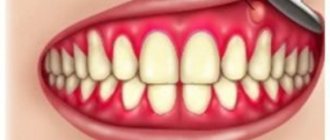
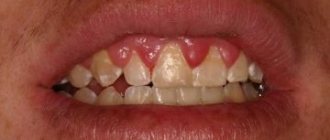
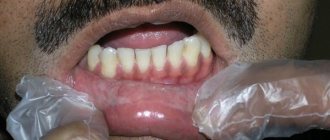
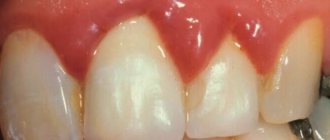
What is angioedema of the larynx? Most likely, most respondents not related to medicine will not be able to answer this question. But if you voice another name for this condition - Quincke's edema - everything will fall into place.
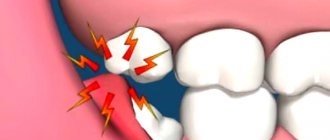
Angioedema of the larynx is an acute, rapidly developing edema of the deep layers of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and mucous membrane. Angioedema of the larynx is very dangerous, because in the absence of emergency help, the airways can completely block, leading to asphyxia and death.
Angioedema of the larynx is an aggressive reaction of the body to external stimuli. When interacting with an external factor, the body releases biologically active substances into the blood as protective measures - histamine, bradykinin, etc. This whole process occurs with the expansion of blood vessels and an increase in their permeability. Ultimately, the lymph from the capillaries leaks into nearby tissues, causing severe swelling. The mechanism of angioedema formation is similar to the appearance of allergic urticaria. Only in the latter case, the vessels dilate in the upper layers of the skin, so urticaria is not dangerous, but in case of angioedema of the larynx - in the deep layers of the skin.
This is a relatively new medical condition. It was first described in his works at the end of the 19th century by the German physician Heinrich Quincke. Swelling of the throat develops very quickly - several hours or even minutes can pass from the moment of interaction with the irritant. Therefore, treatment and assistance for swelling of the throat should be urgent.
Causes of throat swelling
The choice of treatment tactics is closely related to the cause of throat swelling. It can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory in nature. Etiological factors of throat edema:
- pathologies of the immune system;
- respiratory diseases;
- allergic reaction;
- a bite of an insect;
- tumor process;
- injuries.
Sometimes you can discover the cause on your own: people remember an injury or an insect bite. But in most cases, it is worth seeing a doctor to establish the correct diagnosis.
What causes angioedema of the larynx?
In most cases, this is the body’s response to allergens entering it. These allergens are purely individual. They may cause a negative reaction in one person and not at all in another. The difference in the perception of allergens depends on the characteristics and strength of the immune system.
But there is also non-allergic angioedema, which can develop in response to various physical factors (cold, overheating, strong solar radiation, vibration), severe stress (emotional stress or increased physical activity, prolonged lack of sleep), lack of vitamins and essential microelements. The disease is associated with a deficiency of a special enzyme, the C1 esterase inhibitor, which blocks the action of vasoactive peptides. In this case, an immunological reaction develops like an allergy in the absence of an allergen. Most often, non-allergic Quincke's edema is a genetic failure that prevents the production of the necessary enzyme by liver cells.
The most common factors that provoke angioedema:
- medicines;
- Food;
- household chemicals;
- flowering plants, pollen;
- mushrooms, fungal spores;
- dust;
- animal hair;
- alcohol;
- stinging insect bites;
- ultraviolet;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- stress;
- indigestion (undigested fragments of food proteins (peptides) can cause allergization of the body and provoke Quincke's edema);
- liver diseases.
Once in the body, allergens provoke the release of serotonin, histamine and other mediators of allergic reactions into the blood. These substances cause pathologically strong permeability of the vascular walls located in the subcutaneous fatty tissue and submucosal layer. As a result, blood begins to leak from the lumen of the vessels, which leads to the development of angioedema. However, this condition may not develop instantly. Having accumulated allergens in critical quantities, the body can react sharply after some time.
