2870
Considering that dentistry has in its arsenal a lot of new techniques and developments in the field of prevention and treatment of severe and advanced diseases, it is not always possible to maintain the health and functionality of dental elements into old age.
To restore lost units, dentists often resort to removable prosthetics. Clasp systems have proven themselves to be excellent, the production of which will be discussed in the article.
General overview
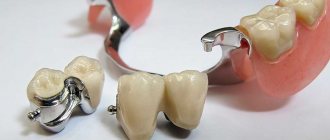
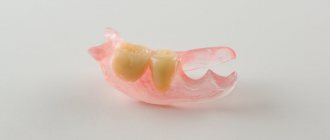
Clasp denture is one of the types of removable orthodontic structures. This is a very light, elegant, reliable and comfortable device to wear that does not distort diction.
All models of clasps are technically complex. They are based on a durable metal frame, a saddle-shaped acrylic base, artificial units and fastening devices.
All parts of the device are connected to each other by an arc. It also performs a fixing function. The frame itself can be made in two versions - solid cast or soldered. The second one is much easier to produce, cheaper, but not so convenient to use.
An important condition for the installation of these products is the presence in the mouth of several fairly stable and strong teeth. It is these units that will hold the removable structure.
The degree of sensitivity of the tissues and mucous membranes of the gums, the condition of the periodontium, and the size and shape of the alveoli are also of great importance.
What is a clasp?
The clasp is a titanium, chromium-cobalt or gold-platinum frame in the shape of an arc with special fasteners. The main advantage of such dentures is their ability to rest not only on the gums, but also on the body of the jaw, palate, alveolar processes and healthy teeth.
Thanks to this design, the chewing load and pressure are evenly distributed over the entire dentition, preventing the process of loosening and premature loss of healthy teeth.
Nowadays, clasp prosthetics is becoming more and more in demand and popular.
This is due to a noticeable qualitative leap in the production of prosthetics. Modern clasps have a lightweight, durable, openwork design and practical fastenings that are invisible to prying eyes; they are durable, reliable and easy to use.
Purpose of structures
A clasp denture is one of many structures designed to reconstruct the integrity of the dentition in the absence of natural units on it.
Its installation is possible for the following indications:
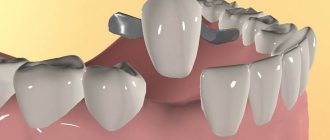
- the presence of end bilateral and unilateral defects of the row;
- inability to place a non-removable device;
- loose teeth associated with periodontal diseases;
- the presence of single or included defects;
- replacement of anterior units;
- pathological abrasion of teeth.
The clasp is very often installed during preparation for prosthetics to preserve the overall aesthetics of the face. It can be used to correct deep bites, treat periodontal disease and bruxism.
Indications for installation
Splinting clasp prosthetics is used in the following situations:
- Loss of 3-5 adjacent teeth if there is no reliable support on either side.
- Gum pathologies accompanied by frequent bleeding.
- Loss of a tooth and loosening of several of its neighbors.
- Bruxism, abnormal deep bite.
- Formation of voluminous gum pockets, exposure of tooth roots.
- Periodontal diseases.
If teeth are loose and periodontal tissue is damaged, splinting should be done as soon as possible. If this is not done, the radical units will begin to fall out. Under the influence of high chewing load, the teeth will begin to tilt in different directions and change their original position. Clasp splinting prosthetics allows you to avoid all these consequences.
Varieties
4 types of clasp devices have been developed. Each of them differs in its design features, manufacturing technology and material, and method of fastening.
With clasp fixation method
This is one of the most popular and inexpensive models. Clasps are small flattened hooks that tightly grasp the supporting units, securely hold the device in the oral cavity, preventing it from moving, and do not damage the enamel. They are part of a one-piece cast structure, and are made to match the parameters of the supporting teeth.
The indication for placing hooks on the clasp is the standard (or slightly larger) size and shape of the supporting elements.
They are also installed if the system is used as a medical splinting device (but then in this case several fastening links are placed on it).
The load when chewing food is distributed in such a way that the teeth remaining in the oral cavity experience minimal pressure, i.e. they account for only a third of it. The main part is distributed between the structure and the gums, which prevents the development of tissue atrophy.
