an early stage there is no pain or discomfort, so patients rarely go to the dentist, not even suspecting the presence of caries. But it is at the spot stage that caries is easiest to cure. The progression of the disease can be stopped using conservative methods without drilling or installing a filling. At this stage, remineralization, simple and deep fluoridation, and the infiltration method are effective.
- Superficial caries.
At this stage of development of the disease, a small carious cavity forms within the enamel. The patient may have the first complaints: the tooth reacts to cold and hot, sour and sweet, food gets stuck in the resulting hole.
- Average caries.
The carious cavity becomes larger and affects the dentin - the bone tissue of the tooth under the enamel. At this stage, acute toothache most often appears; food stuck in the hole causes severe discomfort, and the patient complains to the dentist. It will not be possible to cure average caries without preparing the tooth, so an operative approach is used in treatment - using a drill, the affected tissue is removed and the cavity is filled with special composite materials.
- Deep caries.
The carious lesion affects the deepest layers of dentin and approaches the dental nerve. All the symptoms that were there before intensify, sometimes becoming chronic. Frequent complications of deep caries are pulpitis and periodontitis (inflammation of the pulp and tissues surrounding the tooth root).
It is better to treat caries in the early stages, while there is no carious cavity in the tooth. Conservative methods will help stop the pathological process without drilling and filling. If a hole has already formed in the tooth, then you cannot do without a drill. What if you don't treat it? Many people have been afraid of dentists since childhood and put off visiting the doctor as much as possible. This should not be done under any circumstances, because caries is dangerous for the body due to its consequences. With an advanced form of the disease, you can lose a tooth or develop purulent inflammation. There are even cases of death from complications of deep caries. Therefore, it is imperative to treat the disease!
Features of treatment. Prevention
The treatment method for complicated caries is as follows:
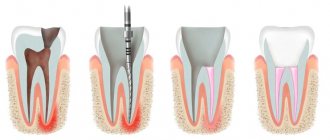
1. Filling a carious cavity . The algorithm of actions is as follows:
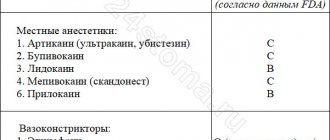
- occlusal points are determined;
- To relieve pain, dental anesthesia is performed (treatment can also be carried out under anesthesia);
- the surface is cleaned of food deposits;
- an insulating system is applied;
- preparation or grinding of teeth is carried out using a drill, which is used for drilling;
- treatment of carious cavity with antiseptics and other drugs;
- application of dental adhesive;
- closing the treated area with a filling or installing a composite material; grinding, polishing surfaces.
When treating pulpitis, the sequence of actions also includes work to remove the nerve (depulpation).
2. Laser treatment of complicated caries - therapy using diode laser radiation, which has high bactericidal properties. Provides the elimination of bacteria and thorough laser treatment of dentin. The main feature of this technique is the minimal amount of pain for the patient.
In order to prevent the development of complicated caries, preventive measures should be taken:
- regular oral care;
- minimal sugar consumption;
- cleaning tooth enamel with fluoride toothpaste;
- compliance with oral cavity cleaning technology;
- using dental floss for minimal cleaning of spaces between teeth;
- rinsing with 0.1 - 0.2% chlorhexidine solution and special rinses;
- using chewing gum containing xylitol;
- fluoridation.
A periodic consultation with a dentist will make it possible to identify the disease at an early stage and eliminate the disease faster, easier and cheaper.
A dangerous complication of caries is pulpitis.
The most common consequence of untreated caries is pulpitis. It occurs when the infection extends beyond the tooth and spreads to the pulp - the neurovascular bundle, or dental nerve.
The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels and provides nutrition to the dental tissues. Therefore, with pulpitis, the tooth may lose vitality. In severe cases, inflammation spreads to neighboring tissues.
A characteristic symptom of pulpitis is acute, prolonged pain that is difficult to tolerate. It often has a pulsating nature and can radiate to the temple, ear, or throat. The peculiarity is that attacks of pain appear at certain intervals, last about 5 minutes, and can intensify when lying down. It is necessary to begin treatment of pulpitis as quickly as possible.
Spread of caries
The disease has been known since ancient times. Archaeological excavations of ancient settlements have confirmed that people have long suffered from such pathology. The growth of the disease was noted at the end of the 18th century and continues to this day. It is noted that in some regions of the globe the prevalence rate reaches 97%, especially in Asia and Africa.
