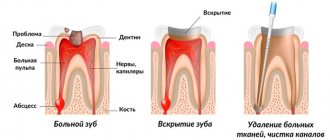
Most people have experienced dental problems at least once in their lives. The reason for this is that the protective layer of tooth enamel is eventually unable to withstand one or another external influence and is damaged. As a result, at the site of damage to the enamel, dental tissue becomes accessible to bacteria that can destroy it. This begins the irreversible process of formation of a carious cavity in the tooth, which, if timely measures are not taken, sooner or later will eventually reach the pulp chamber. Microorganisms penetrate into the opened pulp, as a result of whose vital activity an inflammatory process begins, usually causing severe pain.
Of course, it is best when a carious cavity is detected at the very beginning of its formation. Modern dental technology allows you to quickly and almost painlessly repair a tooth damaged by caries. High-quality materials used for filling ensure reliability and long-lasting treatment results.
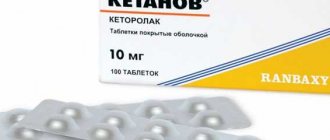
Ketonal for toothache
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to detect caries in the early stages of development, especially when molars are affected, and a person learns about his problem only when the tooth begins to hurt. Some people who are afraid of dentists try to endure toothache, deceiving themselves that the pain will go away on its own. Yes, indeed, a toothache can subside on its own for a while. However, this does not mean that the diseased tooth will recover. The destruction and inflammation of dental tissues will progress and, ultimately, can lead to pathologies that require complex and expensive treatment, tooth loss, and even death.
Therefore, even a slight pain in a tooth is a call to go to the dentist’s office. However, due to certain circumstances, a person cannot always do this without barely feeling pain. And a tooth can hurt so badly that a person’s life turns into a real nightmare. The only way out of this situation is the use of painkillers, the most popular of which are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Most often, people use analgin to relieve pain, since it is inexpensive and is sold freely. However, this drug, like other medications containing metamizole, may be practically powerless against acute pain. In this case, stronger analgesics such as ketonal will be needed. What is ketonal , and how to use it for toothache ?
How to use ketonal for toothache
The active component of this medicine is the organic substance ketoprofen, a derivative of propionic acid, which has an anti-inflammatory effect and is similar in its pharmacological characteristics to ibuprofen. Like other similar drugs, ketoprofen blocks enzymes that regulate the biochemical formation of prostaglandins during the inflammatory process, and thereby relieves inflammation and alleviates its symptoms, such as fever, swelling and pain.
Although the main area of use of ketoprofen is the treatment of injuries, bruises and arthritis, this medicine can be used in the case of toothache.
Ketoprofen can be administered into the body in the following ways:
- orally – in the form of tablets, capsules and granules to obtain a drinking solution;
- rectally - in the form of suppositories inserted into the rectum;
- parenterally - in the form of a solution for injections;
- externally - in the form of gels, ointments, aerosols.
The rate of absorption of the drug depends on the method of its use. It takes the longest to be absorbed when used in the form of suppositories - up to four hours, and fastest when injected - up to half an hour. When taken orally, absorption lasts a maximum of two hours. When using anti-inflammatory medication, noticeable improvement is observed approximately seven days after the start of treatment.
Like other drugs, ketoprofen is deactivated by the liver and excreted in the urine and, partly, in bile. This substance is not able to accumulate in the body.
Ketonal for toothache
How does ketonal help with toothache?
This drug relieves pain and other symptoms of the inflammatory process quite well. However, it is not very effective in reducing body temperature. This medicine soothes pain, regardless of where the inflammatory process is localized. Therefore, it can be used to eliminate any pain of inflammatory origin, including dental pain.
When buying ketonal in the form of tablets or capsules, you should always pay attention to how much of the main active ingredient they contain, since several versions are available, differing in the concentration of ketoprofen. Accordingly, forms of the drug with different contents of a given analgesic will require different dosage regimens.
The maximum daily amount of ketoprofen is two hundred milligrams. Therefore, those tablets that contain one hundred milligrams of the main drug can be taken twice a day. The same dosage forms, where there is twice as much ketoprofen, should be taken no more than once a day.
