Cycloferon is prescribed for the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases. The drug exhibits immunomodulatory and antiviral properties. A course of use of the product improves the functioning of the immune system and reduces the risk of developing pathologies of a bacterial or viral nature. To treat an infectious process, it is used as part of complex therapy. This medicine can be prescribed to adults and children over 4 years of age. Side effects are rare.
Immunomodulators are a relatively new class of drugs that can regulate the functioning of the body's defense systems. These drugs are better tolerated than antibiotics and older antiviral drugs.
Composition and release form
The active component of the product is acridone acetic acid in the form of acridone acetate meglumine. This substance determines the medicinal properties of the drug. Additional components depend on the dosage form.
Release forms:
- Solution. Contains water as an excipient.
- Liniment. Contains propylene glycol and catapol.
- Tablet form. Contains calcium stearate, propylene glycol, polysorbate, hypromellose, polymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate.
Cycloferon tablets
Auxiliary components of tablets are needed to stabilize the dosage form and absorb the active substance in the desired part of the gastrointestinal tract.
Action of Cycloferon
According to the manufacturer, meglumine acridone acetate increases the production of interferons in the body. Normally, these substances are released by cells in response to the penetration of viruses into tissues. Interferon binds to other cells and stops the spread of pathogens. It is this property that determines the immunomodulatory activity, since taking the medicine improves the performance of the immune system.
Interferons accumulate in the lungs, liver, spleen and other organs. The production of this substance plays an important role in the preventive defense of the body.
Additional properties
- Antiviral activity. Increasing the production of interferons can be called a nonspecific measure of body defense. The medicine is also able to fight the infectious threat in the early stages of the disease. Acridoneacetic acid disrupts the replication of influenza virus, adenovirus, cytomegalovirus and other pathogens.
- Moderate antimicrobial effect. Treatment with this remedy helps fight certain bacterial infections. This property is due to the general immunostimulating effect.
- Correction of immune status. The therapy eliminates immunodeficiency and restores the most important functions of the body's defense system.
- Penetration of drugs through the blood-brain barrier, which isolates the central nervous system. The medicine is used to treat tick-borne encephalitis and other viral pathologies that affect the brain.
- Improving the production of granular leukocytes. These immunocompetent cells protect tissues and organs from various threats.
- Antitumor effect, which consists in destroying cells with genetic mutations and suppressing the growth of tumors.
- Elimination of autoimmune processes in which the body's defense system attacks healthy tissue.
Topical Cycloferon
Interferon inducers activate all components of the immune defense.
Adverse reactions
Cycloferon is well tolerated, but any medicinal substance can negatively affect tissues and organs. Allergy is the only reported adverse reaction. The immune system of some people sees a threat in acridoneacetic acid or auxiliary components of the product. Sometimes serious complications arise.
Characteristic signs of allergies:
- Skin rashes (urticaria).
- Dizziness and weakness.
- Redness and swelling of the skin.
If allergy symptoms appear, the patient should stop taking the medication and consult a doctor.
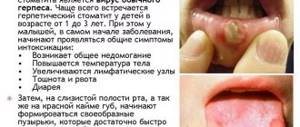
Symptoms of stomatitis
According to clinical manifestations, stomatitis is divided into:
- catarrhal;
- ulcerative;
- aphthous.
What is catarrhal stomatitis
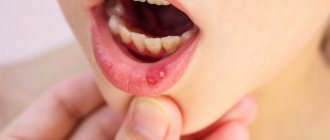
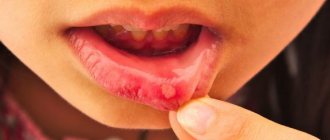
Catarrhal stomatitis is the most common lesion of the oral mucosa. In this case, the oral mucosa becomes swollen, painful, hyperemic, and may be covered with a white or yellow coating. Hypersalivation (increased salivation) is noted. Bleeding gums and bad breath may occur.
