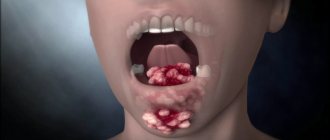
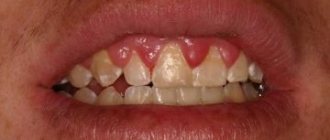
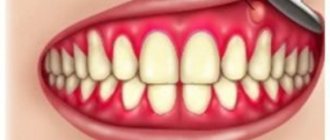
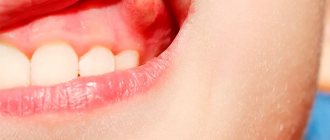
Gum cancer is included in the group of malignant neoplasms of the oral cavity along with carcinomas of the tongue, floor, cheeks and palate. Malignant processes in different anatomical structures of the oral cavity proceed differently, the reasons for their development and treatment methods are similar.
- Causes of gum cancer
- Stages
- Symptoms of gum cancer
- Risk group
- Diagnosis of gum cancer
- Treatment for gum cancer
- Prevention
- Forecast
- Possible complications of gum cancer
Causes and risk factors
Gum cancer is a neoplasm of the soft tissue of the upper or lower jaw that appears due to uncontrolled cell division. They grow into nearby organs and, if left untreated, metastasize. The exact causes of the development of malignant gum tumors are unknown. Risk factors that increase the likelihood of disease include:
- age over 40 years;
- male gender (women get sick 5 times less often);
- advanced oral diseases – caries, gingivitis, periodontal disease;
- smoking, alcohol or chewing tobacco abuse;
- mechanical injuries to gums and teeth;
- piercing of the lips and tongue (a foreign body injures the mucous membranes and promotes the growth of bacteria);
- neglect of personal hygiene;
- genetic predisposition;
- autoimmune diseases, herpes virus, papillomavirus.
- working with toxic or radioactive materials;
- congenital pathologies of the jaw structure.
Sometimes gum cancer is caused by excessive oral hygiene. Dentists recommend brushing your teeth no more than 2-3 times a day - too frequent a procedure leads to microtrauma to the tissue. Too frequent rinsing of the mouth with alcohol-containing solutions leads to drying out of the mucous membranes and disruption of the oral microflora, which also leads to the development of malignant tumors.
People with the herpes virus and HPV (human papillomavirus) are diagnosed with cancer more often than others. Herpetic infection often causes a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane and inflammatory processes. HPV contributes to the development of cancer of the cervix, anus, vagina and oral cavity. To identify infections, it is necessary to get tested, undergo treatment, and then get vaccinated to prevent re-infection.
According to statistics, more than 95% of patients diagnosed with oral cancer smoke a lot (more than 2 packs of cigarettes per day) and drink alcohol.
Dangerous symptoms
It is clear that diagnosing dental cancer is not so easy. It is worth being wary in cases where there is the appearance of long-term non-healing ulcers on the oral mucosa, deformations that are sometimes already noticeable to the eye, pain in untreated and intact teeth, when sensitivity changes. These are alarm bells that need to be responded to urgently and immediately run to the dentist. The earlier a tumor is detected, the greater the chance of minimizing losses.
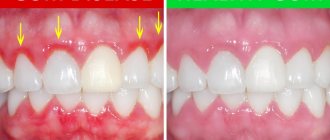
It is also worth considering such an important sign as bleeding gums. If in a normal state, in order for blood to flow, you need to damage the gum, then in the case of cancer, light pressure will be enough. Also, swelling of the gums and increased body temperature may appear in parallel.
What does gum cancer look like?
The disease affects the lower jaw more often than the upper jaw. The characteristics of the neoplasm depend on the type of tumor and the stage of the disease. In the initial stages, it can be asymptomatic - an inconspicuous compaction or ulcer appears on the gum. As the pathology progresses, the affected area enlarges, and the patient’s well-being worsens.
The difficulty is that the signs of gum cancer resemble the symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. Patients do not pay attention to the small tumor or try to cure it on their own, which leads to a worsening of the condition.
Comments
And I want to get a piercing in my mouth, my relatives tell me that it can cause cancer...
Elsa (10/19/2020 at 11:13 pm) Reply to comment
- Piercing can indeed become one of the factors that increases the risk of developing cancer in the oral cavity. After all, there is a possibility that it will periodically or systematically injure soft tissues and mucous membranes. However, if you carefully maintain oral hygiene, promptly treat dental diseases and are attentive to any inflammatory processes in the mouth, then the risk is minimal.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (10.24.2020 at 09:29) Reply to comment
And if you are cured of gum cancer, can it appear again?
