October 7, 2019
A bitter taste in the mouth that constantly occurs is a reason to be wary and go to a doctor for examination. An unpleasant phenomenon does not always indicate that a serious disease has developed in the body, but the percentage of cases where the causes of its occurrence are completely harmless is very small. The editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal advise you to read the article in order to have useful information on this topic and to rule out possible pathologies in time.
There can be many causes of bitterness in the mouth
Gallbladder and liver diseases
If the taste of bitterness in your mouth has become your constant companion, then the first thing to rule out is stagnation of bile, which occurs due to pathologies of the gallbladder and liver. Bile is produced in the liver, then it enters the gallbladder, where it is stored until food enters the stomach. This beneficial liquid helps the stomach digest food. As soon as you eat, bile enters the duodenum - this is a natural phenomenon. With pathologies of the gallbladder and liver, the fluid does not come out completely or stagnates, a lot of it is formed, and a bitter taste appears in the mouth.
In case of pathologies, our internal organs try to get rid of bile and can even arrange an “emergency discharge” of it, causing some of the liquid to enter the esophagus and even the oral cavity.
In case of liver disease, it can cause bitterness
What does bitterness in the mouth mean? The phenomenon may indicate the development of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cancer, dyskinesia (impaired motility of the gallbladder). Unpleasant sensations in the mouth appear most often in the morning, as soon as you wake up, and also after playing sports. They may be accompanied by tingling and discomfort in the right hypochondrium, belching, dry mucous membranes, and indigestion. The bitter taste may alternate with a metallic or “iron” taste.
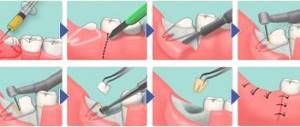
Treatment of dental alveolitis
The main tasks facing the dentist:
- elimination of the infectious focus;
- eliminating the risk of developing complications of dental alveolitis;
- maintaining healthy teeth.
To do this, he injects the patient with anesthesia and performs mechanical cleaning of the hole, removing pus and necrotic fragments from it. If tissue decay covers a large area, drugs that selectively destroy dead tissue are used to treat alveolitis of the tooth socket. The affected area is treated with antiseptic agents, and an application of anti-inflammatory pharmacological drugs is made. Depending on the situation, an Alvostaz compress or an iodoform gauze swab can be used.
Since the treatment is carried out in a complex, the dentist may additionally prescribe:
- physiotherapy that stimulates tissue regeneration;
- treating the inflamed area with Chlorhexidine or Hexoral;
- taking antibiotics or anti-inflammatory pharmacological drugs that have an analgesic effect.
If the patient strictly follows all the recommendations, the clinical manifestations of alveolitis will disappear within a week, and the hole will heal within half a month.
Dental diseases
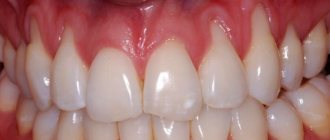
A bitter taste in the mouth sometimes has quite obvious reasons for its occurrence, both in women and men. It can be caused by pathogenic bacteria that multiply due to poor hygiene, inflammation of the gums, the development of gingivitis and periodontitis, caries, pulpitis, and periodontitis. Then in almost all cases it will be accompanied by the appearance of bad breath, and there may also be signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane: bleeding and swelling of the gums.
Inflammation and bleeding of the gums causes this problem.
Galvanic syndrome
Do you have a bitter taste in your mouth and are wondering what it means? Perhaps the problem lies in the fact that you have dentures made of dissimilar metals installed in your mouth.
Read the article on the topic: electric current in the mouth. Find out what to do to recover quickly!
The problem needs to be solved, because if everything is left as is, the disease will progress, general health may worsen, and nervous disorders may begin.
Galvanosis can occur from different metals
Gastrointestinal diseases
What does bitterness in the mouth mean? There is a very high probability that the culprit is diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which are accompanied by such a phenomenon as reflux. For example, gastritis, pancreatitis, ulcers, colitis, enteritis. Reflux is the release of acid from the stomach into the esophagus and larynx. To get rid of acid, our salivary glands begin to secrete alkaline saliva, which extinguishes this acid. This saliva has a very bitter taste and is accompanied by heartburn. With such pathologies, the tongue acquires an unhealthy yellowish tint.
