According to obstetrics statistics, dental caries is the most common pathology of the gestational period (pregnancy period).
Up to 92% of women with a normal clinical pregnancy and up to 95% of women with signs of gestosis (complicated pregnancy) are exposed to caries. Almost 80% of women during the gestational period show signs of hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity of tooth enamel).
It has been noted that caries during pregnancy is diagnosed more often in women who are emotional, do hard work, and do not pay due attention to nutrition and dental hygiene.
Features of diagnosis during pregnancy -
At the very beginning of communication with a pregnant woman, the dentist must collect a thorough medical history, which will allow him to develop dental treatment tactics in order to minimize the risk of adverse effects on the fetus. It is especially important to find out the gestational age, history of previous pregnancies and pregnancy-related diseases - such as diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia. Sometimes an obstetrician-gynecologist is involved to assess the risks.
Can pregnant women have x-rays taken?
During pregnancy, X-ray examinations are not carried out only if during the examination the X-rays pass through or in close proximity to the fetus. In addition, dentistry now uses highly sensitive X-ray films and sensors, which require an 8-10 times lower dose of X-ray radiation than before. Therefore, the use of x-ray examination together with special protective equipment (lead apron) is absolutely safe for the fetus, even if you take several targeted x-rays.
The radiation dose from 1 image taken on a modern radiovisiograph is almost equal to the radiation dose of any person to natural background radiation in 1 day (2-5 μSv). In addition, numerous studies have estimated that the dose to the fetus is only approximately 1/50,000 of the dose that a woman would receive during an X-ray (assuming a standard lead apron was used). In the article at the link above you will find what dosages of radiation a person receives during an X-ray examination of the upper and lower teeth.
Therefore, the only thing you should avoid is regular radiographs, and, probably, the period from 1 to 8 weeks inclusive (the first trimester) is more dangerous than others. Since it is during this period that the fetus is most sensitive to the effects of teratogenic factors. In other words – dental x-rays should not be a cause for concern at this time. This is confirmed by many studies, for example, a British clinical study of a group of 7375 mothers (who had X-rays taken during pregnancy) did not reveal any increased risks to the fetus. And there are a lot of such studies.
Are there any special features of dental treatment for pregnant women?
Before treating caries in pregnant women, the dentist carefully collects a medical history (information about previous pregnancies, concomitant diseases and pathological conditions - such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, preeclampsia, eclampsia). In some cases, consultation with a gynecologist who is caring for the patient’s pregnancy is necessary. Expectant mothers undergo X-rays only when absolutely necessary and only on modern digital equipment with minimal radiation. Particular attention is paid to the selection of anesthetics: they should not be toxic.
Can pregnant women have anesthesia?
There are a large number of clinical studies on the safety of local anesthetics in the treatment and extraction of teeth in pregnant women. In Table No. 1, you can see 5 local anesthetics that can be used in pregnant women according to the FDA (corresponding to safety categories B and C). First of all, these are well-known anesthetics such as, for example, Lidocaine or Ultracaine DS, etc. The table also shows the permitted concentrations of vasoconstrictors.
Table No. 1 –
*according to the FDA (Food and Drug Administration, USA)
It should be noted that the use of a vasoconstrictor (vasoconstrictor component) not only allows you to reduce the dose of the administered anesthetic and increase the duration of its action. The presence of a vasoconstrictor makes it possible to reduce the possible systemic toxic effects of the anesthetic. This occurs due to the fact that the vasoconstrictor slows down the entry of the anesthetic into the bloodstream from the injection site, and therefore allows for a reduction in peak concentrations of the anesthetic in the blood (24stoma.ru).
The safety of the use of vasoconstrictors in pregnant women has been shown in many clinical studies (for example, the study by Haas D. “An update on local anesthetics in dentistry”). It is known that vasoconstrictors do not affect uterine blood flow - provided their dosages and anesthesia technique are observed. It is optimal to use the vasoconstrictor epinephrine at a concentration of 1:200,000, and to minimize the systemic effect of epinephrine in pregnant women, it is important to perform an aspiration test during each injection, because it will guarantee the absence of intravascular administration.
