Necrosis is a serious pathology accompanied by the death of gum tissue. It is quite rare in dental practice. The danger of this process lies in its irreversibility, asymptomatic course in the early stages of development and serious complications that it can lead to if the necessary measures are not taken in time. Find out what can trigger necrosis of gingival tissue, what the dead areas look like, what symptoms should alert you and where to go if they are identified.
Possible reasons
Gum necrosis can be associated with various negative factors. The process of cell death is triggered by:
- chemical burns - doctor’s mistakes when killing the dental nerve with arsenic, treating gum fibromatosis using liquid nitrogen;
- prolonged exposure to low temperatures - applying ice to the gum after implantation and other dental procedures;
- chronic periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that affects all periodontal structures; in severe cases, soft tissues die;
- mechanical injuries of the gums - rubbing of the mucous membrane with a prosthesis, cuts with subsequent infection, jaw fractures, serious bruises;
- hormonal imbalances - pregnancy, age-related changes in the body, taking certain groups of medications;
- bad habits - smoking, use of narcotic and psychotropic substances.
To establish the cause of gum necrosis, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive diagnosis. If the pathological process is not stopped, dangerous complications can arise. The most common include osteomyelitis of the jaw, sepsis, and loss of chewing function.
Main symptoms of gum necrosis
The symptoms of necrosis are quite characteristic and are difficult to confuse with other diseases. The main thing is to make a diagnosis in the early stages. With gum necrosis, two forms of its development are noted:
- Necrosis of the dry type - with it, the death of dead tissue is noted due to gradual drying out. It is quite easy to separate such areas with a scalpel and, after draining the entire cavity, disinfect them with a specially prepared antiseptic solution.
- Wet type necrosis is characterized by the presence of serous-purulent contents in the cavity of the gum area. It can be cured only after certain measures are taken to convert the wet type to the dry type.
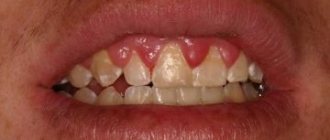
Necrosis is accompanied by hyperemia, increased pain reflex, and significant swelling of the gums.
Clinical picture
Symptoms of gum necrosis directly depend on the stage.
- Early. Signs of tissue necrosis are weak. You may notice loss of enamel shine, roughness of teeth, and pale gums.
- Average. The interdental papillae swell. A gray coating forms on the oral mucosa. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Heavy. The gum tissue swells greatly, becomes black, and numerous ulcers appear on it. Appetite disappears, body temperature rises to 39 °C.
- The last one. The epithelium dies. There is severe pain in the gums. The necks of the teeth are exposed, and the dental units begin to loosen.
Preventive measures to protect against gingival necrosis
Preventing the spread of pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity. Why it is necessary to observe basic sanitary and hygienic measures:
- regularly brush your teeth using special hygiene products (pastes, powders, gels);
- rinse your mouth after any use of food;
- use mouthwashes that contain certain antiseptics;
- remove tartar and plaque in a timely manner using ultrasound at the Valadent professional hygiene center.
Compliance with dietary culture, namely limiting the consumption of alcoholic beverages, spicy and exotic dishes, and those containing a high percentage of sugar. This recommendation is primarily intended for people suffering from gastrointestinal disorders and diabetes. In diabetes, the enzymatic production of the pancreas is disrupted and metabolism is disrupted.
Mandatory visits to the dentist once every six months for a preventive examination at Valadent dentistry.
First aid
If after tooth extraction there is mild inflammation and there is no suppuration, it can be removed at home and prevent the spread of discomfort.
- For 30 minutes after tooth extraction, do not remove the antiseptic tampon placed in the hole.
- Do not eat for 2 hours after removal.
- If there is bleeding after tooth extraction, apply a cold compress, such as an ice cube, to the gum.
If a doctor prescribes rinses for the treatment of inflamed gums, they should be done as carefully as possible. It is important not to wash the protective clot out of the hole. On the first day after surgery, you should avoid rinsing, and on the second day, use antiseptics and herbal decoctions.
During the healing period, it is also recommended to avoid food and drinks that are too cold or too hot, and never touch the socket with your fingers, toothpicks or other foreign objects.
A reliable rinse that will help eliminate gum inflammation is the ASEPTA ACTIVE mouth rinse. This unique two-component rinse with a combination of chlorhexidine + benzidamine has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects and provides an immediate anesthetic effect.
Types of pathology
Depending on the cause of formation and location, necrosis is classified into several types:
- Cervical necrosis , affecting the area in the gum area or even extending under it. The pathology is manifested by the formation of a chalky spot, which quickly turns black. Cervical necrosis can quickly spread to adjacent dental units.
- Acid necrosis , as the name suggests, is caused by exposure to dangerous acids. As a rule, this type of disease is detected in people working in hazardous industries. It can also be observed in people suffering from gastritis. This necrosis begins with demineralization of a small area of tooth enamel, which gradually leads to thinning of the enamel and tooth destruction.
