Home|Facial malformations (cleft lip and palate)|Cleft palate (cleft palate)
Congenital defect of the hard and soft palate (cleft palate pathology) is a common facial malformation in infants. About a hundred babies are born every day in the world with this anomaly, most of whom are boys. It manifests itself as a rupture in the middle part connecting the oral cavity with the nasal cavity. Half of the children with this defect have a cleft lip defect. With timely treatment, cracks in the palate of a child are not dangerous to the life and health of the baby. The Towards Life project allows you to receive qualified medical assistance in correcting such defects free of charge.
Reasons for appearance
Opportunistic bacteria are part of the oral microflora of every person.
Age doesn't matter here. Thrush appears when fungi, like yeast, become active and exceed the permissible number. Also, pathology is formed when pathogenic strains enter the patient’s body. The reason that leads to problems may be internal. Also, negative environmental factors influence deterioration of health. Often, anomalies are caused by non-compliance with hygiene rules, intestinal problems and others. To prevent serious complications, you should consult a doctor promptly. A dental clinic that has modern equipment and uses the latest technologies will help you understand the problem and eliminate it. Advances in dentistry allow you to achieve results quickly. Having identified the true cause of the problem, the dentist will draw up a treatment plan. The problem will be solved when the provoking factor is eliminated.
Candidiasis in the oral cavity
This inflammatory disease is often diagnosed in children. It can affect a newborn. The basis of the disease is pathogenic fungi. They provoke damage to the mucous layer, and the uvula suffers. Candidiasis is suppressed by the defenses of a healthy toddler. But when fungi multiply quickly, the immune system cannot cope with them, as it weakens. The pathology progresses against the background of the following problems:
- Inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- Colds;
- Hormonal instability;
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics;
Children's fragile immunity cannot withstand negativity. All this leads to imbalance. White palate in a baby’s mouth can appear due to severe stress, which reduces the body’s immune strength. The growth of fungi is provoked by excessive dryness of the mucous membranes and an imbalance of acid balance. The first sign of damage to the mucous membrane is itching. At risk are those guys who wear braces, are treated with hormonal drugs, and do not clean their chewing organs well. The disease develops especially quickly when unfavorable factors are combined. The baby's mucous membrane is covered with a cheesy film. Whitish crumbs are difficult to remove; ulcers form underneath them. They may bleed.
Infectious lesions
When the body's resistance decreases, the appearance of pathogenic bacteria is often associated with the appearance of one or another infection. As a result, white spots develop on the palate.
- Fungal strains are highly infectious. Pathogenic microbes quickly colonize the damaged mucosa.
- With scarlet fever, the baby's mouth turns red, a rash appears, and the temperature rises.
- With diphtheria, the film has dirty inclusions.
- With whooping cough, a putrid odor from the mouth is clearly heard.
- With dysentery, the layer is dense, and erosions appear underneath it.
Oral diseases
Oral problems cannot be ignored. Parents should immediately show the toddler to the pediatrician, who will refer the child to the dentist. Pediatric dentistry is a department where the exact cause of the disease is determined and a treatment regimen is developed. Specialists know how to work even with the smallest children. Problems in infants can develop due to dental diseases. Most of them are characterized by inflammation, swelling, the appearance of a film and ulcers. The source of infection is pathogenic bacteria. The main diseases include:
- Stomatitis, in which whitish sores with clearly defined edges appear. Children experience discomfort and refuse to eat. The disease progresses when the mucous membrane is damaged, there are not enough vitamins, allergies develop, and the body's defenses decrease.
- Gingivitis, when the gums and other soft tissues of the mouth are affected.
- Caries, with the active development of which white matter is diagnosed in the oral cavity in large quantities.
Stomach and intestinal problems
In pediatric practice, white spots on the palate of a child are quite common. The provoking factor is diseases of the digestive tract:
- Gastritis, which is characterized by inflammatory processes of the gastric mucosa. In addition to whitish deposits, patients experience pain, spasms, and stool disturbances.
- Dysbacteriosis, which is manifested by bloating, weight loss, problems with stool.
- Enterocolitis, in which, in addition to a film in the oral cavity, accumulation of gases and spasms of the gastrointestinal tract are diagnosed.
