- Types of rinses and how to choose them
- Why do you need a mouth rinse?
- Cons of mouthwashes
- Rules for using rinse aid
To have a healthy and beautiful smile, simply brushing your teeth every day is not enough.
Good oral hygiene includes additional care using mouthwash. In this text we will tell you what you need to pay attention to when choosing this product for yourself. The first mouthwash appeared in 1895, it was created by two Americans - Joseph Lawrence and Jordan Lambert. They developed a mouthwash based on menthol, thymol, methyl salicylate and cineole in a solution of 20% ethanol. The mouthwash was named Listerine in honor of Dr. Joseph Lister, who first performed surgery using antiseptics and proved their effectiveness.
Combination of rinses and application gel –
The selection of rinse aid and gel is carried out in such a way that both antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects are equally realized.
Those. if you choose a rinse with antimicrobial components - such as chlorhexidine, hexitidine, cetylpyridine, triclosan, then in parallel you need to use a gum gel containing anti-inflammatory components (this can be choline salicylate, phenyl salicylate, methyl salicylate, etc.). But if you use a rinse primarily with anti-inflammatory components (for example, Parodontocid mouthwash), then you need to choose a gum gel that contains an antiseptic and/or antibiotic. Such gels include Perio-Aid, PRESIDENT Effect gel and others. For more information about anti-inflammatory gels for the treatment of gum inflammation and patterns of their use, read the article:
→ Rating of the best gels for gum inflammation
Mouth rinses may be unsafe -
You may notice that the instructions for rinses with antiseptics and antibiotics (at least from some manufacturers) recommend using them for 3-4 weeks, and in some cases even up to 1-2 months. It is absolutely impossible to follow such recommendations, because... Long-term use of antiseptics radically changes the composition of the oral microflora, and not for the better. Pathogenic microflora tends to get used to antiseptics (as they say, the fittest survive), and therefore, after the end of the use of antiseptics, the rate of destruction of the attachment of teeth to the bone and gums can only increase. Therefore, the course of rinsing with antiseptics should not last more than 10-12 days.
In addition, clinical studies (source) revealed that after just 7 days of rinsing the mouth with chlorhexidine, the ratio of microflora in the oral cavity changed in such a way that strains of pathogenic bacteria that produce large amounts of lactic acid received an advantage. This leads to a shift in the pH of the oral fluid to the acidic side, to a decrease in the buffer capacity of saliva and a decrease in its ability to neutralize lactic acid, which is secreted by cariogenic bacteria. Thus, the risk of developing dental caries increases.
Important for patients with cardiovascular pathology -
Several reputable scientific studies have shown that chlorhexidine interferes with the ability of oral bacteria to convert nitrates (found in foods) into nitrites. This bacterial activity is called “nitrate-reducing” and is one of the mechanisms for maintaining normal blood pressure. Normally, nitrites entering the blood help lower blood pressure and, accordingly, a decrease in their production will lead to an increase in blood pressure.
This is primarily important for patients who already have chronic cardiovascular pathology. This information is confirmed by the clinical study “The increase in plasma nitrite after a dietary nitrate load is markedly attenuated by an antibacterial mouthwash. Nitric Oxide" (2008), authors – Mirco Govoni, Emmelie Å. Jansson, and others. If you wish, you can familiarize yourself with this study using the link above, for example, using a browser translator.
Contraindications
A general contraindication to the use of antiseptics is individual hypersensitivity to certain drugs.
Iodine preparations should not be used for diseases of the thyroid gland, Dühring's dermatitis herpetiformis, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
With increased sensitivity or prolonged use of iodine preparations, phenomena of iodism are possible (tissue swelling, runny nose, salivation and lacrimation, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, Quincke's edema, etc.).
Sanguinarine/chelerythrine (sangviritrine) is not recommended for use in cases of fungal infections with symptoms of eczematization, epilepsy, hyperkinesis, bronchial asthma, angina pectoris, kidney and liver diseases.
What you don't need to rinse your mouth with -
Many patients who try to be treated at home sometimes treat their gums with hydrogen peroxide.
