From this article you will learn:
- why does a fistula appear on the gum,
- features of treatment in adults,
- how to treat a fistula on the gum of a child with baby teeth.
The article was written by a dental surgeon with more than 19 years of experience.
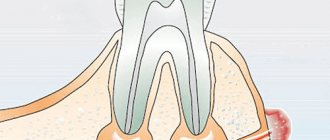
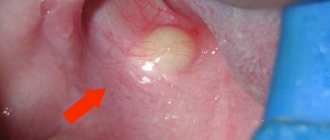
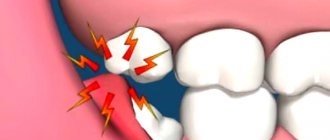
A fistula on the gum is always a symptom of purulent inflammation occurring in the root area of one of the teeth (Fig. 1-2). Most often, fistulas form against the background of exacerbation of apical periodontitis. This dental disease is most often a consequence of untreated caries and pulpitis, and when it occurs, a focus of chronic inflammation forms at the apex of the tooth root. Typically, such chronic inflammation is asymptomatic, but with hypothermia or decreased immunity, an exacerbation can occur - with the formation of pus at the site of inflammation.
The formation of pus in some cases leads to the formation of a fistula tract in the bone, which opens on the surface of the gum with a fistula opening. Accordingly, purulent exudate formed at the site of inflammation will be released from the fistula opening into the oral cavity. As a rule, the fistula opening is always located on the gum in the projection of the root of the causative tooth. In most patients, the appearance of a fistula is always preceded by pain when biting on one of the teeth. After the fistula has formed, the pain usually disappears immediately.
Fistula on the gum: photo
As we said above, a fistula on the gum is most often a companion to a focus of purulent inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. In dentistry, this disease is called “apical periodontitis.” The reasons for its development may be: 1) untreated caries and pulpitis in a timely manner, 2) poor-quality root canal filling, 3) trauma to the front teeth as a result of a blow or fall, which is more common in children. In the first two cases, you can always see caries, a filling or an artificial crown on the causative tooth (Fig. 1-2).
If the cause is an injury, you can usually see a chip on the tooth, or that the crown part of the tooth has acquired a bluish color. But a fistula can appear not only with periodontitis of the tooth. It can occur, for example, as a result of perforation, crack or fracture of the tooth root (allowed by the dentist during root canal treatment), and a fistula can also appear as a result of such gum disease as localized and generalized periodontitis.
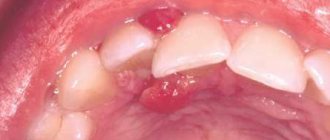
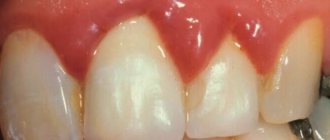
With periodontitis, periodontal pockets form along the surface of the roots of the teeth, from which purulent discharge drains during periods of exacerbation. If the periodontal pocket is very deep, then the outflow of pus from it may be impaired. In this case, an abscess forms in the projection of the periodontal pocket between the gum and the root of the tooth, which dentists call the term “periodontal abscess.” One of the outcomes of a periodontal abscess may be the formation of a fistula, through which pus will escape into the oral cavity (Fig. 3).
What does a fistula on the gum look like (video) –
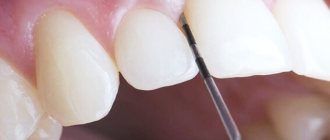
Pay attention to video 1 - how the doctor inserts a thin gutta-percha pin into the fistula opening, used for filling root canals. Through the fistula tract, the pin can be advanced directly to the source of inflammation, i.e. get it right to the top of the tooth root. This clearly shows that the fistula tract connects the fistula opening on the gum - directly with the source of inflammation at the root of the tooth.
Fistula on the gum in a tooth: what is it and what does it look like?
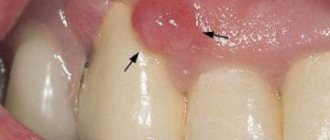
When the soft jaw tissues are in an inflamed state for a long time, microorganisms begin to multiply in them and purulent fluid (exudate) accumulates. When there is too much of it, an exit hole appears, which is called a perforating channel. This pathology is defined as a fistula, which looks like a red bump or pimple with a white dot in the middle or on the side. Its diameter can reach 1 centimeter. Another name you may hear is fistula, which means “tube” in Latin. Usually he appears next to the patient.