There is also an idiopathic form of the disease, the root cause of which cannot be determined.
How to recognize swelling of the throat
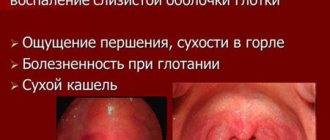
It can be difficult to understand that the throat is swollen, since the process begins inside and it is difficult to see it on your own. Symptoms of pathology:
- pain and discomfort when swallowing;
- labored breathing;
- stiffness of neck movements;
- irradiation of pain to the ear area;
- dry hacking cough;
- sensation of a foreign body in the larynx;
- change in voice timbre;
- visual increase in neck thickness.
Sometimes swelling of the throat is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. This is typical for an infectious process.
How to relieve throat swelling?
Depending on the etiology of throat swelling, there are various methods to alleviate the condition. The insidiousness of this condition lies in the need to provide emergency assistance to save lives.
- What causes swelling in arthritis, and how to relieve it?
There are a lot of medications and improvised means, the use of which reduces swelling and inflammation:
| Pathology | Basics of therapy |
| ARVI, cold | Using infusions of sage, yarrow, chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort for gargling. Using inhallipt, cameton, oracept in the form of a spray for mouth irrigation. |
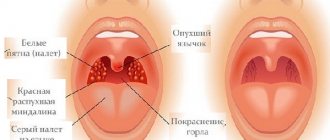
| Angina | Strict bed rest. Gargling with baking soda and table salt, herbal infusions, carrot or beet juice. Spraying the mouth with an antiseptic solution of chlorophyllipt and using it in oil form for rinsing. Taking dissolving pills. |
| Allergy | Swelling is controlled with antihistamines. When an insect bites, apply a tourniquet above the bite and use tablets or injections of diphenhydramine, or suprastin, or prednisolone. Adrenaline hydrochloride is used to irrigate the throat. At the same time, cold wet compresses should be applied to the throat. In extreme cases, artificial ventilation may be necessary. |
| Laryngitis | A characteristic feature of this pathology is the rapid development of swelling of the throat mucosa, requiring immediate first aid before the ambulance arrives. To do this, the patient is seated, the buttons on his clothes are unbuttoned, and warm milk or Borjomi is given to him to drink. The limbs are immersed in a container of hot water, and to relieve swelling, it is recommended to inhale, preferably with baking soda. In the room where the patient is located, it is necessary to increase the air humidity. |
| Pharyngitis | First of all, factors that irritate the mucous membrane of the throat are excluded. The throat is gargled with solutions of baking soda or furatsilin. Chlorophyllipt or ingalipt are used to irrigate the throat. Inhalations are carried out with anti-inflammatory and decongestant herbal decoctions or with alkaline mineral water. It is recommended to take absorbable antimicrobial pills, and, if indicated, antihistamines. |
| Injury | You should try as quickly as possible to get rid of the foreign body in the throat that causes its damage. To do this, you need to stand behind the victim. Having clasped his torso with your arms on both sides, you should press firmly with your fists in the area slightly above the navel. |
| GERD | Taking antacids or flight pump inhibitors (pantoprazole, lamprazole), and also drinking hot milk with soda. Sea buckthorn and rosehip oils will help reduce symptoms. |
Important! Untimely assistance for swelling of the throat significantly increases the risk of complications, and in the worst case, asphyxia.
Diseases accompanied by swelling of the throat
Swelling in the larynx and neck can be a sign of certain diseases. Pathologies in which the throat swells:
- viral infections - ARVI, influenza;
- bacterial diseases - acute respiratory infections, typhus, measles, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, pharyngitis;
- suppuration in the oropharynx - abscess of the tonsils or epiglottis, retropharyngeal abscess;
- some chronic infections - tuberculosis, syphilis;
- inflammation of the cartilage of the larynx;
- allergy;
- endocrine disorders;
- stagnation of blood in the pharynx, neck or larynx;
- tumor formation of a malignant or benign nature.
