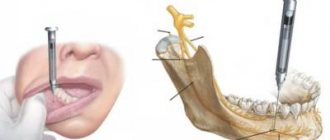
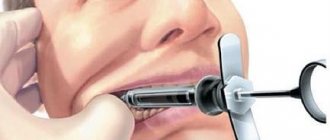
General information, release form
Articaine was first synthesized in 1969, and its widespread use began in 1976. Nowadays, medications based on Articaine are produced by many pharmaceutical companies.
Basic requirements for local anesthetics:
- significant depth of penetration of the product;
- long duration of action;
- high degree of security.
These parameters are influenced by:
- activity of the anesthetic used;
- peripheral vascular tone.
The drug Articaine does not contain a special preservative - paraben, which most often causes hypersensitivity reactions. Contains a minimal amount of the antioxidant adrenaline (metabisulfite).
The stability of the local anesthetic is achieved through high quality glass, rubber components of the carpule, and high activity of the active substance.
It is insoluble in aqueous media, so it is used in the form of a salt, which is water soluble. For the main effects to manifest, its destruction in tissues is required with the formation of fat-soluble substances that are able to penetrate the lipid membrane of the nerve ending. It undergoes changes in tissue structures quite quickly, so the analgesic effect is noted within 1-2 minutes.
Articaine has a slight ability to expand the lumen of blood vessels, so it is advisable to use it with epinephrine (adrenaline). It quickly penetrates into soft tissues, as well as into bone structures, which ensures a rapid onset of effect, as a result of which it is widely used in therapeutic, surgical, and orthopedic interventions in dentistry.
Available in the form of cartridges and solutions for injection in ampoules. Packed in cardboard boxes.
Painkillers in dentistry
Anesthesia in dentistry
Along with the development of dentistry in our country, methods of pain relief for dental interventions are also undergoing changes!
Have you ever thought that when you go to the dentist, you can fall asleep, then wake up and go home completely healthy? No? And now it's real. So, what methods of pain relief are used by dentists in our time?
Application method of pain relief
We treat the gums with a cotton swab with a special anesthetic gel - a private method of local anesthesia. It is not used as an independent method; this method of anesthesia is used to prepare for more complex anesthesia techniques, such as infiltration, for example, so that the patient does not feel the injection of a needle.
Infiltration local anesthesia
Anesthesia in the area of one tooth. Used to treat most dental diseases. The simplest, most accessible and safest method of pain relief. Using a syringe with a needle, the anesthetic solution is injected into the intervention area - under the mucous membrane. The most modern anesthetics today are drugs based on Articaine, used with adrenaline in dilutions of 1:100,000 and 1:200,000. Its important quality is its short (about 20 minutes) half-life and high percentage of its binding to plasma proteins (up to 90-95%), that is, this drug is least likely to have a toxic effect with accidental intravascular administration. In addition, articaine is characterized by maximum diffusion ability in soft tissues and bone and, accordingly, the rapid onset of anesthesia after injection. This compound appeared only a few years ago and is the basis for the most famous drugs: septanest, ubistezin, alfacaine. The anesthetic activity of articaine, sounds convincing, is six times stronger than that of the well-known novocaine, so the dose sufficient for complete anesthesia is only 1.5 ml, and not 4-8 ml, which was injected before. But if necessary, simultaneous use of up to 10.5 ml is possible due to the low toxicity of the drug. The duration of deep anesthesia is up to 6 hours. The duration and strength of anesthesia are greatly influenced by vasoconstrictors - vasoconstrictor substances that are added to anesthetics to enhance their effect. The most well-known vasoconstrictors are adrenaline and norepinephrine. In modern anesthetics, vasoconstrictors are added during production, so their overdose, which usually caused an increase in heart rate in the first minutes, is now quite rare.
Do not forget that any method of pain relief carries a risk to the life and health of the patient. Therefore, you, as a patient, must inform your doctor about the presence of an allergic reaction to any medications, as well as about all concomitant chronic diseases. Since, based on the collected history, you can select an anesthetic drug that will not have side effects. Perhaps, for a more detailed examination, you will be referred to an allergy center or prescribed antihistamines as preparation for dental treatment under anesthesia.
