Cutting through the “eights” is a painful process, which is often accompanied by elevated temperature. Most often, these four root formations begin to appear only in adulthood, which is why they got their popular name. Let's figure out what to do when the gums near the wisdom tooth are swollen, inflamed and painful.
Their additional name is third molars. This is the name of the 6th, 7th and 8th row, that is, that part of the jaw that is intended for chewing rough food. This determines their specific structure (large root base, width) and strength. But this is also the main root cause of painful processes during growth, because the larger the area of the upper edge, the more difficult it is to tear the skin and pass through it. Moreover, the bone tissue has already been formed, so the “eights” need to literally break their way, which leads to the formation of edema, suppuration, tumors and other unpleasant consequences.
Reasons: why the gums near the wisdom tooth become inflamed when it comes out
Remember the symptoms with which a six-month-old baby starts teething for the first time. Things are somewhat better for five- and six-year-olds. But in both cases, the same painful process occurs - the dental plate literally tears, injures the mucous membrane in order to erupt and come out. All this can cause pain, inflammation, and itching. Children are prepared for this procedure, while an adult experiences everything much more difficult, because over 20-30 or more years of life a person could have suffered many dental diseases, which only add to the difficulties.
In addition, the oral cavity is more likely to contain pathogens that spread due to food debris and bad habits. And bacteria can cause suppuration and intensify the infectious process.
The main reasons why gums hurt due to wisdom teeth are:
- Physiological structure of the jaw plate.
- Various diseases and pathological conditions.
Let's take a closer look at the factors and possible pathologies.
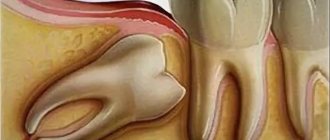
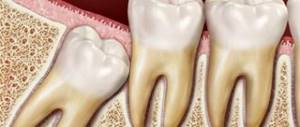
Atypical growth of the third molar
Most often, doctors encounter a situation where the figure eight erupts in the wrong direction. That is, it tends with its upper end not upward, but to the side. Thus, it “squeezes” the closest neighbors, and also pinches the nerve endings, leading to a shift in the entire row and even to malocclusion in cases where no measures were taken.
There are two types:
- Sloping location. During this process, the bone formation compresses the facial nerve and irritation occurs not only of the mucous membrane, but also of the cheeks or even the neck. The patient may mistakenly localize the pain as throat pain or confuse the symptom with an ENT disease.
- Horizontal. Even more dangerous, since the molar can compress the root system of the nearest “seven”, causing damage to the nerve endings and cutting off blood flow. All this will most likely lead to the destruction of the 7 and major inflammation of the gums near the wisdom tooth.
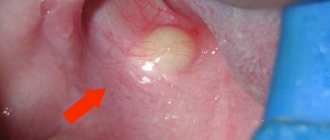
The occurrence of pericoronitis
This term refers to the appearance of a gum “hood” that covers part of the bone tissue. Food particles accumulate under the formed fold, creating an ideal environment for the development and spread of bacteria. Suppuration forms in the lesion, which leads to swelling, swelling of the area, bad breath and the release of purulent exudate when pressed. The latter does not always happen, since often the fold remains tightly closed.
There are several reasons for the occurrence of pericoronitis, including:
- Not enough space on the jaw plate.
- The dental sac is very dense, making it difficult to cut through.
- Thick mucous membrane, which also prevents successful rupture.
Additional symptoms include pain when chewing and swallowing food. With such a pathology, but the correct direction of growth, dentists most often make an incision in the skin fold and sanitize the area with the complete elimination of pus and other signs of infection.
Inflammation of the tissues of the wisdom tooth due to gum disease
Often the “eight” erupts painfully. The back of the jaw begins to hurt and bleed. The most common diseases that occur in patients:
- Gingivitis – the marginal area of the gum, as well as the entire mucous membrane, is subject to an inflammatory process.
- Periodontitis – the surrounding tissue structures are destroyed, which leads to poor stability of the dental plates. They may begin to loosen, and if the disease is serious, they may even begin to fall out.
- Periodontal disease is a severe lesion of the periodontium, which is located near the root.
In all of these cases, the most common symptoms are:
- Swelling.
- Bleeding.
- Pain.
- Redness.
The nearby third molar begins to grow, affecting the affected mucous membrane and nerve endings, provoking even greater pain, which can be accompanied by the appearance of a tumor and even suppuration. When treating, it is necessary to first pay attention to the root cause.
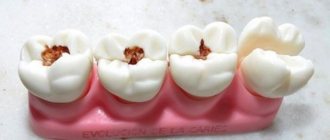
The gums under the wisdom tooth hurt due to caries
In this context, we are not talking about the teething itself, but about the further development of the “eights”. They, like other rows, can be subject to carious changes. This is a long process that develops due to the action of pathogenic microorganisms and additional unfavorable factors. It passes slowly and leads to disruption of the integrity of bone tissue. Cavities are formed, the expansion of which can cause a lot of inconvenience, as well as expose nerve endings. Therefore, caries-prone molars are usually removed. They are healed only in cases where they are planned to be used in the future to install implants.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Its structure is branched and literally covers the entire face, dividing into three bundles:
- ophthalmic;
- maxillary;
- mandibular.
