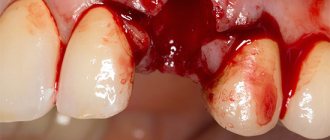
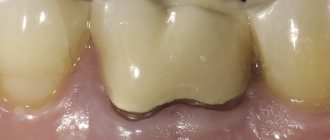
What to do if your child has a pink tooth
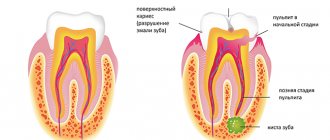
The tooth consists of both hard and soft tissues. Inside it is soft pulp and nerves. The pulp is made up of a semi-solid material called dentin. Dentin helps form the bulk of the structure and protect the sensory nerves and blood vessels inside. Enamel is a thin coating over dentin that adds another layer of protection. Enamel helps protect dentin and pulp from bacteria. Caries that gets into the enamel and dentin and reaches the pulp can lead to its death. When decay reaches the pulp, it creates a pathway for bacteria to infect the tissue. A healthy pulp will respond to infection the same way as any other part of the body: with inflammation.
Another thing that can cause redness is injury. If you are struck in the jaw by a fall or while playing sports, it can damage blood vessels. The tooth needs blood, so when there is no more blood, it dies. This usually happens slowly over time and does not cause as much pain as when decay reaches the pulp.
During eruption, root resorption occurs. The root is absorbed and begins to dissolve. Once the root is completely resorbed, the baby tooth will fall out - so there will be no visible root. If resorption continues, a pink tint may appear. It may take about 2-3 weeks for the color to change. If the tooth turns red, this is the result of thinning or translucency of the enamel. This looks strange, but is not a cause for alarm. Parents can always consult a dentist if the child is bothered by pain or the shade becomes more intense.
The damage is usually irreversible, but sometimes it can be repaired, especially if it is caused by tooth decay. The dentist will make a diagnosis and recommend treatment.
Pink teeth need to be treated
Author Andrey Belyakov
06/13/2007 15:21 (Updated: 05/04/2021 18:36)
Health » Dentistry » Prevention
Nobody likes going to the dentist. But you can’t hide your teeth under clothes, so sooner or later you have to go. However, before we sit down in the dentist's chair, we start asking a bunch of questions. Dentist Leonid Rakov answered some of them to Pravda.Ru .
Is it possible to correct an overbite at the age of 45?
Modern methods of orthodontic treatment make it possible to correct misaligned teeth at any age. The main thing is that the teeth themselves are present.
To carry out treatment, special locking braces are glued to the teeth, with the help of which the teeth are moved. But in adults, treatment will be longer than in childhood. It will take from one and a half to two and a half years.
In addition, adults, as a rule, simultaneously with correcting the bite, have to undergo prosthetics of part of the teeth.
If a person puts on braces, will his diction change?
When treated with braces, diction is not impaired, since they are glued to the labial surface of the teeth and do not interfere with articulation.
Is it possible to restore a tooth if it is completely destroyed on top?
In most cases, this is possible using pin systems or core inlays made in a laboratory specifically for your tooth.
Sometimes it is necessary to carry out preparatory measures, and as a rule, the teeth restored from the roots are covered with a crown on top. Today there are methods of implanting teeth in place of lost ones.
After the nerve was removed, the tooth changed color and became pink. What is the reason and can it be fixed?
Changes in the color of a pulpless tooth occur for several reasons. Here, apparently, an outdated paste composition, which has such side effects, was used to fill the canal. It is possible that mistakes were made during the filling itself.
It is advisable to refill the canal and then try to “whiten” the tooth from the inside. If this cannot be done, various types of camouflage are used: vinyls (veneering only the front surface of the tooth) and crowns.
At what month of pregnancy is it better to have dental treatment?
Teeth need to be treated before conceiving a child. If you don’t have time, then it’s better not to go to the dentist in the first three and last three months of pregnancy. The exception is acute toothache.
In the second trimester, it is better to go to the doctor in the afternoon, especially if you feel nauseous in the morning. Be sure to notify your doctor about your pregnancy, this will help him decide on pain medications and choose a treatment plan.
X-rays should only be taken if absolutely necessary. And from the fifth month, teeth should be treated only in a sitting position, not reclining.
The child has black spots on his teeth. What could this be from and what should I do about it?
The child needs to be shown to a dentist and gastroenterologist. Most likely you will have to undergo examination for dysbacteriosis and infection with worms. It is with these pathologies that teeth are most often covered with black dots.
Today there are modern means and devices that will remove plaque quickly and painlessly. Teeth are cleaned with a stream of special fine powder based on soda and water droplets under pressure. But if the cause is not treated, the plaque will return.