Depending on the diagnosis, it becomes clear how to treat a swollen throat. If the cause is not clear, the effectiveness of therapy is in question.
Symptoms of Quincke's edema.
The first sensations that a person experiences are a burning sensation and a slight tingling sensation at the site of future swelling. Then swelling occurs. Dangerous swelling appears on the face (lips, eyelids, cheeks) and neck. The tongue is very swollen. It gets to the point where a person’s face becomes like a ball, and the patient is not even able to fully open his eyes.
In the first minutes after interaction with the irritant, symptoms may appear in adults and children, such as lacrimation, problems breathing through the nose, the appearance of a dry cough and hoarseness in the voice. Another important symptom of angioedema of the throat is “wheezing”, heavy breathing. All these symptoms very quickly gain momentum and become intense. It’s as if a person was bitten by a swarm of bees - this is what angioedema looks like externally.
In addition to external changes, this dangerous condition has other symptoms: decreased blood pressure, excessive sweating, and rapid heartbeat.
Angioedema of the larynx is the most dangerous manifestation of angioedema, when swelling affects the throat and airways. An emerging cough, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, a feeling of a lump in the throat, problems with speech - all these symptoms indicate incipient asphyxia (suffocation).
When the first symptoms of Quincke's edema appear, you need to call an ambulance so as not to waste precious time. If the swelling of the larynx is not relieved soon, the person may die. Even if death was avoided and treatment of angioedema was not delayed, prolonged absence of normal breathing can lead to damage to brain activity.
Diagnosis of pathology
Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis based on a complete examination. If you have a history of allergies and swelling develops rapidly, you should call an emergency medical team. Before doctors arrive, it is worth opening the windows or taking the person out into the fresh air, removing tight clothing, and giving an antihistamine according to age. If the course is not so rapid, you can consult a therapist.
Examination plan:
- taking anamnesis (hypothermia, additional symptoms, contact with patients, etc.);
- inspection;
- general blood analysis;
- swab from the surface of the oropharynx (if necessary);
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland (as directed by an endocrinologist).
If the therapist could not determine the cause of the edema, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist or allergist. The next step will be to contact an endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist, and phlebologist. But most often the problem is solved in the therapist’s office.
First aid
After calling medical workers, it is important to help the patient:
- eliminate from the room all possible allergens that could cause such a reaction;
- if swelling occurs after an insect bite, you need to apply a tourniquet above the bite site;
- give the victim alkaline water (dissolve a teaspoon of baking soda per liter of plain water) and an antihistamine;
- provide a flow of fresh air;
- take the victim out of the stuffy room, try to keep him cool;
- try to calm him down and prevent him from panicking.
How to help with throat swelling
If swelling of the throat develops rapidly, only an injection of adrenaline and glucocorticoids can help the patient. Therefore, it is better to call doctors and give the patient an antihistamine. They are available in tablets, drops, and injection solutions. Injections of the drug work the fastest.
If swelling of the throat occurs for other reasons, complex treatment is prescribed. Drugs used as therapy:
- anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce swelling that occurs due to inflammation;
- antibiotics - to treat diseases caused by bacteria;
- diuretics - reduce swelling when severe;
- glucocorticosteroids - act as an emergency measure for severe swelling;
- antihypoxants - prevent the development of tissue oxygen deficiency.
To alleviate the condition, inhalations with antiseptic solutions are also used. They allow you to speed up your recovery.
Read also: Sore throat when swallowing
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
Treatment options for children and adults
Treatment of laryngeal edema depends on the cause that caused this phenomenon.