Experts' opinion
The study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic products of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases, carried out in the department of periodontology of the Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery of Rosmedtekhnologii in Moscow, made it possible to prove the effectiveness of many of the products in the line.
Analysis of the results obtained revealed a fairly high effectiveness of Asepta gum balm and Asepta mouth rinse for moderate periodontitis. Gum gel and Asepta rinse also turned out to be effective. In addition, no phenomena of mucosal irritation or brown staining of fillings were recorded. This indicates that the use of this rinse for a two-week period provides an obvious clinical effect in the absence of negative side effects.
Treatment of caries during pregnancy -
Below you will find recommendations on which trimesters of pregnancy certain dental interventions are allowed, as well as which local anesthetics, analgesics and antibiotics can be used in pregnant women (as well as during breastfeeding).
First trimester of pregnancy -
The first trimester is the period from conception to the 14th week. In the first trimester, there are 2 particularly dangerous periods when it is undesirable to carry out dental treatment in pregnant women -
- The most unfavorable period for dental treatment is the period from the moment of fertilization until the implantation of the fertilized egg (approximately the 17th day). This period is characterized by significant sensitivity of the embryo to drugs, toxins, stress... Dental treatment during this period will give a high probability of spontaneous abortion.
- On the 18th day, the formation of organs and tissues in the embryo begins. Clinical features of this period are nausea, vomiting, increased salivation, heartburn, increased gag reflex, and frequent fainting. During this period, it is undesirable to carry out dental treatment for pregnant women, because treatment can lead to disruption of the formation of organs and tissues in the fetus. This period ends at week 8 inclusive.
Conclusions : It is advisable to exclude dental treatment during pregnancy from the moment of fertilization to 8-9 weeks inclusive. An exception can be made only for emergency interventions - in case of acute pain or purulent inflammation. Treatment of pulpitis during pregnancy, acute periodontitis, as well as exacerbations of chronic periodontitis can serve as an example of emergency interventions, because These diseases occur with severe pain and the development of purulent inflammation.
Treatment of caries during pregnancy, chronic pulpitis or chronic periodontitis (i.e. diseases that are not accompanied by acute symptoms of inflammation) is optimally carried out in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. In the 1st trimester, pregnant women can undergo preventive measures - remineralization of teeth or professional teeth cleaning with polishing brushes and paste, but without ultrasonic scaling. It is important to teach a pregnant woman proper oral hygiene.
→ Analgesics and antibiotics for pregnant women
Second trimester of pregnancy -
The second period is called “fetal” because At this time, the fetus is growing rapidly. It lasts from 14 to 28 weeks. The risk of undesirable effects of dental treatment on the fetus in this trimester is considered low, because organogenesis has already been completed.
Conclusions - during this period it is necessary to carry out the prevention of dental diseases (professional hygiene), treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women, as well as treatment of those teeth that have a high risk of exacerbation in the third trimester. If there is no such risk, then it is advisable to postpone treatment to the postpartum period. This decision must be made by the dentist.
Third trimester of pregnancy -
This period lasts from 29 weeks until birth. As fetal weight increases (especially in the supine position), fetal pressure on the aorta and inferior vena cava increases, resulting in decreased cardiac output. This may be accompanied by rapid heartbeat, a sharp decrease in blood pressure, and even loss of consciousness. This is important to consider because... During dental treatment, patients are in a semi-lying position.
In the later stages of the third trimester, the sensitivity of the uterus to external influences increases, which can lead to premature birth. Also during this period, the pregnant woman experiences increasing fatigue and anxiety, which can also complicate the implementation of therapeutic measures.
Conclusions - the first half of the third trimester is considered safe, and the risk to the fetus is not only low, but completely absent.