What is ulcerative stomatitis
Ulcerative stomatitis is a more severe disease than catarrhal; it can develop independently or be an advanced form of catarrhal.
Unlike catarrhal stomatitis, which affects only the superficial layer of the mucous membrane, with ulcerative stomatitis the entire thickness of the mucous membrane is affected.
The initial symptoms of catarrhal and ulcerative stomatitis are similar, but subsequently with ulcerative stomatitis there is an increase in temperature to 37.5 C, weakness, headache, enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes. Eating is accompanied by severe pain. If such symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor.
What is autonotic stomatitis?
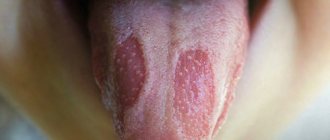
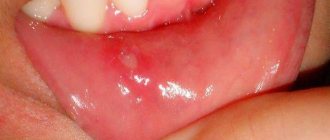
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of single or multiple aphthous ulcers on the oral mucosa, in which the ulcers are large and deep. Aphthae are oval or round in shape, with clear boundaries in the form of a narrow red border and a grayish-yellow coating in the center.
The disease begins with general malaise, increased body temperature, and the appearance of pain in the mouth at the site of aphthae formation. Treatment for such an ulcer is usually quite difficult, and after it heals, marks remain. This disease should be treated by a doctor.
With a weakened immune system, infectious stomatitis may occur, which is caused by various microbes that live on the surface of the oral mucosa and remain inactive until the immune system is weakened.
If you have had stomatitis once, the likelihood of recurrence of the disease is very high, although the frequency of these recurrences is extremely variable. If the disease recurs three to four times a year, this frequency can be called typical. In some people, however, stomatitis can become almost chronic - the ulcers do not have time to heal before new ones appear.
As a rule, people first suffer from stomatitis between the ages of 10 and 20, after which, as they grow older, it recurs less frequently and with less pain.
Stomatitis affects approximately 20% of the population.
There is no evidence that stomatitis is contagious.
Absorption and excretion
The active ingredient must enter the bloodstream and penetrate the tissues for the development of all medicinal effects. Taking tablets leads to the absorption of acridoneacetic acid in the intestine, where food is absorbed into the blood and lymphatic vessels. Approximately three hours after taking the tablet, the required concentration of the substance in the blood plasma is achieved. The injection method of administering the drug facilitates the absorption of the active ingredient. The use of liniment helps to limit the area of therapeutic action.
Cycloferon is excreted in urine and feces. The substance does not accumulate in the body.
Indications for use of Cycloferon
Different dosage forms have different indications. Improving the functioning of the immune system is the general effect of the solution, liniment and tablets. First of all, the medicine is prescribed for the prevention and treatment of viral infections. Taking the product several days or weeks before expected contact with pathogens helps to significantly reduce the risk of infection. If the patient is already suffering from symptoms of the disease, drug therapy eliminates complications and speeds up recovery.
The medicine is usually prescribed together with other medications, such as antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Complex therapy helps to successfully treat serious viral and bacterial pathologies. Monotherapy with acridoneacetic acid is suitable for the prevention and relief of symptoms of uncomplicated colds.
Indications for use of tablets
- Influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections. Characteristic symptoms of these diseases include nasal congestion, cough, sore throat, weakness and fever. Viral particles usually enter the body by airborne droplets through the respiratory system.
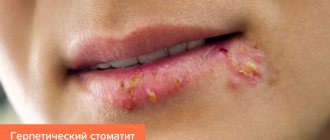
- Treatment of herpes infection. This is a viral disease manifested by skin rashes and frequent relapses. Warts usually appear on the external genitalia and lips. Decreased immunity leads to exacerbation of infection. The use of immunomodulators as part of complex therapy improves the prognosis.
- Reducing the risk of developing infection in children over 4 years of age. Suitable for healthy children and patients suffering from immunodeficiency.