A number of factors have been cited as the reason for this phenomenon. This is primarily due to the nature of the diet, or more precisely, to the excess of carbohydrates in food or its lack. They also pay attention to the quality of drinking water, or more precisely, to the content of useful microelements and fluorine in it. Social problems also play a role in the spread of caries - some social groups simply do not have the financial opportunity to visit a professional dentist for timely detection of the development of the disease and treatment.
How is pulpitis treated?
Pulpitis can be treated biologically or surgically. The first is applicable if the disease is in its early stages. The dentist strives to preserve the pulp by eliminating only the inflammation. If possible, pulpitis of primary teeth is treated using a biological method, when it is especially important to preserve the tooth root. Treatment is carried out in several stages. First, the dentist prepares the carious cavity, opening it as wide as possible. Then he treats it with an antiseptic, puts a swab with an antibacterial agent and covers the tooth with a bandage. During the next appointment, if the patient has no complaints, the cavity is treated with medication, filled with a special composition that stimulates dentin production, and a temporary filling is placed for a period of 5 to 7 days. During the third appointment, the dental crown is filled.
When the biological method of treating pulpitis is ineffective, surgical treatment is used. In this case, the inflamed neurovascular bundle is removed completely or partially. Without a nerve, a tooth becomes unviable and its service life is reduced.
Surgical treatment is performed with local anesthesia. First, the carious cavity is prepared, the pulp is removed, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic, medication is injected, and first the root canals are filled, and then the dental crown. As with the biological method, surgical treatment is carried out over several visits to the dentist.
If pulpitis is not treated, it will progress and can lead to very serious complications:
- flux - inflammatory process in the periosteum;
- periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth;
- pulp necrosis - death of its cells;
- sepsis is a blood infection that can develop when an infection enters the bloodstream.
You can avoid such complications if you do not delay your visit to the dentist and begin treatment for the disease at the first symptoms.
Classification
In practice, as a rule, a depth classification of caries is used, that is, the disease is divided according to the depth of damage to the hard tissues of the tooth. At the same time, it is also divided according to the degree of complication - without it or with its presence. Complicated caries may include a number of associated problems, for example, periodontitis or pulpitis.
Uncomplicated caries is usually classified according to the depth of penetration of the pathology. So, the first stage of the disease is a spot - a visually observed darkening of the enamel due to demineralization of a local area. There is also a softening of this spot and loss of smoothness of the enamel. As for pain, at this stage they are absent, which may cause the development of the problem to be ignored. People think that if there is no pain, then there are no pathological phenomena, but this is a big mistake.
The next stage, superficial caries, is manifested by the development of spot surface roughness and pigmentation. Characteristic signs of this stage are the appearance of pain from being too hot or too cold. Treatment at this stage most often involves filling the affected area.
Average caries develops against the background of neglect of the previous stage of the disease. There is damage to dentin and the appearance of obsessive pain from irritation factors. The destruction runs deeper.
Deep caries is the last stage of disease classification. This stage is characterized by damage to the peripulpal dentin, so it is extremely important to begin treatment immediately, otherwise a depulpation procedure will be required. The pain at this stage can be quite long and severe. Pain indicates damage to the dental nerve, so do not delay going to the dentist.
Periodontitis as a dangerous consequence of caries
Against the background of untreated caries and dental pulpitis, the infection penetrates even deeper. As a result, periodontitis develops. This is a disease in which the tissue around the tooth root becomes inflamed - periodontium. Essentially, it is a ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth in the jaw and provides shock absorption. With periodontitis, an abscess may form near the diseased tooth, and in this case, treatment will require opening the tooth and cutting the gum.
Periodontitis can occur in acute and chronic forms. Acute is characterized by a rapidly developing inflammatory process. The tooth darkens, becomes loose, the patient complains of acute pain, inflammation of the cheek may occur, and swelling appears in the area of the affected tissue. In a chronic course, pronounced symptoms may be absent, and pain occurs only during periods of exacerbation. Chronic periodontitis requires long-term complex therapy, which can take several months. The disease greatly weakens the immune defense and generally negatively affects the condition of the body.
Treatment of complicated caries in our clinic
YuliSTOM dentistry offers comprehensive services for the diagnosis and professional treatment of complicated caries. Experienced specialists, professionals in their field, work with each patient. The effectiveness of treatment is ensured through the use of modern equipment, materials and technologies. All procedures are carried out in clinical conditions that are comfortable for the client.
The cost of services depends on the complexity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient. Current prices can be found on our website in the “Prices” sections.
