How the disease develops
Chronic tonsillitis is formed as a result of a recurrent course of sore throats involving the palatine tonsils. Initially, inflammation affects only the lacunae and crypts of the tonsils. Over time, the inflammatory process goes beyond the lacunae and spreads to the lymphoid tissue, which makes up the bulk of the tonsils. Subsequently, the chronic inflammatory process is localized only in the tonsil tissue, where microabscesses form. The tonsils themselves enlarge and loosen due to the development of scar connective tissue, which over time replaces most of the lymphoid tissue of the organ. With each new exacerbation, the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis become more intense.
With a complicated course of tonsillitis, infiltrates appear in the peri-almond tissue, more often at its upper pole. If the disease develops negatively, an abscess forms at the site of the inflammatory infiltrate, requiring surgical treatment.
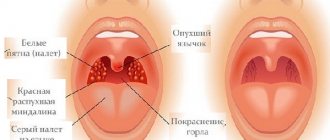
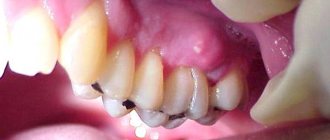
Rice. 2. The photo shows chronic tonsillitis. The tonsils are enlarged, loose, with abundant growth of connective tissue.
Signs and symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis occurs in 2 forms - simple and toxic-allergic of 2 degrees. Angina with the disease recurs up to 3 times a year. Less often - up to 6 times a year. The presence of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils is a reliable sign of tonsillitis, even if it is asymptomatic. Asymptomatic sore throat occurs in 4% of cases.
Concomitant diseases and tonsillitis aggravate each other. In patients suffering from hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, tuberculosis, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, etc., tonsillitis is severe and has complications.
Signs of chronic tonsillitis
The following signs indicate chronic tonsillitis:
- Fusion of the anterior and posterior arches with the tonsil.
- Swelling of the area of the upper angle formed by the arches (Zach's sign).
- Hyperplasia of the upper edges of the arches (B. S. Preobrazhensky sign).
- Hyperemia of the anterior arches (Gise's sign).
- The size of the tonsils depends on the constitutional characteristics of the person, is a variant of the development of the organ, or is a manifestation of an allergic condition. Enlarged (hyperplastic) tonsils promote and maintain the inflammatory process. The surface of the tonsils can be loose or smooth.
- In chronic tonsillitis, the accumulated pus in the lacunae can be liquid or thick. Upon examination, the presence of purulent plugs in the lacunae is noted. Pus in the lacunae causes an unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth, which is an important sign of chronic tonsillitis.
- Enlargement of the cervical and submandibular lymph nodes is an important sign of chronic tonsillitis. This sign becomes especially important in the absence of inflammation in other parts of the head area. Each of the above symptoms may have varying degrees of severity. The disease often occurs against the background of chronic pharyngitis.
The presence of pus in the lacunae and the recurrence of sore throats throughout the year, occurring with symptoms of toxicosis, are reliable signs of chronic tonsillitis, which in themselves are highly reliable.
Rice. 3. The photo shows chronic tonsillitis. The main signs of the disease are evident; pus and purulent plugs are visible in the lacunae.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis. Simple form
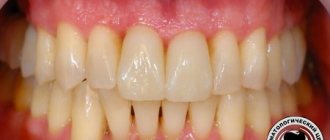
Each of the above symptoms can have varying degrees of severity and are often recorded in chronic tonsillitis. The function of other organs is not impaired. There are no symptoms of intoxication. Treatment is conservative. If pus in the lacunae persists as a result of several courses of treatment, then tonsillectomy is indicated.
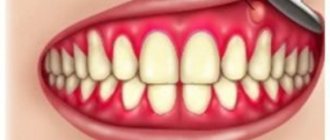
Rice. 4. The photo shows chronic tonsillitis. Pus and purulent plugs in the lacunae are visible. The tonsil on the right is enlarged.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis. Toxic-allergic form
The infectious-allergic background, which is created as a result of frequent exacerbations of chronic tonsillitis, is the trigger for the development of associated diseases: paratonsillitis, parapharyngitis and rheumatism. The human body responds to the introduction of streptococci by producing antibodies, thanks to which they are destroyed. But often antibodies begin to attack structures similar to streptococcus, which are the connective tissue of the heart and joints, as a result of which heart defects and arthritis develop. In addition, streptococcal enzymes themselves have a cardiotoxic effect.