The tablet form is equally suitable for adults and children.
Indications for use of the injection solution
- Acquired decrease in immunity, accompanied by the frequent occurrence of infectious diseases.
- Cytomegalovirus infection. Symptoms of this pathology appear against the background of immunodeficiency.
- HIV infection. Prescribed along with other medications to improve the functioning of the immune system and reduce the concentration of viral particles.
- Viral hepatitis. Liver inflammation often remains asymptomatic for many years. Timely therapy is required.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system: tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme disease, meningitis. The active substance accumulates in the brain tissue and prevents further damage to the organ.
- Connective tissue pathologies caused by immune disorders.
- Damage to the joints, accompanied by impaired mobility and destruction of articular cartilage.
ANNOTATION (open – close)
Purpose: to determine the clinical and pathogenetic effectiveness of the liniment cycloferon in the complex therapy of herpetic stomatitis in patients with chronic tonsillitis. Material and methods. 60 patients were examined and treated. The parameters of endotoxicosis, infectious load and immunity were studied. Results. It has been established that the use of cycloferon liniment in the complex treatment of herpetic stomatitis in patients with chronic tonsillitis makes it possible to reduce the infectious load in periodontal pockets and the severity of local inflammation, normalize immunity parameters, reduce endotoxicosis, which speeds up the recovery process and reduces the frequency of relapses of stomatitis. Conclusion. The clinical effectiveness of cycloferon liniment for herpetic stomatitis against the background of chronic tonsillitis is due to a decrease in the activity of the local inflammatory process due to a reduction in the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, infectious load in the oral cavity, and endotoxicosis
A. A. Shuldyakov - State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Saratov State Medical University named after. V. I. Razumovsky Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, Head of the Department of Infectious Diseases, Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, O. G. Khlamova - MUZ "City Dental Clinic No. 1" of Engels, dentist, A. V. Lepilin - State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Saratov State Medical University them. V. I. Razumovsky Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, Head of the Department of Surgical Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, T. D. Tsareva - Saratov State Medical University named after. V.I. Razumovsky Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia, assistant at the Department of Infectious Diseases, Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Introduction. At the present stage, in developed countries there is a clear trend towards an increase in the incidence of herpes infection (HI), one of the clinical variants of which is stomatitis [1–4]. Manifest forms of HI usually develop against the background of maladaptation of the immune system, as well as a number of pre- and comorbid conditions [1, 2], which in recent years have become increasingly common in human pathology and are one of the factors that significantly complicate the management of patients with HI due to with a possible mutually aggravating nature of the course of diseases.
In the structure of diseases of the lymphoid apparatus of the oropharynx in adults, chronic tonsillitis (CT) currently has the largest share, occurring in almost 20% of the population [5]. In the pathogenesis of chemotherapy, a major role is played by disorders of the immune system, sensitization, persistence of opportunistic flora, endogenous intoxication and cytokine imbalance [5].
The high probability of comorbid conditions in such common diseases in the human population as herpetic stomatitis (HS) and HT leads to increasing attention to the study of the characteristics of the course and mechanisms of development of HS in people with HT.
Comorbid conditions place increased demands on the treatment of patients with oral pathology. In recent years, in the complex therapy of patients with inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, the use of immunotropic drugs, including liniment cycloferon (LC) has been recommended [6]. Cycloferon in various forms has been successfully used in the treatment of various forms of HI [1, 2]. Thus, there is a natural interest in the possibilities of using LC for HS in patients with chemotherapy, taking into account its local and systemic potencies.
Purpose of the work: to study the clinical and laboratory effectiveness of LC in the complex treatment of patients with herpetic stomatitis against the background of chronic tonsillitis.
Methods. 60 patients with HS on the background of chemotherapy were examined, who were divided into two main groups: in the 1st group (30 people), LC was added to the complex treatment, in the 2nd group (30 people), treatment of stomatitis was carried out using generally accepted methods. In both groups, etiotropic treatment of HS was carried out using the tablet form of acyclovir. The course of LC was 10 days with 2 applications of the drug per day on the mucous membranes of the mouth and gums. Study design: open randomized.