Pink teeth. Resorcinol-formalin method
Topics: teeth, braces, dentistry, pregnancy
How to treat a pink tooth in a child
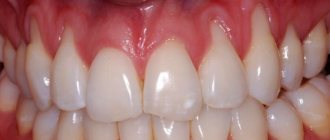
A pink tooth in a child should not cause panic. It is important to know that this is usually not a serious situation. The problem often occurs in young children and, as a rule, it is harmless - there is no harmful effect on the health of the jaw. A red tooth in a child is a sign of resorption.
If the pink discoloration is persistent, it may indicate a more serious problem and parents should consult a dentist.
The doctor can:
- put a seal;
- remove dentin;
- apply intracanal bleaching.
Treatment depends on various factors and the exact cause of the change in shade.
Reasons for changing the shade of enamel
Conventionally, the reasons that teeth become yellow or dark can be divided into two main groups: external influences (food dyes, smoking, poor hygiene) and internal influences (health conditions, removal of the dental nerve, etc.). Let's look at them in more detail.
Nutritional Features
Quite often, the enamel turns yellow or darkens due to regular exposure to drinks and products that contain coloring pigments - coffee, tea, seasonings, chocolate, beets, etc. Coloring substances accumulate in the micropores of tooth enamel and dentin, which leads to a change in shade teeth.
Environmental factors
Tooth enamel can change its shade as a result of extremely poor ecology, when a person works in hazardous industries and consumes bad water, in particular, with a high fluoride content (white spots appear). Darker shades can form when the body is exposed to lead, bromine, mercury and other hazardous substances.
Hygiene factors
Poor oral hygiene leads to discoloration of teeth due to plaque formation. It occurs due to irregular, poor-quality cleaning or due to incorrectly selected products. As a result, the enamel becomes darker due to the accumulation of large amounts of deposits.
Age-related changes
Over the years, tooth enamel becomes thinner, through which darker dentin begins to show through. It is for this reason that yellow teeth appear in most people in old age.
Various diseases and their treatment
Another common cause of darkening of the enamel is diseases of the internal organs, as well as their treatment with certain drugs. The use of certain types of antibiotics, for example, tetracycline, leads to the appearance of dark stripes on the enamel (especially if it was taken during the formation of the child’s teeth during intrauterine development or their growth in the first years of life). With fluorosis, white spots may appear on the enamel, which over time become yellow-brown.
On a note! In the absence of the dental nerve (pulp), the tooth darkens over time - this is a completely normal and physiological process. Unfortunately, whitening is usually not effective in this situation, so it is worth considering the installation of veneers or lumineers.
If the tooth becomes red, this indicates damage or inflammation of the dental nerve, which requires surgical treatment by a dentist.
Bad habits
Smoking causes permanent plaque to form on the surface of the teeth, causing them to turn yellow. If you can’t give up the habit, you should strengthen your oral hygiene, as well as regularly carry out comprehensive professional hygiene at the dentist - every 3-5 months to better cleanse your teeth of plaque.
What to do if an adult’s tooth turns red
As resorption occurs, the pink or red color becomes more noticeable and the structure changes. If you catch the early stage of dying, there is a chance to preserve the external structure. The internal, damaged pulp can be cleaned out and replaced with a hard filling material that will help protect the structural integrity. Preserving as much of the original structure as possible is important for oral health. Gaps in your smile can lead to poor jawbone health, uneven bites, bacterial growth, and cosmetic problems.
If severe damage is observed, removal will likely be the best option. It is recommended to get an implant to maintain the health of your jaw and mouth.
Restorations in the area of the neck and root of the tooth, taking into account the principles of “white and pink” aesthetics
L. A. Lobovkina , Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category, head of the medical and preventive department of Branch No. 6 of the Federal State Institution “GVKG im. Burdenko" of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (Moscow)
A. M. Romanov, chief physician of the Implamed clinic (Moscow)
The cause of the formation of defects in the cervical area can be diseases of both carious and non-carious origin. Among diseases of non-carious origin, the most common are enamel erosion, abfraction and wedge-shaped defect.
Erosion occurs as a result of the direct effect of acid on the hard tissues of the tooth, leading to demineralization of the enamel. If the acid exposure is short-lived, the tooth surface can be remineralized by inorganic substances from saliva without affecting the tooth tissue.
With longer and more frequent exposure to acids, especially concentrated ones, irreversible damage to the hard tissues of the tooth occurs. Unlike carious lesions, the occurrence of erosion is not associated with the influence of microorganisms [3].
The appearance of acid in the mouth can be caused by various reasons: vapors of acids of industrial origin, excessive consumption of sour fruit juices, sports drinks, lemonade, yogurts and other foods containing acid (ascorbic, acetic).