Factors contributing to the appearance of a fistula tract
Among the provoking factors that are important to exclude:
- poor oral hygiene;
- presence of untreated caries;
- pulpitis;
- malocclusion;
- frequent stress;
- unbalanced diet;
- physical fatigue;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- habit of eating a lot of sweets;
- smoking.
Why do fistulas form on the gums?
There are many situations in which microbes can begin to multiply. We suggest you look into some of them.
Caries and pulpitis
How soon do you go to the dentist when you notice discoloration? Many people put it off until the last minute, until they get tired of enduring the pain. But it is much easier and more comfortable to remove the affected area before it spreads to the pulp - the neurovascular bundle that nourishes and protects the jaw from the penetration of harmful microorganisms.
If you do not begin to solve the problem when the first symptoms appear, the nerve may die and the bacteria will quickly spread to neighboring teeth.
Periodontitis
After the infection penetrates from the pulp chamber into the root and further into the apex, pus begins to spread, affecting the tissue. At this time it is under pressure, so it can easily form a fistula tube. This process is called periodontitis. Typically, a fistula occurs only after prolonged inflammation.
What causes a fistula on the gum: cysts or granulomas
When periodontitis takes on a chronic granulomatous form, a cyst grows - a small sac covered with epithelium and filled with purulent fluid. Its diameter can vary from one to six centimeters, and the granulomas themselves do not reach five millimeters. Cystogranuloma does not release exudate into other tissues, but if it is close to the surface, then over time a fistula canal appears.
Perforated root
When a dentist cleans the space inside a tooth, he can sometimes make the mistake of pressing hard on the file - the needle that processes the root tract. Or it can be directed incorrectly, which causes a hole (perforation) to form, which always leads to an inflammatory process. When the doctor notices that he is making a mistake, he must immediately close the canal. But not everyone does this, and subsequently the tooth has to be removed, since it can no longer be treated.
In modern clinics, after treatment procedures, a final x-ray is performed to ensure the effectiveness of the work performed. The doctor must not only show, but also decipher them to the patient. If he doesn’t do this, don’t hesitate to ask yourself.
Periostitis
Almost everyone has encountered this disease, despite the fact that many people are hearing this name for the first time. In the people, inflammation of the periosteum is commonly called gumboil. When it appears, a person feels severe pain, swelling of the gums and facial tissues, and an increase in temperature. Most often it ends with the appearance of a hole from which purulent deposits emerge.
Periodontitis
A fistula can form not only as a result of complications of diseased teeth, but also due to poor cleaning. The plaque that appears on the surface gradually hardens, transforming into a periodontal pocket. Microbes accumulate there, which subsequently leads to inflammatory processes. The gingival ligaments break down and it becomes difficult for the pus to escape, so it creates a hole.
Complications from treatment
There are also unpleasant situations when caries or pulpitis are removed poorly; in such cases, it continues to develop under the filling. When removing any unit, certain difficulties may also arise, for example, if this is done with non-sterile instruments, the infection easily penetrates through the affected area. Therefore, do not be lazy to read reviews about a specialist before going to him.
It is better to give preference to private clinics; they are equipped with modern equipment that helps the doctor eliminate the problem even in hard-to-reach areas.
These are the most common reasons why a fistula appears on the gum. But don’t forget about other situations:
- with oncological diseases of the jaws, several fistulas with copious purulent discharge may form;
- inflammation is possible when wisdom teeth cannot erupt;
- if the crown does not fit tightly to the denta, bacteria can accumulate under it;
- In case of injuries or damage to the gums, infection can also occur.
Also, it is worth paying attention to some factors that provoke the onset of the disease and complicate its course:
- poor oral hygiene;
- disturbances in occlusion (closing of the jaws) and malocclusion;
- exposure to too high or low temperatures, as well as their changes;
- stressful, neurotic state;
- overwork, chronic fatigue;
- weakened immunity;
- metabolic disorders, poor nutrition, lack of essential substances;
- abuse of carbohydrates and foods high in sugar;
- smoking.
Content:
- Causes of the problem 1.1. Advanced caries, pulpitis 1.2. Granuloma 1.3. Periodontitis 1.4. Perforation at the root 1.5. Periostitis 1.6. Periodontitis
- Risk group for developing a fistula on a tooth
- Factors contributing to the appearance of a fistula tract
- How to recognize the disease
- How to cure a fistula
A fistula or fistula is a perforation of the gum tissue.