Inclusion criteria for the study: patients with mild to moderate HS (15 people in each group), men and women aged 20–40 years with an established diagnosis of chemotherapy (compensated/subcompensated).
Exclusion criteria: patients with other forms of stomatitis, tonsillitis, acute infectious diseases, chronic diseases of internal organs in the acute stage, oncological diseases of any localization, chronic alcoholism, a history of mental and behavioral disorders, pregnancy, lactation, refusal of the patient to participate in the study for at any stage, individual intolerance to the drug (for patients with LC).
When diagnosing HS, in addition to clinical signs of the disease and anamnesis data, the results of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for HSV-1, 2, as well as the determination of IgM and IgG for HSV-1, 2 (ELISA) were taken into account. In accordance with the most commonly used classifications of HS, based on clinical and morphological characteristics [1, 3, 4, 7, 8], HS was divided into three degrees of severity: mild, moderate and severe. The study included patients with mild and moderate forms of stomatitis. In all patients, index parameters and test results were assessed [9]: oral hygiene index (Greene J., Vermillion J., 1969), bleeding index (Muhleman H., Son S., 1971), papillary-marginal-alveolar index ( C. Parma, 1960). There were no significant differences in the severity of pathology, age, gender, frequency of concomitant diseases and index dental indicators (Table 1) before the start of therapy between groups 1 and 2.
The diagnosis of “chronic tonsillitis, compensated/decompensated” was established in accordance with the classification of I. B. Soldatov (1975) [5].
The parameters of interleukin-1b (IL-1b), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) in the fluid of periodontal pockets (PPV) were assessed using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent test system of Cytokin LLC (St. Petersburg). The level of malondialdehyde (MDA) was studied by the method of M. S. Goncharenko and A. M. Latinova (1985), the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) - by the method of R. Fried (1975). The frequency of occurrence of microbial infections (CMV, C. albicans, C. trachomatis) in the gastrointestinal tract was studied based on the detection of microorganisms using the PCR method. As a control group, laboratory parameters were studied in 15 practically healthy individuals who had no complaints about their health and had no signs of oral diseases, comparable in gender and age to the patients examined.
Statistical analysis was carried out using a Pentium IV computer and software packages for statistical processing "Microsoft Excel for Windows 4.0" ("Microsoft Corp") and "Statistika 6.0" indicating the mean values, standard error of the mean (m) - format ( M±m), significance of differences using Student's t-test for independent samples.
Results. When assessing clinical and laboratory data in the two groups before the start of treatment, it was revealed that the groups were comparable in all indicators (Tables 1–3). 10–12 days from the start of therapy (Table 1) in patients with HS against the background of chemotherapy, it was stated that in group 1 (cycloferon), the bleeding, oral hygiene, and papillary-marginal-alveolar indices were significantly closer to normal values than in the group comparison (group 2).
In group 1, with the use of LC in patients with HS, general infectious symptoms disappeared faster (p<0.05) than in the group with conventional treatment methods (group 2) (temperature after 3.1±0.3 days in group 1 and 4.2±0.3 days in group 2, signs of intoxication after 3.5±0.4 days and 4.8±0.4 days, respectively), as well as signs of local damage and inflammation ( hyperemia of the oral mucosa after 4.2±0.4 days in group 1 and 5.5±0.2 days in group 2, pain after 2.9±0.3 days and 4.1±0 .4 days, erosion on mucous membranes after 6.4±0.5 days and 8.3±0.4 days, respectively).
LC was well tolerated, no side effects were recorded.
Clinical examination of patients made it possible to establish that exacerbation of HS was observed within 6 months in the 1st group in 6.7%, in the 2nd - in 20% of cases. Exacerbation of chemotherapy in 10 and 26.7%, respectively.