A significant disadvantage of a product with clasps is its low aesthetics (the fastening cannot be positioned otherwise than on the front side of the teeth, so it is noticeable when communicating and smiling).
Fixed with micro-locks
Instead of clasps, miniature locks (aka attachments) can be built in. They consist of two parts, one of which (matrix) is built into the structure itself, and the second (matrix) is installed into a metal-ceramic crown that is placed on the support.
Fixation of the device occurs due to the automatic snapping of parts of the lock when putting on the prosthesis.
3 variants of micro-locks have been developed: rail, crossbar and spherical.
The model with attachments differs from the previous one in its higher aesthetic characteristics, since it is invisible to prying eyes. It is also more compact, lighter, and the fixation itself is more reliable. The load during meals is distributed evenly.
It is installed when the coronal part of the supporting element is sufficiently large and there are no pathologies of periodontal tissues.
A significant disadvantage of the device is the inevitability of grinding of the supporting units.
Fastenings with retractable (telescopic) crowns
These are two-piece caps that fit on top of each other. One is located on a support, the second is built into the structure.
The use of fastening is justified in the absence of a large number of teeth, the smoothness and small size of the remaining fragments, and chronic pathologies of periodontal tissue.
The load during chewing is placed only on the supporting elements, which minimizes the risk of damage to the mucous membrane and tissues. The system stands out for its high aesthetics, lightness and ease of use.
Despite all its positive characteristics, experts very rarely recommend its placement, since the product is difficult to manufacture and requires deep grinding of the supporting teeth.
Splinting (on beam) fastening
It is used for periodontitis, lack of most of the teeth, severe instability of the position of the remaining ones, but subject to the condition that the elements on which the structure is supposed to be attached are of sufficient height.
The device is two-part, that is, it consists of a non-removable part (beam) connecting the caps, and a removable part (matrix) mounted in the body. It is fixed on the inside of healthy teeth with metal plates that repeat the exact shape.
The duration of wearing the structure depends on the duration of treatment of the disease, but even long-term use does not damage the enamel or rub the mucous membrane.
Important! The doctor decides which type of clasp will be installed, based on the results of the patient’s examination.
Types of clasp dentures
Orthopedic dentists use several types of clasp fixation of the prosthesis with different methods of attachment to the jaws. Each option has its own pros and cons, which experts take into account each time when deciding which method will work best in a particular situation.
On attachments
The technique using attachments guarantees a good result when the patient has sufficient crown height and there are no periodontal lesions. The bottom line is to use special micro-locks. Miniature clasps are installed not on the teeth themselves, but on special crowns that have a protrusion in the form of a ball, cylinder, or rectangle. The clasp arch is snapped onto this protrusion.
Such dentures are comfortable, strong, durable, provide a uniform nutritional load, and most importantly, they are absolutely invisible to the prying eye. The type of attachment: crossbar, spherical, rail - is usually determined by the prosthetist, taking into account all the clinical features of the oral cavity. The clasps easily snap into place when installing the prosthesis and also easily open when it is necessary to remove it, for example, for cleaning.
The disadvantage of fastening with attachments is the high cost of manufacturing the prosthesis due to the complexity of the technology.
An important detail: the German “Bredent” and “MK-1” are considered to be some of the best micro-locks for clasp prosthetics. There are analogues made in Russia, the cost of which is much cheaper.
Clasp
In this case, the installation of the clasp prosthesis occurs with the help of hooks, which are called clasps. As a rule, they are cast together with the frame. This manufacturing technique provides the product with high strength and a long service life. There are no complaints about the distribution of the food load: the third part falls on the teeth, the rest on the gums. This is a very important factor for people with insufficiently strong teeth.
The clasp fastening method is cheaper than other clasp technologies. However, for many patients it turns out to be unacceptable due to an aesthetic problem: others can see the clasps when a person is talking or smiling. More often than others, clasps are installed by older people, who value primarily the unique strength of such clasps and ease of use. Sometimes dentists themselves recommend fastening with clasps when the use of other methods is impossible for one reason or another.
On clamps
To enhance the fixation of the prosthesis, there are special fastening designs.