The functions of the tonsils and their appearance are normal
Before diagnosing throat diseases, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with general information about the functions and appearance of the tonsils. These formations are accumulations of lymphoid tissue and are often called tonsils.
- Red throat in a child: how to treat it at home if it constantly hurts and hurts to swallow?
Tonsils perform two main functions: protective and hematopoietic. They produce antibodies that fight pathogenic microorganisms, preventing them from entering the body. The tonsils also form lymphocytes - cells of the immune system.
A healthy person has 4 tonsils: 2 paired and 2 unpaired, they are located at the junction of the nasopharynx and pharynx. Normally, these formations are the size of a walnut and are colored light pink. Also signs of normal tonsils include:
- absence of redness and plaque;
- the mucous membrane is not inflamed, there is no pronounced vascular pattern;
- the tonsils do not come into contact with the palatine arches and do not extend beyond them;
- When pressing on the tonsils with a medical spatula, no pus or mucus is released.
The combination of all these signs indicates a person’s health. However, for some people, increased size of the tonsils is the norm - this is an individual characteristic of the body.
Causes
Conventionally, all causes of spots on a newborn’s gums can be divided into harmless and dangerous. The first group does not require specific treatment and usually goes away over time.
Non-dangerous reasons include:
- Bon's nodes - a small number of white spots are localized on the surface of the gums, have a round shape, and usually do not bother the baby. Structurally, these formations are glandular or dental tissue. The popular name for this condition is “pearl oyster”. The manifestations disappear with age.
- Epstein's pearls are white cystic tissue formed by epithelium, localized on the palate. It also looks like pearls, which is why it got its name.
- Natal teeth grow in the first month after birth, or before it. Outwardly, they resemble small bumps on the gums of a baby. This condition necessarily requires consultation with a pediatrician. This is due to the fact that these can be not only baby teeth, but also additional ones, which will interfere with the formation of a correct bite. Another danger is the increased fragility and mobility of these incisors. They can fall out prematurely and cause suffocation for the baby. Often they need to be removed.
- Inadequate oral hygiene. If you don’t take care of your baby’s gums every day, then white plaque can be quite difficult to avoid. Most dentists agree that oral cleansing should begin before teething symptoms appear. It is the remains of breast milk or special formula that can cause gum disease.
Pathological causes of white ulcers or spots on the gums include:
- Acute calcium deficiency, which can cause problems with teeth and gums in newborns. Poor maternal nutrition, alcohol abuse, smoking - this is not a complete list of reasons that can cause calcium deficiency in a breastfed child.
- Stomatitis of a herpetic nature - it is under the influence of the herpes virus that the oral mucosa of an infant is damaged. The initial appearance of white dots quickly leads to the formation of ulcerations, on which a yellowish coating forms. Usually the baby refuses to eat due to unpleasant itching on the gums, his body temperature rises and his lymph nodes become enlarged.
- Aphthous stomatitis - initially manifests itself with slight swelling and redness, later aphthae - white spots - form. In addition to direct symptoms, indirect ones also appear: increased moodiness and tearfulness, increased salivation, a rather repulsive odor from the mouth, increased temperature and decreased appetite. Several factors can provoke the appearance of white spots in infants: acute vitamin deficiency, trauma to the mucous membrane, decreased immunity, bacterial infection, allergic reaction.
- Stomatitis caused by candida is characterized by the appearance of white areas on the baby’s gums, which are painful and unpleasantly itchy. Thrush in the mouth of a baby most often occurs as a result of primary infection during passage through the birth canal. A characteristic feature is the presence of bloody discharge from ulcers covered with a white coating. This type of stomatitis also causes bad breath.
Purulent cysts are specific neoplasms characterized by the accumulation of pus under the surface of the gums. Their occurrence is most often associated with the entry of bacteria into the root of the tooth. The main thing is to prevent the bush from breaking, because this will lead to infection entering the oral cavity and infecting the entire body.