All contraindications and restrictions to the use of local anesthetic come down to the main points:
1) Allergic reactions to local anesthetic
A history of an allergic reaction is an absolute contraindication to the use of a local anesthetic. It should be noted, however, that intolerance to the local anesthetic, indicated by many patients, is often not a true allergic reaction, but is of a stressful nature or is associated with the intravascular administration of a vasoconstrictor.
2) concomitant diseases
Cardiovascular diseases (arrhythmia (heart rhythm disturbance), heart pathology, coronary heart disease, hypertension, coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction), cardiac arrhythmia, patients undergoing treatment with MAO inhibitors or cyclic antidepressants. Patients suffering from hyperthyroidism, tremors of the limbs, nervousness, weight loss while maintaining appetite, excitability, increased feelings of fear, fixed gaze, tachycardia, heart rhythm disturbances.
3) Age restrictions
It should be borne in mind that for children the minimum toxic doses of all local anesthetics are significantly less than for adults. To achieve guaranteed complete anesthesia and minimize the likelihood of toxic effects, the most effective and safe modern local anesthetic drugs based on articaine, mepivacaine or lidocaine should be used, limiting the dosage of the drug used.
4) Pregnancy
With any therapy, it is necessary to assess the degree of benefit and risk of treatment, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy.
The drugs used in our clinic:
- Septanest 1:200000 This drug is the optimal local anesthetic today for most dental interventions (such as treatment of caries, chronic forms of pulpitis, crown preparation). This drug has a strong analgesic effect, at the same time, since articaine has the shortest half-life among modern local anesthetics, the drug is safe from the point of view of possible toxic effects. Due to the very low concentration of adrenaline, these drugs can be used for concomitant diseases that are a relative contraindication to its use. That is, for cardiovascular diseases, pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, concomitant drug therapy with glucocorticosteroids.
- Septanest 1:100000 Used for dental interventions associated with acute inflammatory processes (acute pulpitis and periodontitis, exacerbations of chronic pulpitis and periodontitis), in this case a higher concentration of adrenaline and a longer action are required, however, such drugs may be of concern for patients with concomitant pathologies .
- Scandonest 3% – without adrenaline. It is used in cases where there are concomitant chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, heart pathology, coronary heart disease, hypertension, coronary insufficiency, recent myocardial infarction, heart rhythm disturbances, diabetes mellitus.
Anesthetics Septanest 1:200000, Septanest 1:100000, Scandonest 3% are supplied in ready-made form, in disposable glass capsules of 1.6 ml. The injection is made directly from the carpula using a special syringe and needle. The drug is not poured out of the factory packaging and is not mixed with anything, and it is impossible to insert any other ampoule into the anesthesia syringe, which eliminates injection errors.
Carpule syringes and needles are a new word in pain relief technology.
A carpule syringe is a metal instrument into which a disposable carpule containing an anesthetic is placed and a disposable needle is screwed on.
Thus, the carpule-needle system is similar to a disposable syringe, having a number of advantages over it:
- finer needle
- smooth stroke of the piston in the carpule
- guarantee against foreign substances entering the anesthetic
- more reliable, threaded needle fastening
All this allows you to make the injection as painless as possible.
Our clinic uses French injection needles. The thickness of the disposable needle is only 0.3 mm, which makes the injection virtually painless. But in addition, the injection site is numbed by smearing it with a higher concentration of anesthetic.
A typical problem for many patients is that they are “not affected” or “weakly affected” by anesthesia. In fact, this is not a problem for patients, but for doctors. Indeed, due to the anatomical features of teeth and bone structure, some teeth are difficult to freeze. But difficult does not mean impossible. A special device allows for intraligamentary anesthesia, that is, injecting an anesthetic directly to the tooth, along the periodontal ligament. This method is effective even when conventional measures do not bring results.
Anesthesia on the upper jaw is more painless during administration. Its effect comes faster. On the lower jaw, anesthesia takes longer to set in. This is due to the different structure of bone tissue. During anesthesia of the lower jaw, you will feel a “numbness” in half of the jaw. During anesthesia in the upper jaw, there is “numbness” in the area of 2-3 teeth. This is due to the anatomical features of the jaw.
If you took painkillers for several days before visiting the dentist, anesthesia may reduce its effectiveness. The same goes for drinking alcohol.
Let's summarize:
- Choose dentistry that uses modern anesthetics.
- Discuss the presence or absence of allergic reactions.
- The variety of sensations depends on the diagnosis and localization of the process.
- Do not drink alcohol or take painkillers on the day of your doctor's appointment.