Telescopic crowns
This type of fastening is best able to hold the clasp denture. Crowns are placed on teeth that have been ground and covered with metal. In terms of design and comfort, they are similar to bridge prostheses. They are chosen when there are a small number of remaining teeth or weak roots that cannot support a real bridge.
The telescopic crown consists of 2 parts:
- stationary – location of the supporting teeth;
- removable - attached to the prosthesis itself.
The method is necessary for low patient crowns. Telescopic retainers are also recommended for smooth teeth and periodontal diseases. The main load from the prosthesis falls on the supporting teeth, which can be either natural or artificial.
In the mouth, telescopic fasteners are almost invisible, but the popularity of the method is limited by its high cost. Disadvantages also include the need for significant grinding of teeth.
An important detail: usually about 5 telescopic crowns are needed for prosthetics, in some cases you can get by with two.
Splinting
Splinting dentures are most often used when there is excessive mobility of the jaw row. They are equipped with a special type of hooks that, while holding crowns, remove part of the load from loose teeth and direct it to healthy ones. In order not to damage the periodontal ligaments, the supporting teeth must be reinforced with metal-ceramics.
An important detail: these are the only dentures that can combine restorative and therapeutic tasks - compensation for lost teeth and treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Material used
All structural elements of the system are made using different materials. So, for the manufacture of the frame and arc, a cobalt-nickel alloy or stainless steel .
The alloy product is hypoallergenic and has a high biocompatibility with periodontal tissues.
Less popular is the system, the parts of which are made of steel. Its disadvantage is that an oxide film forms very quickly at the soldering points (its appearance indicates the beginning of the oxidation process).
The base on which the artificial chewing elements are placed is usually made of acrylic (a type of plastic). Despite the lightness of the material, it is quite durable.
All small elements (including fasteners) are made of titanium, which reduces the overall weight and parameters of the product. It is this fact that reduces the adaptation period to the system to 3-5 days.
For artificial chewing elements, metal-ceramics or ceramics (plastics are used less frequently).
Where does the process of making removable dentures begin, and what material is used?
Find out about the effectiveness of denture retaining spacers here.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/komu-podoydut-akri-fri.html you will find a selection of positive and negative reviews about Akri Fri removable dentures.
Technologies
The design of the clasps is complex, so they are made only in dental laboratories equipped with special equipment. Two technologies are used for this:
- Casting with removal of the model from the blank. The method involves taking a wax impression from a plaster model and then placing it in a refractory compound. The wax is removed and replaced with liquid metal.
- Casting a refractory sample, during which the base is modeled.
This method has two advantages over previous technology. Firstly, the metal does not “shrink”, and secondly, the possibility of changing the parameters of the wax blank during its removal from the model and packaging into a refractory mass is excluded.
Important! Cast structures are very thin, reliable, lightweight and very accurate, so the period of getting used to them is very short.
Production
The production of clasps is a labor-intensive, lengthy process that takes place in several stages. All of them are created individually for each patient using casts of his jaws using special equipment in specialized workshops.
Clinical stage
Includes several visits to the dentist, during which:
- Initial examination of the patient. The doctor analyzes the general condition of the oral cavity and dentition, determines the type of occlusion, selects supporting units and determines their quality.
Also draws up a plan to eliminate the defect. If any pathologies, injuries, or ulcers are found in the mouth, then the installation is postponed until complete recovery. - Preparation of supporting units for prosthetics. If necessary, the dentist treats them and grinds them down.
- Taking impressions of both jaws to create two models: diagnostic and auxiliary.
The process then continues in laboratory conditions. Afterwards, the patient is invited for a trial fitting of the design. If there is a need to correct it, eliminate identified flaws and inaccuracies, the product is again sent to the laboratory for finishing and adjustment. - Final placement of the system in the mouth , checking balance.
After fixing the system, the specialist advises the patient on care and operation.
Laboratory stages
After receiving the impressions, the production of the clasp continues in the laboratory. This process is also multi-step:
- Creation of a diagnostic version of a model made of marble plaster, which takes into account all the features and details of the anatomical structure of the patient’s mouth.
- Modeling the type of bite by precisely positioning the jaws relative to each other.