Of course, hydrogen peroxide is a good antiseptic, and it is excellent in treating many infectious processes (for example, purulent wounds). It can also be used in dentistry, but not for rinsing the mouth, but for rinsing periodontal pockets with a syringe. When hydrogen peroxide comes into contact with any organic matter, it begins to foam, releasing atomic oxygen. When rinsing periodontal pockets, 3% peroxide is drawn into a syringe and the sharp edge of the needle is broken off (so as not to pierce the gum). Then the blunt end of the needle is inserted along the tooth root into the lumen of the periodontal pocket and washed under pressure. As a result, all infection and pus are washed out of the pockets.
But when rinsing the mouth, peroxide will react most quickly only with oral fluid, and other than a full mouth of foam, you will not get any effect. You won’t be able to rinse your pockets with a syringe at home yourself. For this you need a doctor, because... if you suddenly inject peroxide not into the lumen of the periodontal pocket, but directly into the soft tissue of the gums, you will receive a severe chemical burn with subsequent necrosis.
Gargling with infusions of medicinal herbs –
Many patients prepare their own rinse solutions by brewing medicinal herbs such as chamomile or oak bark. Such infusions actually have a good astringent effect, moderate anti-inflammatory, and also a weak antiseptic effect. And this can really help reduce swelling and bleeding of the gums, but such herbal infusions also have one big disadvantage.
The fact is that self-brewed herbal infusions contain a lot of pigments and tannins, which are very quickly deposited on the teeth in the form of pigment plaque. This plaque forms very quickly, and it will serve as a good basis for the already microbial plaque to attach to the surface of the teeth. But it is microbial plaque and tartar that cause gum inflammation. Therefore, if you use solutions with herbs, it is better in the form of ready-made rinses (since manufacturers remove from them all pigments that stick to tooth enamel).
In what cases are rinses ineffective?
The author of the article has 10 years of experience as a “periodontologist” (documents on advanced training of the state standard in the “Parodontology” program - can be viewed in the editorial section), and we would like you to listen to our experience. The fact is that knowing what to rinse your mouth with when your gums are inflamed is not enough to cure their inflammation (24stoma.ru). Various mouthwashes (even the strongest ones), anti-inflammatory gels are only secondary means.
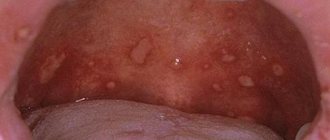
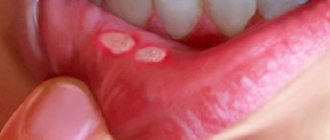
There are 2 main types of gum inflammation – gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the initial stage of inflammation, the main symptoms of which are: swelling, redness or bluishness of the gums, pain and bleeding when brushing teeth, bad breath (Fig. 3-4). With periodontitis, these symptoms are accompanied by mobility of teeth, suppuration from periodontal pockets, destruction of bone tissue around the teeth, and in later stages, changes in the position of the teeth (Fig. 5).
Gingivitis and mild periodontitis –
The cause of gum inflammation in both cases is soft microbial plaque, as well as hard supra- and subgingival dental deposits (Fig. 3-5). This is the main cause of inflammation, which is a consequence of insufficient oral hygiene. And the most important part of treatment should not be to reduce symptoms, but to eliminate the real cause of gum inflammation. And for this purpose, dental plaque is removed by a dentist (usually this is done using ultrasound).
Antiseptic rinses act only on the most superficial layer of microbial plaque or tartar. They do not act on the deeper layers, which also consist of pathogenic bacteria, and therefore the use of antiseptics does not lead to complete “disinfection”. Therefore, rinsing with antiseptics and gels for gums (without removing dental plaque) lead only to temporary improvement, and the inflammation in this case will be constant chronic - with periodic exacerbations.
Television advertising very actively promotes all sorts of products for gums, but it does not say that the main treatment is precisely the removal of dental plaque. Remember that a mild form of gingivitis can unnoticeably turn into a severe form of periodontitis if you try to treat the inflammation only with antiseptic rinses and anti-inflammatory gels - without periodic removal of dental plaque by the dentist.
→ How to properly treat gingivitis → Treatment regimens for periodontitis
Toothpastes for gum inflammation -
In complex therapy for the treatment of gum diseases, you can use not only rinses and gel applications, but also special anti-inflammatory toothpastes for gums, which will reduce bleeding and swelling of the gums even faster. Some of these pastes are also suitable for preventing inflammation. We hope that our article on the topic: How to rinse the mouth with gum inflammation was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. PubMed.gov scientific research base, 4. “Optimization of conservative treatment of patients with periodontitis” (Komleva A.S.), 5. Composition of products taken from official websites manufacturers.
