Inflammation of trigeminal neuralgia: causes
What are the causes of inflammation, neuritis, trigeminal neuralgia? The causes of trigeminal neuralgia are various inflammatory (inflammation), traumatic (damage), toxic, infectious (infections, including herpes - postherpetic neuralgia), allergic, infectious-allergic, metabolic effects.
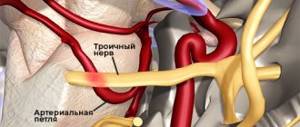
Compression of nerves (pinching) in bone, musculoskeletal and osteoarticular canals, prolonged microtrauma, especially in combination with hypothermia, and foci of focal infection also play an important role.
Help at home
Acute toothache requires immediate contact with a dental clinic. And home treatments are in no way a substitute for visiting a doctor. They should be used only if the patient is outside the city and there are no medical facilities nearby. Or at night, when you need to wait several hours before seeing a doctor.
First of all, the patient should be offered anti-inflammatory drugs. They also have analgesic and antipyretic effects. Among them are Solpadeine, Nimesulide, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen and their analogues.
Traditional methods of treatment include rinsing with soda solution or chamomile infusion. They have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect and will help slightly relieve pain.
It is worth remembering that these methods have a temporary effect. They are not curative and do not eliminate the cause of the disease. Therefore, you should not delay contacting a specialist. This will help avoid serious complications and tooth loss.
Inflammation, trigeminal neuralgia symptoms
Trigeminal neuralgia is clinically manifested by short-term attacks of excruciating pain, most often in the area of the 2nd and 3rd branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is characterized by the presence of trigger zones on the skin and mucous membranes. Touching them provokes attacks of pain. In most cases an attack of pain is accompanied by severe local and general autonomic disorders, the following symptoms: facial hyperemia (redness of the face) and swelling on the affected side, lacrimation, rhinorrhea (discharge of watery mucous discharge from the nose), hypersalivation (salivation, increased secretion of the salivary glands), Possible increased blood pressure (BP), chills-like trembling, difficulty breathing.
If a pulpless tooth hurts
After nerve removal, some people experience mild pain. In dentistry it is usually called “post-filling”. It may be a variant of the norm or indicate that depulpation was performed poorly.
In the first case, we are talking about tissue restoration after therapy. As soon as the regenerative processes are completed, the painful symptoms will disappear on their own.
In the second case they mean:
- Extension of material beyond the root apex. It comes into contact with soft tissues and irritates them. This problem can be detected using an x-ray.
- Violation of canal filling technology. They need to be treated.
- Damage to the tooth root. Repeated treatment is indicated.
- Allergy to materials used during filling. Then the lips and gums swell. It is necessary to refill the roots using another material that will not cause such a reaction.
If, after dental therapy aimed at eliminating inflammation of the nerve of the tooth, something bothers you, it is always better to contact a specialist and undergo the examination prescribed by him. This will avoid many troubles.
Trigeminal nerve, anatomy, innervation, where the trigeminal nerve is located
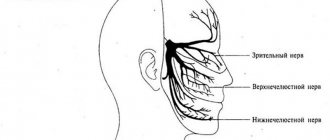
The trigeminal nerve, nervus trigeminus, the 5th pair of human cranial nerves is a mixed nerve that contains sensory, motor and autonomic fibers. The functions of the trigeminal nerve are varied.
The sensory fibers of the trigeminal nerve originate from the cells of the trigeminal ganglion, which is called the ganglium trigeminale. It is located in the recess of the pyramid of the temporal bone. The dendrites of these cells form 3 branches and 3 trunks.
1 branch of the trigeminal nerve, the first branch (nervus ophthalmicus) - the ophthalmic nerve passes in the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, later through the superior orbital fissure into the orbit. Then it breaks up into branches, innervates such structures as the outer part of the conjunctiva, the skin of the outer corner of the eye, the upper eyelid, the lacrimal gland, the skin of the scalp to the temporal and parietal regions, the skin of the forehead, the skin of the root of the nose, the cornea, the frontal sinus, the main sinuses , nasal mucosa, nasal skin, posterior cells of the ethmoid bone.