With gastrointestinal disease, a yellow coating appears on the tongue and an unpleasant taste
Intestinal parasites
A bitter taste in the mouth may indicate extremely unpleasant reasons. For example, the fact that parasites (giardia or helminths, pinworms and roundworms) have appeared in the body and are actively living. Parasites literally stick to the inner lining of the small intestine, which causes its reflex contraction, as well as tissue damage. As a result, indigestion occurs and gastrointestinal pathologies occur.
Parasites can also cause this symptom
Nowadays, it is not so easy to catch these parasites, but small children who put everything they can and cannot put into their mouths still quite often become victims of parasites, and adults can also become infected from them. Often helminthic infestations are called the “dirty hands” disease.
Neuropsychiatric disorders
If there is a bitter taste in the mouth, on the tongue and on the lips, then here's what it can mean: the person has developed severe depression1, chronic stress or schizophrenia.
Surprisingly, even ordinary stress or nervous overstrain can contribute to the appearance of bitterness, and our physiology is to blame for everything: in the process of a nervous breakdown, all organs become tense (this occurs due to the release of adrenaline and norepinephrine into the blood), the tone of the gallbladder is disturbed, and muscle spasms occur. .
Stress can contribute to bad taste
Thyroid pathologies
When bitterness in the mouth has become a symptom that accompanies you constantly, what does it mean? The reason may again lie in the reflux of bile into the esophagus, but in this case, such a phenomenon is provoked not by pathologies of the liver and gallbladder, but by disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system and hormonal imbalance. For example, this serves as one of the symptoms of diseases such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus. With diabetes, in addition to bitterness, a person may experience dry mucous membranes, but sweating, on the contrary, increases - these are signs of increased blood sugar levels. Also, with all of the above pathologies, the taste of iodine may periodically appear.
Improper functioning of the thyroid gland can cause pathology
Why you don’t need to remove white plaque after tooth extraction
In some cases, patients intentionally or accidentally remove a blood clot or fibrinous film from the socket. This is not necessary, since removing a clot or film can provoke negative processes.
First of all, an open wound provides access for bacteria to the circulatory system and tissues of the maxillofacial apparatus. Infection can cause serious consequences and require long-term treatment with antibiotics. Also, removing the clot and white plaque increases the pain, since an open wound is more sensitive to any irritants, including drinking drinks and food, during a conversation.
Finally, plaque on the gums after tooth extraction does not need to be cleaned off because this can cause re-bleeding and prolong the wound healing stage.
In any case, there is no need to intentionally remove plaque; this can cause:
- serious complications;
- severe pain;
- improper gum formation;
- long recovery process after tooth extraction.
To avoid accidentally damaging the socket, blood clot or fibrinous film, you must follow the recommendations given by the doctor after the operation.
Causes of bitter taste not associated with serious illnesses
- consumption of low-quality and stale food: a bitter taste in the mouth often appears due to the consumption of expired or specific food products. For example, pine nuts are rich in healthy fats, but if they are stored for too long, the fats in them begin to oxidize and become bitter.
- overeating at night: especially if the food was fatty and “heavy”. A similar phenomenon is also caused by products that provoke increased gas formation in the intestines (cabbage, beans, baked goods),
- love for carbonated drinks: champagne, mineral water with gas,
- drinking alcohol,
- decreased activity of taste buds: this problem is most often encountered by older people, whose hormonal levels change with age and some receptors become insensitive. A problem also arises for people who smoke, because... with constant exposure to smoke on the mucous membrane, dystrophy of the taste buds occurs,
- taking medications and herbal decoctions: choleretic, as well as antifungal and antihistamines can have this effect,
- pregnancy: the taste of bitterness in the mouth and the reasons for its appearance in women are often associated precisely with bearing a child. The symptom is typical for the second half of pregnancy, since it is during this period that the growing and developing child begins to put pressure on the internal organs and displace them, which increases the likelihood of bile reflux into the esophagus,
- hormonal changes in the body: for example, in women at the onset of menopause,
- a lack or excess of vitamins in the body: for example, a lack of zinc or an excess of B12 contributes to the appearance of a bitter taste.