ANTISEPTICS: DRUGS OF CHOICE
Stepanova Olga Ivanovna Assistant, Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Pharmacy, First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenova, Ph.D. Belyatskaya Anastasia Vladimirovna Associate Professor of the Department of Pharmaceutical Technology of the Pharmaceutical Faculty of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenova, Ph.D.
Now it is difficult for anyone to imagine the “pre-antiseptic” period, when a huge number of patients died from even the most insignificant infections in modern terms. Also N.I. Pirogov noted that most of the wounded die not so much from the injuries themselves, but from “hospital infection.”
The modern (scientific) history of antiseptics is associated with the names of the Viennese obstetrician I. Semelweis and the English surgeon J. Lister. It should also be mentioned that at the same time or even earlier, many other doctors used their chemicals to prevent suppuration and treat wounds. The Russian surgeon N.I. should rightfully be included among them. Pirogov, who in 1847–1856. widely used a solution of bleach, ethyl alcohol, and silver nitrate.
So, let’s remember what antiseptics are, and how they differ from similar terms - “disinfection” and “chemotherapeutic drugs”.
Antiseptics (Latin anti - against, septicus - rotting) is a system of measures aimed at destroying microorganisms in a wound, pathological focus of the body, organs and tissues, as well as in the patient’s body as a whole, using mechanical and physical methods of influence, active chemicals substances and biological factors. This is in contrast to disinfection, which is a procedure involving the treatment of germ-contaminated objects and the environment in order to destroy them to such an extent that they cannot cause infection when the object is used. As a rule, during disinfection most microbes (including all pathogenic ones) are killed, but spores and some resistant viruses may remain in a viable state.
Antiseptic preparations and disinfectants for the most part have significant toxicity to humans, mainly because they act indiscriminately. For this reason, the use of antiseptics is in many cases limited to topical use. Chemotherapeutic drugs - antibiotics and synthetic chemotherapeutic agents - are selective against microorganisms and parasites and, accordingly, have less toxicity.
There are a considerable number of classifications of antiseptic agents today. The most popular of them are presented below.
According to the mechanism of action, antiseptics are classified into mechanical, physical, biological and chemical.
Methods of mechanical action on microbes trapped in a wound include: removal of infected foreign bodies from the wound; excision of infected, damaged or non-viable tissue at the time of primary surgical treatment of the wound; opening of abscesses; use of the mechanical properties of hydrogen peroxide (foam formation) to wash the wound; vacuum treatment of wounds. Relatively new methods of antiseptic treatment of a wound, predominantly mechanical, include treating the wound with a pulsating stream of antiseptic, which easily removes necrotic sloughing tissue, pus and small foreign bodies. This method was proposed in the mid-80s. Academician M.I. Kuzin and prof. B.M. Kostyuchenko. Its widespread implementation is hampered mainly by the lack, unfortunately, of appropriate equipment.
Drainage of wounds, use of ultraviolet irradiation (UVR); low frequency ultrasound; laser scalpel; plasma scalpel; antibiotic electrophoresis; UHF refers to physical impact.
Use of antibiotics; immune drugs; extracorporeal detoxification on xenoorgans; the use of proteolytic enzymes is a biological effect on pathogens.
According to the method of application, antiseptics are distinguished - general and local. The latter, in turn, is divided into superficial and deep. With general antiseptics, a chemical or biological factor is introduced into the internal environment of the body (intravenously, intramuscularly, endolymphatically, etc.), affecting the body as a whole. This type of antiseptic is also called chemotherapy. Local antiseptics implies the local action of antiseptic factors. With superficial antiseptics, an effect is applied to the surface of the wound or to the integument of the body (treating the surface of the wound with a laser beam, washing the wound with an antiseptic solution, etc.). With deep antiseptics, factors act in tissues or cavities affected by the infectious process (introduction of antibiotics and chemical antiseptics into tissues and cavities of the body by puncture, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, etc.). The same measures are sometimes called local chemotherapy.
Antiseptics are most often produced in the following dosage forms: tablets, patches, films, powders, solutions, drops, sprays, etc.
Today, most antiseptics can be found in the assortment of almost any pharmacy.