Toxic-allergic form I is characterized by low-grade body temperature, increased fatigue, weakness, pain in the heart and joints, and tachycardia. Symptoms of the disease during periods of exacerbation are pronounced. Outside of exacerbations, all symptoms are absent. ECG changes are transient. Local associated diseases manifest themselves in the form of paratonsillitis and parapharyngitis.
In toxic-allergic form II, symptoms such as low-grade body temperature, pain in the heart and joints bother the patient even outside the period of exacerbation. Laboratory diagnostics confirm damage to the kidneys, liver, heart and vascular system. Local associated diseases manifest themselves in the form of paratonsillitis and parapharyngitis. Associated diseases of a general type manifest themselves in the form of rheumatism, nephritis, endocarditis and tonsillogenic sepsis - diseases that have a common infectious-allergic nature.
Rice. 5. The photo shows chronic tonsillitis. The tonsil on the left is significantly increased in size. Pus and purulent plugs in the lacunae are visible. The main signs of the disease are present.
Symptoms of paratonsillar abscess
Peritonsillar abscess usually develops on only one side. A patient who is already recovering from a sore throat or an exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis suddenly exhibits a complex of symptoms again:
A sore throat
Suddenly, one-sided pain appears when swallowing. The pain with a peritonsillar abscess is stronger than with a sore throat. It can radiate to the jaw area and ear.
Temperature
The temperature rises again to 39-40°C
More about the symptom
Swelling of the throat
Sometimes the swelling is so severe that not only swallowing is difficult, but also breathing through the mouth.
Complications of chronic tonsillitis
General complications
The peculiarity of streptococcal infection is to cause an autoimmune response, leading to serious complications of internal organs:
- rheumatic damage to the heart muscle;
- joint damage (arthritis);
- kidney damage (glomerulo- and pyelonephritis).
When microbes enter the bloodstream and massively multiply, sepsis and meningitis can occur.
Local complications
Local complications include:
- otitis;
- laryngitis;
- swelling of the larynx;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- mastoiditis;
- abscess and phlegmon of fiber.
Sore throat phlegmonous
Phlegmonous tonsillitis develops in patients with chronic tonsillitis. Initially, lacunar tonsillitis develops. Pus and purulent plugs form in the lacunae. Next, the inflammatory process moves to the lymphoid tissue of the tonsil and to the peri-almond tissue. The focus of inflammation in the peri-almond tissue displaces the tonsil in the opposite direction. Against the background of severe hyperemia, significant swelling of the soft palate is noted. A putrid odor appears from the mouth. Lymph nodes are enlarged and sharply painful.
Rice. 6. Combination of phlegmonous and fibrous tonsillitis. The focus of inflammation in the peri-almond tissue displaces the tonsil in the opposite direction. Against the background of severe hyperemia, significant swelling of the soft palate is noted. A whitish film is located on the surface of the tonsil and extends beyond it.
Paratonsillitis
Peritonsillitis is characterized by the appearance of inflammation in the peri-almond tissue. The disease is one of the local complications of tonsillitis. Swelling, the appearance of infiltrate or abscess are the main signs of the disease. The localization of paratonsillitis varies, but most often the inflammatory focus is localized in the area of the upper pole, where there is no capsule and the tonsil tissue is loose. Localization is one-way. Intense excruciating pain and symptoms of toxicosis are the main symptoms of paratonsillitis.
Peritonsillar abscess
With a complicated course of angina, an abscess (accumulation of pus) may form in the paratonsillar zone. Very quickly the mucous membrane over it becomes thinner and an opening occurs (usually the abscess is opened surgically). The patient's condition quickly returned to normal after the autopsy. Pain of a “tearing” nature, which intensifies when swallowing, increased salivation, strong odor from the mouth, toxicosis and lockjaw are the main symptoms of the disease.
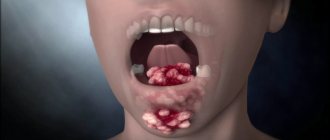
Rice. 7. The photo shows a peritonsillar abscess. The spherical formation displaces the palatine arches and soft palate in the opposite direction.
Cellulitis, paratonsillitis and abscess are sequential stages in the development of purulent inflammation of the tissue of the tonsils
Conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis can be conservative or surgical (removal of tonsils or tonsillectomy, removal of part of an organ). In the first stages of development of chronic tonsillitis, occurring in compensated or decompensated forms (during periods of exacerbation), as well as in cases of contraindications, drug treatment is indicated. If pus and purulent plugs continue to remain in the lacunae after several courses of treatment, or if serious complications develop, surgical treatment is indicated. When diagnosing a patient with toxic-allergic form II of chronic tonsillitis, urgent tonsillectomy is indicated.
Conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Treatment of the compensated form of chronic tonsillitis is carried out during exacerbations of the disease, but at least 2 times a year.
- Antibacterial treatment is carried out during exacerbations of the disease in short courses.
- Irrigation (rinsing) of the throat is an important condition for healing. For this purpose, sprays and solutions with antiseptics are used. Solutions of Miramistin, Octenisept and Dioxidin are widely used.
- Treatment in the form of inhalations is prescribed with drugs such as Furacillin, Tonsilogon N, Dioxidin, etc.
- For the toxic-allergic form of the disease and severe swelling of the tonsils, antihistamines of the 2nd and 3rd generations are used.
- For severe pain, the treatment regimen includes such painkillers as Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Paracetamol, Naproxen, Adavil, Aspirin for adults.
- The use of physiotherapeutic procedures occupies one of the important places among the methods of conservative treatment of chronic tonsillitis. Among them, the leading place is occupied by ultraviolet irradiation, exposure to high-frequency electromagnetic fields UHF (microwave), methods of using ultrasonic aerosols, therapeutic mud and ozokerite.
- An important component of drug treatment is increasing immunity. Vitamin therapy, the use of biostimulants and immunocorrectors stimulate the restoration of the patient’s immune status.
Removing tonsil plugs
Washing tonsils and removing plugs
Rinsing the tonsils and removing plugs should be carried out by a doctor. Stage 1. By pressing on the area of the outer arch of the tonsil, pus can be released from lacunae and purulent plugs. When removed independently, the plugs can penetrate into deeper areas of the lacunae and subsequently cause aggravation.
Washing of the tonsils on an outpatient basis is carried out using a syringe. At its end there is a cannula tube. The purulent plug is washed out of the lacuna under the pressure of the antiseptic solution. In case of tortuosity of the lacunae, the procedure may be ineffective. Usually 5 treatment sessions are prescribed. The lack of effect after 2 - 3 courses of full treatment is an indication for tonsil removal.
Rice. 8. Rinsing lacunae with a syringe.
Semi-surgical treatment method
A semi-surgical method for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis or lacunotomy is used to dissect scar changes that lead to narrowing of the mouth of the lacunae. This technique is carried out using the Surgiton apparatus.
Rice. 9. The Surgiton device is widely used in various fields of medicine.
Removing traffic jams using hardware
In some cases, removal of plugs is carried out using the Tonzillor device. The essence of the method is to create a vacuum in the tonsil area and subsequent deep rinsing of the lacunae using ultrasound and phonophoresis. The device has a large number of applicators, allowing it to be used by both adults and children. Typically 10 treatment sessions are performed. If necessary, the procedure is repeated after six months. In some cases, when the patient is bothered by painful sensations, the procedure is carried out using anesthetics TheraFlu LAR, Strepsils Plus, etc.).
Rice. 10. Tonsillor device.
The method of removing pus and purulent plugs from lacunae and crypts of the tonsils manually (washing the lacunae) and using the hardware method is widespread in the treatment of this disease. The effect is achieved purely mechanically with subsequent restoration of the drainage function of the tonsils.
Causes of paratonsillar abscess
As a rule, a paratonsillar abscess develops as a complication of tonsillitis or chronic tonsillitis. With tonsillitis, scars can form in the tonsils, preventing pus from leaving the lacunae (lacunae are natural narrow and highly branched cavities in the body of the tonsil). Pus that does not find a way out accumulates inside, from where it penetrates into the tissue surrounding the tonsil.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis using surgical method
Removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy), as a method of surgical treatment of chronic tonsillitis, is used in case of ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, the transition of the disease to the stage of decompensation, or the development of serious complications, including from internal organs. Surgery is performed only in the remission stage of associated diseases. The use of this technique allows you to remove the purulent focus, ensure a quick recovery, eliminate relapses of the disease and prevent serious complications. A developed peritonsillar abscess is a reason for emergency surgery. Often, along with opening the abscess, the tonsils are removed.
