June 4, 2021 Last revised: December 21, 2021 Medicinal products
Author of the article:
Lukanina Lyubov Valerievna (Author's page | All articles) is a dentist-therapist, periodontist. Specializes in the fields of: endodontics, aesthetic and functional restoration, professional hygiene and periodontology.
Stomatitis is one of the most common ailments of the oral cavity; it has many causes, and sprays, rinses, gels and ointments are recommended for treatment. That’s what we’ll talk about today about ointment for stomatitis.
Causes of stomatitis
Many factors can contribute to the appearance of stomatitis in an adult:
- pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi that have developed against the background of reduced immunity;
- mechanical damage to the oral cavity;
- stress, hypothermia, lack of sleep are factors affecting the body’s defenses;
- poor quality nutrition, lack of vitamins or dehydration;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- smoking;
- side effects from chemotherapy or medications that reduce salivation;
- hormonal disorders;
- incorrect bite, poorly made dentures or braces, etc.
Causes
The main cause of the disease is infection with the Candida fungus, an opportunistic pathogen that is widespread among humans and animals. Candida is a yeast-like unicellular fungus that is part of the normal microflora in a significant proportion of healthy people. Most often it can be found on the surface of various mucous membranes of the body, for example, in the intestines, mouth, pharynx and tonsils. Today, about 150 varieties of this microorganism are known, 20 of which are capable of causing diseases in humans. The destructive effect of Candida on the mucous membranes and other tissues of the human body is due to the release of a large number of enzymes that break down proteins, fats and other cell components. As a result of this, symptoms characteristic of candidiasis such as burning, dryness, and soreness occur.
When unfavorable conditions occur, Candida becomes covered with a special protective shell, which helps the fungus survive in the external environment and travel from host to host. Infection can occur in various ways - airborne, household contact, intrauterine. Newborn children are infected, as a rule, from medical personnel, or during childbirth, when passing through an infected birth canal.
At an early age, the child’s body does not have a developed immune system, if only for the simple reason that he has had virtually no contact with infectious agents and has not developed the appropriate antibodies. This is why children under one year of age are especially prone to developing candidiasis. However, this disease also occurs in older children. In this case, its appearance and development is often preceded by the formation of multiple carious lesions of the teeth. Caries, which is a constant source of infection, contributes to the weakening of local and general immunity, resulting in the rapid and active proliferation of opportunistic and pathogenic microflora. Various fungi of the genus Candida also fall into this category.
Factors that can provoke the development of candidiasis in a child’s mouth are also various concomitant diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, acute or chronic infections, and other somatic ailments. Poor oral hygiene, taking antibiotics, hormones and immunosuppressants, and insufficient or unbalanced nutrition also increase the risk of developing candidiasis.
For active reproduction of the fungus, certain conditions are necessary - in particular, this microorganism is most active at temperatures from 30 to 37 degrees Celsius. The level of acidity that is optimal for the growth of Candida occurs in a person’s mouth when consuming large amounts of sweets, flour and other foods containing many simple carbohydrates.
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the reasons that caused inflammation of the oral mucosa, the following types of stomatitis in adults are distinguished.
Infectious.
Inflammation can be caused by various pathogens that develop against a background of weakened immunity. There are:
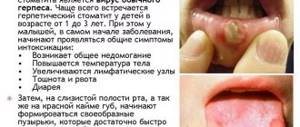
- viral stomatitis.
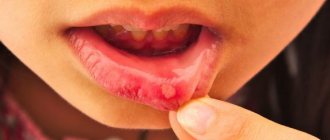
It can appear against the background of influenza, chickenpox, measles, herpes, rotavirus or adenovirus infection. Stomatitis in such diseases usually manifests itself in the form of blisters with a clear liquid inside, which easily burst and do not heal for a long time, turning into ulcers covered with a white or gray coating. In addition, a person often has a fever, weakness, headaches and other symptoms characteristic of ARVI; - bacterial stomatitis.
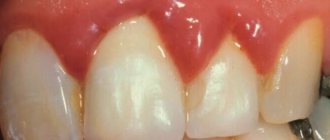
Inflammation occurs due to the pathogenic activity of staphylococci, streptococci and other microorganisms. Stomatitis often accompanies people with chronic dental diseases (deep caries, periodontitis, gingivitis), and diseases of the upper respiratory tract (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, etc.). In addition, the infection can be introduced from the outside through wounds on the mucous membrane, for example, by eating unwashed foods during the eruption of wisdom teeth, etc. With bacterial stomatitis, the mucous membrane becomes swollen and red, and reacts to spicy, sour foods. Then increased salivation and bad breath appear, ulcers and cracks form. Gums may begin to bleed; - fungal stomatitis.
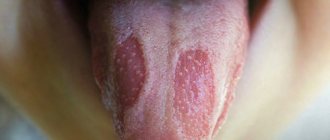
This inflammation is most often provoked by a fungus of the genus Candida, which is present in small quantities on the mucous membrane of any person. However, due to the weakening of the body's defenses, it can begin to multiply, causing stomatitis. The disease often affects older people, pregnant women, and people with blood diseases, HIV, diabetes, or undergoing treatment with antibacterial drugs or chemotherapy. With fungal stomatitis, a white cheesy coating appears on the oral mucosa, hiding the eroded tissue.
