From this article you will learn:
- how to treat aphthous stomatitis in children,
- symptoms and treatment of aphthous stomatitis in adults,
- list of effective drugs.
Aphthous stomatitis is a disease in which one or more round ulcerations appear on the oral mucosa, which are covered with a necrotic coating of a gray or yellowish tint. Such ulcers (synonymous with aphthae) are not the result of acute infections, and therefore are not contagious, but nevertheless, such damage to the mucous membrane will require specific therapy.
According to statistics, up to 20% of the population suffers from this form of stomatitis. Young children and adults between the ages of 20 and 30 are especially susceptible to this disease. In people of more mature age, there is a dependence: the higher the age, the less likely it is to develop. Aphthous stomatitis has a code according to ICD 10 - K12.0. Below you can see what this disease looks like in children and adults.
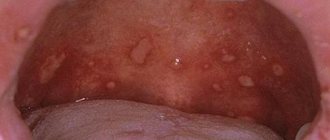
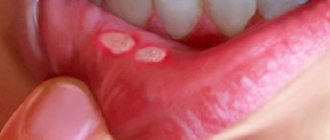
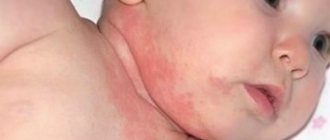
Aphthous stomatitis in children: photo
Aphthous stomatitis: photos in adults
The most important thing in treating stomatitis is to first correctly determine its form. Indeed, depending on its form, and it can be either herpetic or aphthous stomatitis, treatment for both adults and children will be completely different. Therefore, if you are not very sure of the diagnosis, it is best to familiarize yourself with the symptoms of both forms before starting treatment.
Origin of aphthous stomatitis
Until now, doctors researching this disease have not figured out the exact cause of its occurrence. There are several versions about this:
- aphthous stomatitis is caused by a bacterium - streptococci; the appearance of the disease is influenced by hereditary factors;
- the disease is caused by trophoneurological changes (for example, trophoneurosis is a disease of the autonomic system, which is characterized by a violation of tissue nutrition);
- blood diseases are also considered one of the causes of aphthous stomatitis;
- problems with teeth
or gums; - lack of vitamins in the body.
Today, most scientists and doctors believe that the leading role in the appearance of aphthous stomatitis is played by immunity, and specifically by its weakening.
Also factors in the occurrence of the disease are frequent stress or other chronic diseases of the throat, oral cavity or gastrointestinal tract: tonsillitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, gastritis, gastroduodenitis, etc.
Moreover, some doctors associate aphthous stomatitis with irritable bowel syndrome, but, again, the main influencing factor in this case is stress.
The cause of the disease may be a trauma to the oral cavity or a burn while eating food or hot liquid. In some cases, the chronic disease itself develops after deformation of the inside of the lips or cheeks by spicy foods (crackers, chips, other solid foods), teeth
and
dental implants
.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are usually used during follow-up treatment, when acute manifestations are eliminated.
For the treatment of stomatitis the following is used:
- infusion of chamomile flowers;
- paste from ground burdock seeds with salt and butter;
- decoction of oak bark;
- aloe juice;
- a decoction of the rhizome of snakeweed;
- yarrow decoction;
- infusion of ground rhizome of bergenia;
- infusion of pomegranate peel.
Physiotherapeutic agents include treatment of lesions with ultraviolet rays.
Symptoms
The main symptom of chronic aphthous stomatitis is inflammation on the inside of the mouth. The clinical picture is as follows: aphthae usually have a round, spherical shape. Their size is no more than 1 cm. Touching the aphthae causes burning and stinging, so often at the time of exacerbation, children become excessively nervous and capricious.
There are three forms of aphthous stomatitis:
- light;
- medium-heavy;
- heavy.
With a mild form, aphthae appear sporadically several times every 2-3 years, with a moderate form - several aphthae per year. The severe form is characterized by the constant occurrence of painful ulcers in the mouth. Therefore, treatment of stomatitis must begin immediately - after detecting the first signs of the disease.
As for the general condition of the patient, mild and moderate forms do not have a significant effect on the body. But severe chronic aphthous stomatitis can cause another serious disease - regional lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes).
Speaking about the tolerance of aphthosis and pain, the patient feels irritating, painful sensations in the oral cavity only during the inflammatory process, that is, immediately after the appearance of aphthosis. What is natural is that the severity of the disease leads to an increase in ulcers and their depth.
Diagnosis of aphthous stomatitis
At first glance, it may seem that determining the presence of aphthous stomatitis is not so difficult: there are characteristic signs in the form of aphthous stomatitis, swelling of the oral cavity, pain - it would seem that everything is simple. However, this is not at all true.
It should be understood that, along with a disease such as stomatitis, similar symptoms are:
- acute recurrent herpetic stomatitis;
- chronic oral injuries.
Therefore, it is imperative to carry out differential diagnosis using virological testing, as well as immunofluorescence (an effective method for detecting antibodies to known antigens).
The following factors must be considered before making a diagnosis:
- Patient's symptoms.
- Along with developing diseases.
- Age.
- Test results.
Symptoms and treatment of stomatitis may differ depending on the stage and the presence of other diseases. For example, if the patient has concomitant diseases of the oral cavity, the number and frequency of aphthae may increase.
Therefore, for high-quality treatment of stomatitis in adults and children, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnosis in order to determine an accurate diagnosis.
