Do you have a sharp sore throat, painful swallowing and a fever? This may be tonsillitis, which can occur in acute or chronic form. Often, in the absence of adequate treatment, the acute form of the disease becomes chronic. And chronic, in turn, can occur with periods of exacerbation and remission.
With tonsillitis, the main immune barrier of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, the palatine tonsils, is primarily affected. Their main function is to protect against foreign viruses and bacteria entering the body.
Causes
The causes of tonsillitis are various pathogenic microorganisms:
- streptococci in the throat;
- candida;
- Moraxella;
- herpes viruses;
- chlamydia;
- staphylococci;
- adenoviruses;
- pneumococci;
- Epstein-Barr virus.
Factors that contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- injuries;
- breathing through the mouth;
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged inflammation in the nasal cavity or mouth.
How to diagnose a sore throat?
The main method of making a correct diagnosis remains culture of a throat smear for hemolytic streptococcus. Currently, express methods have been developed that make it possible to identify this pathogen in 90% of cases. But even if microbiological analysis is carried out using the standard method of growing a colony of microorganisms on special media, it is better to wait for its results before prescribing treatment for sore throat in children with antibiotics. Haste here is not justified, since it has been proven that starting the treatment of sore throat in children with these medications on the 2-3rd day of illness effectively prevents its complications.
A good knowledge of the clinical picture helps the doctor distinguish between viral and bacterial forms of acute tonsillitis. If the disease is caused by viruses, then usually children with tonsillitis have the following symptoms: cough, runny nose and other catarrhal phenomena, the tonsils are red and covered with a loose white coating, mucus is visible on the back wall of the pharynx (rhinopharyngitis), conjunctivitis is often observed. Streptococcal tonsillitis differs from viral tonsillitis in the absence of cough and minimal catarrhal symptoms, but sometimes it is accompanied by soreness of the lymph nodes.
Classification
Tonsillitis can be acute or chronic.
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis), depending on the clinical characteristics, is divided into the following forms:
- Catarrhal is the mildest and goes away quickly with the necessary treatment.
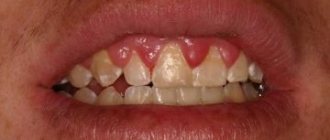
- Lacunar - the mucosa is covered with pus-filled depressions that can cover the entire surface of the tonsils.
- Follicular - small cavities are formed filled with pus.
- Phlegmonous - the affected tonsil is red and enlarged in size, a purulent plaque forms, under which the tissue of the tonsils can melt, forming phlegmon.
- Fibrinous - the tonsils are covered with a yellowish film, which can spread beyond the tonsils.
- Herpetic - blisters form, which gradually fester, dry out, and become crusty. Accompanied by abdominal pain, vomiting, fever, diarrhea.
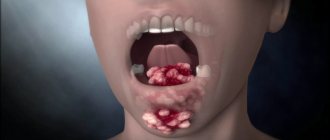
- Ulcerative-necrotic - the tonsils are covered with ulcers under which the tissues die, if they are torn off they will bleed. Gray or greenish plaque, putrid odor from the mouth.
Chronic tonsillitis can be simple and toxic-allergic. Simple chronic tonsillitis manifests itself only with local symptoms, toxic-allergic is accompanied by a significant deterioration in the general condition of the body (lymphadenitis, complications of the cardiovascular system, joints, kidneys, etc.)
Complications of bacterial tonsillitis
Depending on what causative agent of sore throat is identified and how long the treatment is delayed, the risk of complications increases. Thus, staphylococcal tonsillitis is dangerous due to the development of a pharyngeal abscess due to the spread of inflammation inside. Streptococcal tonsillitis threatens to damage the heart, kidneys and liver and can provoke rheumatism or glomerulonephritis, lower back pain.
The likelihood of complications with bacterial tonsillitis is higher than with viral tonsillitis, so you need to seek medical help in a timely manner and not attempt treatment on your own.