Ketonal is a potent analgesic that can relieve toothache. However, the extent to which it makes sense to take it depends on the intensity of the pain. So, in the case of caries, even before the onset of pulpitis, a slight aching pain may be felt, but strong drugs are not needed to calm it. Here you can, for example, use drops from tincture of valerian and mint and camphor oils. However, in the case of pulpitis and periodontitis, the pain is much more intense and can be unbearable. In this situation, it really makes sense to use analgesics such as ketonal.
How to take Ketonal tablets for toothache
There are several types of ketonal tablets. In order to choose the right option, you should take into account the nature of pain and the specifics of a particular case.
If a visit to the dentist is scheduled for the near future, for example, the next morning, then it is generally undesirable to take analgesics. The use of painkillers can create difficulties in diagnosing a diseased tooth. In addition, the medication taken the day before may affect the pain relief provided in the dentist's office.
If you are unable to go to the dentist in the next couple of days, it is best to use the drug Ketonal Duo in the form of capsules, each of which contains one hundred and fifty milligrams of ketoprofen. The peculiarity of this medication is that it consists of white and yellow granules that differ in the rate of release of ketoprofen, and, accordingly, the speed of onset of the effect and its duration. If you take Ketonal Duo for toothache , the white granules will take effect within fifteen minutes. Yellow ones begin to act later, but their effect is longer. Thus, this form of medication provides both a quick and long-lasting effect. After using Ketonal Duo, the pain goes away almost immediately and does not return for a long time, and you will not have to take the medicine again soon.
Ketonal DUO for toothache
Ketonal is a strong medicine. However, it cannot cure either pulpitis or periodontitis. In case of dental diseases, this drug only makes the pain subside for a while. In case of inflammatory processes in the tooth, only a dentist can solve the problem. Therefore, if you have a toothache, you need to go to the doctor as soon as possible.
Ketonal DUO in the treatment of pain syndrome
Pain is the most common symptom of a wide variety of diseases. The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defines pain as an unpleasant sensation and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage [1]. Pain is heterogeneous, has many characteristics and occurs due to various pathophysiological mechanisms underlying a particular disease. That is why, for successful treatment of pain syndrome, drug therapy should be selected in accordance with the type of pain and the characteristics of its pathogenesis.
Classifications of pain syndrome
In medical practice, acute and chronic pain are distinguished. Acute pain is caused by tissue damage and decreases as it heals, is characterized by a sudden onset, short duration, clear localization and, as a rule, is a symptom of some disease. Acute pain performs a signaling function, warning of danger and ensuring the mobilization of the body's defenses aimed at eliminating the damaging factor. Pain is called chronic if it persists after the healing process is complete. There is still no consensus on the time criterion for pain chronicization, that is, it is unclear at what point in time chronicization occurs. According to the International Association for the Study of Pain, pain is considered chronic if it lasts at least 3 months, and in accordance with the criteria of DSM-IV (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of mental disorders) - at least 6 months. In any case, chronic pain is not accompanied by signs characteristic of acute pain, does not have a protective function and becomes the cause of suffering for the patient. However, the main difference between chronic pain and acute pain is not the time factor, but qualitatively different neurophysiological, psychophysiological and clinical relationships. According to the generally accepted pathophysiological classification, pain is divided into nociceptive, neuropathic and dysfunctional.
Nociceptive pain
occurs when peripheral pain receptors - “nociceptors”, are irritated, localized in almost all organs and systems (coronary syndrome, pleurisy, pancreatitis, gastric ulcer, renal colic, articular syndrome, damage to the skin, ligaments, muscles, etc.) due to damage and /or inflammation of soft tissues. With this type of pain, the factor that caused it is usually obvious, the pain is well localized (nociceptive pain is usually localized in the area of damage). When describing nociceptive pain, patients most often use the terms “squeezing”, “aching”, “pulsating”, “cutting”. In the treatment of nociceptive pain, a good therapeutic effect can be obtained by prescribing simple analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). When the cause is eliminated (cessation of irritation of the “nociceptors”), nociceptive pain goes away [2].
Neuropathic pain
occurs due to damage to various parts (peripheral and central) of the somatosensory nervous system [2]. The causes of neuropathic pain can be damage to the afferent somatosensory system at any level, from peripheral sensory nerves to the cerebral cortex, as well as disturbances in descending antinociceptive systems. This type of pain occurs in diabetic polyneuropathy, postherpetic and trigeminal neuralgia, post-stroke condition, and phantom pain. The general characteristics of neuropathic pain are: duration, persistent nature, variety of sensory manifestations (hypersthesia, hyperpathia, allodynia, loss of various types of sensitivity), combination with autonomic disorders (hyperemia or decreased blood flow, hyper- or anhidrosis in the pain area) and motor disorders. Standard analgesics and NSAIDs are ineffective in the treatment of neuropathic pain [3].