- Measurement of pressure on those units that are supposed to be used as reference for the system.
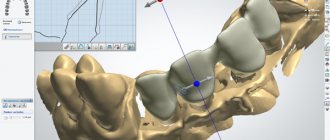
- Drawing a diagram of the future design on the layout , its graphic representation.
- Simulation on the same model of the process of grinding teeth-supports.
- Creating a model of the system frame, casting the frame.
- Installation of artificial chewing elements on wax balls, and the formation of a restored fragment of a row from them.
- This structure is placed in a plaster mold , melted, the wax is removed, and an acrylic mass is poured in its place.
- Connecting all parts into one structure, grinding and polishing.
Next, the finished product is sent to an orthopedic doctor to secure it in the patient’s mouth.
The video presents an option for making a clasp prosthesis with clasp fixation.
Essential elements
The clasp denture consists of three main elements: clasps, arches and base. Each of them is made from certain materials, components and performs its own functions. In addition, each element is carried out in different ways.
Clasps
The main function is to hold and securely fasten the prosthesis. They are made by bending wire or by casting. The main materials for manufacturing are various metal alloys.
The placement of the element is based on its anatomical shape. A line runs along its protruding part; in dentistry it is called the equator. It separates the gingival and occlusal parts.
The structure, secured with retaining clasps, when vertical pressure is applied to it, begins to settle towards the mucous membrane, to which the load is transferred.
Let's figure out which removable dentures are better
Support clasps transfer the load to the supporting molars, and part of it is applied to the mucous membrane of the upper palate.
Support-holding type clasps consist of several parts:
- Shoulders. Adjacent to the surface of the tooth.
- Body. This is a fixed part located above the equator of the structure.
- Process. Goes to the basis.
On the surface of the molar there is a special pad that protects the prosthesis from immersion in the mucosa. It is also intended to transfer vertical pressure to the teeth, which act as support teeth.
Arc
Intended for connecting parts of the prosthesis. It must be made of durable materials, as it acts as a resistance block. This allows you to give an advantageous load on the supporting molars.
Also, the element must be sufficiently rigid and have high physical and mechanical properties. During manufacturing, the arc is often given an oval, semi-oval or semi-circular shape. In order to protect the tongue and oral mucosa from injury, its edges should be round.
Basis
The base is an element of a removable structure on which artificial teeth and various structural parts and their branches are attached. It is fixed to the supporting molars using connecting parts and rests on the alveolar process.
The shape and size of the element are given in accordance with the presence of teeth, the structural features of the oral cavity, as well as functional tasks.
Depending on how many natural teeth can accept chewing pressure and the level of load, the base area is determined.
All parts of the prosthesis, when manufactured correctly, are ideally selected, the load is distributed evenly and there is no discomfort or pain when chewing food.
Creation time
The creation of clasp systems takes more time than the production of other removable structures:
- the device with clasps takes about 10-12 days;
- analog product with attachments – at least 20 days;
- the system on telescopic crowns will be ready in 3-4 weeks.
But these are only approximate times for the technician to complete the work. Depending on how busy it is, production may take longer, or vice versa, it may be halved.
Useful recommendations on where to place a covering prosthesis, and what to look for when choosing a specialist.
This material is devoted to the design of the Sandwich denture.
Here https://zubovv.ru/protezirovanie/semnyie-p/byugelnyie/na-nizhnyuyu-chelyust.html about the features of making a clasp denture for the lower jaw.
How to get used to wearing
The clasp prosthesis does not cause any serious problems during the process of adaptation. The design practically does not cause atrophy of the underlying tissues, and already in the first days it allows you to eat and talk normally.
To get used to the prosthesis quickly, you should take the temporary discomfort as calmly as possible: do not be afraid of the pain that occurs when chewing or slurred diction. After a few days, such symptoms will disappear.
If you have difficulty chewing, it is recommended to eat more often, but in small portions. Problems with diction can be solved by reading aloud, singing, and talking with loved ones.
Contraindications
In addition to prescriptions for the use of clasp dentures, dentists identify conditions in which their installation is impossible. These restrictions can be divided into 2 groups: absolute and temporary (conditional).