This period is favorable for dental treatment. In this case, the position of the pregnant woman in the dental chair should be “slightly on the left side”, at an angle of 15 degrees. In this position, the fetal pressure on the aorta and inferior vena cava will be less. But from the second half of the 3rd trimester, only emergency interventions can be performed.
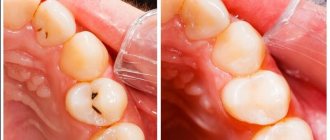
Methods for treating caries in expectant mothers
If the initial stage of caries is identified, treatment is carried out using methods that do not require anesthesia and do not cause discomfort:
- Remineralization - the enamel is covered with gels with a high content of calcium, zinc, and phosphorus. Remineralizing compounds are used not only on areas with signs of early caries, but also on other teeth to strengthen the enamel and prevent the occurrence of caries.
- Fluoridation – a solution is applied to the teeth, saturating the enamel with fluoride ions. The procedure helps strengthen the enamel and increase its resistance to caries.
- Icon technology - the carious spot is treated with an etching gel, after it is washed off and the surface is dried, a liquid Icon filling is applied, which polymerizes under the influence of a special lamp.
For the treatment of medium and deep caries the following is used:
- Mechanical preparation using a drill. Includes: local anesthesia (if necessary), opening the cavity and removing affected tissue, installing a filling.
- Laser treatment – preparation of a carious cavity occurs painlessly and silently; the procedure ensures complete sterility, since it is not the instrument that comes into contact with the tooth tissue, but the laser beam.
Treatment of caries is carried out depending on the stage of pregnancy.
Dental treatment while breastfeeding –
Dental treatment for a nursing mother is not only possible, but necessary. Dental treatment during lactation may be temporarily contraindicated only in certain psychological conditions associated with severe stress and fatigue. However, if the child is breastfed, it is still necessary to observe certain precautions related to the exposure of the child to various medications through breast milk (for example, local anesthetics used for anesthesia).
Chemical compounds from painkillers, anesthetics, antibiotics, etc. can penetrate into breast milk. everything that has penetrated a woman’s blood. You can learn about what medications can be used during breastfeeding from our article:
→ Drugs approved for pregnant and lactating women
Clinical signs
The manifestation (onset) of the disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course. In most cases, pathological processes in the form of formations of light or dark spots on the surface of teeth are discovered by chance during routine examinations.
The main sign of the development of caries with the formation of cavities is increased dental sensitivity to the effects of cold, hot, salty, sweet or sour in the diet.
Symptoms of deep localized caries are manifested by short-term pain in the affected tooth when chewing, pain under the influence of chemical and thermal irritants, which goes away when they are eliminated.
Persistent intense pain indicates deep damage to the internal tissues of the tooth.
Dental treatment during menstruation –
There are no special contraindications for dental treatment on such days. However, if your periods are accompanied by increased nervousness, severe weakness, as well as a severe psycho-emotional state, then it is better to postpone dental treatment to more favorable days. Surgical interventions should also be avoided during this period, because starting 2-3 days before the start of menstruation in women, blood clotting decreases, which can lead to bleeding (for example, after tooth extraction).
Blood clotting indicators are fully restored approximately 2 days after the end of menstruation.
Caries in pregnant women: causes
There is a widespread belief among women that rapid tooth decay during pregnancy is associated with the fetus’ increased need for calcium and phosphorus.
But the increased need for calcium is compensated by the mother’s body not by leaching it from the teeth, but primarily by increasing its absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and reducing its loss in urine and sweat. This mechanism is hormonally determined. But besides this, the body has another mechanism that maintains a constant concentration of calcium in the blood of any person (including pregnant women). Maintaining normal calcium concentrations in the blood occurs due to slow osteoporosis of bone tissue. But the teeth do not suffer, and here's why. The fact is that mineralization of tooth enamel with calcium occurs due to calcium ions contained in saliva, the concentration of which in saliva is strictly tied to the concentration of calcium in the blood. And since, due to osteoporosis of bone tissue, its concentration in the blood is normal (and, accordingly, in saliva too), then the mineralizing function of saliva also does not suffer.