For inflammatory edema, the following medications are used:
- As a means of symptomatic therapy, herbal decoctions and rinsing infusions can be prescribed. Agents that suppress pathogenic microorganisms. The drug is selected based on the sensitivity of the pathogen to the action of certain groups of medications. The patient may be prescribed Amoxiclav, Bioparox, Ingalipt;
- Antipyretics (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- Expectorants (Prospan, Mucaltin).
Also, for swelling of the larynx, diuretics (Indapamide, Furosemide), antihistamines (Tavegil, Diazolin), anti-inflammatory drugs (Prednisolone) can be prescribed.
Herbal decoctions and rinses can be prescribed as symptomatic therapy. Sage, nettle, and oak root are used as raw materials.
If the swelling progresses to laryngeal stenosis, the patient is administered vasoconstrictor drugs. Thanks to this manipulation, the lumen of the larynx expands, which prevents asphyxia. Oxygen inhalation may also be required.
If any measures do not eliminate the swelling, a tracheotomy of the respiratory tract is performed. The essence of this manipulation is the excision of throat tissue, followed by the insertion of a tube that provides oxygen to the lungs.
Urgent Care
- The first thing a person who is near a patient should do is call an emergency medical service.
- In case of Quincke's edema in the larynx, it is necessary to eliminate all sources of the allergic reaction that provoked this condition.
- As noted above, swelling can develop after taking medications or an insect bite. In this case, you will need to apply a pressure bandage in the area above the bite or injection site. If this is not possible, then apply a cold compress. This will make it possible to narrow the lumen of the capillaries and slow down the process of further spread of the irritant throughout the body.
- To make breathing easier with Quincke's edema in the throat, the patient's clothes should be unbuttoned or loosened and a strong flow of fresh air should be provided.
- When a person is unable to breathe on his own, an urgent conicotomy is needed. This will require dissection of the trachea in a certain area and insertion of a tube for air intake. This procedure requires medical qualifications.
Symptoms and help for Quincke's edema
Quincke's edema is an acutely manifested disease in which swelling appears on the skin, in the subcutaneous layers of the fat layer, as well as on the surface of the mucous membranes. Most often, edema, named after the famous German doctor Quincke, appears on the face, neck, hands and feet on the back. Quincke's edema can often be observed on the surface of the body. The most dangerous consequences are considered to be due to Quincke's edema, which occurs on the membranes of the brain, joints, and internal organs. When the disease develops symptoms acutely, help with Quincke's edema must be immediate to prevent dangerous complications. Symptoms can be so sudden that it is very difficult to predict their occurrence and respond correctly. The disease can manifest itself in young people, children, the elderly - no one is immune from it. The reasons that cause symptoms of edema are various allergic reactions. Anything can be an irritant: pollen from plants, poison, insect bites, food products, cold, sunlight. The allergic reaction that manifests itself with this type of edema leads to severe disruption of the functioning of many internal organs, and internal tissues can also be destroyed.
This disease is popularly called giant urticaria. Another reason for its development may be a pseudo-allergic reaction. This is a reaction that is provoked not by allergic irritants, but by the pathological development from the moment of birth of the complement system - a group of proteins without which immune processes and allergic reactions are impossible.
The symptoms of the disease can be recognized by external manifestations: areas of the body near the lips, on the cheeks, on the eyelids, and near the scrotum become inflamed and swell first. When pressing on the body, it is impossible to push through the area of swelling - it is so dense and hard. The fluid that accumulates during angioedema contains a lot of proteins, which gives it a high density. If the swelling does not affect the functioning of internal organs, then specific treatment may not be required; it will go away in a few days. But it’s worth sounding the alarm if the patient has difficulty breathing, he is choking, coughing, wheezing, and has shortness of breath. And help with Quincke's edema in this case must be provided immediately to prevent death.