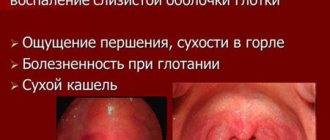
Medicines used for sore throat
For sore throats, products from the halogen group, united under the trade name (TN) Strepsils, are in wide demand among patients, produced in the form of lozenges (sometimes mistakenly called lollipops or lozenges) and dosed spray for topical use.
Strepsils (2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol + amylmetacresol + excipients); Strepsils with vitamin C (2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol + amylmetacresol + ascorbic acid (vitamin C) + excipients); Strepsils Plus (2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol + amylmetacresol + lidocaine hydrochloride + excipients); Strepsils with menthol and eucalyptus (2,4-dichlorobenzyl alcohol + amylmetacresol + levomenthol + eucalyptus oil + excipients); Strepsils Intensive (flurbiprofen + excipients).
The drug contains truly effective antimicrobial agents. The active substance amylmetacresol destroys the microbial shell itself, and the second substance - dichlorobenzyl alcohol - causes dehydration, i.e. dehydration of the microorganism.
Indications for use: treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx (relieves pain and soothes irritation in the throat). Thus, there is a targeted effect on suppressing the vital activity of microbes. Side effects: rarely - allergic reactions.
Hexetidine ( Stopangin ) - a pyrimidine derivative - an antiseptic for topical use in ENT practice, has broad-spectrum antimicrobial as well as antifungal activity, and an analgesic effect when applied to the mucous membrane; In addition, it has an enveloping effect. The antimicrobial effect is associated with the suppression of oxidative reactions of bacterial metabolism (thiamine antagonist). Release form: spray for topical use and solution for topical use (transparent, light red in color. Composition: hexethidine spray - a mixture of essential oils (anise, eucalyptus, orange flower essential oil, sassafras, peppermint; menthol, methyl salicylate). Hexetidine solution is a mixture of essential oils: anise, eucalyptus, sassafras, peppermint, clove oil; menthol, methyl salicylate. Indications for use: infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and larynx (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, stomatitis, aphthous ulcers of the oral cavity, glossitis , periodontitis, bleeding gums), fungal diseases of the oral cavity and larynx, injuries of the oral cavity and larynx), oral hygiene to eliminate bad breath.
Contraindications: atrophic pharyngitis, children under 6 years of age, first trimester of pregnancy, individual intolerance to the components of the drug. Important! Side effects: burning of the mucous membrane (quickly resolves spontaneously), allergic reactions, if the drug is accidentally swallowed, nausea may occur (passes spontaneously).
Hexethidine ( Hexoral ) is available in aerosol form. Stopangin and Hexoral have a common active ingredient and quite a lot in common in their composition, so their scope of action is identical. But Hexoral, unlike Stopangin, can be used by pregnant women in the first trimester of pregnancy, and in other cases the decision remains with the doctor.
Chlorhexidine (chlorhexidine) is a versatile antiseptic, which today can be purchased not only in the form of a solution, but also in cream, gel, and patch. The drug kills germs, bacteria, some viruses, and is effective in purulent processes. An additional advantage of chlorhexidine solution is its affordable price. The bacteriostatic effect of solutions is manifested in concentrations of up to 0.01%; the bactericidal effect is manifested at a concentration level above 0.01% (at a solution temperature of 22ºC and its effect on the affected area of the skin for 1 minute or more); the fungicidal effect is manifested at a solution concentration of 0.05% (at a temperature of 22ºC and exposure of the solution to the affected area of the skin for 10 minutes); the virucidal effect (suppressing lipophilic viruses) occurs at a concentration level in the range of 0.01–1% (suppression of bacterial spores is possible only when using a warm solution). A 0.2% solution of the drug can be used to prevent sexually transmitted infections (in particular ureaplasmosis, chlamydia, trichomoniasis, syphilis, gonorrhea and genital herpes). Disinfectant treatment and sanitation with a solution should be carried out no later than 2 hours after the end of sexual intercourse. A 0.5% solution of the drug can be used to treat wounds, skin cracks, burns, open mucous membranes and infected abrasions in order to disinfect them. Indications for the use of chlorhexidine: disinfection of wounds on the skin and even mucous membranes; course treatment of fungal diseases; prevention of sexually transmitted diseases; course treatment of stomatitis, periodontitis and gingivitis.
If to treat a cut it is enough to apply a solution to the wound, then to solve the problem of the diseases mentioned above, the order and frequency of actions is established by the attending physician. When using Chlorhexidine, individual allergic reactions, dry skin, itching, and dermatitis are possible. The most common side effect is dermatitis. However, complaints about antiseptics are extremely rare in medical practice.