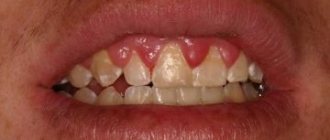
Visually, the formation resembles an abscess - it is round, with purulent masses inside and a red border outside. It can reach up to one centimeter in diameter. Serves as a channel for draining pus. A fistula on a tooth indicates that a pronounced inflammatory process is occurring in the deep layers. Due to damage to the periodontal zone, an accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms and dead cells occurs. To get rid of them as they accumulate, the human body acts very smartly - it creates conditions for the appearance of a fistula.
If this drainage channel did not exist, pus would accumulate in large quantities. One can only guess what dangerous consequences this would lead to.
Fistula on the gum: symptoms
The signs of this pathology are very obvious, so it is quite easy to determine:
- a reddish lump appears, from which liquid flows, unpleasant to the taste, sometimes bloody;
- the person feels pain, which becomes stronger when cleaning or chewing, and after the release of pus, it decreases;
- the tissue around the sore tooth may swell, sometimes along with the cheek or lip;
- the breath smells rotten, and the taste of food changes due to exudate;
- unreasonable weakness and apathy arise;
- temperature rises;
- Nearby lymph nodes enlarge.
Possible complications
Many people do not understand why a fistula on the gum is dangerous, so they do not use the services of a dentist, believing that the disease goes away along with the pain. This is completely wrong: despite the comfortable sensations, bacteria still continue to multiply in the affected area, and this leads to unpleasant consequences that are life-threatening:
- tooth loss;
- sinusitis, sepsis (blood poisoning);
- the appearance of cysts;
- suppuration in the brain;
- the formation of polyps and ulcers on the heart valves;
- abscess of facial and cervical tissue;
- destruction of the jaw.
If the condition reaches such pathologies, then the treatment will be long and painful.
Surgery
For a fistula on the gum, 3 types of surgical interventions are possible:
- emergency care: the abscess is opened and the exudate is drained through a hole in the gum;
- tooth-preserving operations: resection of the root apex, amputation, hymesection, corono-radicular separation, replantation, manipulations to remove cysts (cystotomy, cystectomy);
- radical interventions: tooth extraction, maxillofacial surgeries of varying complexity, etc.
During treatment, the doctor will try to save the tooth.
Emergency care for the formation of a fistula is always used. Tooth-preserving operations are resorted to if one or more roots of a unit are severely damaged and cannot be subjected to endodontic treatment.
And radical interventions are used when it is impossible to save teeth, and the inflammation has turned into a severe complication involving a large area of bone and soft tissue: periostitis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, sinusitis, etc.
How and how to treat a fistula on the gum: conservative methods
They are used only when there are no complications and the diseased tooth can still be saved. In the process, the abscess is cleaned, inflammation is relieved and damage is restored. There are three techniques that are most often combined: endodontic, medicinal and physiotherapeutic.
Endodontics
This type of therapy can be carried out in different ways, depending on why the fistula appeared and how the disease progresses:
- First, you need to get to the pulp chamber by preparing the dental cavity. It is possible to cut off dead tissue with a dental bur. If only caries is present, then only the affected enamel and dentin (bone substance) can be removed.
- With pulpitis, the chamber is opened and the nerve is removed. If necessary, sealers and fillers that were used to fill the canals are removed from the “dead” tooth. In addition, you need to take pictures or use an apex locator to measure their exact length, since it is very important to reach the apical foramen. To make the work easier, special softening agents can be used.
- Next, the doctor must expand the canals for future filling and treat them with antiseptics or endodontic devices. They are then left open for several days and rinsed with antiseptic solutions. This helps remove purulent fluid through the roots.
- After this, temporary filling is done with calcium hydroxide sealers for 1-3 months, which can be repeated up to three times.
- Then the holes are finally filled using gutta-percha pins, a final photograph is taken and the supragingival part is restored using fillings or crowns.
How to treat a fistula in the gum with antibiotics
Such drugs are prescribed to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms that lead to the occurrence of an inflammatory process. Since a solution or injection applied topically is not as effective, an antibiotic is needed. If the cause is a cold or hypothermia, you need to take Amoxicillin or Augmentin. In addition to them, it is possible to use Ciprofloxacin, Lincomycin, Tsiprolet, Ofloxacin, Flemoxab solutab, Sumamed. Sometimes it is supplemented with Metronidazole.