At the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, otorhinolaryngologists will quickly conduct an examination, identify the pathogen and prescribe treatment. Our specialists regularly undergo training and improve their skills; they use modern physiotherapeutic techniques and drug therapy regimens in treatment.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Common symptoms of tonsillitis in adults are:
- swelling of the tonsils, soft palate, uvula;
- the presence of plaque, sometimes there are ulcers;
- signs of intoxication: pain in muscles, joints, head;
- malaise;
- pain when swallowing;
- diarrhea, vomiting (most often these symptoms of sore throat occur in young children).
The incubation period for tonsillitis can last from 6-12 hours to 2-4 days. The deeper the tissues are affected, the more complex the disease, the longer the infectious-inflammatory process progresses and the higher the risk of complications. In children, the most common form of tonsillitis is the catarrhal form of tonsillitis, which, without effective treatment measures, can develop into the follicular stage or chronic tonsillitis.
Chronic tonsillitis is characterized by periodic exacerbations (after hypothermia, emotional stress and other factors). The symptoms of chronic tonsillitis are less pronounced than those of acute tonsillitis. There is usually no pain or fever; there may be only slight pain when swallowing, a sore throat, and bad breath. The general condition of the body worsens, but this is less pronounced than with acute tonsillitis.
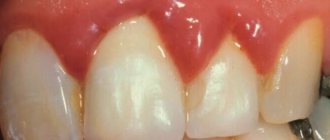
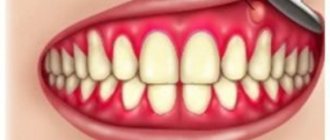
A characteristic symptom of tonsillitis is a noticeable enlargement of the tonsils. In acute tonsillitis, the palatine tonsils are bright red; in chronic tonsillitis, they are stagnant red. Depending on the form of the disease, the tonsils may be covered with plaque, films, pustules, and ulcers.
Symptoms of bacterial sore throat in children
Babies under one year old are very difficult to tolerate the disease. Parents notice the following signs of illness:
- Drowsiness, decreased or lack of appetite, crying and moodiness.
- Refusing the bottle.
- Vomiting after eating.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Increased salivation.
- Temperature rises to 40°C.
Older children experience the same symptoms as adults. They complain of discomfort in the throat and pain when eating, so they eat practically nothing. Outdoor games give way to sleep. The voice becomes hoarse, and sometimes the pain in the throat radiates to the ears.
Complications
Advanced tonsillitis can cause the development of other diseases, disability and even death. At the same time, doctors divide its complications into:
- Early - they appear even before complete recovery. Most often these are purulent capsules in the pharynx, inflammation of nearby organs and tissues, which can develop into sinusitis, otitis media, purulent lymphadenitis, peritonsillitis, meningitis or mediastinitis (leakage of pus into the chest cavity).
- Late – they can occur after a few weeks. This is glomerulonephritis, rheumatic carditis or articular rheumatism.
Treatment of tonsillitis
Acute viral tonsillitis. If inflammation of the tonsils is caused by a common ARVI, then treatment in adults is carried out as follows:
- Drink plenty of fluids, predominantly a dairy-vegetable diet, rest.
- Frequent rinsing with decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs and antiseptic solutions. Usually these are rivanol, chlorhexidine, iodinol, decoctions of sage, calendula, chamomile.
- Resorption of tablets (lozenges) with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects: lisobakt, lizak (active ingredient - lysozyme), strepsils, travesil and others.
- Antibacterial agents for viral sore throat are prescribed in cases where a secondary infection has occurred.
- If the temperature rises above 38.50C, take antipyretics. In this case, preference is given to drugs that contain paracetamol or ibuprofen (Nurofen). It is strictly forbidden to give aspirin to children as a medicine to reduce fever. If the temperature remains high, then the doctor may prescribe nimesulide (nimesil, nimegesik) to adult patients and children over 12 years of age, and at a younger age - analgin with diphenhydramine or its analogues.
Acute bacterial tonsillitis. The same drugs are used as for viral tonsillitis, and mandatory treatment with antibiotics is also carried out, which are selected based on the sensitivity of the specific pathogen.