Consequently, the use of LC in the complex treatment of patients with HS against the background of chemotherapy, with virtually no side effects of the drug, promotes the dynamic disappearance of the main clinical symptoms of the disease, reduces the number of exacerbations of stomatitis and chemotherapy.
Table 1
Index indicators in patients with herpetic stomatitis against the background of chronic tonsillitis in the dynamics of the disease (M±m)
| Index | Groups | |||
| 1st group (cycloferon) n=30 | Group 2 (traditional methods) n=30 | |||
| before treatment | 10–12th day | before treatment | 10–12th day | |
| Hygiene index | 2,37±0,04 | 0,92±0,04* | 2,23±0,06 | 1,14±0,05 |
| Mullemann index | 2,61±0,12 | 1,02±0,11* | 2,64±0,1 | 1,25±0,09 |
| Papillary-marginal-alveolar index, % | 42,4±1,12 | 9±1,12 | 42±1,12 | 11,3±1,12 |
Note: * ─ the differences are significant (p<0.05) when comparing the 1st and 2nd groups.
Analysis of indicators of endotoxicosis (EnT), lipid peroxidation (MDA) and antioxidant potential (SOD) 10–12 days from the start of therapy (see Table 2) found that against the background of the use of LC in group 1, these parameters were significantly closer to normal than in group 2 with traditional methods of therapy.
The use of LC in complex therapy of stomatitis made it possible to quickly stop the processes of local inflammation, which was reflected in a more dynamic normalization of the level of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1b and TNF-α) in the gall bladder in group 1 compared to group 2.
A significant effect of the use of LC was a more pronounced reduction in the infectious load in the gastrointestinal tract: in the 1st group, two weeks from the start of treatment, the frequency of Cytomegalovirus isolation was 20%, Candida albicans - 23.3%, Chlamydia trachomatis - 10%, in the 2nd group 30, 26.7 and 20%, respectively (see Table 2).
Discussion. To date, it has been proven that LC is characterized by immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects [2, 4, 5], and this dosage form of cycloferon also has antimicrobial properties [4, 5]. The drug has been successfully used in the treatment of various forms of herpes infection and immunodeficiency states of complex origin [2–4]. Our results indicate the pathogenetic orientation of the clinical effects of liniment in patients with comorbid pathologies (HS against the background of chemotherapy), accompanied by the formation of an immunodeficiency state [2–4]. Thus, under the influence of LC, clinical signs of local inflammation decreased with a decrease in the level of proinflammatory cytokines, and the infectious load in the oral cavity was reduced. In our opinion, it was these effects that ensured a decrease in the level of endogenous intoxication, stabilization of lipid peroxidation processes and, ultimately, the dynamic disappearance of general infectious symptoms and signs of intoxication syndrome against the background of comorbid pathology. The immunomodulatory potencies of LC [2, 4, 5] served as the most likely mechanism for reducing the number of exacerbations of stomatitis and tonsillitis in patients with concomitant pathology against the background of complex therapy using an immunotropic agent, which is also extremely important, since it is one of the main goals of treatment of patients with chronic herpetic infection and chronic tonsillitis.
Conclusion. In a complex of therapeutic measures in patients with herpetic stomatitis against the background of chronic tonsillitis, along with etiotropic drugs, it is advisable to use cycloferon liniment in a course of 10 days, two applications per day on the mucous membranes of the mouth and gums, which contributes to a more vigorous regression of the main clinical manifestations of the disease and reduces the frequency of exacerbations such as stomatitis , and tonsillitis.
The clinical effectiveness of cycloferon liniment for herpetic stomatitis against the background of chronic tonsillitis is due to a decrease in the activity of the local inflammatory process due to a reduction in the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines, infectious load in the oral cavity, and endotoxicosis.