The development of the disease can be so unpredictable that you cannot waste a minute helping the patient. First of all, call an ambulance, and begin to provide assistance for angioedema yourself before it arrives. If you know what caused the allergic reaction to worsen, immediately eliminate the irritating allergen. The patient needs to be reassured, not to panic, and to be protected from complications of the reaction during a nervous experience. The patient should feel that there are reliable people next to him who are ready to provide both psychological and pre-medical assistance. A sudden attack should not deprive you of your sober mind. Open the windows or balcony doors in the room - the flow of oxygen should be maximum. Remove from the neck and waist all items of clothing that may restrict movement and complicate breathing. Clothing should be completely removed from the throat by unbuttoning the shirt or removing the tie. The patient needs to be seated; it is better not to put him in a horizontal position. Doctors recommend taking a hot foot bath, but it is better to ask the emergency room doctor about this measure of assistance, so as not to harm the patient.
The swollen area can be stopped: to do this, when you notice the first symptoms of swelling, apply something cooling to this area. Drops can be placed into the nose, which have a constricting effect on blood vessels. Naphthyzine, proven by time and generations, helps well in this case. If the patient's condition worsens, it is allowed to give him drugs with an antihistamine effect. When the ambulance arrives, the patient will immediately be given powerful antiallergic drugs and then offered hospitalization. In no case should you refuse, since the patient may require treatment in intensive care. Be sure to tell the doctors what medications the patient was given before their arrival, and also inform them what exactly served as an irritant and provoked an exacerbation of the allergic reaction. At home, you can give the patient injections with the intramuscular administration of antiallergic drugs only if the swelling recurs repeatedly, and people around you are firmly convinced that these are precisely these symptoms. If there is a tablet of diphenhydramine or suprastin, you can offer the patient to place it under the tongue.
Preventive actions are practically useless. You can minimize the risk by excluding eggs, dairy products, fish dishes, nuts, citrus fruits, and chocolate from your daily menu. These foods can trigger angioedema, even if they are not the main cause of its appearance. The following can be recommended to the patient. If the symptoms of the reaction have appeared in the past, then make yourself a special card on which you indicate your name, surname, date of birth, telephone number of the doctor who is aware of your health and treated you last time. In this case, people nearby will be able to get their bearings and provide timely assistance with Quincke’s edema, without knowing what is happening to you.
Parents whose children have already experienced edema before should know all the methods of providing first aid at home by heart. There should be no panic or confusion; coordinated and clear actions will help maintain the child’s health. Adults should be attentive to the first symptoms of the disease - a cough that turns into whistling coming from the chest.
Symptoms and help for Quincke's edema
Quincke's edema is an acute, suddenly developed, limited swelling of the skin and subcutaneous tissue and (or) mucous membranes. Rare localizations of the pathological process include swelling of the meninges, the mucous membrane of the uterus and bladder, and the synovial membrane of the joints. More often, Quincke's edema is observed in women; It is less common in children and the elderly.
There are allergic and pseudo-allergic (usually hereditary) forms of Quincke's edema. Allergic Quincke's edema is often combined with urticaria. Patients with Quincke's edema often have other diseases of an allergic nature: bronchial asthma, hay fever, etc. The causes and mechanisms of development of allergic Quincke's edema are the same as for allergic urticaria. With angioedema of pseudoallergic origin, the main changes are reduced to a genetically determined disruption of the activation of the complement system, the formation of a kinin-like peptide, under the influence of which edema develops. The cause of pseudoallergic angioedema can be minor physical, thermal or chemical effects.
Clinically, Quincke's edema is characterized by acutely occurring and spontaneously resolving, often recurrent local edema of the skin, subcutaneous tissue and (or) mucous membranes. Swelling of the tissues of the face, the back of the hands and feet is most often observed. In the area of edema, the skin is usually pale or pale pink, and in most cases there is no itching. Local changes persist for several hours or days and then disappear without a trace.