External signs of a sore throat
The condition of the oral cavity is influenced by the environment, past diseases, and inhaled microbes, so an absolutely healthy pharynx is rare. According to statistics, by the age of seven, almost every child suffers from various chronic throat diseases. You can determine whether the throat is affected or not by the following signs:
- The tonsils become red and increase in size, swollen follicles are clearly visible on them, which are sometimes filled with pus, and there is a white, yellowish or gray coating. With herpetic tissue damage, blisters and small ulcers form.
- The soft palate becomes inflamed and a rash may appear on it.
- The back wall of the pharynx looks swollen, loose, the follicles are enlarged. Upon examination, a pronounced network of small vessels can be detected. The presence of ulcers indicates infection with the herpes virus (see also: symptoms of herpes on the tonsils in a child). The tongue is hyperemic.
- The tongue is coated. If it has a brown or gray tint, affecting the tongue and teeth, this may indicate chronic pharyngitis.
Location of plaque on other parts of the body
White plaque on a baby's butt and groin can be caused by a large number of skin folds, which cause severe friction of the skin. It is in these places that various bacteria often multiply. White plaque in a baby's groin can cause a very unpleasant odor.
In some cases, a white coating appears behind the ears of the baby. This is not a serious problem since the ears are an exposed part of the body. To treat white plaque in the ears of a baby, it is enough to apply Bepanten ointment to the affected area after the doctor’s permission.
White plaque in a baby's armpits may appear for the same reason as in the groin area. Due to skin friction, diaper rash and plaque may appear here. Irritation in this area is also common.
FREE CONSULTATIONS!
We are pleased to announce the start of free admission at the Konstanta Clinic for patients under 18 years of age by maxillofacial surgeon, pediatric surgeon L.A. Eremeyshvili. for questions:
- Congenital facial pathologies: cleft lip and palate;
- Benign neoplasms of the face and oral cavity;
- Diseases of the temporomandibular joints;
- Pathology of the frenulum of the oral cavity: lips and tongue.
Correction (plasty) of tongue frenulum is provided free of charge for children under 1 year of age.
*Valid for residents of Yaroslavl and the Yaroslavl region.
You can make an appointment by phone or through the website (4852) 37-00-85 Daily from 8:00 to 20:00
Sign up for a consultation
Congenital cleft palate or cleft palate is a fairly common malformation of the facial region. This pathology is ranked 4th among all developmental defects, and it is diagnosed with a frequency of 1:700 births. Often, a cleft palate is not an independent deviation, but part of a hereditary syndrome.
Thrush in the mouth of a newborn (stomatitis)
The oral mucosa usually contains many microorganisms.
One of these normal microorganisms that live on any mucous membrane is the fungus Candida albicans, the uncontrolled growth of which is inhibited by the presence of normal bacteria.
If the balance of the normal microflora of the oral cavity is disturbed, thrush can develop, which is one of the most common diseases in newborns and infants.
The child may be restless, capricious, abandon the breast during feeding or refuse the breast (bottle) altogether, since sucking may cause him pain. After some time, small spots grow to form large light films or a curd-like coating.
Causes of thrush
It is possible for a newborn to become infected with thrush from the mother when he passes through the birth canal if the mother had candidiasis during pregnancy.
Babies who were born premature or with weakened immune systems are also predisposed to the appearance of thrush.
Babies who have been prescribed antibiotic treatment or who often regurgitate, since the fungus lives in an acidic environment that forms in the baby’s mouth for some time after regurgitation. And also during teething, when the immune system is slightly weakened.
Thrush in infants is not usually associated with other diseases. For children in the first 6 months of life, treatment and hygiene are indicated.
If the baby is already more than 6 months old and basic hygiene rules are observed, but the treatment does not give a positive effect (or gives a short-term effect), it is necessary to conduct a more detailed examination of the child’s entire body, as this may be a symptom of a more serious illness or a weakened immune system.
Treatment and oral hygiene
The danger of thrush is that it makes the mucous membrane easily vulnerable and thereby opens the gates of infection. If thrush is not treated, then in its advanced state it spreads to the entire oral cavity.
To treat thrush, various topical preparations (solutions, creams) that contain antifungal components are used. For example, nystatin drops or Candide solution are used (a few drops of Candide solution are applied to a cotton swab or gauze and wiped the child’s oral mucosa 2-3 times a day).