Conflict of interest. The work was carried out within the framework of the research project of the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Saratov State Medical University named after. V.I. Razumovsky Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia. State registration number - 02.0304.233.0329.
table 2
Parameters of lipid peroxidation and cytokines in patients with HS against the background of chemotherapy in the dynamics of the disease depending on the method of therapy (M±m)
| The indicator being studied | Healthy individuals (n=20) | Groups | |||
| 1st group (cycloferon) n=30 | Group 2 (traditional methods) n=30 | ||||
| before treatment | 10–12th day | before treatment | 10–12th day | ||
| MDA, (nmol/ml) | 2,82±0,12 | 5,29±0,14* | 3,1±0,13* ** | 5,26±0,15* | 3,97±0,13* ** |
| SOD activity (arbitrary units) | 310,5±20,5 | 224,1±5,7* | 277,8±6,5* ** | 229,1±8,2* | 252,1±6,1* ** |
| Wed. molecules (optical units) | 0,26±0,01 | 0,41±0,03* | 0,30±0,01* ** | 0,4±0,04* | 0,36±0,01* ** |
| IL-1b, mg/ml | 1,13±0,06 | 3,21±0,08* | 1,63±0,05* ** | 3,17±0,09* | 1,96±0,04* ** |
| TNF-α, mg/ml | 1,27±0,07 | 4,15±0,09* | 1,89±0,03* ** | 4,21±0,08* | 2,31±0,05* ** |
Note: *─ the differences are significant (p<0.05) when compared with a group of healthy individuals; ** ─ differences are significant (p<0.05) when comparing groups 1 and 2.
Table 3
Microbial landscape of periodontal pockets of the mouth in patients with HS against the background of chemotherapy, depending on the method (% detection by PCR)
| Index | Groups | |||
| 1st group (cycloferon) n=30 | Group 2 (traditional methods) n=30 | |||
| before treatment | 10–12th day | before treated | 10–12 days | |
| Cytomegalovirus | 40 | 20 | 36,7 | 30 |
| Candida albicans | 46,7 | 23,3 | 43,3 | 26,7 |
| Chlamydia trachomatis | 26,7 | 10 | 30 | 20 |
Contraindications
Some people cannot use the medicine for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes due to the high risk of complications. Thus, any dosage form of acridoneacetic acid is contraindicated for children under 4 years of age. Tablets and solution are prohibited from taking in case of liver cirrhosis, since this condition interferes with the removal of the drug from the body.
General contraindications:
- Carrying a child.
- Lactation period.
- Allergy to medicinal components.
Tablets should be taken with caution in the presence of inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Damage to the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines is possible. It is recommended to consult your doctor first.
Causes of stomatitis
The cause of stomatitis can be various factors - those that act directly on the oral mucosa (local effects), as well as diseases of the body - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, weakened immune defense, allergic reactions, metabolic disorders and many other.
Local is associated with the participation of a direct factor: trauma, chemical, thermal, radiation exposure, as a result of which redness, erosion, and ulcers occur on the mucous membrane.
Stomatitis that occurs as a result of dental problems deserves a separate discussion. In this case, the cause is the patient’s failure to comply with oral hygiene, excessive dental plaque, decayed teeth, and oral dysbacteriosis. In addition, stomatitis can occur due to violations in the technique of dental procedures. They are caused by microtraumas, the use of dissimilar metals in treatment and prosthetics, and exposure to chemicals.
Instructions for using Cycloferon
The rules for using different dosage forms of the drug differ. It is important to read the instructions carefully before starting treatment. If in any doubt, it is recommended to consult a doctor. The specialist will evaluate the patient’s symptoms and conduct a diagnosis. Self-medication of serious infectious and immunological pathologies is fraught with the development of complications.
Taking pills
- Therapy of acute respiratory infections in adults: taking tablets on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8. The patient should start taking the medicine immediately after the first cold symptoms appear.
- Therapy of acute respiratory infections in children: taking the drug on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23. The total number of techniques is from 5 to 10.
