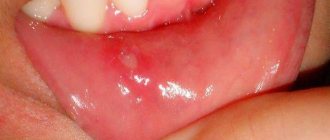
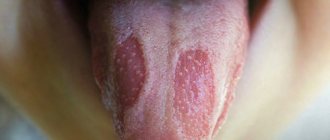
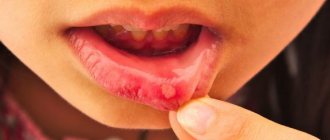
Stomatitis refers to inflammatory processes affecting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. There are various forms and types of this disease, differing in pathogens and routes of infection. This article discusses the main types of stomatitis, information about whether they are contagious and ways to provide protection against them.
Aphthous
It is this variety that is the safest for others in the sense that in most cases it cannot be transmitted from a carrier .
Despite this, in case of possible contact with a person who has been diagnosed with aphthous stomatitis, it is better to take the necessary precautions:
- The fact is that sometimes this type of disease occurs against the background of various viral infections.
In this case, in addition to the likely appearance of aphthae (ulcers on the oral mucosa), there is also general redness and inflammation, especially in the throat area. With this etiology of aphthous stomatitis, others may become infected with the viral infection itself , since at a time when aphthae has already appeared, the initial infection can still be transmitted by airborne droplets, that is, by talking, sneezing, coughing, etc. - Another option when this variety will be contagious is in newborns and children up to six months with an initially traumatic route of occurrence . At this age, the mucosal defense mechanism, that is, local immunity in the oral cavity, does not yet work in children.
A large number of pathogens accumulate in the affected areas, which can be transmitted to another child through contact, for example, sharing toys, pacifiers, dishes and hygiene items. Therefore it is better to avoid this.
Emergency measures
If preventive measures do not help to avoid the disease, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. He will be able to correctly determine the type of stomatitis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
If it is not possible to contact a specialist in a timely manner, the following measures must be taken to eliminate the cause of the disease:
- take medications that improve immunity;
- add vitamin-rich foods to your diet and take vitamin complexes;
- if the mucous membrane is red and painful, itching and swelling appear, you should take an antihistamine;
- To prevent the development of a viral infection, it is important to take an antiviral drug on time;
- To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, it is worth using local treatment: rinse the mouth with solutions based on chamomile, sage, oak bark;
- ulcers can be treated with an oil solution of rose hips, sea buckthorn or vitamin A;
- To reduce the possibility of the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, it is worth treating the affected areas with a solution of potassium permanganate.
These measures will reduce the likelihood of the infection spreading, but you should contact the clinic as soon as possible.
Only a doctor can determine the correct treatment regimen based on an examination of the patient’s oral cavity.
Viral
This variety is definitely contagious and quite dangerous for others , since it can be transmitted to a very large number of people in a fairly short period of time.
The disease is caused by several main types of viruses:
- adenoviruses;
- enteroviruses;
- herpes simplex;
- parainfluenza and influenza;
- chicken pox.
Next, we will talk about all types of viruses, except herpes, since there is a separately considered herpetic stomatitis, caused specifically by the herpes virus.
Can treatment with folk remedies for candidal stomatitis be an independent measure to combat the infection?
In a separate article we will talk about ways to get rid of white mouth sores.
Read the link https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/bolezni-polosti-rta/stomatit-bpr/samyie-populyarnyie-i-deystvennyie-mazi.html, for whom Metrogyl Denta ointment for stomatitis is recommended.
Routes of infection
Each of them is quite easily transmitted from the carrier to surrounding people. And not only for children, as many believe, but also for adults.
There are several different ways of contracting viral stomatitis , each of which is equally likely.
- Aerosol or airborne . That is, the main causative agent of the disease enters the body of others through the release of saliva or sputum along with moisture when coughing, sneezing, or exhaling air.
- Contact . During direct contact with an infected person, viruses can enter the skin or mucous membrane of another person through kisses, hugs, handshakes, etc.
- Household . This refers to the use of hygiene items, dishes, toys and other things shared with the patient.
- Internal , that is, through the blood.
The virus, in the process of activity, is, among other things, in the patient’s blood. Therefore, you can also become infected by direct contact of contaminated blood with a wound or affected mucous membrane, or if disinfection measures are insufficient before using scissors, razors, etc.
How long does the dangerous period last?
In order to subsequently take proper safety measures, it is very important to know how long the dangerous time for infection lasts, when it begins and ends.
On average, the disease lasts about a week (5 to 10 days). All this time it is believed that it is possible to get the disease from a carrier. When this period ends, that is, all symptoms and manifestations pass, in most cases the danger of infection disappears.
However, you should also remember about the preliminary period, which is called incubation . Despite the absence of main manifestations and symptoms, the disease is already beginning to develop and the carrier becomes potentially dangerous.
This period may vary depending on the specific type of virus. On average, it lasts five to seven days. However, sometimes it can last up to two weeks or more.
If we talk about newborn children and infants up to several months old, then the incubation period of viral stomatitis rarely lasts more than three days.
Herpetic
The source of the disease, as mentioned earlier, is the herpes simplex virus. Its peculiarity is that once “settled” in the body, herpes will manifest itself periodically throughout life.
