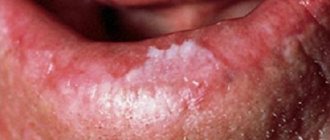
Features of white spots on the skin with vitiligo
The formation of milky white or pink areas can occur in any area of the skin.
The predominant localization is the area of the arms, face, as well as the inguinal folds and elbow bend. There was no development of depigmentation on the palms or soles. The localized version of the disease is associated with the appearance of spots on limited areas of the body. The most pronounced vitiligo is after sunbathing, since against the background of healthy skin the area turns out noticeably paler. The progression of the disease is accompanied by an increase in spots more than 10 cm in diameter. In some cases, a rim with pronounced pigmentation may appear.
The main characteristics of the formations include:
- edges (they are smooth), lesions can grow and merge;
- shape - most often it is oval or irregular;
- the relief is usually smooth and unchanged;
- the surface is clean: without peeling and rashes of various types.
Pronounced changes are accompanied by loss of pigment over almost the entire area of the skin, which can be confused with albinism. In this case, there is no loss of sensitivity. When the area is localized on the scalp, a change in hair shade is observed. The disease is not life-threatening. The main problem it poses is due to a violation of the patient’s adaptation to society, which is caused by appearance features.
There are various causes of hypopigmented spots on a child's face, ranging from conditions that resolve on their own within a few weeks to conditions that can last a lifetime.
Causes of white spots on a child's face
White spots can be caused by the following skin conditions:
Milia
Milia are also called milk spots. These tiny white bumps usually appear on the face and rarely on the upper torso or limbs. Although milia can be seen at any age, it is common in newborns.
Causes and diagnosis of milia
Milia occurs due to entrapment of keratin (skin scales) beneath the surface of the skin. If there is no improvement after a couple of weeks, you should consult a doctor. Diagnosis is made by visual examination and no tests are required.
Prevention and treatment of milia
There is no cure for milia and it often goes away within a few weeks or months. There is no need to treat milia in children.
How can you reduce milia at home?
- Wash your child's face daily with mild soap and water.
- Pat your face dry after washing.
- Be careful not to scratch the milia to prevent skin damage and infection.
- Do not apply lotions or oils to your baby's face.
Note: Some may confuse baby pimples or Epstein pearls with milia. However, acne can cause red bumps and pustules on the face. Epstein's pearls are small, white-yellow cysts that often resemble milia, but they appear on the roof of the mouth and gums.
Pityriasis alba (lichen alba)
Pityriasis alba is a self-limiting skin condition that causes dry, thin, scaly and pale patches on the face. It is common in children and adolescents and is considered a type of eczema or dermatitis.
The name of this condition comes from the characteristic appearance of the skin.
Causes of white ptyriasis
The causes of white ptyriasis have not yet been clarified. However, atopic dermatitis and dry skin often coexist with it. Exposure to the sun can make it more visible by tanning the surrounding skin.
Suspected causes such as under- or over-bathing, low serum copper levels, ultraviolet radiation, or Malassezia yeast have not yet been proven to cause hypopigmentation.
Symptoms and signs of ptyriasis alba
One or more white spots, varying from 0.5 to 5 cm in diameter, are a characteristic sign of pityriasis alba. It may also cause mild itching in some children.
Diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor
The condition can be diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor. A skin biopsy may show mild spongiotic (fluid accumulation between cells) dermatitis with decreased melanin pigment. A skin scraping may also be taken to rule out a yeast infection.
Treatment of white lichen
Treatment is not recommended in asymptomatic cases. Moisturizers are helpful for dry skin, and mild hydrocortisone (topical steroid) creams can help reduce itching and redness in the area.
Tacrolimus ointment, pimecrolimus cream, and calcineurin inhibitors have been shown to be effective in the treatment of pityriasis alba.
The appearance of the skin may gradually return to normal over several months or two to three years.
Prevention of white deprivation
Limited sun exposure may help reduce your risk of developing this disease.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a depigmentation of the skin due to the loss of melanocytes, which are the cells that produce the skin pigment called melanin. Vitiligo can affect both sun-exposed and unprotected areas of the body. Also, with the disease, depigmentation of the lips and gray hair are often observed.
Causes of vitiligo
The exact causes of vitiligo are unknown. The disease may be associated with dysfunction or loss of melanocytes (the cells that produce the pigment melanin), which give the skin its color. This may be due to genetic factors or an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks the melanocytes.
Vitiligo can occur at any age, but the onset of the disease is typical in children and adolescents.