Chlorhexidine should be used with extreme caution by women during pregnancy and lactation, people with individual intolerance to the drug, as well as children under adolescence.
Allantoin + Povidone-iodine ( Yox ) is an aerosol with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect, available both in the form of a spray and a solution for topical use. Indications: infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, tonsillopharyngitis, glossitis, stomatitis). It is used for treating the oral cavity and pharynx during surgical interventions on the respiratory tract and oral cavity, as well as in the postoperative period; for the treatment of infections of the mouth and throat that occur during chemotherapy, as well as for streptococcal sore throats as an additional remedy in antibiotic treatment. The mechanism of action is a direct effect on the proteins of microorganisms. Important! Possible side effects - iodism (increased iodine content in the body) and rarely - allergic reactions; Contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding, children under 6 years of age, as well as in hyperthyroidism, heart failure and hypersensitivity to iodine.
Gramicidin C + Cetylpyridinium chloride ( Gramicidin NEO ) is a combined drug for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the throat and oral cavity, produced in the form of lozenges, and belongs to biological antiseptics of microbial origin. The drug contains an antibiotic for topical use, gramicidin C, and an antiseptic, cetylpyridinium chloride. The mechanism of action is associated with an increase in the permeability of the cytoplasmic membrane of the microbial cell, which violates its stability and causes cell death. Gramicidin C has a pronounced antimicrobial effect against pathogens of infectious diseases of the oral cavity and pharynx. Side effects: allergic reactions due to individual sensitivity. Important! Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components included in the drug; children under 4 years of age; pregnancy (first trimester).
The antiseptic agent Cetylpyridinium chloride is included in other combination drugs: Cetylpyridinium chloride + Benzocaine ( Septolete plus ) is available in lozenges; Cetylpyridinium chloride + Lidocaine hydrocholide ( Kalgel ), produced as a dental gel, used for teething and Cetylpyridinium chloride + Lidocaine hydrocholide ( Theraflu LAR Menthol ), lozenges.
Acetylamine-nitropropoxybenzene ( Fallimint ) is a nitroacetanilide derivative, available in the form of dragees, when dissolved it creates a feeling of coolness in the mouth and larynx, has an antitussive, antiseptic, analgesic and weak local anesthetic effect. Does not have a drying effect on the mucous membranes, does not cause a feeling of numbness in the mouth. Indications: tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, gingivitis, stomatitis, reflex cough, preparation for instrumental examinations of the oral cavity and pharynx, taking impressions and fitting dentures. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, pregnancy, lactation, children under 5 years of age, sucrase or isomaltose deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Medicines for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa and after dental interventions
Rotocan , produced in the form of a solution in orange glass bottles, belongs to the group of alcohols; it contains a water-alcohol extract from a mixture of medicinal plant materials - chamomile flowers, calendula flowers (marigolds) and yarrow herb in a 2:1:1 ratio. Pharmacological action - anti-inflammatory. The drug enhances the processes of reparative regeneration, has hemostatic and antispasmodic properties, and has a positive effect on the trophism of the gastric mucosa. Rotocan is low-toxic and does not have allergenic, teratogenic or mutagenic properties. It is used for inflammatory diseases of the oral mucosa and periodontium of various etiologies, such as aphthous stomatitis, periodontitis, ulcerative necrotizing gingivostomatitis. Important! The use of the drug is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the plants contained in it; side effects are possible - allergic reactions.
Miramistin + Benzyldimethyl [3-(myristoylamino) propyl] ammonium chloride monohydrate ( Miramistin ) belongs to the group of detergents, available in the form of a solution for topical use of 0.01%. Indications: treatment and prevention of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity - stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontitis. It is also used for hygienic treatment of removable dentures. Side effects: in some cases, a slight burning sensation may occur at the site of application, which goes away on its own after 15–20 seconds and does not require discontinuation of the drug; allergic reactions. Contraindications: individual intolerance to drugs.