Eating citrus fruits more than twice a day increases the risk of developing erosion by 30-40 times. Erosion occurs in people who practice excessive oral hygiene using improper brushing techniques and abrasive toothpastes. In the future, this can lead to the formation of a wedge-shaped defect [3].
As for abfractions, the main reason for their appearance is considered to be the occurrence of stress from bending stress in the cervical region of the teeth (Lee WC, Eakle WS., 1984).
Subsequently, this was repeatedly confirmed by various studies (Heymann HO.et al., 1991; Grippo JO., 1991) which proved that abfractions arise as a result of biomechanical overstrain associated with excessive occlusal forces during static compression (swallowing, bruxism) and dynamic functions (chewing).
As a result of an atypical occlusal load, bending stress occurs in the area of the tooth neck, and chronic fatigue gradually develops in the hard tissues of the teeth, followed by their destruction in this area.
Modern theory explains the etiology of abfractions as the process of destruction of enamel prisms as a result of the piezoelectric effect, resulting in the expulsion of calcium ions from the crystal lattice of calcium hydroxyapatite molecules of enamel prisms.
Atypical occlusal loads associated with the action of lateral forces on the tooth also lead to the appearance of gingival recession - the epithelial attachment moves apically from the area of the tooth subject to overload.
Treatment of abfractions, as a rule, comes down to restoring the tooth using a composite or ceramic restoration. In any case, it is necessary to eliminate the occlusal trauma that caused the appearance of abfraction and create optimal occlusal contacts by eliminating premature contacts.
In recent years, surgical treatment has been successfully used to eliminate recessions, which largely depends on identifying all the causes of their development, as well as on competent planning and selection of a rational treatment method (Zhdanov E. V., 2005).
The main criteria when choosing a particular technique are the width and depth of the recession, the width and thickness of the attached mucous membrane apical to the recession, the biotype of the gums, the etiology and presence of risk factors, the aesthetic expectations of the patient and the degree of his cooperation. Determine the patient’s expectations from the proposed treatment and discuss all possible outcomes, including unsatisfactory ones.
The beauty of a smile depends not only on the appearance of the teeth, but also on the condition of the surrounding soft tissues. A good aesthetic result is a harmony of various parameters, so its achievement is a very complex and lengthy process (Striegel M., 2008).
Periodontal diseases distort the natural garland-shaped shape of the upper gum line, which dramatically worsens the aesthetic characteristics of the teeth and smile. Therefore, when making restorations, especially the frontal group of teeth, attention should be paid not only to restoring the anatomical shape of the teeth, but also restoring the optimal structure of the adjacent soft tissues (Ryakhovsky A. N., 2008).
You can change the shape, size and position of your teeth as long as you like, but if the gum margin is very thin, irregularly shaped or inflamed, your smile will not be beautiful [1].
The ideal condition of the gums is characterized by the following features:
- The gum contour on the central incisors is smooth and symmetrical;
- The gum contour on the lateral incisors is located 1 mm lower than on the central ones;
- When you smile, only a small part of the gum is visible;
- The length of the central incisors and canines should be at least 10-12 mm; The lateral incisors should be approximately 1–1.5 mm shorter [4].
Relief of the gum surface. In the presence of teeth, the vestibular surface of the alveolar process is uneven and has convexities corresponding to the roots of the teeth. Closer to the teeth, the gums have irregularities that give them an “orange peel” appearance. The gums can form a thin ridge near the tooth itself (Ryakhovsky A.N., 2008).
Gum color may vary between different racial groups due to the presence of pigmentation. Normally, the gums are pale pink in color.
All defects localized in the gum area can be divided into aesthetic classes (according to Schwenk/Striegel):
Class 1: Only white aesthetic correction is required.
Class 2: Correction of function and white aesthetics required.
Class 3: Correction of white and pink aesthetics required.
Class 4: Correction of function, white and pink aesthetics required.
Class 5: Prior orthodontic or surgical treatment is required [5].
Before planning the treatment of cervical defects, it is necessary to accurately diagnose and establish the causes of their occurrence, as this affects the volume of preparation, the shape of the cavity and the choice of filling material. In addition, it is important to identify whether the process has spread under the gum and whether there is a need to correct the mucous membrane of the gingival margin.
Existing functional problems should be solved with the help of orthodontic treatment or plastic surgery (Ryakhovsky A. N., 2008).
I would like to note that in cases where the defect is localized in the area of the tooth root and it is planned to be restored in the future with a composite material that matches the color of natural hard tissues, visually such a tooth will look longer due to an increase in the visible part of the tooth.
Therefore, taking into account the principles of the relationship between “white” and “pink”, to obtain an optimal aesthetic result it is preferable to use a material that imitates the color of the gum, for example “Amaris Gingiva” (VOCO).