Pregnancy often causes nausea and bitterness in the mouth
Authorized Products
- Beef, turkey, lamb, chicken, lean pork - the meat is cooked boiled, baked, you can make dishes from boiled and rolled meat, as well as steamed cutlets, soufflés or quenelles.
- You can bake it with milk or sour cream sauce, without a rough crust.
- Soups can be prepared with weak meat broth, but it is better with vegetable broth. Cereals and vegetables are not rubbed (chopping and grinding is necessary in the presence of duodenitis, esophagitis or gastritis in the acute stage). Ready-made soups can be seasoned with butter and egg-milk mixture.
- It is not recommended to fry soups.
- Dried gray bread, bread with bran. Any fresh bread causes bloating.
- Dishes from low-fat and moderately fatty fish - boiled lumpy fish and steamed (baked) cutlets.
- Any cereals are allowed. With concomitant gastritis, duodenitis and colitis, preference is given to coarse cereals (semolina, buckwheat, rice) and corn, pearl barley, and millet are excluded. They are boiled in water or with milk and served raw.
- Milk is added to dishes, and if tolerated well, you can drink whole milk, make jelly or milk cream.
- Non-acidic kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk or yogurt should be included in the diet daily. Cream and sour cream should also be chosen that are not very fatty and used when preparing dishes.
- Medium-fat cottage cheese is consumed in its natural form, as well as in the form of casseroles, soufflés or puddings.
- Butter and vegetable oils (up to 2 tablespoons per day) are added to prepared dishes.
- For drinks, preference is given to tea with milk, natural fruit teas, juices from sweet fruits, rosehip infusion and herbal teas (mint tea, which increases reflux, is excluded).
- Any vegetables (excluding sorrel, radish, spinach, radish, mushrooms, fresh garlic) are consumed baked, boiled and raw. You can make a stew from prefabricated vegetables, puree from various vegetables, salad from fresh vegetables with butter. The ratio of raw and thermally processed vegetables is determined by individual tolerance.
- With increased bloating, which can be caused by raw vegetables, and the appearance of pain in the intestines (with concomitant colitis), the quota of raw vegetables in the diet is significantly reduced in favor of boiled and baked ones.
- With concomitant esophagitis and duodenitis, only non-coarse vegetables with a low fiber content (beets, cauliflower, zucchini, pumpkin, potatoes, carrots) are allowed and only in boiled form.
- Sweet fruits are consumed raw, baked, in the form of purees, jelly, jellies and compotes.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried figs | 3,1 | 0,8 | 57,9 | 257 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| pearl barley | 9,3 | 1,1 | 73,7 | 320 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| noodles | 12,0 | 3,7 | 60,1 | 322 |
| buckwheat noodles | 14,7 | 0,9 | 70,5 | 348 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| milk candies | 2,7 | 4,3 | 82,3 | 364 |
| fondant candies | 2,2 | 4,6 | 83,6 | 369 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
| Maria cookies | 8,7 | 8,8 | 70,9 | 400 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
Eggs | ||||
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| peach juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,5 | 40 |
| plum juice | 0,8 | 0,0 | 9,6 | 39 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
The “character” of bitterness will tell you about the problem
If you have a bitter taste in your mouth and are thinking about what it all means, then see the table below.
| Symptom | Possible pathology |
| Bitterness appears in the morning | It is necessary to check the liver and gallbladder |
| The taste accompanies constantly | Gallstone disease, cholecystitis, gastrointestinal oncology, hormonal imbalance, thyroid problems, mental disorders |
| An unpleasant symptom appears after you have eaten | Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and duodenum, consumption of poor quality food |
| The taste is present situationally, for a short time | Taking medication, taking antibiotics, smoking, allergies, stress |
| Bitterness + bad breath | Dental diseases (gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease), gastrointestinal problems. |
| Bitter taste combined with heartburn | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
However, we advise you not to engage in self-diagnosis, but to go to see a doctor who can definitely confirm or refute the diagnosis based on blood tests, examination and ultrasound. To begin with, it is better to visit a gastroenterologist; you also need to see a dentist who will rule out diseases of the oral cavity.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 13 ratings, average: 4.46 out of 5)
prevention
- Smulevich A.B. ‹‹Depression in general medicine: A guide for doctors››. Section VII. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Recognizing depression.