- Don't start the disease.
- Calm down and tune in for a good result.
pharmachologic effect
The mechanism is based on the effect on the endings of both sensory nerves and nerve fibers, which creates conditions for disrupting the generation of an exciting impulse and its conduction to other structures. Articaine interacts with receptors that are responsible for the functioning of sodium channels. By influencing them, the flow of sodium ions through them is blocked, as a result of which an anesthetic effect develops.
The duration of action is about 20 minutes. It is destroyed into products that are non-toxic to the body, which makes it possible to re-introduce the substance. In an acidic environment, the effectiveness of the drug decreases.
Features of the chemical structure of ultracaine
In solution, the anesthetic interacts with water molecules and transforms into an active ionized form, shifting the acid-base balance to the alkaline side. In an acidic environment, a neutralization reaction occurs as a result of which the amide bond is destroyed and the anesthetic becomes inactive. Human tissue fluid normally has a slightly acidic environment, but in the area of inflammation the acidity increases. Therefore, inflamed tissues are less pain relieved.
In addition to the amide group, which connects the lipophilic and hydrophilic parts, the articaine molecule (the active ingredient of ultracaine) contains a more reactive ester group. In the acidic environment of tissue fluid, it undergoes hydrolysis first of all, ensuring the preservation of amide groups, therefore, in general, the effect of ultracaine in comparison with lidocaine is longer.
Analogs
Articaine-containing medicinal substances are produced by many pharmaceutical companies. They bear the following patented names:
- Alfacaine (manufactured in France);
- Articaine Inbisa (producing country - Spain);
- Ubestezin (made in Germany);
- Primacaine (manufacturing country – France);
- Cytocorine (made in Italy);
- Ultracaine (manufacturing country – Germany);
- Septanest (made in France).
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
Articaine provides a high degree of action and a minimal number of adverse reactions of the body. Has minimal toxicity. The maximum concentration after administration into the submucosal membrane of the oral cavity is observed 25 minutes after administration. With infiltration anesthesia, the effect is noted after 1-2 minutes, with conduction anesthesia - after 2-2.5 minutes.
Its transformation mostly occurs in the liver; the inactivation process also occurs in the bloodstream and tissue structures under the action of blood plasma enzymes (cholinesterase). The resulting metabolites do not have an anesthetic effect. Binds to blood proteins and is excreted by the kidneys. On the first day, about half of the administered dose is eliminated.
Differences between regional and infiltration anesthesia and the advantages of ultracaine
Regional methods of pain relief include spinal and epidural anesthesia, anesthesia in the area of large nerve plexuses, as well as conduction anesthesia in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. In this case, a drug depot is created in the area of passage of the conducting nerve trunk and the sensitivity of the entire zone of its innervation is blocked. The anesthetic is delivered directly to the fiber and almost immediately gains access to the nerve cell membrane, minimally interacting with tissue fluid.
Infiltration anesthesia involves injecting the drug directly into the area that needs to be numbed. By saturating the tissue, the anesthetic inactivates the smallest nerve endings, so pain is not felt. In this case, part of the anesthetic, without reaching the point of application of its action, is inactivated by tissue fluid, especially if anesthesia is carried out on inflamed tissue.
The differences in the effects of ultracaine and lidocaine are fully manifested during infiltration anesthesia, especially under conditions of inflammation. The effectiveness of conduction anesthesia differs slightly.
The advantages of ultracaine appear during infiltration anesthesia. Due to its resistance to tissue fluid, ultracaine acts better and penetrates deeper into tissues than lidocaine with a similar administration method. Less susceptible to the action of an acidic environment, ultracaine provides a satisfactory level of pain relief during infiltration of inflamed tissue.
Indications
In commonly used concentrations, the drug in question does not have surface anesthetic activity, but when administered by injection, its effect is superior to other drugs of the same group (Lidocaine, Mepivacaine). Therefore, the main indication for the use of Articaine is local anesthesia of a conduction or infiltrative type.
Articaine with adrenaline is used for pain relief during traumatic dental procedures in the form of the following types of local anesthesia:
- infiltration (impregnation of tissues of the surgical field);
- conduction (introduction of a substance along the nerve);
- intraligamentary (intraligamentous);
- intraseptal (intraseptal - the substance is injected into the septum of the bone between the sockets of the teeth);
- intrapulpal (injection of anesthetic into the dental pulp).