Diagnosis of vitiligo
Vitiligo can be diagnosed through a physical examination. Rarely, a skin biopsy is performed to help confirm the diagnosis by the absence of melanocytes (pigment cells) on the skin. Thyroid disease and diabetes are checked as these may increase the risk of vitiligo in many people.
Treatment of vitiligo
Mild vitiligo may not require treatment: the spots will disappear over time. However, there are several treatments available to make your skin tone even.
Corticosteroid creams, photochemotherapy (PUVA), narrow band ultraviolet B (UVB) therapy, and depigmentation are a few treatment options. Using sunscreen can reduce tanning of the skin around vitiligo patches, and concealers can hide white spots on the skin.
Although vitiligo can be distressing to many people due to its appearance, it is not a medically dangerous condition. Vitiligo is not an infection, skin cancer, or a contagious disease.
Shingles
Shingles is a fungal skin infection that causes lighter or darker patches on the skin. The disease occurs at any age, but is most often seen in adolescents and young adults.
Causes of herpes zoster
Shingles is caused by a yeast that is usually present on the skin. Their excessive growth under the influence of environmental factors can lead to the appearance of spots on the skin. Malnutrition and excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) can also lead to yeast growth.
Note: Shingles cannot be passed from one person to another (not contagious) since most people have Malassezia yeast on their skin. This condition is not caused by poor hygiene.
A weak immune system, oily and moist skin, or hot and humid climates may increase the risk of contracting shingles. Children taking corticosteroid medications may also be susceptible to this condition.
Signs and symptoms of shingles
Although white patches can appear on the face, they are often found on the chest, back, and forearms. The spots may be pink or light brown and have scales. Skin changes are usually limited to the outer layer of the skin and often do not cause any pain or itching.
Diagnosis of herpes zoster
A physical examination is sufficient to diagnose shingles. In rare cases, doctors may collect a skin scraping to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Shampoo containing selenium sulfide is the main treatment method. If the condition does not go away, then you can use antifungal or anti-dandruff shampoos. The skin may improve over a short period of time in many children. However, it may take several months to achieve an even skin tone. To prevent relapse of the disease, monthly use of shampoo is recommended.
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis (IGH) is a skin condition with small, white, oval patches.
IGH is more common in older, fair-skinned people than in children and often goes undetected.
Causes of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
The exact cause of hypomelanosis is unknown. Although this has not yet been proven, it is believed that it may be related to sun exposure.
Diagnosis of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
A physical examination is sufficient to determine the condition. Rarely are biopsy samples taken. There is usually a decrease in the number of melanocytes in the affected areas, although they are not completely absent as in vitiligo.
Treatment of idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
IGH spots are benign and do not require medical treatment. Most procedures are aimed at improving the cosmetic appearance of the skin.
Home remedies may include regular use of sunscreen and physical barriers to prevent sun exposure, as it can promote or accelerate hypomelanosis.
References:
- Milia; Healthychildren; The American Academy of Pediatrics
- Milia; MedlinePlus; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Pityriasis alba; DermNet NZ; The New Zealand Dermatological Society
- Donald N. Givler, et al.; Pityriasis Alba; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Pityriasis alba; C. S. Mott Children's Hospital; The University of Michigan 6. Pityriasis alba; The Australasian College of Dermatologists (ACD)
- Vitiligo; The mission of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
- Vitiligo; National Health Service
- Diagnosing Vitiligo; NYU Langone Medical Center
- Vitiligo: Diagnosis and Treatment; The American Academy of Pediatrics
- Tinea Versicolor; Harvard Medical School
- Pityriasis Versicolor; National Health Service
- Falon Brown and Jonathan S. Crane; Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis; The United States National Library of Medicine
- Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis; DermNet NZ; The New Zealand Dermatological Society
Is vitiligo curable?
Modern advances in cell biology are used in clinical practice to treat the disease, increasing patient recovery.
Among the most effective methods of therapy are the following:
- Performing implantation of an uncultured suspension with keratinocytes and melanocytes, transplantation of cultured melanocytes.
- Ultraviolet phototherapy. Light exposure leads to a positive effect on the processes of melanin synthesis. A prerequisite is strict adherence to individual radiation doses.
- PRP therapy. An increase in the number of platelets in depigmented areas leads to acceleration of regenerative processes and restoration of melanocyte function with normalization of melanin production.
- Needling or needle therapy. The procedure helps melanocytes enter depigmented areas through tiny punctures in the skin.
- Blister procedure. The technique is based on the use of donor tissue with ultra-thin section transfer.
The use of surgical methods to eliminate white spots in vitiligo is possible only under certain conditions (stable forms without a tendency to increase the affected area). The doctor will select the optimal treatment tactics after examination using the latest diagnostic equipment and offer various options for solving the problem of white spots on the skin.