We perform treatment, restoration, prosthetics, implantation, sedation, extraction and other procedures, which result in healthy teeth and a snow-white smile.
How is periodontitis treated?
The approach to treating periodontitis may vary depending on its type, severity, patient history and other factors.
The chronic form of the disease is treated according to the following scheme:
- The area of the diseased tooth is numbed with anesthetics.
- First, the affected tissue and old fillings are removed from the root canal, the tooth is depulped, and, if necessary, the root canal is expanded using dental drills or a microscopic incision.
- At the second stage, the root canal is cleaned and washed with antiseptic solutions. An antibacterial drug is placed into the canal cavity, which relieves the inflammatory process and fights infection.
- The tooth is covered with a temporary filling, and antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
- The patient is sent home, where he must strictly follow all the dentist’s recommendations. The next appointment is usually scheduled after three or four days.
- At the second stage of treatment, a control photograph is taken. If the inflammation is stopped, the dentist removes the temporary filling and medicine from the root canals, rinses the cavities with an antiseptic, and fills the canals with a special composite material. It contains substances that help restore dental tissues and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. This filling of the canals is temporary and is needed in order to completely stop the inflammation and reduce the risk of re-developing periodontitis in the future. It is done for several months, and the tooth is again covered with a temporary filling.
- A few months later, the patient comes for a follow-up appointment with the dentist, where a tooth photograph is taken again to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. If the inflammation has completely stopped, the final stage of treatment begins - replacing temporary fillings with permanent ones and restoring the dental crown with a permanent light-curing filling. After this, the process of treating chronic periodontitis is considered complete.
- Unfortunately, it is not always possible to carry out conservative treatment of this disease. In advanced forms, the dentist is forced to resort to surgical treatment, when part of the root or the entire tooth is removed.
Treatment of periodontitis is long, complex and expensive, and the disease itself is a source of chronic infection, negatively affects the entire body, and weakens the immune system. It is easier and safer to contact the dentist on time and treat early caries. The consequences of an advanced disease are dangerous for the body.
Predisposition
Why absolutely all people have microbes in their mouths, but only some people’s teeth deteriorate - this has always been a mystery to dental specialists. It turned out that the likelihood of the disease is influenced not only by factors of poor nutrition and lack of oral hygiene, but also by a number of specific predispositions.
For example, the very structure of the teeth can be considered as such a factor - caries often occurs in places where plaque accumulates in teeth with flask-shaped fissures (chewing fold on the surface). It is in this place that microbial plaques form. The spaces between teeth also play a role - tight ones collect more food debris and are very difficult to clean.
In addition, the quality of tooth enamel and the quality of the thin film on its surface - pellicles - are important. The structure of the facial skeleton and the dental bite itself are also important.
As for other predisposition factors, experts distinguish among them geographical, gender and age.
The geographical factor, according to experts, is determined by the climatic characteristics of the country of residence. For example, in Russia, the incidence of caries ranges from 60 to 99%, depending on the region. Reasons such as average temperature, amount of precipitation, and mineral content in soil and water play a role here. It has been proven that there is a clear connection between the likelihood of caries in a particular group of people in a particular area and the fluoride content in drinking water. Moreover, even within one region there can be significant differences in the percentage of caries incidence.
The gender factor is quite simply explained - women are more susceptible to caries than men, and the reason for this is usually pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman’s body directs most of its resources to maintain the condition of the unborn child, so cases of dental disease during this period are not uncommon. In addition, according to statistics, women love sweets more than men.
By the way, women are strongly recommended to visit the dentist either before a planned pregnancy or in its first weeks. At this stage, it is possible to easily cure any dental ailment, but in the later stages of bearing a child, surgical intervention may be contraindicated, especially since anesthesia will be used during treatment.
As for the age factor, scientists have proven that after two years of life the likelihood of developing caries increases. Around age 11, there is a 60% chance of developing the disease. The likelihood decreases when you reach approximately 40 years of age.
It would not be amiss to note the professional factor of predisposition. Thus, a person working in hazardous work involving acids and alkalis is exposed to a much greater risk of illness than, say, an office manager. This predisposition factor also cannot be ignored.
What is the danger of caries for the gastrointestinal tract?
Caries and its complications have a harmful effect not only on teeth, but also on other organs and systems of the body. In particular, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - pancreatitis, gastritis, duodenal and stomach ulcers - often occur against the background of dental caries.