Allergic.
From the name it is clear that the cause of this form of stomatitis is the effect of allergens on the human body. The disease may be accompanied by severe swelling, redness and itching of the mucous membrane.
Review of the 10 most popular ointments for stomatitis
For the ointment to be effective, you need to correctly determine the type of inflammation of the mucous membrane. In addition, you need to solve internal problems of the body, if any. But the following remedies have proven to work best in the treatment of stomatitis:
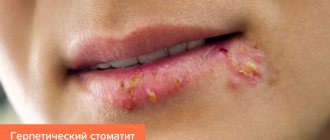
Acyclovir
Inexpensive antiherpes drug. The main character of the ointment is an analogue of the DNA component (deoxyguanosine). A complex compound with a difficult name easily penetrates the herpes virus (into its DNA) and carries out destructive work in its internal structure. Thus, acyclovir inhibits herpes and prevents it from acting on the oral mucosa.
The ointment is best applied as an application. We apply it to a cotton swab and treat not only the inflamed mucous membrane, but also its healthy areas. It is better not to do this with your hands because you can transfer herpes to healthy skin. We use it five times a day (or once every 4 hours). The duration of therapy is from weeks to ten days. Before treatment, rinse the mucous membrane with soda or a strong infusion of chamomile.
The advantage is that a small tube will last for a long time and you can treat herpes not only in the mouth. Analogs of the drug are acigerpin, zovirax and vivorax, gervircax, and also herparax.
Oxolinic ointment
Chemists call oxoline naphthalene-1,2,3,4-tetron. It copes with many viruses, including those that contribute to inflammation in the oral cavity. Suitable for children and as a prophylactic. Use two to four times a day only on inflamed areas of the mucosa. For stomatitis, a concentration of 0.25 is needed.
There are no contraindications, but some side effects are possible, for example, a slight burning sensation or blue discoloration of the mucous membrane. Three percent oxolinka is suitable even for babies under one year old. Not dangerous for pregnant women. It also helps with herpes stomatitis, so it is quite a universal remedy. Cost - from 20 rubles to 120.
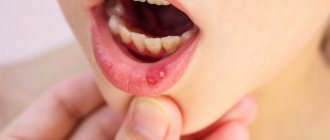
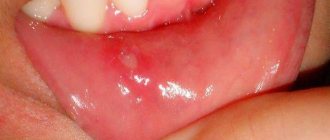
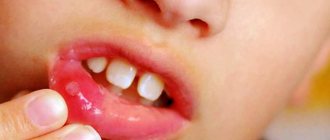
What is aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is one of the manifestations of the disease, which can be recognized by its characteristic signs. Initially, slight redness appears on the mucous membrane, then swelling, accompanied by burning or pain. Afterwards, aphthae form - round or oval white sores with a red halo. In addition to painful sensations, a person begins to worry about increased salivation and bad breath. Sometimes the temperature rises. The aphthous form of stomatitis can be triggered by various reasons: infections, allergies, gastrointestinal diseases, vitamin deficiency, injuries, insufficient oral hygiene, etc.
Symptoms of oral thrush in a child
Diagnosis and treatment of oral thrush in newborns is complicated by the fact that the child cannot yet explain that something hurts. In addition, parents often confuse the manifestations of candidiasis with the usual plaque that remains after feeding the baby. Therefore, if a child becomes irritable and whiny, refuses food and pacifiers, this is a good reason to suspect thrush.
First of all, it is necessary to examine the oral cavity. At the initial stage, you may notice white spots or redness on the gums, tongue, inner cheeks and lips. As thrush develops, a white, curd-like coating appears on the mucous membrane, underneath which is hidden eroded (bright red, irritated) tissue, which may begin to bleed when trying to clean off the plaque. Older children usually complain of burning and itching in the mouth, as well as pain when eating.
In severe cases, the fungus begins to spread to neighboring tissues - the palate, the walls of the pharynx, the lips. Advanced thrush looks like a solid white film in the mouth, the mucous membrane begins to bleed more, and the pain intensifies. In this case, candidiasis begins to be accompanied by elevated temperature, lethargy, and later by disturbances of the intestinal microflora.
In severe cases of the disease, treatment for oral thrush in children takes a long time and may even require hospitalization. Therefore, at the first suspicion of candidiasis, it is necessary to show the child to a doctor.