Remember that only a doctor can prescribe medications. Don’t self-medicate, but come to Dentika: the clinic’s specialists will select the right type of therapy, prescribe medications and relieve you of your problems in the optimal time frame.
Ointments and gels
Experts believe that external treatment quickly removes pus, disinfects the wound, relieves pain and heals the fistula itself. Ointments are not very effective in this matter, since they are immediately washed off by saliva. Antibacterial and anesthetic gels such as Cholisal, Kalgel, Dentol, Dentinox and others are more suitable for this work. Solcoseryl is prescribed as a healing agent.
Anti-inflammatory and painkillers
Sometimes the pain becomes unbearable, the doctor may prescribe Ketonal, Ibuprofen, Nise, Arcoxia, Naproxen, Ketorol, Ketoprofen and other drugs for internal or external use. Always read the instructions carefully before taking the tablet.
Antihistamines
With the help of Claritin, Tavegil and Suprastin, doctors eliminate allergic reactions and swelling, and remove toxins. You should not overuse medications; it is better to consult a specialist and undergo a course of treatment.
Rinses
The dentist may recommend rinsing the mouth with special solutions: chlorhexidine, furatsilin, Miramistin, Stomatofit, Chlorophyllipt, Betadine. Folk remedies also remain effective: soda-salt solutions, decoctions of chamomile, sage and other herbs.
Physical methods
To achieve a faster effect of treatment, dentists supplement it with physical therapy:
- ultrasound or laser treatment;
- ultraphonophoresis;
- fluctuarization;
- magnetotherapy;
- coagulation, etc.
Medicines
How to remove a fistula using medications? If the process of tissue damage has gone too far, the dentist will prescribe antibiotics in the form of intramuscular injections or tablets.
Important! You cannot treat a fistula yourself with antibiotics, because you do not know the nature of the bacteria that have affected the tissue.
Most often, the dentist prescribes Gentamicin or its derivatives. In other cases, the following drugs may be prescribed:
- Doxycycline;
- Amoxicillin;
- Amoxiclav;
- other drugs.
It is worth noting that any medical drug has side effects on the body, so the dentist prescribes the medicine taking into account the patient’s health condition.
After eliminating the source of infection, a course is carried out to restore the integrity of the affected tissues. Sometimes the doctor prescribes laser therapy if there is a risk of bleeding - the laser beam cauterizes the wound surface.
A common and painless method of restoring the mucous membrane is ultrasound. After tissue treatment with ultrasound radiation, regenerative processes occur many times faster.
The dentist prescribes medications to help close the formed canal. These include Betadine and Chlorhexidine. An ordinary saline solution can also help regenerative processes.
Note! To avoid damaging the affected gum surface, it is recommended to use brushes with soft bristles.
To make the wound heal faster, use gels/ointments - Metrogyl Denta, Asepa, Solcoseryl and others. If severe pain overcomes, lubricate your gums with pain-relieving gels.
How and what can be used to cure a fistula on the gum of a pregnant woman
Some expectant mothers refuse to visit the dentist for fear of harming the baby. Indeed, while the fetus is developing, it is better not to perform operations or take medications, but inflammation and ulcers will be much more dangerous for the child if they are not cured.
Usually only those treatment methods are used that are approved by obstetricians and gynecologists. Sometimes only purulent formations are cleaned, and the main methods of therapy are used only after childbirth. In any case, each situation must be considered individually with the attending physician.
Prevention
The development of a fistula is not a pleasant situation, so it is better to take care that it does not occur at all:
- Brush your teeth regularly at least twice daily;
- if you notice carious formations, go to the doctor as soon as possible;
- Visit your dentist at least twice a year, as it is not always possible to see any problems on your own;
- watch what you eat, reduce your consumption of sweets and spicy foods;
- drink less coffee and alcohol.
Following these rules will save you not only from dental diseases, but also from other health problems.
When a fistula appears on the gum in a tooth, its causes and treatment, as a rule, become interrelated. Therefore, before you start taking any measures, you need to find out why the pathology arose. And this can only be done by a qualified specialist using special equipment.
You should not self-medicate at home; it is better to immediately make an appointment with a doctor at Dentika. Then you will be able to cope with the disease without pain and unnecessary effort.