Among the means of antibacterial therapy, doctors most often prescribe:
- amoxicillin with clavulonic acid (augmentin, amoxiclav, flemoclav and others);
- cephalosporins (cephalexin, ceftriaxone);
- macrolides (azithromycin, clarithromycin);
- fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ciprolet).
Antibiotics can be prescribed either orally or by injection. Often, treatment of tonsillitis in children is carried out with protected amoxicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides.
Acute tonsillitis caused by a fungal infection. Treatment of tonsillitis caused by fungi usually begins with the abolition of antibacterial agents, which increase dysbiosis of the mucous membranes. Instead, depending on the severity of the disease, antimycotic drugs are prescribed - nystatin, quinozol, levorin (these can be drugs for oral administration or local treatment of the throat). In addition, it is recommended to periodically lubricate the tonsils with aqueous solutions of aniline dyes, for example, methylene blue.
Drug treatment, do you need an antibiotic?
Treatment of tonsillitis in a child should be comprehensive!
To treat tonsillitis in a child, the following groups of medications are used:
- Antiseptics. These include special solutions for rinsing and treating the inflammatory focus, as well as various aerosols for irrigating the oropharynx: Hexasprey, Miramistin, Tantum Verde, Hexoral, Cameton.
- Antihistamines. These drugs are used to relieve swelling of the tonsils and pharyngeal mucosa. The best drugs in this group are considered to be the latest generation of drugs that do not have sedative properties: Cetrin, Suprastin, Telfast.
- Analgesics. Used for acute pain when swallowing and sore throat.
- Immunomodulatory drugs. For children from this group of drugs, it is advisable to use natural-based immunomodulators.
- Antipyretics. They are used in case of high temperature in a child - more than 38 degrees. Children are usually prescribed Paracetamol or Nurofen.
In addition, the otolaryngologist can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures for tonsillitis. For example, in the chronic form, it is recommended to undergo laser treatment twice a year. Specialists often prescribe ultraviolet irradiation, climatotherapy, and aromatherapy.
One of the frequently asked questions by parents is: “Do I need to take antibiotics for tonsillitis?” Otolaryngologists necessarily prescribe antibacterial drugs for exacerbation of the chronic form of the disease, as well as for acute tonsillitis, the causative agent of which is pathogenic bacteria.
Useful video - How and when to remove tonsils:
The best syrup for dry and wet coughs for children under one year old
Children are usually prescribed drugs of the penicillin, macrolide and cephalosporin group. Such antibiotics for the treatment of tonsillitis include Sumamed, Augmentin, Flemoklav Solutab, Clarithromycin, Azithromycin, Cefadroxil.
To prevent the development of dysbiosis during antibiotic treatment, probiotics are used, for example Linex, Laktovit, Hilak Forte.
It is important to remember that such drugs are prescribed by an experienced otolaryngologist. Parents, in order to avoid aggravating the problem, as well as not to harm their child, are not allowed to independently select medicine and treat the patient with it. The choice of antibiotic is made taking into account the individual characteristics of the child’s body, the form and severity of the disease, and it also depends on the pathogen that provoked the development of the disease.
- Why do joints hurt after a sore throat - complications in acute and chronic tonsillitis
Gargling and inhalation
At elevated body temperatures, inhalation is prohibited!
The complex treatment of tonsillitis in children also includes a rinsing procedure. It is done using medicinal solutions such as Furacilin, Miramistin, Iodinol. It is recommended for young children to treat their tonsils with a gauze swab, since they do not yet know how to gargle properly.
The rinsing procedure can be done with saline solution. The finished drug can be purchased at pharmacies. At home, you can prepare it by dissolving a teaspoon of salt, preferably sea salt, with boiling, cooled water. You can rinse the oropharynx with a solution with the addition of essential oils or infusions of medicinal herbs, for example, calendula, chamomile, marshmallow, sage, St. John's wort. You can treat the disease by gargling with beet juice.
Inhalations are considered an effective method of treatment for tonsillitis.