During the eruption of the 8, pinching or squeezing, or irritation may occur. This also happens when the dentition moves apart (horizontal atypical growth), and at the time of extraction. Usually the pain is very strong, shooting. And its localization depends on what exactly was pinched.
Causes of pericoronitis
The disease most often results from:
- epithelial injuries due to difficult long-term tooth eruption;
- impacted (formed, but not erupted outward) teeth;
- atypically located tooth roots;
- thickening of the gum mucosa;
- accumulation of soft plaque under the hood and, accordingly, infection of tissues;
- reduction in the size of the dental arch, lack of space for teething;
The catalyst for pericoronitis of wisdom teeth is often a source of infection in the oral cavity. Very often the disease is provoked by caries, stomatitis or periodontitis. Sometimes the disease occurs against the background of ignoring the rules of personal hygiene, prolonged stress, hypovitaminosis and other conditions accompanied by decreased immunity.
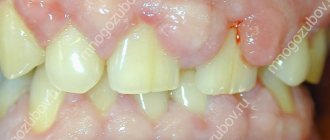
Symptoms when gums hurt from wisdom teeth
It is quite difficult not to notice this manifestation, since the pain that arises is considered one of the most powerful. But if they are localized incorrectly, you can confuse a dental problem with otitis media (shooting in the ear) and other ENT diseases. Symptoms of inflammation are as follows:
- Pain that worsens when chewing food.
- The mucous membranes around are swollen.
- Cheeks, lips, cheekbones became swollen.
- The second and third molars may become loose.
- Formation of a purulent fistula.
- Changes in the color of the integument; they can become deep red, white or bluish.
- Bleeding, especially when brushing with a toothbrush.
- The affected area becomes hot. Often the process of teething occurs in conjunction with a general increase in body temperature.
- Halitosis, that is, bad breath.
- Large and painful lymph nodes on palpation.
- Pain when swallowing and forcefully opening the mouth.
- Itching, pulsating sensation.
But sometimes it happens that the appearance of crowns is accompanied only by the fact that the gums above the wisdom tooth are swollen, but there are no additional symptoms. But it is still necessary to visit the dentist, since the formation of pathology can occur in a hidden form. For any dental services you can contact the Dentika clinic. Professional dentists and polite medical staff work here.
Can third molars be treated?
Wisdom teeth, like any other teeth, can be treated. But only if they erupt correctly, do not threaten the health and position of the rest of the dentition, and there is confidence that the treatment will be successful. If the specified conditions are met, it makes sense to preserve the “eight” for the following indications:
- If the sixth and seventh teeth are sick or severely damaged and must be removed, in this case the wisdom tooth is left as “the best of the worst” in order to provide the patient with at least some conditions for chewing, and the doctor - the basis for future prosthetics.
- If the six and seven have already been removed and it is necessary to preserve the abutment tooth for installation of prosthetic structures.
- In the presence of an antagonist tooth, completely healthy and subject to preservation.
In case of curved roots that complicate endodontic intervention, severe tissue destruction, dystopia or retention, no competent dentist will undertake to treat the “eights” - he will definitely recommend removal.
What to do in case of inflammation
The first right decision is to see a doctor.
Depending on the nature of the discomfort, the teething process may be complicated by additional diseases. Only a dentist (often a surgeon) can solve the problem, who, as a rule, cuts the dental “hood”, or prescribes pulling it out along with the root, or, less often, removing the nerve. But the condition can be alleviated if the gums behind the wisdom tooth become inflamed, even at home. We will present several effective methods.
List of painkillers
Analgesics are intended to relieve pain. They block nerve impulses that travel from the spasmodic area to the brain.
You need to understand that taking such tablets is not a panacea, but only the elimination of a symptom, and the effect lasts on average for 8-12 hours. We strongly recommend that you do not abuse analgesics and do not prescribe them yourself. Be sure to contact your dentist if problems arise. When visiting the clinic, a specialist may prescribe for you:
- "Tempalgin". Additionally lowers the temperature. Daily dose – 3 capsules with an equal time interval.
- "Ketanov." A very effective medicine that helps relieve mild fever. You cannot take it for more than 2 days in a row at a dosage of 10 mg every 4-6 hours. Therefore, it is used as an emergency aid, for example, before visiting a doctor.
- "Ascophen." Consists of acetylsalicylic acid and paracetamol. You need to take 1-2 tablets three times a day after meals.
- "Xefocam." A non-steroidal drug that mainly consists of lornoxicam. Drink no more than 16 mg per day, dividing the medicine into 2-3 doses.