Benzalkonium chloride + peppermint leaves oil + thymol + eucalyptus rodentosa leaves oil + Levomenthol ( Septolete lozenges ). It is a combination of an antiseptic from the group of quaternary ammonium compounds (benzalkonium chloride) and active natural substances (menthol, peppermint essential oil, eucalyptus essential oil, thymol). Benzalkonium chloride has a bactericidal effect on gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as a fungicidal effect against Candida albicans and some lipophilic viruses. Menthol and peppermint essential oil have a moderate analgesic and deodorizing effect. Lozenges relieve sore throat when swallowing, as well as a sore throat. Thymol has an antiseptic effect, which enhances the effectiveness of the drug. Eucalyptus essential oil reduces mucus secretion in the upper respiratory tract and makes breathing easier. The drug does not contain sugar, which allows it to be taken by patients with diabetes. Indications: pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, gingivitis, stomatitis. Important! There are contraindications: children under 4 years of age, deficiency of the enzyme lactase, isomaltase, galactosemia, hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. Side effects: allergic reactions, nausea, diarrhea.
Products used for burns
Dexpanthenol ( Bepanten plus cream, 5% in aluminum tubes) in skin cells quickly turns into pantothenic acid, which plays an important role in both the formation and healing of damaged skin. Quickly absorbed. When applied to the surface of a wound, it protects against infection, promoting healing. Easy to apply and wash off. The composition of Bepanten Plus cream is as follows: 1 g of cream contains 50 mg of dexpanthenol, 5 mg of chlorhexidine dihydrochloride. The composition includes additional substances: cetyl alcohol, DL-pantolactone, stearyl alcohol, liquid paraffin, white soft paraffin, lanolin, polyoxyl 40, stearate, water. Important! Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug is possible, and a side effect is an allergic reaction (urticaria, itching).
Products used for open wounds
Hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide solution, 40 and 25 ml bottles) from the “oxidizing agents” group is suitable even for infants. For example, they are recommended to treat the umbilical wound of a newborn. The main advantage of hydrogen peroxide in comparison with brilliant green and iodine is that the solution can be applied to an open wound. At the same time, hydrogen peroxide does not “sting”. After treating the surface of a fresh wound with a solution of hydrogen peroxide, you can notice how the antiseptic foams. At this moment, a disinfection process occurs: atomic oxygen is released, which rids the wound of germs, pus and dead tissue. The antiseptic effect of hydrogen peroxide is not sterilizing; when it is used, only a temporary decrease in the number of microorganisms occurs. Indications for use: for washing and rinsing for stomatitis, tonsillitis, gynecological diseases. Small superficial wounds, small capillary bleeding from superficial wounds, nosebleeds.
Nitrofural ( Furacilin ) is a derivative of nitrofuran. Indications for use: purulent wounds, bedsores, burns II–III degree. and many more etc. (see instructions for use).
Important! Side effects: in some cases, dermatitis occurs. Sometimes when taken orally, dyspeptic symptoms (loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting), dizziness, and allergic rashes are observed. Long-term use of drugs can cause neuritis. With long-term (months) topical use, graying of hair and skin depigmentation (leucoderma) are observed in areas exposed to the direct action of the drug. Contraindications: increased individual sensitivity to nitrofuran derivatives. Orally administered with caution in case of impaired renal function. Release forms: powder, tablets for oral administration (rarely); combined tablets for external use, 0.02% furatsilin solution (1:5000) for external use, 0.2% furatsilin ointment (1:500); Furacilin paste for hands and face against exposure to various irritating chemicals.
The low solubility of furatsilin in water (1:5000) limits the use of this well-known drug due to the inconvenience associated, first of all, with the preparation of the solution - long-term dissolution of factory-made tablets or powder in boiling water. Currently, on the basis of the departments of pharmacology and pharmaceutical technology of the pharmaceutical faculty of the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education of the First Moscow State Medical University named after. THEM. Sechenov of the Russian Ministry of Health has developed a rapidly dissolving dosage form of Furacilin - effervescent tablets.
Antiseptics for local preventive use for every day
Sanitelle antiseptic hand gel in disposable sachets is easy to use, destroys 99.9% of the most common bacteria, fungi and viruses within 15 seconds. The gel contains: ethyl alcohol 66.2%, deionized water, glycerin, propylene glycol, aloe vera extract, vitamin E, functional additives. Contraindications: individual intolerance to the drug.
All of the above antiseptics are dispensed without prescriptions and are freely available in pharmacies, however, if you have wounds or non-healing ulcers of unknown pathogenesis, you should definitely consult a doctor. Drug abuse also has a number of dangers associated with their side effects and individual characteristics of the person.