- Treatment of herpes in adults: taking tablets on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 11, 14, 17, 20, 23. No more than 40 tablets per course.
- Treatment of herpes in children: single doses on days 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 11, 14 until symptoms disappear.
A single dose depends on age. Adults and children over 12 years of age are recommended to take 450 to 600 mg of the active substance at a time. This is three or four tablets. Children aged 7 to 11 years are prescribed a daily dose of 300-450 mg. Children aged 4 to 6 years should be given one tablet (150 mg) per day.
Using the solution
- Herpetic infections: ten injections. A single dose for adults is 250 mg.
- Infectious lesion of the brain: 12 injections. A single dose for adults is from 250 to 500 mg.
- Chlamydia: ten injections. A single dose for adults is 250 mg.
- Hepatitis A, B, C, D: 10 injections for adults and 15 injections for children. A single dose for adults is 500 mg.
- Hepatitis B, C, D: ten injections for adults and children. A single dose for adults is 500 mg. Further therapy is carried out with three injections per week for 3 months.
- Human immunodeficiency virus: ten injections for children and adults. A single dose for adults is 500 mg. Next, a single administration of the drug every three days for 3 months.
- Autoimmune pathologies of connective tissues: five injections. A single dose for adults is 250 mg. Four courses of therapy at two-week intervals.
The liquid is introduced into the body once every 24 hours using intramuscular or intravenous injections every other day. The dosage for children is selected according to body weight: from 6 to 10 mg per kilogram.
Using liniment
- Herpetic infection: treatment of inflamed tissues twice a day for 5 days.
- Inflammation of the urethra: internal treatment of the mucous membrane with 5 ml of the product twice a day. Duration of therapy is from 10 to 15 days.
- Inflammation of the glans penis: treatment of the skin with 5 ml of the product once a day. Treatment duration is up to two weeks.
- Fungal or bacterial infection of the vaginal mucosa: administration of 5 ml of the drug once or twice a day for 10-15 days.
- Periodontal inflammation: applying a small amount of liniment to the gums after antiseptic treatment. Every day for two weeks.
It is important to read the instructions for correct application of the product. If using the topical form of the medication on your own causes difficulties, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Additional instructions
- The topical form of the drug should not come into contact with the eye area. If the liquid accidentally gets on the mucous membrane of the eye, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the conjunctiva with clean water.
- If there are pathologies of the thyroid gland, you must first consult a specialist.
- The product enhances the effect of antimicrobial drugs and does not affect the effectiveness of other medications.
- The speed of psychomotor reactions does not decrease during therapy. You can drive a vehicle.
Frequent stomatitis. How to quickly cure stomatitis
Go back
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. Persistent stomatitis, regardless of the cause, indicates a decrease in immunity and, as a result, the development of inflammation.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Pain, burning, mouth ulcers, swelling of the tongue and lips, as well as other parts of the oral mucosa, are the most common symptoms of stomatitis. Pain with stomatitis can occur both when eating or talking, and at rest with severe inflammatory changes in the oral mucosa. Advanced or long-term untreated stomatitis can affect most of the oral mucosa. In such a situation, patients with stomatitis are hospitalized.
Cause of stomatitis
The oral mucosa is the body's first barrier when encountering an infection.
Whether we eat or drink water, talk or breathe, every time a large number of different microbes rush into our body through the mouth. Often the causes of stomatitis in adults and children come down to poor hygiene and lack of adequate oral care. One of the most common causes of stomatitis is infection. Moreover, this group can include bacteria, viruses, and fungi. How ORALSEPT helps ORALSEPT® affects the cause of inflammation (bacteria and fungi) and relieves the symptoms of inflammation.
Read more
Frequent stomatitis in adults. Causes There are many causes of stomatitis, which occurs several times during the year. As a rule, repeated episodes of stomatitis develop against the background of disruption of both local and general immunity.