- The radiation type is formed as a result of harmful radiation. It is observed in people whose work involves hazardous radiation, as well as in patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy. In addition to the fact that the tooth is destroyed, the general condition of the mucous membrane worsens, and the periodontium may become inflamed.
- Computer necrosis is a relatively new type of pathology that affects people who spend a lot of time at the computer. Such necrosis can develop after several years of sustained, constant exposure to a computer on the human body. The pathology practically does not manifest itself at all; it can only be visualized by darkening of the tooth enamel.
After diagnosing the disease and making a diagnosis, the specialist selects the most suitable treatment option. If cervical necrosis is diagnosed, the tooth surface is treated with a composition that reduces the sensitivity of the enamel. Then the tooth is filled. If a tooth has darkened due to exposure to a computer, the necrotic tissue is removed, the resulting cavity is filled several times with a special compound, and only then a filling is placed. If necrosis has developed under the influence of dangerous acids, it is first necessary to eliminate their exposure, and only then carry out remineralizing therapy. Treatment of necrosis is carried out comprehensively, in addition to filling, medications and vitamins are prescribed, as well as applications with special pastes.
Prevention
Prevention of this pathology, first of all, consists in eliminating aggressive factors that provoke tissue death, or limiting their impact.
In addition, it is necessary to adjust the diet, reducing the consumption of sour and sweet foods to a minimum.
It is also worth paying special attention to the quality of oral hygiene and regularly visiting the dentist.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags treatment necrosis tooth decay
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Schutz implants: features of creation and installation
Next article
Chronic caries: characteristic signs, treatment methods
Treatment of the pathological process
How to treat gum necrosis? Treatment of pathology and its effectiveness are determined by the form and stage of the pathological process, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases. Necrosis is irreversible, which means it will not be possible to restore dead tissue. In order to prevent further development of the process of death and intoxication of the body, first of all it is necessary to remove dead cells.
Further therapeutic measures are aimed at restoring blood circulation to the affected areas, restoring normal conduction of nerve endings and cell regeneration, and strengthening the immune system.
How to treat gum necrosis? There are two treatment strategies, which depend on the form of the pathology:
- in case of dry necrosis, to stop the spread of infection, the affected area is treated with antiseptic agents. Then, dead tissue is surgically removed, and normal blood flow is established in areas that have not lost functionality,
- with wet necrosis, the disease is initially transferred to the dry form. So, the affected area is treated with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, then all abscesses and ulcers are opened and drained, and treated with antiseptics. If the patient’s condition worsens on day 2-3, the necrotic tissue is urgently removed.
As can be seen from the treatment methods considered, it is impossible to get rid of necrotic tissues without surgical intervention - they are already dead and cannot be “revitalized”. But what to do then? There are 2 options here - either taking a course to restore periodontal tissue (using injections into the gums, replanting regenerating membranes, etc.), or plastic surgery to correct the level of the gums.
Symptoms and manifestations of gum necrosis
Read on the topic: what is plasma lifting in dentistry and why it gives good results after use.
Since during the pathological process the infection leads to local inflammation and intensively spreads throughout the body, causing general intoxication, the patient is additionally prescribed drug therapy. This is taking antibiotics, applying medicinal ointments (methyluracil, for example) and gels to the gums, rinsing the mouth with various solutions (Rotokan, for example, or chamomile infusion).
What factors provoke it?
The development of this pathology can be influenced by a variety of and completely different factors. Dental tissue necrosis can be provoked by both internal and external causes.
Domestic
Internal factors include the following:
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- pregnancy period. As a rule, necrosis was observed with frequent pregnancies following one after another;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, for example, hypothyroidism;
- imbalance of hormone production (especially in adolescence);
- regular human intoxication;
- genetic predisposition.
Internal factors mainly lead to the occurrence of cervical necrosis .
External
External factors include everything that can negatively affect tooth tissue directly :
- excessive or prolonged exposure to substances containing acids or harsh chemicals. For example, medicines, products, industrial substances;
- receiving high doses of radiation. Most often observed in the treatment of cancer diseases;
- constant exposure to electromagnetic radiation.
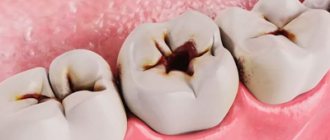
Loss of dental tissue due to erosion
Tooth erosion
- progressive loss of dental tissue (dentine and enamel) of an insufficiently studied nature.
Some authors suggest that the cause of tooth erosion, like the wedge-shaped defect, arises solely from the mechanical action of the powder and the toothbrush. Others believe that the appearance of erosion is due to the large amount of consumption of citrus fruits and their juices. In any case, our dentists will be able to help in any clinical situation - they will provide high-quality treatment and save you from dental erosion.