Removal of tonsils (tonsillectomy) using the traditional method
Chronic tonsillitis and a history of frequent tonsillitis are reasons for surgical removal of the tonsils. Complicated paratonsillitis and tonsillogenic sepsis are subject to emergency surgical treatment. The arsenal of modern medicine is rich in many methods for removing tonsils. The technique of excision with scissors and a wire loop is often used. Removing tonsils with a capsule is the main task of the surgeon. Contraindications to surgery are severe heart failure, severe diabetes mellitus, kidney disease with developed organ failure, diseases of the hematopoietic system and active tuberculosis. During the preparation for surgery, a number of laboratory tests and sanitation of the oral cavity are carried out.
Rice. 11. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis using surgical techniques. Scheme for removing tonsils using the traditional method
- Before the operation, medicinal preparation is carried out, the purpose of which is to suppress the patient’s anxiety level, the functioning of the secreting glands and enhance the effect of anesthetics. The drug mixture contains a narcotic analgesic, atropine and an antihistamine.
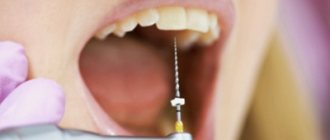
- Local anesthesia includes spraying the oropharynx with lidocaine and infiltration anesthesia with anesthetics (novocaine, trimecaine, lidocaine).
- The injection sites for anesthetics and the course of the operation are shown in Figure 12.
- The steps of the operation are shown in Figure 12.
- After the operation, the patient goes to bed. The neck area is alternately cooled with an ice pack. The secreted saliva is collected in the diaper and not swallowed. To reduce pain, the prescription of narcotic analgesics is indicated.
- Bed rest is prescribed for 2 days.
- Two days later, a light rinse with antiseptics is indicated.
- During tonsillectomy in patients with a complicated course of the disease, a course of antirheumatic treatment after surgery is indicated.
Rice. 12. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis using surgical techniques. Figure “a” shows the places where the anesthetic is injected. Figures “b”, “c”, “d” and “e” show the stages of the operation.
Emergency surgery
Emergency surgical intervention is performed for complications of tonsillitis - paratonsillitis in the abscess stage, ineffectiveness of previous autopsies, sepsis, parapharyngitis, neck phlegmon, etc. In case of paratonsillitis, the abscess is either opened or removed along with the tonsil.
Laser removal is a popular tonsillectomy technique.
Surgeries on the tonsils using a laser system are divided into radical and operations to remove part of the organ, which allows the doctor to choose the optimal method of treating chronic tonsillitis.
- Radical tonsillectomy involves complete removal of the organ.
- Ablation involves removing part of an organ.
There are several types of laser. Their choice for surgery depends on the condition of the tonsil tissue, the extent of the inflammatory process and the final medical goal. There are the following types of laser beam:
- Fiber optic.
- Holmium.
- Infrared.
- Carbon.
Laser removal of tonsils using infrared ray
The technology of using laser tonsil removal using an infrared ray allows you to cut and connect tonsil tissue. In the surrounding tissues, the temperature rises slightly - by 2-3 degrees. Advantages of using laser for tonsillectomy:
- The duration of the surgical intervention is kept to a minimum and is about half an hour.
- Coagulation of blood vessels makes the operation bloodless.
- Pain after surgery is less pronounced.
- There is no postoperative tissue swelling.
- There is no risk of infection spreading to surrounding tissues.
- The recovery process has been reduced to 4 days.
- Complications in the postoperative period are minimized.
- Rapid restoration of working capacity.
Children under 5 years of age are not allowed to undergo laser tonsil removal surgery
Rice. 13. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis using surgical techniques. Scheme for laser removal of tonsils (radical tonsillectomy). The operation is performed under local anesthesia. The tonsil is grabbed with forceps and separated from the underlying tissue with a laser beam, which is emitted by a device with a special attachment. Coagulation of blood vessels makes the operation bloodless.
Rice. 14. Chronic tonsillitis. In the photo on the left you can see a hypertrophied tonsil, on the right - the condition after bloodless laser removal. In place of the tonsil, a niche is visible.
Treatment
Therapy involves the use of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Tonsils are treated with solutions containing iodine. The throat needs to be regularly gargled with herbal decoctions and antiseptic solutions, and inhaled.
Drug treatment is reduced to the use of antibacterial drugs. The choice of antibiotic is made depending on the type of pathogen. Aerosols and dissolving throat tablets are used. Medicines quickly relieve inflammation.
Physiotherapy procedures used:
- steam inhalations
- exposure to ultrasound
- laser therapy
- shortwave UV radiation
In severe cases, surgical removal of the tonsils is indicated. Surgery is indicated for frequent sore throats and complications of tonsillitis.