Makar (04.11.2020 at 13:41) Reply to comment
- Dear Makar, this pathology can recur in the presence of the provoking factors listed in the article.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (09.11.2020 at 10:10) Reply to comment
Hello! How is gum cancer treated? Is the tumor removed by surgery? Or can you do without surgery in the initial stages? I am concerned about the appearance of my mouth and teeth after treatment.
Shakhova R. (11/20/2020 at 07:04 pm) Reply to comment
To be honest, I have never even heard or encountered it, thank God. Prevention lies in good oral hygiene or is it still not known why gum cancer can occur in the first place?
Olga (11/20/2020 at 7:47 pm) Reply to comment
It's scary of course. The fault may not only be due to poor care of the gums or teeth, but also to weak immunity itself. those. inflammation can start from within the body and express itself in such a sudden way.
Artyom (11/20/2020 at 9:31 pm) Reply to comment
You can still somehow try to cure the initial ones, but the severe ones are already quite bad. I don't recommend people to smoke. And not often and not constantly, preferably not at all. This can cause cancer to form suddenly.
Karina (11/20/2020 at 9:47 pm) Reply to comment
Is it worth getting examined if the gums above the crown often swell? The prosthesis has been in place for many years, but the problems began relatively recently. Is there any kind of cancer prevention at all?
Emma (11/20/2020 at 9:49 pm) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Symptoms of the disease
Malignant gum tumors manifest themselves with local and general symptoms. The severity depends on the stage of the disease, age and general condition of the patient.
- Pain. A key symptom that appears in the first stages of the disease, since as the tumor grows it begins to put pressure on the nerve endings. The pain syndrome is of a bursting, pulsating nature, and as the tumor progresses, it covers the entire jaw and radiates to the ear and temple. Patients with advanced gum cancer cannot chew or speak normally, and the pain is not relieved by conventional analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Edema. Swelling or thickening occurs at the site of the tumor. At first the tumor does not interfere, but over time it prevents him from eating and speaking normally.
- Bleeding. The symptom appears due to tissue breakdown and develops even with the slightest pressure on the gums. Over time, the gums bleed several times a day.
- Unpleasant smell. The breakdown of tissue and the proliferation of bacteria in the oral cavity during cancer provokes an unpleasant odor that is difficult to mask with toothpaste or chewing gum.
- Change in sensitivity. The affected area of the gum becomes overly sensitive to high and low temperatures, or, conversely, becomes numb.
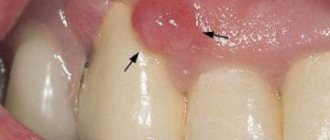
- The appearance of spots and ulcers. With cancer of the gums, white or purple spots appear on the mucous membrane, sometimes small ulcers appear in their place.
Common symptoms of gum cancer include fatigue, weight loss, low-grade fever, and swollen lymph nodes. They can appear in the first stages of the disease, before the development of local symptoms, or after their appearance.
Symptoms of the initial stage, first signs, photos
A tumor on the gum is not immediately recognized and grows slowly. One of the first signs of gum cancer is bleeding of the gums for several months, but there is no swelling or swelling yet. This condition can easily be confused with ordinary periodontitis or gingivitis. However, bleeding and pain are difficult to relieve, and the patient’s usual medications do not help relieve these manifestations. Other symptoms appear almost immediately:
- increased local sensitivity of the affected area to cold and hot;
- a change in the appearance of the mucous membrane of the gums, which makes it possible to distinguish cancer from benign palillomatosis or fistula: the appearance of red veins, dots, tubercles with tissue defects - erosions, ulcers with clearly defined edges;
- the initial stage of gum cancer is characterized by the location of a tumor formation on the lower jaw near the front group of teeth in the form of knobby growths up to 1 cm in size, their edges are smoothed, without clear boundaries and shape;
- Pressure on the affected area causes aching pain and bleeding.
Dark pigmentation is visible under the mucous membrane - below in the photo of cancer.
Later, the cancer grows on the epithelium of the tongue, upper jaw, and larynx. In the latter case, a constant soreness appears and the patient is tormented by a cough.
Pain occurs in the lips, submandibular and postauricular lymph nodes, swelling spreads throughout the jaw, moving to the chin and cheek, and unpleasant bursting sensations. It becomes difficult to chew, yawn and talk. The pain persists at rest, since the tumor affects the nerve endings of the facial area.