What then stimulates tooth decay in pregnant women?
Firstly, during heartburn and after vomiting, a large amount of gastric juice enters the oral cavity, i.e. hydrochloric acid, which helps wash out calcium from tooth enamel. Therefore, in case of heartburn and after vomiting, first of all you need to rinse your mouth with a soda solution (this will neutralize the acid), and it is not recommended to brush your teeth immediately. Immediately after exposure to acid, the surface layer of tooth enamel becomes porous and can be easily removed with abrasives.
Therefore, after heartburn or vomiting (as well as after drinking wine, fruit or fruit juice), it is recommended to brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush only after 30-40 minutes, using toothpaste with fluoride. Until this point, it is better for you to use a soda rinse, and after it you can immediately use a fluoride rinse. The second very important point is that studies show that 90% of pregnant women have worse oral hygiene (compared to the period before pregnancy).
The third reason is that insufficient hygiene is aggravated by eating disorders, i.e. constant snacking between main meals (anything containing flour, sugar and starch is especially harmful). Naturally, after snacking, people are not accustomed to brushing their teeth at all, and as a result, cariogenic bacteria in the oral cavity receive constant 5-6 meals a day, while constantly producing organic acids that destroy teeth. At the same time, after the next snack, it is absolutely not enough to simply rinse your mouth and chew gum, because... this does not allow removing plaque, as well as food debris that has accumulated between the teeth.
Consumer Reviews
tancha66 about Asepta Fresh mouth rinse
“Today I would like to dedicate my review to a product that helped me solve the problem of bleeding and painful gums, as well as temporarily reduce toothache. We will talk about Asepta parodontal mouth rinse, and its two varieties - fresh and activ.
From time to time I am concerned about the problem of bleeding and inflammation of the gums, increased sensitivity of tooth enamel, and therefore my attention is always attracted to oral care products. And then I had a toothache, and my appointment with the dentist was only 10 days later. While visiting friends, I noticed a cute bottle - Asepta Fresh mouthwash, which they highly praised and recommended. Naturally, the rinse aid was purchased on the same day.
The bottle is made of durable blue plastic and transparent. My volume is 250 ml. The top is screwed on with a white cap, onto which a transparent measuring cap is placed, this is very convenient. The rinse itself is colorless, transparent, with a pleasant aroma and taste of mint (menthol). The mouthwash is intended for daily use...
...Use as you would any mouthwash. After shaking the bottle, pour 10 ml of mouthwash into the measuring cap and rinse your mouth for 20 seconds. I used the mouthwash 2-3 times a day. After just two or three days, the gums practically stopped bleeding, the swelling and pain decreased. But the toothache periodically made itself felt - this is understandable - a simple mouthwash will not help here, and only painkillers helped.
When I went to the pharmacy again, I noticed this box:
This is also Asepta mouth rinse, but not fresh, but activ. I asked to read the summary. It turned out that this rinse is not intended for daily use, but is used in cases where it is necessary to quickly relieve inflammation, reduce pain in diseases of the oral cavity, a kind of first aid. You can use it only for 5-7 days. What caught my attention and made me very happy was the line: the area of application is toothache of infectious origin. I don’t know yet what the origin of my toothache is), but I also immediately bought this mouthwash. A volume of 150 ml costs 240 rubles.
So, Asepta paradontal activ mouth rinse is sold in a nice box, which contains detailed information about the action of the rinse...
...My feelings after using Asepta paradontal activ mouthwash.
I rinsed my mouth for a week, sometimes twice, sometimes three times a day. This bottle just lasted me 7 days, with a little left at the bottom. Rinse as stated in the instructions for 20 seconds. After the procedure, numbness of the tongue and gums is felt in the mouth, which lasts for 15-20 minutes. The freshness of breath after this rinse lasts longer than after using Asept frash. Not immediately, but gradually, the toothache decreased and almost disappeared. But if you take into account how acute it was, I conclude that Asepta paradontal activ mouthwash is very effective and really helps.