A significant role in the mechanism of progression of erosion of hard dental tissues is assigned to increased function of the thyroid gland, and, in particular, endocrine disorders. According to experimentally obtained data, one of the main symptoms of this disease is considered to be a decrease in saliva viscosity and an increase in its secretion. It has been proven that tooth erosion occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis twice as often as in people with normal thyroid function. At the Dantley Clinic, our dentists will perform remineralization as a treatment option for erosion. The number of patients with erosion of hard dental tissues increases by 20% with an increase in the duration of the disease by just one year.
Erosion is the loss of dental tissue, which will continue to progress without medical intervention. Dental tissues are affected and thinned on one or more sides of the tooth.
Erosion of hard dental tissues mainly manifests itself on the symmetrical surfaces of the lateral and central incisors of the upper jaw, as well as on small molars and canines of both jaws. Erosion practically does not occur on large molars and incisors of the lower jaw. The lesion is most often observed in middle-aged people, and is characterized by a long course - up to 10-15 years. In St. Petersburg, the Dantley Clinic provides remineralization and restoration of teeth to patients of all ages. Over time, a large number of teeth become involved in erosion. Due to the significant impact of adverse factors, including environmental ones (Chernobyl disaster, etc.), the number of cases of dental erosion in fairly young people (18-25 years old) is significantly increasing.
Manifestation of tooth erosion
It is a round or oval enamel defect located in the transverse direction of the more convex part of the labial (vestibular) surface of the dental crown. The bottom of the erosion is shiny, hard and smooth. The gradual expansion and deepening of the boundaries of erosion leads to the loss of part of the dentin and all of the enamel.
There are two transitional stages of damage:
- initial (enamel erosion);
- pronounced (erosion of dentin and enamel).
According to the depth of the lesion, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
first degree (initial)
- only the superficial layers of enamel are affected;
second degree (medium)
— the entire thickness of the enamel is affected, dentin is not involved in the pathological process;
third stage (deep)
— the entire thickness of the enamel, as well as the surface layer of dentin, is affected.
According to the course of the disease, two stages of erosion are distinguished - active and stabilized, but both of them are characterized by a chronic course. With any type of erosion, our dentists will carry out remineralization or filling, reducing the chronicity of the disease to zero.
The active stage is characterized by:
- rapid loss of hard dental tissues;
- increased sensitivity of the affected area to external irritants (sweet, sour, hot, cold, building up to erosion).
The stabilized stage is characterized by:
- slowly progressive loss of hard dental tissues;
- lack of increased sensitivity of the diseased area;
- possible transition from a stabilized stage to an active one.
Treatment of tooth erosion
Local treatment of the active stage:
- The goal is to stabilize the process. This result is achieved through additional remineralization of hard dental tissues using calcium electrophoresis or applications. Daily applications of a 10% potassium gluconate solution are prescribed for 15 minutes for 15-20 days. After which, for 3 days, a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied to the area of erosion for 3 minutes. And the treatment is completed by coating the diseased surface with fluoride varnish. A 10% calcium gluconate solution is used for electrophoresis. The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes. After the electrophoresis session, a swab moistened with a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied to the area of erosion. The entire course of treatment is 10-15 procedures.
- Fluoridation - restoration and strengthening of enamel with fluoride-containing and mineral substances.
- Filling erosion with composite materials fully restores the defect, the teeth look beautiful and natural.
- If there is a large area affected by erosion, it is worth making artificial crowns.
Local treatment of the stabilized stage:
- Phosphorus and calcium preparations, microelements and vitamins are prescribed internally.
- The task is tissue depigmentation. For this purpose, over the course of two or three visits, the affected surface is treated with an abrasive paste with a high fluorine content. Whitening, filling and restoration of the defect area are also used.
Diagnostics
For diagnosis, standard methods are used that would distinguish necrosis of hard tissues from pathologies with similar symptoms and differentiate the varieties.
For this purpose, a visual examination is used, as well as instrumental and hardware examination, using X-ray equipment .
Differential
Marble disease and Stanton-Capdepont syndrome have symptoms similar to necrosis. But unlike them, necrosis spreads much faster.
Fluorosis and enamel hypoplasia, in contrast to necrosis, begin during the intrauterine development of the fetus and manifest themselves immediately after tooth germination. In addition, these pathologies are characterized by symmetry and preservation of the properties of the enamel.
The death of dental tissues from ordinary caries can be diagnosed by the location of the lesion. Caries is characterized by damage to any one zone, where it will only deepen and gradually expand.
With necrosis, the entire surface is affected, regardless of the site of primary localization.
How are the species distinguished?
In order to accurately diagnose pathology, it is necessary to differentiate it not only from other dental diseases, but also to determine the type of disease.
Unlike the others, the computer one immediately affects the pulp, which is shown on X-ray images. For other species, this symptom is unusual.
In addition, the enamel loses its shine and uniformity over the entire surface, and not just at the location of the lesion.
The slowly progressing rate of the disease and the formation of sharp edges will help to distinguish the acidic type, which is not typical for the radiation type, in which flat, ground edges are formed.
Radiation is always accompanied by a general deterioration of the condition of both the oral cavity and the entire body.