Anti-inflammatory therapy when the gums near the wisdom tooth are inflamed
You can relieve inflammation with local preparations (ointments) or medications. The dentist may advise:
- "Nise." You can take no more than 200 mg per day.
- "Nurofen" based on ibuprofen. You are allowed to drink 4 capsules every day.
- "Nimesil". Sold as a powder for suspension, it perfectly eliminates redness, swelling and pain.
Ointments and gels
They promote local anesthesia. The good thing is that you can use them without actually worrying about your general condition. Some of them, for example, are allowed during pregnancy. Another advantage is that they can be applied more often - after each meal and simply as needed. But before use, be sure to read the instructions and consult a doctor. They are usually prescribed to relieve mild symptoms with normal upward eruption, without additional pathologies. Compositions:
- "Dentinox."
- "Traumeel S".
- "Cholisal."
- "Kamistad".
Folk remedies that will help if the gums are inflamed and very painful, where the wisdom tooth is
Rinsing is also good for pain, has an antiseptic effect, relieves inflammation and redness. Suitable for these purposes:
- Soda solution with salt.
- Tincture of calendula leaves and/or chamomile flowers.
- Oak bark decoction.
If you feel unwell, do not self-medicate. Go for a consultation with a specialist who will give you a personal prescription and provide assistance.
Surgery
Excision of the fold is necessary when the sensations become unbearable, the “hood” becomes very inflated, swollen, and a purulent focus forms inside. In this case, the surgeon removes the upper part of the gum and rinses the contents of the sac.
Removal
This is usually required when the “eight” grows in the wrong direction and can injure a nearby tooth or damage nerves. It is also recommended for significant carious lesions.
Types of pericoronitis
Depending on the complexity and localization of inflammation, pericoronitis is divided into:
- Spicy.
The initial stage of the disease, which is characterized by pain, hyperemia and swelling of the gums. In case of acute pericoronitis of a wisdom tooth, there is no purulent discharge and the general condition of the patient does not suffer. With proper timely treatment, this type of disease disappears in 3-5 days.
- Ulcerative.
The disease develops against the background of epithelium damaged by fusospirochetes. A characteristic symptom of ulcerative pericoronitis is the appearance of a necrotic rim along the edges of the gums. Small ulcers form on the mucous membrane. When plaque is removed from the gum surface, bleeding begins.
- Purulent
Pericoronitis, as a rule, occurs in a subacute form and is manifested by severe pain. Pus is released from the source of inflammation, and the temperature rises. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease can provoke the formation of abscesses, phlegmon and periostitis.
- Posteriormolar.
The disease develops when molars erupt incorrectly. A gingival hood forms, which then becomes infected due to the active proliferation of bacteria.
Prevention
It is virtually impossible to change the atypical arrangement of 8s. But it is possible to prevent the pain that occurs due to dental disease. To do this, you should carefully observe daily hygiene, as well as regularly make an appointment with the dentist to heal diseased areas. Also change your toothbrush once a month, rinse after every meal, and floss.
In the article, we told you what to do if the gums near your wisdom tooth are inflamed and painful, and what medications will help solve this problem. Contact Dentika dentistry in a timely manner so that the doctor not only relieves the symptoms, but also eliminates the cause of the sensations.
Possible consequences
Pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth in the lower jaw is a rather dangerous disease, ignoring which can lead to very unpleasant consequences.
Possible complications of the disease may be:
- abscesses, phlegmon of the vestibule of the mouth, buccal area;
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis of the jaw;
- periodontitis;
- ulcerative stomatitis;
- actinomycosis;
- paradental cysts.
In addition, if wisdom tooth pericoronitis affects the lymph nodes, if inflammation develops, the lymphatic system may become a victim of infection.
And, of course, without proper treatment, the disease can become chronic and periodically “harass” the patient with unpleasant symptoms. Inflammation can spread to neighboring healthy teeth. Therefore, in order to avoid complications, treatment of the disease should be carried out as early as possible.
Removal Features
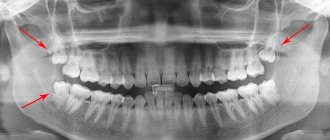
As a rule, operations to remove third molars are always considered difficult, since these are the teeth that usually cause more problems. The operation can be simple, provided that the “figure eight” is located on the upper jaw and does not have pronounced developmental abnormalities. In all other cases (as well as in situations where the tooth is in the upper jaw, but has strong, curved and branched roots), the operation is considered complex and must be performed by a qualified dental surgeon.
Before performing an intervention, the doctor determines possible contraindications for a particular patient, examines an x-ray of the problem area and determines the optimal tactics for the operation. The duration of the procedure ranges from 1-10 minutes for simple removal and up to 20-120 minutes for complex removal, requiring a series of manipulations and suturing of the hole.