Summing up the results of using two varieties of one rinse for two weeks, I want to say that in such a short period of time my problems were solved to one degree or another: gum inflammation went away, painful swelling of the gums disappeared, they stopped bleeding, toothache decreased. I also noticed that the sensitivity of my teeth has decreased, my breath remains fresher longer and the formation of plaque during the day is reduced.
Now in my house there will always be these wonderful products - Asepta fresh mouth rinse for daily use and prevention of oral diseases and Asepta activ mouth rinse - for quickly relieving inflammation in the oral cavity. And, of course, I recommend these products to anyone who experiences any problems with their gums.”
Olga Max about Asepta Plus Remineralization toothpaste (otzovik.com):
“I don’t often see reviews about such an ordinary thing as toothpaste, only if I really liked or didn’t like something.
Now we will talk about Asepta Plus Remineralization, a new toothpaste for me, which I learned about in the vastness of Otzovik. I learned it, remembered it, and at a certain moment this information came in handy.
A brief background, I’ve been using Thai round toothpastes for many years (but it’s not recommended to use them on a regular basis), I like them because they perfectly remove plaque, which ordinary toothpastes can’t cope with, I don’t know why, but in my case it’s like this ... I have tried everything that is on store shelves, from budget options to pastes with an indecently high price tag.
Of course, I find something that suits me, but as a rule, I can’t use the same paste for a long time, because I get used to it and it stops working for me, my teeth are so capricious...
The last time my husband bought some Colgate (for a lot of money), the paste turned out to be a whitening paste, using this, I’m not afraid of this word, sandpaper a couple of times was enough for me... and that’s it, my sensitive enamel rebelled so much that I didn’t know where to run and what do, how and with what to brush your teeth.
After some thought, I went to Ozone to look for a toothpaste, which at a certain moment helped me with a very good, but very expensive toothpaste, but the required product was not on the site and I remembered Asepta, about which I had read good reviews, by a lucky coincidence it turned out to be in a pharmacy nearby with the house and the price, compared to Biorepair Total Protection “Comprehensive protection” is simply ridiculous - 161 rubles, affordable, in principle.
Oh, what a long introduction this turned out to be...(this is always the case when I decide to write a review “quickly”))).
So, back to Asepta. The packaging is standard, there are no innovations here.
Recommended for remineralization (restoration) of tooth enamel and to reduce its sensitivity. Clinical studies have been conducted that have confirmed that the paste delivers on its stated promises by more than 60%.
The composition of the toothpaste is probably not bad, I am not an expert in analyzing the composition of toothpastes, I have enough information from the manufacturer that the paste does not contain sodium lauryl sulfate (it is already excessive in our lives), fluorides and antiseptics...
...The paste itself is bluish-light green in color (I don’t know if this exists in nature))), it seems so to me. Its consistency is a little thinner than standard pastes, so the consumption is a little higher. The aroma is fresh, not strong, like the taste of the pasta. The latter is especially important for me, I can’t stand the thermonuclear, spicy menthol explosion in my mouth... The taste is very harmonious and soft.
The cleansing properties of the paste are excellent, it’s easy to remove plaque from my teeth, the consumption is normal, I’ve been using the paste for about three weeks - I think I’ve spent half of it.
The sensitivity returned to normal after the second use, which I really liked. That is, the manufacturer’s promises are not empty words - the paste works.
Out of curiosity, I went to the Asept website and found a bunch of interesting products for the oral cavity there, I will try it, however.
In the meantime, I am happy to recommend Asepta Plus Remineralization toothpaste.”
Sources:
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on the determination/confirmation of the preventive properties of personal oral hygiene products “ASEPTA PLUS” Remineralization doctor-researcher A.A. Leontyev, head Department of Preventive Dentistry, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor S.B. Ulitovsky First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry
The effect of caries on pregnancy -
Why is caries dangerous during pregnancy? Is it even worth having dental treatment during pregnancy or is it better not to risk it? The answers to these questions are quite simple. For example, with ordinary average caries, the carious cavities contain a large amount of infection, which, against the background of hormonal changes in a woman (excess progesterone and estrogens), creates an increased risk of developing gum inflammation. The second thing to consider is that toothache leads to the release of a number of hormones and changes in hormonal status, which will certainly affect the fetus.