The fact is that with caries and any other dental diseases, pathogenic microflora is activated in the oral cavity. Together with food and saliva, it can easily penetrate the esophagus into the stomach and intestines, causing an inflammatory process. As microbes multiply, they crowd out beneficial microorganisms and lead to the development of gastrointestinal diseases. On the other hand, the state of the digestive organs directly depends on the quality of chewing food. Caries negatively affects this function, because with damaged chewing teeth a person cannot efficiently process food to such a state that the gastrointestinal tract can easily absorb and digest it. As a result, there is an excess load on the stomach, intestines, and duodenum, which leads to pathologies of the digestive organs. In addition, poorly chewed food makes it worse for nutrients to be absorbed.
Modern research shows that even deposits on healthy teeth can threaten the health of the stomach and intestines. Thus, the bacteria Helicobacter pylori accumulate in tartar, which contributes to the development of peptic ulcers. Therefore, not only timely treatment of caries, but also its prevention, in particular proper and regular oral hygiene, helps reduce the risk of gastrointestinal diseases.
TMJ dysfunction
Caries and subsequent pulpitis lead to tooth loss, occlusal disorders, problems with chewing, etc. This changes the load on the temporomandibular joint, causing dysfunction. When the TMJ “does not work” correctly, headaches, neck pain, bruxism, ringing and noise in the ears, and disturbances in the movements of the lower jaw may appear. If the dysfunction persists for a long time and worsens, eating disorders may develop against its background (the patient is afraid to eat solid, chewing foods because of pain), sleep disorders, depression, and other disorders.
You have questions?
We will call you back within 30 seconds
+7
Why is caries dangerous for the heart and blood vessels?
When brushing your teeth, there is a risk of injury to your gums. This can happen due to a brush that is too hard, careless use of dental floss, or sensitivity of the gums themselves. One way or another, cariogenic bacteria enter the resulting wounds, which can be carried throughout the body by the bloodstream. If they get into the tissue of the heart, inflammation of its valves may develop - infective endocarditis.
Studies show that with advanced caries, the risk of developing cardiovascular pathologies increases by 70%. When bacteria enter the blood, they settle on the vascular walls next to atherosclerotic plaques. As a result, the plaque begins to actively grow and can clog the vessel, disrupting normal blood flow. The most dangerous consequences can be thrombosis, stroke, heart attack, atherosclerosis.
Prevention of caries
Caries, like any other disease, is easier to prevent than to treat. This type of prevention works effectively, even in adults.
To significantly reduce the likelihood of caries, you need to:
- Carefully monitor daily dental hygiene: brush your teeth twice a day, use dental floss and irrigator.
- Do professional hygiene once every 6-8 months.
- Follow a proper diet: consume less light carbohydrates in sweets and starchy foods, and eat more solid foods, vegetables, fruits, monitor the balance of vitamins and minerals in the body.
- Do not neglect the procedure for remineralization of enamel, especially during periods when the body and tooth enamel are weakened.
- Come for routine preventive examinations to dentists at GALA DENT on Prosvet at least once every six months. By the way, such examinations once every 6 months are free of charge.
Risk of death from dental caries
Many people underestimate the danger of caries, considering this disease to be frivolous. However, there are known cases of death from complications of untreated caries. How is this possible?
For example, if the inflammatory process from the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw spreads to the maxillary sinuses, sinusitis may occur, which can spread greatly without treatment. When the infection extends beyond the jaws, there is a possibility of a brain abscess, purulent inflammation, sepsis - all these complications can be fatal.
Another danger is the so-called pathological fracture of the jaw. This condition is associated with a cyst in the jaw, which occurs as a complication of advanced caries.
All of these dangers are real and can occur against the background of dental caries. But it is important to understand: only an advanced carious process that has not been treated for many months or even years leads to such serious complications. With regular visits to the dentist, timely treatment of caries at the first symptoms, as well as compliance with the rules of dental hygiene and other preventive measures, the risk of serious consequences for the body is almost zero.
Endocrine disorders
With chronic periodontal inflammation, blood sugar levels increase. This provokes prediabetes and, if the patient is not treated, diabetes. The treatment program for diabetes mellitus necessarily includes sanitation of the oral cavity - if the inflammation is not removed, the glucose level will remain high.
Without treatment, caries also provokes other problems: constant pain, insomnia, disruption of the nervous system, loss of appetite, weakened immunity, etc. Dentists at the Dentospas clinic recommend regular examinations by a dentist and performing dental treatment in a timely manner, without waiting for complications and serious consequences.