Oral mucosa
The oral mucosa (ORM) should normally be pale pink and moderately moist. It is the “entry gate” for many infections and, naturally, serves as the site of manifestation of the first somatic symptoms. It has a dense network of blood and lymphatic vessels, which means that an infection that gets on the oral mucosa can enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. Therefore, attention is paid to her condition and changes. The structure of the mucosa explains its high sensitivity to temperature, pain, tactile and taste stimuli. It performs a protective and suction function. The protective function of the mucosa is to prevent the penetration of infection. In response to the action of pathogens (infectious agents), leukocytes are released - protective blood cells that take part in phagocytosis - the direct destruction of pathogens. Macroelements actively penetrate through the mucosa: potassium, sodium, carbonates, iron and other substances are absorbed. By the way, the oral mucosa is part of the digestive tract, so it is also assessed when making a diagnosis related to the gastrointestinal tract.
Aphthous stomatitis in children
The prevalence of stomatitis among children is an order of magnitude higher than among adults. This is determined by the fact that a child’s fragile body is weaker than an adult’s. Reduced immunological reactivity is a catalyst for the development of a chronic form of aphthous stomatitis, characterized by periodic exacerbations.
One of the main reasons for relapse of the disease in children is a complication of another oral disease. In addition, a sharp change in climate can also affect the occurrence of relapse.
Treatment of chronic aphthous stomatitis in children
Treatment of childhood aphthous stomatitis has a positive prognosis, however, it is worth understanding: if you start eliminating the causes of the disease in the early stages, you can achieve a greater effect and significantly reduce the child’s pain.
To identify the root cause of the disease, you need to contact a pediatrician, who can either independently diagnose or, for a more accurate diagnosis, give a referral to a dentist.
Typically, treatment of chronic aphthous stomatitis in children includes the use of ointments, adhesive pastes, and immunostimulating drugs: ·
- "Metrogil Denta"
- This is a fairly effective remedy in the form of an ointment, used in most cases in the treatment of aphthous stomatitis. Apply to damaged areas of the mouth twice a day after cleaning the mouth;
- "Solcoseryl"
– a paste that has a positive restorative effect on the epithelial tissues of the oral cavity. It is necessary to apply about 4-5 times a day and – necessarily – after eating;
- "Imudon"
is an anti-inflammatory agent that also has an anti-infectious effect. Use every few hours, but not more than 8 tablets per day.
Diet is important in treating the disease. Gentle nutrition and exclusion from the diet of solid foods, which can aggravate the course of the disease, is an important step in the fight against such an unpleasant disease.
Recommended to use:
- vegetable soups;
- fruit and vegetable puree;
- boiled meat;
- dairy products (in particular, natural yogurt and kefir have a positive effect on the body, providing an immunostimulating effect);
- Herb tea;
- natural juices from non-acidic fruits and berries;
In no case should food cause pain when consuming food and liquid. Therefore, a prerequisite for the diet is temperature: food and drinks should be warm - neither hot nor cold.
Treatment of stomatitis in children also includes banal rules that are not followed by everyone: in the morning and before bedtime, you need to thoroughly but gently clean your teeth with a toothbrush
with soft bristles. After eating, it is recommended to rinse your mouth with an herbal solution or warm boiled water.
Treatment of chronic stomatitis in adults
As in the treatment of childhood stomatitis, the fight against the disease in adults begins with finding the cause that caused it. And depending on the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. It is worth noting that an adult can contact both a therapist and a dentist.
Despite the origin of stomatitis, treatment in adults also includes anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and immune-stimulating drugs.
When fighting chronic aphthous stomatitis, folk remedies are used. Treatment of stomatitis at home involves the use of antiseptic and desensitizing agents:
- decoction of chamomile and boric acid for rinsing;
- solution of potassium permanganate for “baths” in the oral cavity;
- sea buckthorn, peach oil for application to affected areas;
- rinsing with a solution of furatsilin, calendula and chlorophyllipt;
An effective remedy for fighting stomatitis is rose hips. You can also take baths and rinse your mouth with it, however, after these procedures it is imperative to rinse your mouth again with warm water after 5-7 minutes - rose hips have a detrimental effect on tooth enamel.
Mouth treatment
The most effective measures for treating the disease are rinsing with physiological antiseptics and irrigating the oral cavity with anti-inflammatory sprays.
For treatment of the oral cavity they are used;
- miramistin solution;
- 0.06% chlorhexidine solution;
- 0.02% solution of furatsilin;
- 0.1% dimexide solution.
During therapy, it is important to select medications that provide a quick cure.
The following medications are used for therapy:
- application of anesthetics with proteolytic enzymes for 10-15 minutes once a day (trypsin, lysozyme, ribonuclease);
- applying epithelializing ointments to ulcers (Solcoseryl-gel);
- rinses with antibacterial drugs: Tantum-Verde in a dosage of 15 ml 3-4 times a day, 5-6 days or use Hexoral, Orasept;
- applications of Mundizal gel to the oral mucosa for 20 minutes 3-4 times a day, 5-10 days;
- balm Stomatofit-A, it contains painkillers, extracts of medicinal plants;
- antifungal drugs;
- painkillers, anti-inflammatory ointments (Benzocaine, Xicaine);
- Diphenhydramine suspension to relieve allergic symptoms.
Preventing stomatitis
In order to prevent aphthous stomatitis and to prevent the occurrence of its chronic form, it is recommended to maintain hygiene, including brushing your teeth
, rinse your mouth after eating, and wash your hands thoroughly.
Eating healthy foods has a positive effect on the body as a whole. One of the effective ways to strengthen the immune system is to take vitamins and vitamin complexes. However, you should not start taking vitamins on your own - you must contact a specialist who will prescribe the drug that is right for you.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.