Treatment with antifungal drugs is usually carried out for 5 to 10 days and only after the conclusion of a pediatrician.
To do this, you need to press your thumb on the child’s chin so that he opens his mouth, and treat the entire oral cavity with a swab dipped in a soda solution. Repeat this procedure every 2-3 hours.
You can also dip the pacifier in a soda solution and give it to the baby after feeding.
For children six months and older, a single use of Diflucan is possible, but the possibility of using this drug and the dosage must be agreed with the pediatrician.
Folk remedies recommend a teaspoon of honey, diluted in half with water and heated in a water bath. Wrap your finger in a bandage soaked in this solution and wipe the mouth. However, it must be remembered that honey is a strong allergen.
If the baby is breastfed and has signs of thrush, then the mother is also prescribed antifungal treatment, since the infection can easily pass between the mother and the infant. And if treatment is not carried out, re-infection is possible in one to two weeks.
Prevention
Every time after eating, give your baby a few sips of warm boiled water to wash away food debris and neutralize the acidic environment that the fungus loves.
If the child is breastfed, do not forget to wash the nipples of the mammary glands with water and a solution of baking soda before feeding), if the child is artificially fed, sterilize the nipples of bottles and pacifiers.
Copyright: kukuzya.ru Any copying of material without the consent of the editors is prohibited.
Treatment of the disease
Thrush is a common cause of white plaque in the mouth, and parents should know how to combat this disease. The pathology is of fungal origin, so its treatment will be quite difficult and will take a lot of time.
On your own, at home, use the following measures:
- At the first stage of the disease, treat the oral cavity with a weak soda solution (read on how to prepare it). Use the same solution to wash nipples, pacifiers, bottles, toys - everything that gets into the baby’s oral cavity. In addition to soda, Iodinol and bactericidal dyes of the aniline type can also be used for processing.
- If thrush is severe, you should immediately visit your pediatrician. In addition to regular use of soda solution, a specialist can prescribe antifungal drugs, immunostimulating drugs and vitamin complexes. Since an organism with a weakened immune system becomes a favorable environment for the spread of the fungus, it needs to be strengthened. In any case, you must agree that a qualified doctor knows how to remove white plaque from a baby.
If it is possible to identify thrush in a child at an early stage, then you can get rid of it in less than a week. If the pathology has already acquired a more severe form, then the situation may be complicated by increased temperature, as well as the spread of plaque even to the pharynx. With a complex form, there is no need to try to remove white spots from the child’s mouth, because they will be replaced by bleeding wounds, which will be even more painful and unpleasant for the baby.
Prevention
The risk of developing candidal stomatitis is especially high in the first 6 months of a baby’s life, since his immune system is just developing. To prevent disease, it is important to follow the following rules:
- rinse your breasts with clean water before feeding;
- offer the baby some water after a meal or burping;
- strictly observe the rules of hygiene for all adults in contact with the child;
- Regularly sterilize bottles and pacifiers.
After an illness, to prevent re-infection, it is worth boiling all toys and children's dishes. If the item cannot be treated with hot water, it is recommended to rinse it with a soda solution.
The main reason for a white palate in a baby is the accumulation of food debris in the mouth after feeding. Traces of formula or milk disappear on their own and are not visible before the next meal. Persistent plaque in most cases is a sign of candidal stomatitis (thrush). This disease is treated with local and/or systemic agents with an antiseptic effect. At the initial stage, thrush is not dangerous, but as it progresses it can lead to the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane and the spread of infection.
Treatment
Treatment of this abnormality in infants is carried out depending on the cause of the plaque and is prescribed by the attending physician. If white formations appear as a result of thrush, it is necessary to disinfect all the child’s toys, pacifiers and jars. Before feeding, mothers should treat their breasts with Mirasmistin. It is necessary to make adjustments to the nutrition of mother and baby:
- exclude sweets, mushrooms, dairy products, black tea, coffee;
- add vegetables, boiled eggs, buckwheat, fish, boiled meat to your diet.