It is also used for:
- uncomplicated removal of one or more teeth;
- preparation of carious cavities and teeth before prosthetics.
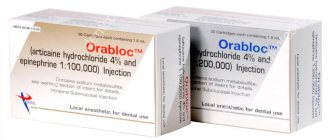
Articaine in combination with epinephrine has found use in the following concentrations:
- 1:200000;
- 1:100000.
The use of a local anesthetic with a higher content of adrenaline (1:100,000) significantly increases the risk of adverse reactions in patients with periodontal tissue pathology, as well as during injection into the palate.
Why is pain relief performed in dentistry?
Before tooth extraction, anesthesia is required, as this operation is very painful. These sensations can trigger a heart attack or put the patient into shock. Therefore, such manipulations are now carried out under anesthesia. Most often, local anesthesia is used. The injected drug blocks the transmission of nerve impulses from the diseased tooth to the brain. The sensitivity of the gums and surrounding tissues is greatly reduced. Therefore, the tooth is removed painlessly.
Many patients do not visit the dentist on time precisely because they are afraid of pain. They drown out unpleasant sensations with pills, which often leads to serious complications. But, the use of painkillers during tooth extraction allows treatment to be carried out without discomfort for the patient.
Contraindications
The use of local anesthetic Articaine is prohibited in the following cases:
- in the presence of a hypersensitivity reaction to Articaine, Adrenaline, sulfites, as well as to any other auxiliary component of the drug;
- for various forms of tachyaarthymia, including paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation;
- if you have a history of bronchial asthma with excessive sensitivity to sulfites;
- with existing angle-closure glaucoma;
- with simultaneous therapy with non-selective beta-blockers (Propranolol, Timolol, Nadolol, Carvedilol);
- severe liver dysfunction;
- excessive concentrations of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream (hyperthyroidism);
- undergoing a course of therapy with drugs that inhibit monoamine oxidase (Selegiline, Pirlindol, Garmaline, Nialamid) or tricyclic antidepressants (Fluoxetine, Amitriptyline, Imipramine, Trimipramine);
- with existing B12-deficiency anemia, methemoglominemia;
- in the presence of severe cardiac conduction disturbances (severe bradycardia, atrioventricular block of II-III degrees);
- in the presence of diseases of the central nervous system;
- with severe arterial hypotension;
- condition of acute heart failure;
- extensive maxillofacial surgical interventions, as well as surgical procedures lasting more than 20 minutes;
- children under 4 years old.
Use with caution:
- during pregnancy;
- in postpartum women with gestosis;
- if there is bleeding in the last trimester of pregnancy;
- with a lack of blood cholinesterase;
- with insufficient kidney function;
- in the presence of diabetes mellitus;
- with hypertension.
Directions for use and dosage
The main feature of Articaine is its high ability to penetrate tissue structures when administered by injection. Therefore, the drug allows you to carry out many interventions (for example, preparing teeth for prosthetics, surgical interventions on soft tissues, tooth extraction) under infiltration anesthesia in the upper and lower jaws.
The absence of side effects during local anesthesia largely depends on the correct calculation of the required dosage of the drug used for anesthesia.
Particular attention is paid to this in pediatric dentistry, which is explained both by the child’s lower body weight and by the peculiarities of the functioning of organs and systems that take part in the change and elimination of drugs, as well as in patients at high risk.
The “gold” standard is the use of a minimal amount of local anesthetic to achieve maximum pain control. Also, the choice of dosage is based on the depth of penetration of the required anesthesia and the time of the required intervention.
4% Articaine with Adrenaline provides a reliable analgesic effect, which manifests itself 1-3 minutes after injection of the drug. Duration of action – 45-150 minutes. In this case note:
- good penetrating ability;
- good tolerance;
- minimal vasospasm;
- no increase in blood pressure;
- no increase in heart rate;
- minimal penetration through the placental barrier.
Therapeutic dentistry
Articaine is used in the indicated dosage and is used for both infiltration and conduction anesthesia for the following purposes:
- preparation of carious cavities;
- treatment of pulpitis;
- carrying out therapy for periodontitis;
- performing periodontal surgical interventions.
To obtain an analgesic effect lasting from 30 to 45 minutes, the drug is administered from the external (vestibular) side in a dosage of 0.5 to 1.8 ml per tooth.