An evening low-grade fever (37 degrees), weakness and fatigue, and weight loss are observed. An elevated temperature is sometimes the first sign, along with bleeding gums.
The metabolism of cancer cells suppresses the function of salivation, so the patient feels dry mouth.
Precancerous condition
The likelihood of developing gum cancer increases several times in the presence of a precancerous condition. This is a change in the structure of the oral mucosa, which is called a harbinger of malignant tumors. The following signs indicate such a phenomenon:
- areas with pronounced vascular network and red plaques (erythroplakia);
- white or gray spots with a keratinized surface – leukoplakia;
- wart-like growths called papillomatosis.
The most common causes of precancerous conditions are smoking, decreased immunity or immunodeficiency states (HIV, AIDS), and radiation therapy. Changed areas do not always degenerate into cancerous tumors, but require increased attention. They should be inspected regularly, recording all changes. If the lesions increase in size, ulcers and defects appear on the surface, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
The doctor will conduct an examination and determine further tactics - observation or removal of the changed areas. The operation reduces the likelihood of developing malignant tumors in areas where dysplasia is observed, but does not provide 100% cancer prevention. Sometimes tumors appear in other parts of the mouth.
To eliminate leukoplakia and erythroplakia in smokers, it is enough to immediately give up the bad habit. Within a few months, the mucous membrane is restored, and the likelihood of developing a malignant tumor is reduced.
Stages of gum cancer
The most common malignant tumors of the gums are squamous cell carcinoma. It is represented by single tumors, papules or plaques, with an ulcerated or keratinized surface. There are several stages in the development of gum cancer, depending on the size of the tumor and symptoms.
| Stage | Tumor size and symptoms. |
| Zero | The tumor is localized in the upper layers of the mucous membrane, there are no external signs. There may be slight redness and thickening of a small area of the gum - it seems to rise above the healthy tissue. There is no severe pain or bleeding. |
| First | The neoplasm grows into the tissue, but does not affect the organs and has a diameter of no more than 2 cm. A pimple, ulcer or white spot with a heterogeneous structure and a noticeable network of blood vessels appears on the compacted, reddened area of the gum. There is no pain, but the person has discomfort when eating, and the gums bleed due to mechanical impact. |
| Second | The pathology progresses, the tumor grows, reaches 2-4 cm and penetrates into the thickness of the tissue. It begins to put pressure on the nerve endings, and the patient feels discomfort. Unpleasant sensations do not have a clear localization, so a person cannot accurately indicate the source of pain. Discomfort increases when brushing teeth, eating, and changing head position. |
| Third | The neoplasm grows deep into the tissue or increases up to 4 cm. Tooth mobility and metastases appear, which most often affect regional (submandibular, cervical) lymph nodes - they enlarge and become painful. Patients feel weak, appetite worsens, temperature rises to 37-38 degrees. |
| Fourth | At the last, critical stage, the disease is easy to recognize visually. The tissues disintegrate, and the pathology affects the gums and bone tissue. Patients cannot lead a normal life, eat or even talk, and some experience severe anemia. |
Gum cancer is an aggressive disease, so the transition from stage zero to stage four can take only a few months. To avoid rapid tumor growth, you need to pay attention to any tissue defects and consult a doctor.
Stages of tumor development
There are 4 stages of developing gum cancer.
- The appearance of small bleeding erosions on the thickened mucous membrane of the gums. Its whitish pigmentation is visible. Possible pain.
- The formation increases to 1.5-2 cm in diameter and becomes purple-red. At this stage, the cancer may have grown into the jawbone, but there are no metastases yet. This makes it difficult to determine the fact that cancer is developing.
- The progressive growth of cancerous tissue covers the entire oral cavity and begins to spread to other organs. First of all, to the regional lymph nodes: submandibular, peri- and postauricular.
- The growth on the gum is enlarged to large sizes (more than 3 cm in diameter). Metastasis occurs to vital human organs (liver, respiratory organs).
The greater the stage of development of the neoplasm, the easier it is to make a correct diagnosis, but the more severe the prognosis. At stage 4, cure is impossible.
How to distinguish gum disease from cancer
It is impossible to recognize gum cancer on your own. Symptoms of oncology resemble manifestations of periodontal disease, gingivitis, periodontitis and other diseases, so only a doctor can make a diagnosis.