How to treat stomatitis
To successfully treat the disease in an adult, it is not enough to simply deal with unpleasant symptoms with the help of local remedies for stomatitis in the mouth, for example, anesthetic gels and ointments. It is necessary to eliminate the underlying cause of inflammation. It is often difficult for a non-specialist to determine what exactly contributed to the appearance of stomatitis, which means that independent treatment may not only fail to produce results, but also aggravate the condition. A doctor must identify the cause and prescribe complex therapy. Treatment of stomatitis in adults may include various drugs and local remedies, depending on the factors that caused the disease. The general treatment regimen is as follows:
- eliminating the causes of the disease with the help of antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal, antihistamine and other drugs. If stomatitis is caused by mechanical injuries from wearing braces or implants, you must visit a dentist to correct the defects;
- symptomatic treatment: the use of local drugs for stomatitis (ointments, gels, compresses), which have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects, as well as antipyretics in the presence of fever, etc.;
- strengthening the immune system: immunomodulating drugs and vitamin complexes, physiotherapeutic procedures can be used.
Only such comprehensive treatment of stomatitis can get rid of unpleasant symptoms and reduce the risk of relapses.
Treatment of oral thrush in children
Treatment of oral thrush in newborns is complicated by the fact that classical therapy with antifungal drugs is not suitable in this case. However, there is a group of medications approved for use in very young children. But only the attending physician can prescribe them.
Comprehensive treatment of oral thrush in infants includes:
1. General strengthening therapy, the purpose of which is to restore and support the immune system.
2. Organizing a proper diet and rest for the child. It is necessary to make sure that the baby receives all the necessary vitamins and microelements.
3. If the cause of candidiasis is frequent regurgitation, then treatment of oral thrush in a newborn should begin with improving feeding techniques. It is necessary that the child grasps the nipple or bottle correctly so that excess air does not enter the stomach. An important point: if the child is breastfed, therapy should be carried out in parallel with the treatment of the mother to avoid re-infection.
Oral care during stomatitis treatment
Local treatment of stomatitis in adults plays an important role in the success of therapy. It is necessary to follow a gentle and low-allergenic diet. Food should be warm and soft, not irritating the mucous membranes. During treatment, you should exclude hard, spicy, sour, and sweet foods from your diet. After every meal you need to rinse your mouth. For this purpose, special remedies for stomatitis (solutions or infusions) can be used, which the doctor will recommend. They have an antiseptic effect and protect the oral cavity from the development of pathogenic bacteria.
An important aspect in the treatment of stomatitis in adults is pain relief, since aphthae and ulcers can cause significant discomfort, interfering with normal eating and talking. In this case, local painkillers such as Cholisal® have worked well. This gel has a local analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect for stomatitis in adults. The antiseptic included in the composition protects the oral cavity from bacteria. The analgesic effect of the gel against stomatitis occurs within 2-3 minutes and lasts from 2 to 8 hours. Such remedies for stomatitis in adults, in combination with the main therapy prescribed by the doctor, help cope with unpleasant sensations in the mouth and speed up the healing process.
Types and categories of ointments for stomatitis
A variety of active ingredients will eliminate any cause of inflammation of the mucous membrane. Ointments against stomatitis are divided into the following types:
- Universal. They relieve inflammation and are needed both for ulcerative stomatitis and for aphthous and catarrhal stomatitis;
- antifungal. For the treatment of candidal stomatitis;
- antiviral. Needed for the treatment of herpetic stomatitis;
- antibacterial, used for aphthous or traumatic stomatitis.
It is important to know! None of the ointments will help if the inflammation of the mucous membrane is caused by allergies. It is not the infection that is to blame here, but internal disorders.
Stomatitis ointment for children
Not every ointment is suitable for a child. Therefore, when fighting inflammation of the mucous membranes in children, you must always consult a pediatric dentist and study the instructions for any product: the dosage can vary greatly.
In addition, it is better to replace ointment for stomatitis in children under one year old with solutions: they are contraindicated for the youngest. Among the products that are acceptable for use for children, it is worth noting:
- Actovegin (antibacterial);
- acyclovir (for herpetic stomatitis);
- Viferon (also an antiherpetic agent);
- Zovirax (like the two previous ointments - antiherpetic);
- lidochlor (relieves pain);
- nystatin (for fungal stomatitis);
- Cholisal (for bacterial stomatitis).
But all of them are suitable only for babies over one year old. By the way, at this age most often stomatitis is candidiasis, so pay attention to fungal remedies.
Prevention of stomatitis
To avoid the appearance of stomatitis in adults, it is necessary to maintain oral hygiene, eat well, stop smoking, promptly treat colds and other diseases, prevent dirt from getting on the mucous membrane, and undergo preventive examinations at the dentist to prevent caries and other dental problems.
Learn about other oral diseases
Noma Periodontitis Damage to the oral mucosa (from wearing dentures, piercings, braces, crowns) Periodontitis
What are the reasons for stomatitis in children?
Various factors can contribute to the development of stomatitis in a child, for example, insufficient hand and oral hygiene, the habit of gnawing objects found on the floor. It is worth understanding that, unlike adults, the mucous membrane in children is more delicate and vulnerable, and the immune system is not yet strong enough to resist infections. In addition, at an early age, the process of salivation has not yet fully formed. Because of this, the child’s mucous membrane often dries out, cracks appear, into which infection enters and inflammation begins. Other causes of stomatitis include long-term use of medications, neuropsychiatric disorders, lack of proper treatment for ARVI and other diseases, unfavorable living conditions, etc.