Surgical dentistry
Instillation of the drug into the submucosal area of the required tooth is used in a volume of 1.8 ml. If the need arises, additional administration of the medication in the same volume is possible in order to achieve complete pain relief. Used for conduction and infiltration anesthesia. Indication: removal of one or more adjacent teeth.
For surgical interventions on the palate (suturing, incisions), administering the drug in a volume of 0.1 ml per injection is sufficient.
Orthopedic dentistry
Used for both conduction and infiltration local anesthesia. From 0.5 to 1.8 ml is injected from the outside of the jaw into the submucous membrane of the area of the required tooth. Additional administration of the drug is possible if necessary, but not more than 7 mg per 1 kg of patient body weight. Indication: odontopreparation.
Uncomplicated tooth extraction, preparation for filling, preparation for placement under a crown should be accompanied by the administration of 0.5 to 1.8 ml of local anesthetic with a vasoconstrictor drug (no more than 1 carpule). If there is a need to administer Articaine from the palatal side, then use 0.1 ml of a local anesthetic.
The maximum dosage allowed for injection of Articaine is:
- for children from 4 to 12 years – 5 mg/kg;
- for children over 12 years of age and adults – 7 mg/kg.
In an outpatient setting, the recommended dose of anesthetic is ½ of the maximum allowable dose.
Before direct administration of the drug, an aspiration test is required to avoid intravascular administration of the drug. The pressure exerted on the piston during administration of the product must be adjusted depending on the sensitivity of the tissue. It is not recommended to administer the drug to areas of the mucosa that show signs of inflammation.
Preparations for infiltration anesthesia
Anesthesia in dentistry is most often carried out using injection solutions. The most common ones for this are “Lidocaine” or “Novocaine” in ampoules. It is these medications that provide pain relief in all budget clinics. For this, special syringes with a thin needle are used. But recently, new technologies have been increasingly used. For example, private medical centers have switched to carpule anesthesia. Its peculiarity is the use of disposable cartridges with medicine. In addition, the needle for such injections is taken very sharp, which ensures the absence of pain during the injection.
In addition to Novocaine and Lidocaine, articaine and mepivacaine have recently been used in dentistry. There are several drugs based on these substances:
- "Ultracaine";
- "Scandonest";
- "Ubistezin";
- "Septanest".
The drug "Novocain" in dentistry
This anesthetic was synthesized at the beginning of the 20th century. And for many years, Novocain in ampoules became the most common means of pain relief during any surgical interventions. This is an inexpensive drug, so it is accessible to everyone; a package costs 30-40 rubles. But recently it has been used less and less due to the high risk of side effects.
The instructions for Novocain warn that after its administration, a drop in blood pressure, dizziness, weakness or allergic reactions may occur. In addition, sometimes it is not very effective, so it is administered together with other drugs. Most often, Novocaine is combined with adrenaline, but this mixture is contraindicated for high blood pressure. The low effectiveness of this drug, as well as the loss of its functions in the presence of purulent inflammation, has led to the fact that it is now used very rarely in dentistry.
Use of the drug "Lidocaine"
This is the most common anesthetic, widely used not only in budget dental clinics, but also in private ones. It is quite effective, completely removing sensitivity for about 1-2 hours. However, it rarely causes side effects. But sometimes intolerance to Lidocaine still occurs. In this case, allergic reactions, a drop in blood pressure, dizziness, weakness, and heart rhythm disturbances occur. Numbness of the lips and tongue often occurs, which can lead to accidental injury.
In order for this drug to work well and not cause negative reactions, it must be administered in the correct dosage. Sometimes it is sold not in ampoules, but in powder, so you need to know how to properly dilute Lidocaine for injection in dentistry. Most often, a 0.5% solution is used, but for conduction anesthesia in difficult cases, 1-2% can be used. The dosage is determined individually according to the severity of the patient's condition.
The drug "Ultracain"
This product is based on the strong anesthetic articaine. Additionally, the drug contains epinephrine. This is an analogue of adrenaline that has a vasoconstrictor effect. It is needed to lengthen the duration of action of the drug. "Ultracaine" is considered a safer and more effective remedy than the previously common "Lidocaine" or "Novocaine".
The instructions note that it has almost no contraindications. It is even used for children and elderly patients. The advantage of the drug is that it begins to act within 10 minutes, and its analgesic effect lasts up to 3.5 hours. The drug is sold in pharmacies at a price of 500 rubles per pack of 10 ampoules.