You should treat the baby's oral cavity with a 1% soda solution and remove plaque with a piece of sterile bandage soaked in warm water. Children from 6 months of age are prescribed Fucis DT, Fluconazole or Diflucan. At this age, instead of a soda solution, you are allowed to rinse your mouth with Miramistin. For children over one year of age, Nystatit is prescribed (in the form of ointment or tablets). It is recommended to remove plaque with the anti-candidiasis agent “Candide”. Some medications for thrush in children can only be used from 3-5 years of age; you should not purchase them yourself at the pharmacy. It is better to seek help from a doctor and be treated with prescribed medications.
If the cause is infectious, it is necessary, along with preventive methods, to treat the infection. After it is removed from the body, plaque will stop forming. The same applies to weakened immunity.
It is necessary to strengthen the child’s immune system by following the pediatrician’s dietary recommendations and taking general strengthening medications.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=1j-ilXm46sE
Risk group
The risk group for the development of oral candidiasis are those children who require regular examination of the oral cavity by their parents and timely implementation of preventive measures.
There is an increased risk of white spots in a child's mouth if:
- The baby is premature (this applies to neonatal candidiasis, when white spots appear in the mouth of an infant)
- The mother is sick with candidiasis (infection can occur during birth through the mother’s contaminated birth canal or after it due to infection while caring for the baby)
- The child has chronic inflammatory foci in the oral cavity (caries), nasopharynx and oropharynx (tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc.)
- The child suffers from viral infections that sharply suppress the immune system (herpetic, cytomegalovirus, etc.)
- Patients from oncohematology clinics
- Children with positive HIV status
- Intestinal dysbiosis
- Increased susceptibility to allergic reactions
- Children with anemic syndrome
- Children with underweight (hypotrophy).
If a child has at least one of the risk factors listed above, then this is a compelling argument for observing the following rules:
- Brushing your teeth after every meal (use special children's toothpastes)
- Regular dental examinations at least once every 6 months
- Periodically rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal plants with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties
- Taking antibiotics and corticosteroids only as prescribed by a doctor, strictly following his recommendations
- Limiting a large amount of sweets in the diet, because... glucose is an integral component of the existence of candidiasis (a child should generally limit sweets, as this significantly increases the risk of not only candidiasis, but also multiple caries).
White coating on the palate of a baby
Contrary to the often wandering philistine opinions, thrush in the mouth of a newborn is in no way related to milk - not at all. The basis of this disease lies (or rather, grows!). mushrooms. Namely: yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. First of all, they manifest themselves as a persistent white coating, which in the mouth of a newborn resembles the remains of milk. Therefore, mothers call this disease thrush, while doctors more academically call it candidiasis. What kind of misfortune is thrush? Thrush in newborns is the same. Continue reading →
There are times when mushrooms actually begin to grow in our mouth, as if in a forest clearing. This often happens in newborns and children under one year old, manifesting itself in the form of a persistent white coating in the baby’s mouth. Many mothers, having noticed white crumbs on the baby’s tongue and gums, believe that these are leftover food (breast milk or formula) that the baby did not swallow, or, conversely, regurgitated. Alas, most often a whitish coating signals that the newborn has developed thrush. What kind of misfortune is thrush? Thrush u. Continue reading →
Found on BB Fairy tales for all occasions. Awakening. So, good morning! Our book, like your baby’s new day, begins from the moment the child opens his eyes. There are so many new and interesting things ahead. You need to be well prepared for all the events of the coming day. The first thing a baby should see is a smiling family face. Your smile will reassure him that everything is fine. Children in the first years of life feel the emotions of others very subtly. Be more attentive to yourself, watch your facial expressions, your internal state. Your excitement, anxiety, fear. Continue reading →
Fairy tales for all occasions for kids Awakening. So, good morning! Our book, like your baby’s new day, begins from the moment the child opens his eyes. There are so many new and interesting things ahead. You need to be well prepared for all the events of the coming day. The first thing a baby should see is a smiling family face. Your smile will reassure him that everything is fine. Children in the first years of life feel the emotions of others very subtly. Be more attentive to yourself, watch your facial expressions, your internal state. Your excitement, anxiety, fear, uncertainty. Continue reading →