The main causes of stomatitis are:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
- Intestinal infections
- Smoking
- Drinking alcohol and hot drinks
- Eating food with lots of spices
- Diabetes
- Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
- Radiation therapy in the treatment of cancer
And this is not a complete list of factors leading to the development of stomatitis.
Frequent stomatitis in a child. Reasons “Don’t put it in your mouth” is one of the most common comments to a child. Children try to learn everything new by tasting it. This is how the infectious agent enters the oral cavity. Stomatitis in children can be a manifestation of both an independent disease - for example, herpes, and a symptom of other infections. Stomatitis often occurs with measles (Filatov's spots) and enterovirus infection, with chicken pox and other diseases. Also, stomatitis in children can often be a manifestation of an allergic reaction or the result of an intestinal infection. The first place among the infectious causes of stomatitis in children is occupied by herpetic and candidal stomatitis.
Herpetic stomatitis in children is characterized by severely painful ulcers in the mouth. The first episode of herpetic stomatitis can last quite a long time, up to 2-3 weeks, until the body forms protective antibodies to the virus. Children refuse to eat due to pain. The disease manifests itself not only with local symptoms, but also with general ones, such as weakness, fever, headache, nausea.
Candidal stomatitis in children can appear literally in the first months of life. With candidal stomatitis, a white, loose (curdled) coating appears on the oral mucosa. Beneath it, a red, swollen, inflamed mucous membrane is visible. The cause of candidal stomatitis is a decrease in immunity and a fungal infection (fungus of the Candida species), which, as a rule, develops due to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract or food allergies. Infants with candidal stomatitis are very restless, often cry, and quickly lose weight.
How to quickly cure stomatitis The main complaint with stomatitis is pain. And therefore, first of all, drugs that reduce pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed. These may be non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, local anesthetics. It is also necessary to prescribe antimicrobial drugs that act on the main cause of stomatitis - infection.
How to quickly cure stomatitis in a child
To quickly relieve pain and inflammation during stomatitis, local remedies are used. But children often do not know how to rinse their mouths, and due to pain they may react negatively to the use of oral medications. In such a situation, using a topical treatment spray will help.
How to quickly cure stomatitis in an adult
Stomatitis in adults often affects general well-being.
In addition, people whose professional activities involve the active use of speech cannot fully perform their work when stomatitis occurs. In such a situation, either a temporary refusal to work for treatment or the use of drugs that quickly relieve pain and inflammation, and which can be taken with you and used on the go, is required. Remedy for stomatitis – what to choose? More recently, when treating stomatitis, doctors prescribed several drugs at the same time: for pain, inflammation, anti-infectives. It was a set consisting of gels, rinses, tablets for oral administration and topical use. Currently, in the treatment of stomatitis, agents are used that act directly on the site of inflammation and have a complex effect. Oralcept spray in such a situation is the best option. Acting locally on the source of inflammation, it quickly, within a minute*, reduces pain and reduces the inflammatory manifestations of stomatitis. In addition, it has a local antiseptic effect and fights bacterial and fungal infections. Oralcept has a pleasant, delicate mint taste. The compact plastic bottle of the drug with a special nozzle is convenient to carry with you.
*WITH. Simon-Savois, D. Forest. - "Local anesthetic activity of benzydamine", Modern Therapeutic Research, Vol. 23, No. 6, June 1978, Department of Dentistry, University of Montreal, Montreal, Canada
Analogs of Cycloferon
There are indirect analogues of the drug containing another active ingredient. These are medications with a similar therapeutic effect.
Indirect analogues:
- Amiksin is an immunomodulator for the prevention and treatment of infections.
- Galavit is a remedy for strengthening the immune system.
- Arbidol
is a drug for the treatment of acute respiratory viral infections and improves immune function.
Cycloferon analogue
Cycloferon analogues differ in contraindications, side effects and indications. You need to read the instructions.