The most common side effects after Ultracaine are headaches, nausea and muscle twitching, but this is rare. Even less common is a drop in blood pressure or arrhythmia after administration of the drug. Ultracaine is available in several forms, differing in the dosage of the active substance and epinephrine. The most popular is “Ultracain D”, which does not contain additional components, therefore it is less likely to cause side effects.
The drug "Ubistezin"
The price of this painkiller is slightly higher than that of other similar drugs. But, it is widespread in dentistry due to its high efficiency. In addition to articaine, the drug "Ubistezin" includes adrenaline. It provides vasoconstriction at the injection site. Thanks to this, the drug is absorbed slowly and causes fewer side effects. Because of this, its effect lasts longer. Moreover, the effect occurs within 3-5 minutes after the injection, which in some cases is very important. In addition to the general side effects caused by articaine, after an injection carried out in violation of the rules, tissue ischemia or neurological problems may develop.
The price of “Ubistezin” is quite high, since it is mainly sold in large packages. 50 cartridges cost from 1,500 to 2,000 rubles, so they are purchased from dental clinics. This drug is allowed to be used even in pediatric dentistry. Its advantage is the rapid onset of analgesic effect and good tolerability. But, it is contraindicated to use the drug in case of arrhythmia, tachycardia, or the presence of allergic reactions.
Pain relief with Septanest
The drug is produced by a well-known French pharmaceutical company. It has been used in dentistry for a long time, and has already proven its effectiveness. Therefore, in difficult cases or in the absence of contraindications, dentists often choose Septanest. The instructions for use of the drug note that allergic reactions to this drug occur quite often. This can be explained by the presence of a large number of artificial additives. In addition, side effects such as respiratory and cardiac dysfunction often develop.
However, the drug is quite popular. The instructions for use for Septanest allow the drug to be used by children over 4 years of age and pregnant women. Contraindications include only glaucoma, bronchial asthma and heart rhythm disturbances. If necessary, you can use similar anesthetics that also contain articaine: Alfacaine, Brilocaine, Cytokartin, Primacaine.
The drug "Scandonest"
It is an anesthetic based on mepivacaine. It does not contain adrenaline, preservatives or other harmful components. It is used for intolerance to articaine or adrenaline. This drug can be used in the elderly, patients with diabetes, hypertension, bronchial asthma and even pregnant women. In addition to the analgesic effect, mepivacaine has the ability to constrict blood vessels, so additional adrenaline is not required. An analogue of the drug "Scandonest" is the anesthetic "Mepivastezin".
Side effects
Articaine may cause a number of adverse effects:
- from the nervous system: stupor, loss of consciousness, respiratory disorders, respiratory arrest, tremor, twitching of muscle groups, generalized convulsions, dizziness, cephalalgia, hypoesthesia (change in pain sensitivity), paresthesia (burning sensation, pointing), damage to the facial nerve (muscle paralysis faces);
- from the organ of vision: blurred vision, diplopia (double vision), decreased visual acuity, blindness;
- from the cardiovascular system: low blood pressure, poor heart function, cardiogenic shock;
- from the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting;
- from the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions at the injection site - hyperemia, edema, hyperemia of the skin, angioedema (swelling of the upper and lower lips, cheeks, vocal cords), rhinitis, conjunctivitis, urticaria, impaired respiratory function.
Overdose
Administration of an excessive amount of the drug can lead to a variety of manifestations from various organ systems:
- Nervous system. Both depression and excitation can be observed. In the first case, dizziness, shortness of breath, impaired consciousness up to its complete loss are observed. Excitement is characterized by anxiety, causeless restlessness, tremors of the limbs, convulsions, increased frequency of respiratory movements, and increased heart rate.
- The cardiovascular system. Detect cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular fibrillation, arterial hypotension, and cardiac arrest.