Awakening. So, good morning! Our book, like your baby’s new day, begins from the moment the child opens his eyes. There are so many new and interesting things ahead. You need to be well prepared for all the events of the coming day. The first thing a baby should see is a smiling native face. Your smile will reassure him that everything is fine. Children in the first years of life feel the emotions of others very subtly. Be more attentive to yourself, watch your facial expressions, your internal state. Your child will absorb your excitement, anxiety, fear, and uncertainty like a sponge. You for. Continue reading →
Awakening. So, good morning! Our book, like your baby’s new day, begins from the moment the child opens his eyes. There are so many new and interesting things ahead. You need to be well prepared for all the events of the coming day. The first thing a baby should see is a smiling family face. Your smile will reassure him that everything is fine. Children in the first years of life feel the emotions of others very subtly. Be more attentive to yourself, watch your facial expressions, your internal state. Your child will absorb your excitement, anxiety, fear, and uncertainty like a sponge. You are for him. Continue reading →
White spots or dots on the gums, mouth and tongue of a baby
Young mothers are very worried if they notice that not everything is all right with their child. This is especially true for infants: tiny babies quickly react to various changes, begin to act up and get sick
Important attention should be paid to the baby’s oral cavity at the time of teething. If you notice white spots on your baby's gums, you should not ignore it.
- 1 Read more
- 2 Reasons
- 3 Stomatitis
- 4 Prevention
More details
A white spot, bumps, pearls in the mouth and on the tongue are a significant reason for concern. If your child’s gums are also red and the temperature has risen, it is better to immediately show him to the pediatrician. He will find out the reason and help dispel doubts. What could such phenomena mean?
You don't always need to panic. Even if a child has a white pimple in his mouth, natural causes can sometimes contribute to this. White balls and spots in the mouth may appear before the first teeth. If your baby’s teeth itch at 3-4 months, there’s no need to worry either. Expect your first tooth to appear soon.
Causes
Below are the reasons for this phenomenon.
- Epstein's pearls. They are brushes that are formed from epithelial inclusions. They closely resemble real pearls and cones, hence the name. You cannot touch such formations; they will disappear on their own after a while.
- Bon's knots. They occur not only on the gums in the mouth, but also on the cheeks, sometimes on the tongue. These are tiny brushes made from dental plate. May resemble the shape of the first teeth. However, they will also soon resolve on their own, so there is no reason to worry.
- Sometimes white spots and bumps in the mouth are so-called congenital teeth. In this case, the child must be shown to a doctor, since additional teeth must be removed. It is necessary to urgently contact a pediatrician if hematomas appear on the gums and tongue and begin to bleed. This may indicate the development of oral diseases. If left untreated, this can lead to serious problems in the future that can lead to tooth loss.
Stomatitis
Sometimes pearls, bumps, bumps and spots on the tongue may indicate stomatitis - inflammation of the oral mucosa. Infants are more often susceptible to stomatitis, since their body is not yet able to resist viruses and bacteria. Not all parents know the rules for caring for their child’s oral cavity, so they do not pay due attention to it.
The mucous membrane can be severely damaged if not properly cared for.
Therefore, this must be done very carefully; sharp and hard objects are excluded.
White dots, bumps and spots are a characteristic sign of stomatitis. The quantity, appearance, location will depend on the type of disease:
- viral. Occurs against the background of other diseases and inflammatory processes. For example, if a baby has the flu, bronchitis, or chickenpox, there may be white spots and bumps on the gums, and in large quantities. In this case, the baby is shown to the doctor, since tubercles in the mouth are a dangerous phenomenon;
- allergic. Asthma, allergies, atopic dermatitis are companions of white formations in the mouth. Usually they are only on the tongue;
- bacterial. If your baby catches an infection, he may develop a fever. This will be accompanied by a white coating throughout the mucous membrane and on the tongue, as well as blisters that bleed heavily and even hurt. The condition requires immediate medical intervention.
Young mothers often have a lack of calcium in the body. This also affects the baby’s health: an unhealthy white coating appears in the mouth. Sometimes attentive mothers mistake the remaining milk in the baby’s mouth for plaque. In this case, you need to pay more attention to hygiene.