The most dangerous is laryngeal edema, which is observed in 20-25% of cases of Quincke's edema. The patient suddenly develops anxiety, pallor or cyanosis of the face, difficulty breathing, and sometimes hemoptysis. When examining the oral cavity, swelling of the soft palate, uvula and palatine tonsils is revealed; during laryngoscopy, swelling of the epiglottis and laryngeal mucosa is noted. This condition lasts from 3-5 to 20-30 minutes and gradually passes; hoarseness persists for a longer time. However, it is possible that edema may increase or spread to the mucous membrane of the trachea, while the patient's condition worsens and there is a risk of death from asphyxia.
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is accompanied by severe abdominal pain, vomiting and subsequent diarrhea. Changes in the skin and visible mucous membranes in such cases may be absent, which makes timely diagnosis difficult.
The diagnosis of Quincke's edema is based on the clinical picture, the study of an allergic history, the rapid dynamics of the disease, the good effect of the use of adrenaline and antihistamines, and the determination of specific sensitization using a variety of immunological reactions.
Treatment of patients with Quincke's edema in the acute period should be comprehensive, it is aimed at eliminating the allergic reaction, reducing swelling, and reducing the body's sensitivity to histamine. Urgent treatment requires swelling of the larynx, in which it is necessary to immediately inject subcutaneously a 0.1% solution of adrenaline in a dose appropriate for age (0.3-0.5-0.8 ml); intravenously or intramuscularly one of the antihistamines (diprazine, diphenhydramine, suprastin, etc.), hydrocortisone hemisuccinate (75-125 mg) or prednisolone hemisuccinate (30-60 mg). A patient with laryngeal edema requires urgent hospitalization in an intensive care unit or intensive care unit. He needs to be provided with inhalation of humidified oxygen, administration of diuretics: furosemide (intravenous or intramuscular 1% solution of 1-2 ml), 15% mannitol solution (intravenous slow stream or drip at the rate of 1-1.5 g/kg body weight), 30 % urea solution (intravenous drip at the rate of 0.5-1.5 g/kg body weight), etc.; introduction of ascorbic acid, calcium preparations. In case of further deterioration of the condition, urgent tracheostomy is indicated. When the pathological process is localized in the gastrointestinal tract or meninges, the administration of antihistamines and diuretics has a beneficial effect. For pseudoallergic Quincke's edema, it is recommended to administer Z-aminocaproic acid orally (2.5-5 g) or intravenously (2-5 g in 20 ml of 40% glucose solution), contrical (30,000 units in 300 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution intravenously), plasma transfusion. The prognosis is usually favorable.
Prevention consists of strict adherence to an elimination diet and prevention of patient contact with a specific allergen, treatment of foci of chronic infection, periodic use of antihistamines (especially during the flowering period of plants with pollen allergies).
Why does pathology appear?
As already mentioned, Quincke's edema is divided into:
- [allergic];
- pseudo-allergic.
Let's consider the allergic option. In this case, the reaction appears after the body comes into contact with allergens. People who have a history of allergic disease are most susceptible.
Manifestations of these diseases can be bronchial asthma, diathesis in childhood, seasonal rhinitis, conjunctivitis.
Allergies develop when the body comes into contact with allergens for the second time, when it already has antibodies.
The causes of allergic edema are divided into infectious nature and non-infectious nature. Causes of infectious nature:
- Quincke's edema - classification, causes, symptoms
- [Viral diseases];
- Fungal diseases;
- [Bacterial diseases].
Causes of non-infectious origin:
- animal waste products;
- as a result of insect bites;
- exposure to pollen from a variety of plants;
- medicines;
- exposure to food allergens (chocolate, eggs, citrus fruits, honey);
- exposure to industrial dust.
The reasons for which non-allergic angioedema develops is the presence of pathology in the compliment system, which is responsible for the formation of an allergic response. It is represented by a complex of proteins.
In case of congenital pathology, this system is activated independently, without the allergen entering the body.
The reaction can be triggered by exposure to cold or stress.
The following factors can contribute to the development of Quincke's edema:
- the presence of chronic liver damage;
- diseases of the stomach, intestines, pancreas, gall bladder;
- the presence of worms and parasites in the body.