Characteristic signs of malignant tumors are clearly defined boundaries of the affected area and diffuse pain. The discomfort is not localized in one place, so it seems to the person that the entire gum hurts. Symptoms of inflammatory processes (gingivitis, periodontal disease) in soft tissues decrease or disappear after using special hygiene products or medications. Signs of gum cancer are difficult to treat with conventional medications, and pastes, gels and ointments have no effect.
The key sign of a malignant gum tumor is pain. It appears in the early stages. If a person constantly feels pain in the gum area for no reason (caries, periodontal disease, etc.), it is necessary to exclude the development of a malignant tumor.
Diagnosis of gum cancer
If suspicious growths or defects appear on the gums, you should contact your dentist. Making a diagnosis includes several stages, instrumental and laboratory research methods.
- Blood tests. A complete blood count shows an elevated white blood cell count and low hemoglobin. Additionally, studies are conducted for tumor markers and infections (herpes, human papillomavirus).
- Fluorescence analysis. The study makes it possible to differentiate the affected area from healthy tissue using different luminescence spectra.
- X-ray. It is carried out in order to determine the growth of neoplasm tissue into the bone.
- MRI and PET. Tomography shows the exact location of the tumor, its structure and size, reveals metastases in the lymph nodes and the degree of organ damage.
- Biopsy. Histological analysis most accurately determines malignant tumors, their structure and stage of pathology.
Differential diagnosis of gum cancer is carried out with other malignant and benign neoplasms, leukoplakia, and syphilitic lesions of the oral cavity.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment for gum cancer depends on the stage of the tumor process, age and general health of the patient. Comprehensive treatment is usually prescribed, including chemotherapy, radiation and surgery. It is strictly not recommended to use folk remedies to treat gum cancer. You can get rid of a malignant tumor only if you use complex therapy, including surgery.
Operation
Surgery involves removing the tumor and nearby tissue (depending on the extent of its spread). In the early stages, the operation is most effective - the surgeon removes the tumor along with parts of the teeth, bone tissue and epithelium. The tissues are sent for histological analysis to confirm the type of cancer. If the tumor grows into the jaw and metastasizes, all submandibular tissues and affected lymph nodes are removed, then prosthetics are performed on the missing area.
Contraindications to surgical treatment of gum cancer include chronic diseases of the lungs, cardiovascular system, liver, and kidneys. In such cases, the patient is stabilized in a hospital setting, and then the feasibility of surgery is discussed again.
Irradiation
Surgery for gum cancer is combined with radiation therapy. It avoids relapses and metastasis, but has side effects. An individual treatment regimen is developed for the patient. Therapy is used before removal of the tumor, and after the operation its base is irradiated, and, if necessary, regional lymph nodes. Radiation exposure is used in courses and sessions with breaks so that the body has time to recover.
Chemotherapy
Anticancer drugs are used when there are contraindications to surgery. Medicines are given orally (in tablet form) or by injection. Typically, the following drugs are used to treat gum cancer:
- anthracyclines;
- platinum preparations;
- vinkalkaloids;
- epipodophyllotoxins.
The treatment regimen and number of courses are selected individually. Chemotherapy provokes serious side effects - gastrointestinal disorders, hair loss, decreased immunity. In parallel with the introduction of chemotherapy, antibiotics are used to prevent infectious diseases, vitamins, drugs to improve digestion and a special diet.
Removing teeth without treating the underlying disease for gum cancer accelerates the development of pathology. The tumor grows through the hole into the bone tissue and metastasizes faster.
Immunotherapy
Treatment with EGFR inhibitor drugs, which block abnormal cell proliferation. The only drug approved by international organizations for the treatment of gum cancer is Cetuximab (Erbitux). It is used in combination with radiation and chemotherapy, increases the effectiveness of treatment, but increases the likelihood of developing side effects - baldness, acne, degenerative processes in the mucous membranes.
Palliative care
Such treatment is used in the last stages of gum cancer, when the tumor has metastasized to the kidneys, liver, lungs and other organs, and there is no hope for the patient’s recovery. The goal of palliative care is to improve a person's quality of life and relieve symptoms, primarily pain. For this purpose, strong painkillers, antidepressants and psychotropic drugs are used, which help the patient accept his condition.
Complications
Cancer can metastasize to the bones of the limbs, liver, and lungs of the patient. Spread to the lymph nodes leads to their inflammation and the development of purulent infection. Bacteria complicate the process on the gums, causing suppuration and necrosis. This is treated with antibiotics.