Types and manifestations of anomalies
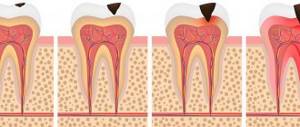
The defect in newborns is manifested by a complete cleft of the soft and hard palate, passing through, or a small crack only in the soft tissues. According to the degree of bifurcation, the defect is classified into:
- complete – with splitting of soft and hard tissues up to the incisive foramen;
- incomplete - with a cleft only in the soft palate or with partial cleft of the hard palate;
- through – one- or two-sided clefts of the hard and soft palate with the inclusion of the alveolar process;
- hidden - the gap cuts only the muscles while preserving the oral mucosa.
“Cleft palate” in newborns, in addition to a cosmetic defect, is accompanied by a number of symptoms indicating disorders of the vital functions of the body. From the moment the baby is born, disturbances in sucking and swallowing of food appear. Shallow breathing develops, leading to oxygen deficiency and a tendency to inflammation of the middle ear, which negatively affects hearing. With the active growth of the baby, disorders of the speech apparatus (pronunciation of sounds through the nose) and delayed development of all body structures are detected.
Treatment of oral thrush in children
Superficial and local forms of candidiasis require local therapy by lubricating or irrigating the child’s mouth with disinfectant and alkalizing preparations. Thrush in newborns on the tongue or palate is treated with a sterile cotton swab dipped in a solution of soda, potassium permanganate, tannin or antifungal agents. If there are symptoms of concomitant diseases, treatment involves a set of measures to eliminate all identified pathogenic microorganisms.
Antifungal drugs
If the white plaque that appears in the baby’s mouth spreads quickly and is difficult to treat locally, the doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medications. The most effective drugs against oral thrush in children include Fluconazole, which is well tolerated and rarely causes side effects:
- name: Fluconazole;
- description: synthetic fungal sterol inhibitor, used as intensive therapy for oral candidiasis in children;
- Application: on the first day of use, the daily dose is calculated based on 6 mg per 1 kg of child’s weight, then - 3 mg per 1 kg;
- pros: quickly eliminates pain;
- disadvantages: delayed excretion of the active substance in infants.
The drug Clotrimazole, used in the treatment of fungal diseases, has no restrictions on the age of patients:
- name: Clotrimazole;
- description: antimycotic solution with a wide spectrum of effects, inhibiting the activity of peroxidases, promotes the destruction of fungal cells;
- application: apply 10-20 drops of solution to fungal-affected areas of the mucous membrane 3-4 times a day;
- pros: eliminates symptoms of thrush on the 3rd day of use;
- cons: there are side effects.
Local treatment
All manipulations during local treatment of the oral cavity of a newborn should be performed carefully, without strong pressure. It is necessary to treat the baby’s mouth before eating, so as not to provoke a gag reflex.
White plaque is cleaned with a cotton ball soaked in a solution of medications. One of the effective remedies against thrush is Pimafucin:
- name: Pimafucin;
- description: antifungal antibacterial agent with fungicidal action;
- Application: 1 ml 4-6 times a day,
- advantages: good tolerability by newborns;
- cons: high price.
A quick effect is obtained by treating the affected areas with an aqueous suspension of Nystatin. It is recommended to alternate this remedy with a solution of sodium bicarbonate (5%):
- name: Nystatin;
- description: local antifungal drug;
- Application: dissolve 1 granule in 5 ml of boiled water, treat the oral cavity every 6 hours;
- advantages: does not affect normal flora;
- cons: there are contraindications.
Folk remedies
Treatment of fungal infections of the oral cavity in newborns with the help of medications can be combined with the use of traditional medicine recipes. Homeopathic remedies for eliminating and preventing white plaque in the mouth include:
- Rinsing with a solution based on honey and turnip juice. Squeeze the juice from the boiled turnips and combine it with 1 tsp. natural honey. The resulting solution is used to wipe the mucous membrane an hour after feeding the baby.
- Treatment with viburnum and honey. Squeeze the juice from the viburnum berries, mix it with the same amount of honey and bring the resulting mixture to a boil three times (it should look like jelly). Clean your mouth before each feeding.