As a rule, in most cases (radiculopathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, cancer, complex regional pain syndrome), pain is of a mixed nature, including both nociceptive and neuropathic components [2]. In the treatment of mixed pain, various therapeutic approaches are used. The peculiarity of dysfunctional pain is that the examination fails to identify the cause of the pain or organic diseases that could explain the origin of the pain. Among the main reasons contributing to the development of this type of pain are not organic pathology, but psychological and social factors. Typical examples of dysfunctional pain are fibromyalgia, tension headaches, and psychogenic pain (somatoform disorders) [4]. Another characteristic of the pain syndrome that influences the choice of analgesic therapy is its intensity. It is generally accepted to divide pain into mild, moderate and severe.
Pain therapy
Currently, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs occupy a leading position in the treatment of pain syndrome. Due to their mechanism of action, NSAIDs have proven themselves to be best for acute nociceptive pain of mild to moderate intensity. The advantage of NSAIDs is that they have not only an analgesic but also an anti-inflammatory effect. The therapeutic effects of NSAIDs are based on reducing the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid through inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX). There are two isoforms of COX: COX-1 is constantly present in all tissues, COX-2 is synthesized against the background of inflammation. Of particular interest are new dosage forms of NSAIDs that make it possible to maintain a pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect and at the same time reduce the degree of undesirable effects on the gastrointestinal tract [5–7].
Ketonal DUO: advantages of the new form
New NSAIDs include Ketonal (Lek, Slovenia), the main active ingredient of which is ketoprofen. According to its chemical structure, ketoprofen belongs to the group of propionic acid derivatives. It non-selectively inhibits the enzymes COX-1 and COX-2 and, partially, lipoxygenase. The powerful anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of ketoprofen is due to the fact that it has both a peripheral and central mechanism of action, therefore it is used even in cases of severe pain. In peripheral tissues, ketoprofen suppresses the synthesis of prostaglandins, stabilizes lysosomal membranes, and has distinct anti-bradykinin activity. Due to its high lipophilicity, the ketoprofen molecule penetrates the blood-brain barrier, where it realizes its central effect: it reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins and blocks excitatory amino acid receptors in the spinal cord. Ketonal DUO is an innovative form of NSAID. It differs from both regular and extended-release forms in the way it releases the active substance. Modified release capsules contain two types of pellets: white (about 60% of the total) and yellow coated pellets (about 40%). Ketoprofen is quickly released from white pellets and slowly from yellow ones, which determines the combination of rapid and prolonged action of the drug [8]. One capsule of Ketonal DUO contains 150 mg of ketoprofen, which does not exceed the standard daily dose of the drug. Ketonal DUO modified release capsules have the following advantages:
- contain the optimal daily dose of ketoprofen, which allows you to reduce the frequency of taking the drug to once a day, which is convenient to use;
- provide a more stable concentration of the drug in the blood over a 24-hour interval;
- minimize the irritating effect of the drug on the gastrointestinal tract;
- increase patient compliance due to a single daily dose of the drug.
Ketonal DUO: proven effectiveness
Currently, extensive experience has been accumulated in the use of ketoprofen in various clinical situations. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted by R. Lange, R. Lentz (1995) in parallel groups in 345 patients showed the advantage of ketoprofen for the relief of acute pain over drugs such as naproxen and ibuprofen [9]. Ketoprofen is successfully used for “low back pain” syndrome. In a randomized, double-blind, multicenter study by H. Zippel, A. Wagenitz (2007) involving 370 patients, ketoprofen at a dose of 50 mg 2 times a day intramuscularly was more effective than diclofenac at a dose of 75 mg 2 times a day intramuscularly. Patients receiving ketoprofen showed a more pronounced reduction in pain with good tolerability [10]. B.R. Gelfand et al. (2002) compared the analgesic effectiveness of ketoprofen and ketorolac in patients in the postoperative period. The results of the study showed that the severity of pain on the visual analogue scale was significantly lower in the group receiving ketoprofen compared to the group of patients taking ketorolac. Adverse events were observed in 4% of patients taking ketoprofen and in 14% of patients taking ketorolac. No serious adverse events were observed in patients receiving ketoprofen as analgesic therapy [11].