Absolute restrictions include the following conditions:
- insufficient height of supporting teeth or their absence;
- pathological changes in structure in the periapecal tissues of these units;
- atrophy of the alveolar processes;
- severe malocclusion of the lower jaw;
- low, or, on the contrary, high fixation of the frenulum of the tongue;
- mental disorders;
- diabetes;
- pathologies that weaken the immune system;
- malignant formation in the oral cavity.
Important! Identification of one of these conditions is the basis for refusal to perform prosthetics and a reason for selecting another method of correcting the dentition defect.
The group of relative contraindications includes:
- pregnancy at any stage and the period of breastfeeding;
- exacerbation of existing chronic diseases;
- recovery period after surgery;
- insufficient number of supporting teeth;
- drug or alcohol addiction;
- heart failure in the active phase;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- viral or infectious diseases.
Important! Considering that a significant part of the limitations can be eliminated, prosthetics with clasp devices is a real way to reconstruct the dentition.
Advantages and disadvantages
Clasp prosthetics have the following significant advantages over other removable orthodontic structures:
- Compact and lightweight.
- Good fixation in the mouth.
- Correct pressure distribution during eating.
- When the system is attached to the upper jaw, it does not cover the entire palate, which means it does not lead to a change in the taste perception of food or impaired diction.
- Easy to care for.
- Duration of operation.
- Possibility of installation for the treatment of periodontal diseases.
- Various fixation methods.
- Short adaptation period.
The invention of structures pushed into the background all other removable systems. Today, clasps are considered the best options for replacing lost teeth.
But even despite the large number of advantages, this device has a number of disadvantages:
- For placement it is necessary to perform turning.
- The process of atrophy of jaw tissue develops.
- Some types of fastening (clasps) are not aesthetically pleasing.
- High cost compared to other designs.
But even these shortcomings do not affect the demand and popularity of clasps among patients.
Distinctive features of clasp splinting developments
If we compare a splinting prosthesis with a conventional clasp prosthesis, it is usually more convenient to use. This is explained by the fact that its basis is smaller. It also does not cover the palate and leaves the tongue free. This means that neither diction nor a person’s taste sensations change.
It is important that splinting clasp systems do not cause atrophic changes in the gums and bone tissues of the jaw. Therefore, when wearing them for a long time, the patient does not experience any significant discomfort.
Rules of care
The service life of the system, subject to strict adherence to all rules of care, is approximately 10 years. Also, their implementation will help prevent inflammation of the mucous and periodontal tissues:
- It is good to rinse your mouth with water or mouthwash after each meal.
- Clean the structure twice a day, being sure to remove it before the procedure.
- Treat in the same way as natural teeth, using paste and a classic brush. Highly abrasive pastes should not be used for the procedure.
- Each time after removal, treat with an antiseptic (it is better to do this before going to bed).
- Rinse only with warm water. Do not use alkalis or highly acidic products.
- Eliminate hard and sticky foods from your diet, and avoid hot foods and drinks.
- Protect from accidental falls and breakages.
It is also necessary to perform position adjustments and professional dental cleanings at least once a year.
.
The above rules of care are simple and easy to follow. Compliance with them will ensure the preservation of the functionality of the system and comfort during operation.
Price
The cost of clasp structures is high in comparison with other removable products. But, despite this fact, their use today is one of the most popular services in dental clinics.
This table provides information on the average cost of various clasp systems. These figures already include payment for oral cavity preparation services.
| Type of prosthesis | Price, thousand rubles |
| Simple for one jaw | from 15 |
| System for 2 jaws | about 25 |
| Splint system | from 20 |
| Micro-lock design | about 40 |
| Product on telescopes | about 70 |
The figures given are subject to change. Their upward fluctuation depends on the complexity of the design itself, the type of material used in production, and the type of fastening used.
Reviews
Clasp dentures are considered a worthy replacement for lost dental units. They received a lot of positive ratings from experts and people who tested their characteristics from their own experience.
They note reliability, quality, comfort, convenience and long-term operation without repair.
You can talk about your experience and share your impressions of dentition reconstruction with clasps by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags clasp denture removable dentures
Did you like the article? stay tuned