The consequences of chemotherapy and radiation therapy are manifested:
- hair loss;
- gastrointestinal disorders (nausea, vomiting);
- weight fluctuations;
- ulceration of healthy tissues when they enter the irradiation zone.
Rehabilitation
After treatment for gum cancer, it takes time to recover. The patient needs to give up bad habits, follow a gentle diet (do not eat cold, hot or spicy food) containing proteins and vitamins. Side effects of radiation and chemotherapy include disruption of the digestive tract and liver, so you need to eat small portions, do not starve, but do not overeat.
It is recommended to take hepatoprotectors to restore liver function, walks in the fresh air and light physical activity. Patients should regularly visit their oncologist and undergo preventive examinations to prevent the recurrence of a malignant tumor.
If the patient has undergone a large-scale operation with the removal of a large amount of tissue, his swallowing and speech functions will be impaired. A person has to learn to swallow and speak again, and speech is sometimes only partially restored.
Forecast
The success of gum cancer treatment depends on timely diagnosis, age and health of the patient. The main danger is represented by metastases, which quickly spread to the lymph nodes, and then, with the flow of lymph, spread throughout the body, reaching the lungs, liver, kidneys, and bone tissue.
The first and second stages of the disease have the most favorable prognosis - in 80% of cases, complete recovery occurs. When the disease moves to the next stage and metastasizes, therapy is effective only in 40% of cases. The last stage is the worst to treat - five-year survival is observed in only 15% of patients.
In mature patients (over 40 years of age), the prognosis worsens due to age-related changes occurring in the body, decreased functioning of the immune system and poor ability of tissues to regenerate. Chronic diseases, including pathologies of the kidneys, liver, cardiovascular system, and diabetes are another factor that negatively affects the possibility of a full recovery. They are a contraindication to certain types of therapy and increase the likelihood of death.
Gum cancer rarely metastasizes to the brain; this phenomenon is diagnosed only in 5% of cases. In 70-80% of patients, metastasis to the lymph nodes is noted, which is no less dangerous to health.
Prevention of gum cancer
Since the exact causes of the disease are unknown, anyone can develop gum cancer. To reduce the risk of a malignant tumor, you must follow simple rules:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- do not take medications without a doctor’s prescription;
- if you have a piercing, remove the earring from time to time - the foreign body injures the mucous membranes, causing inflammatory and oncological diseases;
- Brush your teeth regularly, but do not use hard brushes or alcohol-based mouth rinses too often;
- eat right, take vitamins and microelements;
- undergo preventive examinations at the dentist at least twice a year.
If suspicious ulcers, spots or other defects appear on the gums, you should consult a doctor. Timely diagnosis will help identify malignant neoplasms in the early stages, as well as cure other diseases of the oral cavity that can trigger the development of cancer.
Sources used:
- The American Dental Association (ADA)
- Donald L. Bartlett, James B. Steele. Critical Condition: How Health Care in America Became Big Business and Bad Medicine. — 2004.
- Trezubov, Vladimir Nikolaevich. Clinical dentistry: textbook: Study guide. — 2015.
- Mann KG Biochemistry and physiology of blood coagulation // Thromb Haemost.. - 1999.
Survival prognosis
The relative five-year survival rate (the probability, relative to people without cancer, that the patient will live 5 years from the date of diagnosis) for malignant gum tumors is 59%. Indicators for individual stages are unknown. In general, the later cancer is diagnosed, the worse the prognosis.
The Medicine 24/7 clinic employs doctors who have extensive experience in treating gum cancer and other malignant tumors of the head and neck. Our surgeons perform interventions in an operating room equipped with modern equipment; we use the latest generation of antitumor drugs. Make an appointment with an oncologist at the Medicine 24/7 clinic, trust our professionals.
The material was prepared by the deputy chief physician for medical work of the Medicine 24/7 clinic, candidate of medical sciences Sergeev Petr Sergeevich.
Sources:
- Gelfand I.M., Romanov I.S., Minkin A.U. Treatment tactics for squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity stages ct1-2cn0m0 // Head and Neck Tumors. 2014. No. 2.
- Kostina I. N. Structure, localization of tumor and tumor-like diseases of the oral cavity // Problems of dentistry. 2014. No. 4.
- Lutskaya I.K. Manifestations of diseases of internal organs and AIDS on the oral mucosa // International reviews: clinical practice and health. 2013. No. 6 (6).