It has good transparency, color stability, high strength, low abrasion. “Amaris Gingiva” is a material with a double effect: not only for modern defect elimination, but also for “restoring” aesthetic properties by correcting the gingival margin line (Fig. 1).
Fig.1. "Amaris Gingiva"
It is typical that the main shade of the restoration is created by the opaque material. Therefore, in the Amaris Gingiva set there are four types of opaques: light gum (light), dark gum (dark), natural (nature) and white color (white). By mixing shades, you can choose an individual tone. Also included is a gingival, translucent enamel material.
Clinical case
Patient M. complained of an aesthetic defect. The examination revealed the following aesthetic problems.
Pink aesthetics: disharmonious shape of the upper edge of the gums in the area of teeth 2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 1.2, 1.3,1 4.
White aesthetics: loss of hard tissues of teeth 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.3, 2.4, absence of tooth 2.2 (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2. Initial clinical situation.
The patient was offered a surgical treatment to correct the gingival margin of teeth 2.1, 2.3, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, which he refused. After agreement, it was decided to restore only tooth 2.1 using a material that imitates the color of the gum.
First, the parameters of the teeth were measured with a micrometer. The clinical crown height of the central incisors was determined as the distance from the incisal edge to the marginal gingival level along the vertical midline [2].
Odontometry showed that the length of tooth 2.1 is 2.4 mm longer than tooth 1.1. If an existing defect is restored using a conventional composite material, the ideal proportions of “white and pink” will be violated and the restored tooth will then look longer (vampire teeth). Based on this, we chose the pink material “Amaris Gingiva”.
The preliminary stages included professional, individual oral hygiene, discussion with the patient of the features of the restoration and mutual responsibility for the results of the work.
The choice of color shades was preceded by mechanical cleansing of the vestibular surface of the tooth, symmetrical to the one being restored, and adjacent teeth using a brush and fluoride-free paste (for example, Klint, VOCO). Next, the gum color was selected by comparing the color scale included in the material set with the shade of the gum. When performing this stage, the conditions of the optimal light-color environment were observed.
In this clinical situation, a light shade was chosen: the patient’s gums are pale pink due to ischemia. After anesthesia, preparation of tooth defect 2.1 was carried out with pear-shaped and spherical burs. To ensure a smooth transition of the material, a bevel of the enamel was created towards the cutting edge using fine-grained flame-shaped burs (with red or yellow stripes) (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Tooth 2.1 after preparation.
After medicinal treatment of the formed cavity with a 2% chlorhexidine solution, adhesive preparation of hard tooth tissues was carried out by applying the self-etching bond “FUTURABOND HP” (VOCO). The superstable emulsion of nanoparticles contained in Futurabond HP, obtained using the patented Sol-gel technology, allows the material to be applied in only one layer and photopolymerizes for 10 seconds, which ensures extreme adhesion strength and ease of use. A special feature of Futurabond NR is that it releases fluorides, which prevent the development of “secondary” caries.
Next, the opaque shade “Amaris Gingiva”, pre-selected by color, was introduced into the cavity. After this, gingival translucent enamel material is applied in layers no thicker than 2 mm and cured with a halogen lamp for 40 seconds. It should be remembered that the contour of the gingival margin can be flattened, rounded or dome-shaped. In this patient, when modeling the gum contours, the location of the gingival margin on symmetrical teeth, a sign of root deviation, was taken into account.
Surface treatment was carried out immediately after curing of the material using fine and ultra-fine grain diamond burs, polishing discs, and heads. At the same time, the macro- and microrelief of the surface was recreated. In order to reduce the marginal permeability of the root surface and to add shine to restorations, it is recommended to coat them with Easy Glaze filled light-curing varnish (VOCO, Germany). The final appearance of the restoration of tooth 2.1 is shown in Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Tooth 2.1. Final appearance after restoration with Amaris Gingiva material.
Thus, the composite material for correction of the gingival margin “Amaris Gingiva” has been widely used in dental practice. Excellent aesthetics, resistance to gingival fluid, and adhesion to tooth root cement allow it to be used in difficult clinical situations and obtain excellent aesthetic restorations.
The list of references is in the editorial office.
Why does a filled tooth suddenly turn pink?
If dental treatment was successful, but the healed tooth hurts, this does not indicate any problems, but gives reason to consult a dentist. If the filled tooth turns pink, this may be the result of the fact that the paste contained resorcinol and formaldehyde. But most often the change signals pulpitis, periodontitis, traumatic injury or rupture of a vessel in the pulp.
If a tooth turns red, you should immediately contact your dentist to get a diagnosis. A potential infection should not be left unattended; it is important to ask what treatment options are available and make an informed decision.