It is better for children to do them using a special device that can be purchased at pharmaceutical institutions. This device is called a nebulizer.
Inhalations are carried out using various medicinal solutions. Procedures using herbal decoctions are also considered safe and effective for children. For these inhalations, you can use the following plants, which have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties:
- Sage
- Eucalyptus
- Calendula
- Pine needles
- Oak bark
- Coltsfoot
- Chamomile
It is useful to perform inhalations using aromatic oils. For tonsillitis, mint, peach, eucalyptus, rose and sage oils are considered effective.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating tonsillitis involve using various infusions and decoctions for gargling.
- Basil oil is used to treat inflamed tonsils.
- To increase immunity, take decoctions of marshmallow, chamomile, and horsetail.
- For rinsing, you can use a decoction of burdock, oak bark, St. John's wort, raspberry, propolis tincture, poplar buds, sage, water with apple cider vinegar, cranberry juice with honey, and even warm champagne.
- Rinsing the nasopharynx with warm salted water will help cure the disease at home. It is drawn in through the nose, pinching the left and right nostrils in turn, and then spit out.
- Salt dressings and cabbage compresses on the throat area, as well as onion inhalations, will help improve the patient’s condition.
Chronic tonsillitis is treated with folk remedies for 2 months, then take a break for two weeks and repeat the same procedures, but with other ingredients. Alternative treatment for tonsillitis should be carried out only after consultation with a specialist. If the expected result is absent or side effects appear, then alternative treatment must be stopped.
Prevention
Preventive measures for the occurrence of tonsillitis include measures to prevent the occurrence of tonsillitis and proper treatment of the disease:
- Sanitation of the nasopharynx and oral cavity;
- Limiting contact with those who have recently been ill or are sick;
- Avoiding overheating and hypothermia;
- Prevention of colds (especially during seasonal exacerbations);
- Measures to strengthen the immune system: regular exercise, proper nutrition, hardening, walks in the fresh air.
Getting proper rest, avoiding stress and following a daily routine will help prevent disease and strengthen the body's defenses.
Treatment of bacterial sore throat in children
After the examination, the ENT doctor gives a referral to donate blood for a general analysis, culture to determine the microflora and its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs. Only based on the results of the examination, treatment tactics are selected and specific drugs of different dosages are prescribed.
The basic treatment regimen is as follows:
- Taking antibacterial agents. Bacterial sore throat cannot be avoided without taking antibiotics. The most commonly prescribed penicillin antibiotics and aminoglycosides in tablet form. Macrolides are prescribed for children. Streptococci are sensitive to these groups of antibiotics, so the proliferation of bacteria quickly stops. Local broad-spectrum antibiotics in the form of a spray relieve inflammation.
- Taking probiotics and eubiotics. They normalize the intestinal microflora after antibiotics.
- Taking antipyretic drugs. If the temperature is above 38°C, then paracetamol-based drugs are prescribed. At temperatures below 38°C, the body fights on its own.
- Rinse with antiseptics to combat pathogenic microflora and wash out pus.
- Taking local medications to relieve sore throat. Dissolving lozenges, tablets, and using a spray relieves local symptoms.
- Vitamin therapy. Vitamin B and C complexes strengthen the body's defenses, helping to recover faster.
- Taking antihistamines. Prescribed for severe swelling of the soft tissues of the throat.
In addition to drug therapy, strict bed rest must be observed. During the first three days, the likelihood of infecting other family members is highest, so you need to provide the patient with a separate sleeping place and household items.
Due to a sore throat, the usual diet is disrupted. The patient eats only liquid and pureed food in small portions, but often. You should drink 2.5-3 liters of clean water to relieve symptoms of intoxication, but you should not drink hot or cold water.
As a rule, improvement after the start of treatment therapy is recorded within 2-3 days. The general course of treatment does not exceed 10 days. If there is a noticeable deterioration in the condition, then this is a reason for hospitalization.
Important to remember! It is strictly forbidden to make compresses, warm the throat and legs, or do inhalations. Such manipulations will increase the proliferation of bacteria.