Consulting specialist
Bersanova Dana Borisovna
Doctor rating: 9 out of 10 (5) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 17 years
Fully or partially limited products
- Mushrooms in any form, pickled and pickled vegetables.
- Fatty meat, canned food, smoked meats, strong meat/fish broths, marinades, duck and goose meat, hot sauces and sauces with preservatives and colorings, cubed broths, dishes with the addition of mayonnaise.
- Fried dishes, mushroom decoctions, stewed meat and fish - due to the high content of extractive substances.
- Sour berries and fruits.
- Fresh onions and garlic, radishes, white cabbage, sorrel, radishes, legumes are irritating and cause bloating. Especially contraindicated for duodenitis and esophagitis.
- Fresh bread, puff pastry, yeast and butter pastries.
- Seasonings, spices, ketchup, tomato paste, vinegar, horseradish, mustard, lemon juice - increase reflux.
- Carbonated drinks, sour juices (citrus, tomato, pomegranate, currant), alcohol, strong coffee and tea, wine, beer, mint tea.
- Halva, chocolate and chocolate candies.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| peas | 6,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 60 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| chickpeas | 19,0 | 6,0 | 61,0 | 364 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
Snacks | ||||
| potato chips | 5,5 | 30,0 | 53,0 | 520 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| vareniki | 7,6 | 2,3 | 18,7 | 155 |
| dumplings | 11,9 | 12,4 | 29,0 | 275 |
Bakery products | ||||
| buns | 7,9 | 9,4 | 55,5 | 339 |
| Rye bread | 6,6 | 1,2 | 34,2 | 165 |
Confectionery | ||||
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| shortbread dough | 6,5 | 21,6 | 49,9 | 403 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream 35% (fat) | 2,5 | 35,0 | 3,0 | 337 |
| whipped cream | 3,2 | 22,2 | 12,5 | 257 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| parmesan cheese | 33,0 | 28,0 | 0,0 | 392 |
Meat products | ||||
| fatty pork | 11,4 | 49,3 | 0,0 | 489 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| bacon | 23,0 | 45,0 | 0,0 | 500 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| salmon | 19,8 | 6,3 | 0,0 | 142 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| salmon | 21,6 | 6,0 | — | 140 |
| trout | 19,2 | 2,1 | — | 97 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| dry red wine | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 68 |
| vodka | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,1 | 235 |
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| soda water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Comments
I am diagnosed with gallbladder dyskinesia. I take the medications prescribed by the doctor, they always helped well, but recently they stopped helping, the bitterness appeared again and plus there was added pain in the right side. What to do?
Aly (10/27/2019 at 09:10 pm) Reply to comment
- First of all, you need to contact your doctor so that he can evaluate the changes, adjust your medication intake and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists. A surgeon may be needed to rule out appendicitis and other abdominal diseases that require surgery. You should not self-medicate.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (02.11.2019 at 09:19) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Menu (Power Mode)
Mechanically gentle nutrition (mashed dishes) is indicated only during exacerbation of diseases. The rest of the time, no sparing is provided. Milk is usually well tolerated, so you can eat milk porridge for breakfast and dinner, supplementing your diet with egg dishes or cottage cheese. Meat or fish dishes are best served with boiled and fresh vegetables.
If you have a “lazy” gallbladder, you need to include vegetables in any form at every meal; eat bran separately, 1-2 tbsp. per day and vegetable oils (in porridges and salads). When consuming bran, do not forget to drink enough.
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|