Ketoprofen is widely used abroad for analgesia in the postoperative period. In the work of F. Aubrun et al. (2000) showed that the administration of ketoprofen leads to a reduction in the dose of morphine in the postoperative period by 33% [12]. Ketoprofen has pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effectiveness in the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Ketoprofen shows an effectiveness that exceeds that of diclofenac, with better tolerability. In a study by I. Jokhio (1998), with a good analgesic effect in 87% of patients taking ketoprofen, good tolerability was noted in 72%, while among patients taking diclofenac, good tolerability was observed in only 50% of cases [13]. A. Calin et al. (1977) found that ketoprofen at a dose of 150–300 mg per day for 3 months also showed better efficacy and tolerability compared with ibuprofen at a daily dose of 1200–2400 mg in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a double-blind, controlled study in parallel groups [14 ].
In Russia, in 2012, a multicenter (including 10 cities of the Russian Federation) open study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of the use of the drug Ketonal DUO in the treatment of dorsalgia. A total of 349 patients took part in the study and received Ketonal DUO at a dose of 150 mg/day for 7 days. The data obtained demonstrated a significant reduction in the level of back pain both at rest and during movement (p
Conclusion
Thus, the powerful analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug Ketonal DUO, as well as proven good tolerability, combined with the convenience of a single dose, allow us to recommend the drug for use in the treatment of a wide range of pain syndromes.
Can ketonal cause harm when taken for toothache?
Despite the fact that ketonal is sold freely in pharmacies, if you have a toothache, you should find a way to contact your therapist and consult with him about the admissibility of taking this drug. In the presence of a number of pathologies or hypersensitivity, the medicine can cause harm to health. Exceeding the dose of medication or taking it for too long can also lead to undesirable consequences.
When exposed to ketoprofen on the body, the following negative reactions may occur:
- Painful sensations in the abdominal area.
- Digestive problems.
- Intense gas formation.
- Headaches, in severe cases taking on the character of migraines.
- Allergic reactions in the form of skin rashes and itching. In severe cases, anaphylaxis is possible.
- Sleep disorder.
- Distortion of taste perception.
- Vision problems.
- Feeling of tinnitus.
- Hallucinations.
- Cardiac arrhythmia.
- Hypertension.
- Anemia.
Other side effects are possible. Ketoprofen poses the greatest danger to the digestive system. Thus, the digestive organs, when exposed to this medication, become more susceptible to peptic ulcers and gastritis.
The effect of ketoprofen on the stomach and intestines is softened if the tablets are taken with milk rather than water.
If too large a dose of medication was taken, the following consequences may occur:
- vomiting, in some cases bloody;
- pain in the abdomen;
- renal failure;
- distortion of consciousness.
If signs of intoxication appear after taking the medicine, you must first do a gastric lavage and take some kind of adsorbent. In case of severe poisoning, medical assistance cannot be avoided.
When should you not take Ketonal for toothache?
When using ketoprofen preparations, it is important to strictly adhere to the instructions regarding permissible doses and dosage regimen given in the instructions. The maximum duration of taking ketonal is three days. In addition, it is important to know in what cases this medicine should not be taken.
Ketoprofen is contraindicated in the following situations:
- with inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- with functional disorders of the digestive system;
- for renal and hepatic pathologies;
- with impaired blood clotting.
Patients under fifteen years of age should not take ketoprofen preparations.
It is important to know about the compatibility of ketoprofen with other medications. Thus, the effect of this medication is enhanced if it is taken in parallel with diuretics or with drugs that inhibit the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme. The risk of gastrointestinal problems increases when ketoprofen is combined with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, salicylates and steroid drugs.
While taking ketonal, you should not drink alcohol. Firstly, alcohol enhances the negative effect of ketoprofen on the gastrointestinal tract. Secondly, ketoprofen, like alcohol, is deactivated in the liver. When ketanol and ethanol are taken together, the liver becomes overloaded, and it may not be able to cope with double work. As a result, the risk of drug poisoning increases, and the negative consequences of drinking alcohol will be more pronounced.