Treatment:
- stopping the administration of the drug;
- the patient is placed on a horizontal surface;
- ensures airway patency and oxygen flow;
- breathing rate, heart rate, and blood pressure are monitored;
- in case of respiratory failure - oxygen supply, intubation, artificial ventilation;
- in the presence of convulsions, short-acting barbiturates (Cyclobarbital, Thiopental, Hexobarbital, Kemital) are administered intravenously with simultaneous oxygen supply and blood circulation control;
- in case of significant disturbances of blood circulation and shock conditions - intravenous infusion of electrolytes (Ringer's, Aminol, Ringer-Locke solutions), glucocorticosteroid hormones (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone), plasma-substituting solutions (crystalloids - saline solution, 5% glucose, colloids - dextrans, starches, gelatins; Reopoliglucin, blood plasma, fluorodecalins), albumin;
- in collaptoid conditions and bradycardia - slow intravenous administration of 0.1 ml of Epinephrine, then drip into a vein under the control of blood pressure and heart rate;
- for tachycardia and tachyarrhythmias - beta-blockers (Metoprolol, Propranolol, Esmolol, Atenolol) into the vein, blood pressure control and oxygen supply.
Drug interactions
When using Articaine simultaneously with:
- medications that depress the nervous system (general anesthetics - Halothane, Ftorotan, hypnotics - Zopiclone, Zolpidem) increase the effect of the latter;
- anticoagulants (Heparin, Warfarin, Fraxiparine, Clexane) indicate an increased risk of bleeding and hemorrhage;
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (Selegelin, Pirlindol, Nialamid) increase the risk of developing arterial hypotension, therefore it is recommended to stop taking these drugs 10 days before the planned dental procedure;
- muscle relaxants (Suxamethonium, Tubocurarine, Orphenandrine, Dantrolene) reveal an increase in the duration of action of the latter drugs;
- with narcotic analgesics (Tramadol, Fentanyl, Codeine, Buprenorphine), an increase in the effects of these medications is observed, depression of respiratory function is noted;
- vasoconstrictor drugs (Oxymetazoline, Xylometazoline, Caffeine, Naphazoline) enhance and lengthen the local anesthetic effect of Articaine;
- cholinesterase blockers (Neostigmine, Galantamine, Physostigmine, Pyridostigmine), Thiotepa, Cyclophosphamide reduce the rate of metabolism of Articaine.
Articaine is an antagonist of drugs used to treat myasthenia gravis due to its effect on striated muscles, especially when used in high dosages, as a result of which additional correction of the treatment of myasthenia gravis is required.
When treating the injection site of a local anesthetic with disinfectant solutions that contain heavy metals, the risk of developing an adverse local reaction in the form of swelling, hyperemia and painful sensitivity increases.
special instructions
When using Articaine, some points should be observed:
- intravenous administration is contraindicated;
- in order to prevent infectious and inflammatory complications, you should ensure the sterility of the needles and syringes used when taking the drug from the ampoule;
- Infiltration mandibular anesthesia of the tongue and soft palate does not work (a conduction anesthesia method is required);
- infiltration anesthesia has the effect of conduction anesthesia during the removal of mandibular premolars;
- it is required to monitor the functions of the cardiovascular, nervous systems, and respiratory tract;
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors should be discontinued 10 days before the administration of Articaine.
Articaine during pregnancy and lactation
The use of Articaine during pregnancy has not been established due to insufficient clinical data. It is possible to use this drug if the potential therapeutic effect outweighs the potential risk of adverse effects on the fetus.
Penetrates through the placental barrier. Does not have a teratogenic effect on the fetus, regardless of the technique of use and dosage.
During breastfeeding, there is no need to interrupt feeding in this manner, since no significant concentrations of Articaine are found in milk.
Articaine is a drug used in dental practice to provide local anesthesia. It has a significant effect, sufficient duration of action, and minimal risk of adverse reactions. It can be used in pediatric dentistry, as well as in the treatment of pathologies in women during pregnancy.
Sources used:
- Solovyova A. A. (2015) Fundamentals of anesthesiology. Local and general anesthesia
- https://esraeurope.org/
- Lidocaine // Medicines / M. D. Mashkovsky
How to improve the quality of pain relief?
A patient who is indicated for anesthesia without adrenaline in dentistry can make sure that the effect of the painkiller lasts longer and is of better quality. To do this, he only needs to follow a few general recommendations:
- Before visiting a doctor, if there is strong anxiety and fear of treatment, it is better to take a sedative, preferably based on herbs (for example, about 30 drops of valerian root tincture).
- The day before visiting the dentist, you should not drink alcohol, since alcohol in the blood weakens the effect of the anesthetic.
- If you are taking any medications or have any allergic reactions, you should inform your dentist at the treatment planning stage.
- It is better not to visit a doctor if you feel unwell or during menstruation.