The influence of dental and gum diseases on the fetus -
Untreated caries in a timely manner leads to the development of a complication such as pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve in the tooth). The fact is that when a carious cavity in a tooth becomes too deep, pathogenic bacteria penetrate into the tooth cavity, where the neurovascular bundle (pulp) is located. However, if pulpitis is not treated in a timely manner, the inflamed pulp dies, i.e. necrosis occurs. As a result, pathogenic bacteria penetrate beyond the teeth through root canals and holes at the tops of the roots of the teeth, causing inflammation there. This inflammation is called periodontitis.
In the presence of an acute or chronic source of inflammation at the apex of the tooth root (i.e., periodontitis), bacteria in the site of inflammation produce toxins that are absorbed into the blood. The same thing happens when a pregnant woman has gum inflammation, i.e. for gingivitis and periodontitis. The presence of any of the above inflammatory diseases triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines, prostaglandins (PGE-2) and interleukins (IL-6, IL-8), each of which can negatively affect pregnancy.
For example, in periodontitis, elevated levels of these inflammatory markers and small amounts of bacteria are even found in the amniotic fluid that contains the fetus. In addition, studies have revealed a clear correlation between the presence of dental inflammatory diseases and premature birth (compared to healthy controls). Premature birth, according to researchers, is associated with two factors.
Firstly, it is the release of PGE-2, which limits placental blood flow, causes necrosis of the placenta and, as a result, restricts intrauterine growth. Secondly, with cytokines that promote contraction of the uterus and dilation of the cervical canal. All this data is taken from clinical studies - 1) Dyortbudak O., Eberhardt R. et al. “Periodontitis - a marker of the risk of premature birth during pregnancy”, 2) Goepfert A.R., Jeffko M.K. et al. “The relationship of periodontal diseases with inflammation of the upper genital tract and early premature birth.”
Forms and stages of development of caries
The systematization of various forms of caries is based on certain parameters;
- time of detection of pathology;
- specific histological features of the pathological process;
- location and depth of the lesion.
The clinical picture of the disease in pregnant women can be either primary, diagnosed for the first time, or secondary , as a consequence of continued destruction (destruction) of dental tissue with the formation of carious cavities in previously filled teeth.
According to the severity of damage to dental tissues, various types of caries are distinguished - enamel shell, hard dentin tissue, bone tissue, or caries with a suspended destructive process.
To manage pregnant patients, the tactics of topographic systematization of the destructive process are used. There are several stages of development.
Initial stage of caries
Superficial demineralization of the hard structure of teeth is focal in nature, manifesting itself in the form of spots. The formation of white spots characterizes an active destructive process, brown spots - slow destruction. In treatment, the use of minimally invasive techniques is permissible.
Superficial caries
The process of destruction of tooth tissue does not extend beyond the outer protective enamel shell and does not disrupt the structure of the enamel-dentin junction. At this stage of the disease development, the first clinical symptoms appear. Treatment includes mechanical debridement methods.
Average caries
It is characterized by the formation of carious cavities without signs of deep damage to the hard tissues of the tooth, and a pronounced clinical course. The basis of treatment is the removal of damaged tissue.
Deep stage caries
The destructive carious process spreads to the internal tissues of dentin, accompanied by the development of intense pain. Lack of timely treatment threatens pulp damage with a high probability of developing complications in the form of periodontitis or pulpitis.
During pregnancy, women are characterized by the development of moderate-intensity caries, which is explained by a decrease in immune defense, a pronounced deficiency of essential minerals, and a lack of dental hygiene.
Systemic and multiple formation of carious cavities is rarely diagnosed.