2nd branch of the trigeminal nerve, second branch (nervus maxillaris) - the maxillary nerve passes (exit) through the round foramen and the pterygopalatine fossa. It further breaks down into branches and innervates the following sections: the skin of the temporal region (temporal region, temple), the skin of the zygomatic region (cheekbone), the mucous membrane of the posterior ethmoid cells and the main sinus, the vault of the pharynx (pharynx), the nasal cavity (nose), the soft palate, hard palate, mucous membrane of the tonsils (tonsils), skin of the infraorbital region (infraorbital region), wings of the nose, upper lip, gums of the upper jaw, upper teeth.
3rd branch of the trigeminal nerve, third branch (nervus mandibularis) - the mandibular nerve leaves the skull through the foramen ovale (exit point, exit point), innervates the following areas: mucous membrane of the cheek, mucous membrane of the lower gum (lower gum), skin of the corner of the mouth (angle mouth), skin of the external auditory canal, anterior part of the auricle, temple, all lower teeth, skin and mucous membrane of the lower lip.
The motor fibers of the trigeminal nerve originate from the motor nucleus nucleus motorius nervi trigemini. The core is located in the bridge tire. Fibers extending from the nucleus leave the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. They innervate the masticatory muscles and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle. The axons of the trigeminal ganglion cells form a root and go to the bridge, where they divide into 2 branches.
The descending branch forms the descending spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for conducting temperature and pain sensitivity. It ends in the nucleus spinalis nervi trigemini. The descending spinal tract and its nuclei are analogous in their function and structure to the posterior horns of the spinal cord. The nuclei and path are divided into 5 segments, as a result of which the innervation of the facial skin in the Zelder zones is located in a ring.
Peripheral nervous system
The trigeminal nerve is an integral part of the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system consists of:
- Nerve nodes
- 12 pairs of cranial nodes
- 31 pairs of spinal nodes
- Branches and nerve endings of nodes
- Receptors and effectors
Don't know your correct bite? See on the website what a correct bite looks like.
See here for details of open bite treatment.
Depending on the location of the nerves and the nodes associated with them, we can distinguish:
12 pairs of cranial nerves arise from different parts of the brain. The cranial nerves include the following types of fibers: autonomic, afferent and efferent.
The nuclei of the cranial nerves are located in the gray matter of the brain. Cranial nerves have their own names and are designated by Roman numerals.
I - olfactory nerve
II – optic nerve
IV trochlear nerve
Of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves, the fifth is the trigeminal nerve (V). Let's take a closer look at the nature of the trigeminal nerve.
Primary trigeminal neuralgia, secondary trigeminal neuralgia
There are primary trigeminal neuralgia (idiopathic, essential, typical) and secondary trigeminal neuralgia (symptomatic trigeminal neuralgia).
With primary neuralgia (mainly of central origin), attacks occur for no reason or are provoked by any movements of the facial muscles.
Secondary neuralgia is usually a complication of the primary disease, has a predominantly peripheral genesis and is often caused by pathological processes in the dentofacial area. The pain is almost constant, periodically intensifying in the form of attacks lasting up to several hours.
Content:
- Causes of the problem
- How does pulpitis manifest?
- Treatment methods 3.1. Conservative way of fighting 3.2. Surgical method
- If a pulpless tooth hurts
A dental disease in which the dental nerve becomes inflamed and acute pain occurs is called pulpitis. It is impossible to cope with it without medical help - not a single painkiller or anti-inflammatory drug will help relieve the symptoms that arise. Therefore, treatment of the tooth nerve is carried out exclusively in a dental clinic. Typically, it requires two visits to the dentist.
Trigeminal nerve, symptoms of trigeminal nerve damage, pathology
Damage to one of the sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve results in a disturbance of all types of sensitivity on the face of a peripheral type in the zone of innervation of this branch. In this case, symptoms : pain, decreased reflexes, extinction of reflexes. When the optic nerve is damaged, the conjunctival reflex, corneal reflex, and superciliary reflex are affected. When the motor part of the mandibular nerve is damaged, the mandibular reflex suffers. When the trigeminal nerve ganglion is damaged, all types of sensitivity in the area of 3 of its branches are lost, herpetic eruptions (herpes, herpetic blisters), and trophic disorders are often observed. A lesion of one of the sensitive nuclei in the pons results in a dissociated type of sensitivity disorder - superficial or deep. When the nucleus and oral parts of the spinal tract are damaged, a violation of superficial types of sensitivity in the mouth and nose occurs. If the caudal region is affected, sensitivity is impaired in the area of the outer part of the face. When the optic thalamus and the posterior third of the posterior limb of the internal capsule are affected, contralateral hypersthesia is observed on the face, trunk (body), and limbs (arms, legs) according to the hemitype. When the motor nucleus and its fibers are damaged, peripheral paresis occurs, which is characterized by symptoms such as insufficient muscle tension when chewing, muscle atrophy, retraction in the temple area, angle of the lower jaw, deviation of the lower jaw towards the affected side when opening the mouth. If bilateral peripheral paresis occurs, the lower jaw droops, as a result of which a man or woman cannot chew, cannot close his teeth, or close his mouth. Central paresis of the masticatory muscles on one side does not occur, since the corticonuclear fibers approach the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve from both hemispheres of the brain. With bilateral lesions, chewing becomes slightly more difficult (difficulty chewing), and the mandibular reflex is significantly enhanced. Small children have difficulty sucking.
Causes of the problem
Inflammation of the nerve of the tooth occurs for the following reasons:
- jaw injury;
- mechanical damage to the crown;
- oral infections;
- periodontitis;
- general hypothermia of the body;
- poor quality caries removal;
- osteomyelitis;
- advanced carious process.
Also, the pathology may be the result of a retrograde infection, which penetrates into the dental unit through the altered root system during an exacerbation of sinusitis or other ailment.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in Saratov, how to treat trigeminal neuralgia in Russia
Sarklinik provides comprehensive treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in children and adults, treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (nervitis, first, second, third branches) in Saratov, Russia, which includes effective reflexology methods. You can cure trigeminal neuralgia in Saratov!
Sarklinik knows how to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, how to cure neuralgia and trigeminal neuritis ! The following types of neuralgia are treated: neuralgia of the 1st (first) branch of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia of the 2nd (second) branch of the trigeminal nerve, neuralgia of the 3rd (third) branch of the trigeminal nerve in children and adults. On the website sarclinic.ru you can see a doctor online for free. If you have neuropathy, nerve damage, pain, a cold, the trigeminal nerve hurts on the left, right, you have a cold, a cold, inflammation on the face, paralysis, paresis, you don’t know how to relieve the pain , then contact a doctor at Sarklinik.
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Aniram | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Urinary incontinence, treatment of women, men, children, adults, postpartum, neurogenic bladder, spina bifida
Asthenia, asthenic syndrome, treatment, symptoms, causes, how to treat in children, adults
Neuralgia and neuritis, intercostal neuralgia: symptoms, treatment in Saratov
Polyneuritis, treatment of polyneuritis, alcoholic polyneuritis, polyradiculoneuritis
Obsessive neurosis: obsessive states, movements, treatment in Saratov, Russia
Comments ()
How does pulpitis manifest?
As a rule, this is a sharp, throbbing pain, quite intense at night. Intensifies when exposed to high or low temperatures. As well as sour, salty or sweet foods. Pressure on the tooth also causes pain. There may be bad breath caused by actively reproducing bacteria. The pain usually spreads to neighboring teeth and even to the other jaw.
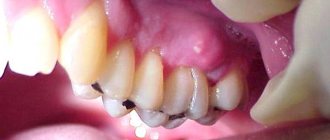
Sometimes soft tissue swelling occurs and the cheek swells. This is how flux manifests itself, which signals the occurrence of purulent processes.
Do not neglect visiting a doctor. After all, pulpitis is not just toothache. It can lead to many serious complications, ranging from tooth loss to blood poisoning.