One of the two types of this virus manifests itself in the form of rashes on the mucous membrane of the mouth and around this area. This is what is called herpetic stomatitis.
It is most common for young children to become infected, between one and three years of age. At this time, the immunity received from the mother is no longer effective, and their own immune systems cannot yet fight such an aggressive pathogen.
Therefore, the main risk group for getting the disease is children aged 1-3 years .
Methods and routes of transmission
However, this does not mean that the possibility of infection in adults is excluded. The period of greatest activity of the virus occurs at the time when characteristic bubbles appear . It is the liquid that is inside them that serves as the method of transmission.
However, there are many more ways in which you can become infected from the source of the disease . Usually this is contact and household, but if the bubbles burst, aerosol and also internal are possible.
Bacterial
Children most often suffer from this type of stomatitis. They have not fully formed the normal microflora in the oral cavity, as well as the mechanisms of functioning and protection of the mucous membrane. Therefore, children can easily transmit this disease to each other through contact and airborne droplets .
Adults can also become infected . However, for this, a healthy person must have damage to the mucous membrane (wounds or cuts caused by mechanical means).
When in contact with a sick child or another adult, pathogens of bacterial stomatitis can accidentally enter the damaged mucosa. Then the probability of infection is extremely high.
Symptoms of the disease
Stomatitis can be recognized by the following signs:
- ulcers, wounds, erosions and rashes on tissues;
- red color of the mucous membrane;
- plaque on the tongue, inner surface of the cheeks, palate;
- unpleasant taste;
- swelling of tissues;
- heavy salivation;
- bad breath;
- itching and burning – in some cases;
- discomfort and pain;
- bleeding gums – occasionally;
- increased body temperature;
- lymphadenitis.
Symptoms in children are always more pronounced. The child often feels severe pain. Adults tolerate the disease easily. Its symptoms usually do not cause severe discomfort.
When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to protect yourself and, possibly, others.
Fungal
This type of disease is more common in infants, as well as elderly people , which is associated with insufficient protective reactions of the body. However, infection of adults is no exception.
The most likely causative agent for this type of stomatitis (candidiasis) is fungi of the genus Candida. They have several varieties, each of which has its own “audience” of infected people .
- parapsilosia – children from birth to six months. Transmission occurs through shared dishes, household items, toys, that is, mainly through household means.
- albicans - present in the body of most of the adult population. Additionally, it can be transmitted to another person through sexual contact.
- glabrata – more common in older people.
- sake – occurs most rarely and is not typical for a certain age category. It is transmitted through direct contact, as well as through household and hygiene items.
Other types
In addition to the above, dentists identify several more types of this disease:
- traumatic , when long-term constant microtrauma of the oral mucosa occurs, for example, a chip on a tooth, or a one-time, but severe injury that affects the tissues quite deeply;
- allergic , caused by internal disorders;
- after radiation or chemotherapy , as their consequence.
Stomatitis of this etiology is very unpleasant for the patient, but is completely safe for others and in the vast majority of cases is not contagious.
However, there is an exception here . This is the case when, with traumatic stomatitis, pathogenic microorganisms from the affected area on the patient’s mucosa fall directly onto a cut or similar wound in the second person’s mouth.
The body's defenses may not be able to cope with such penetration, and as a result, infection occurs.
Is it possible to get stomatitis through a kiss?
Is stomatitis transmitted by kissing? Dentists often hear this question from their patients. Periodic or regular contact of foreign pathogenic microorganisms with the mucous membrane, especially if there are lesions in the mouth, may well provoke the development of stomatitis. This is why pediatricians do not recommend that mothers kiss their babies. Their weak immune system is unable to fight off the disease.
Stomatitis is a common disease among adults and children. But it occurs more often in children. A weak immune system, improper dental treatment, microorganisms and viruses are the causes of the disease. However, you can protect yourself from them by following the rules of hygiene, eating right, taking vitamin complexes and visiting the dentist annually. It is easier to prevent any disease than to spend a lot of time, effort and money on treatment.
Author: Natalya Stagurskaya, dentist, especially for Karies.pro
Precautions and prevention
In addition to ways to protect yourself from infection, there are also preventive measures that will help avoid the occurrence of all types of stomatitis.
How and how to treat stomatitis in adults with folk remedies? Effective recipes for getting rid of illness.
In this publication we provide instructions on how to take Imudon and reviews from those who have used this remedy.
Here https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/bolezni-polosti-rta/stomatit-bpr/aftoznogo-u-vzroslyih-i-detey.html we will talk about the features of the treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis.
How to protect yourself?
If you are sure that someone in your immediate environment is sick with stomatitis, certain precautions should be taken .
- The best way is to completely eliminate contact . This is possible, for example, for children going to kindergarten.
- For adults, you can limit contacts .
- Do not eat from the same dishes and do not share toys, things, etc.
- Wear a gauze bandage if aerosol transmission is possible.
How contagious various types of stomatitis are for others and how to protect your child and yourself from infection, watch the video:
Preventive measures
- Carry out high-quality and complete oral hygiene.
- Wash your hands thoroughly in a timely manner.
- Always use only personal equipment (toothbrush, scissors, etc.).
- Do not overuse products that can cause damage to the oral mucosa.
- Timely dental examinations.
A balanced diet, the proper amount of vitamins and minerals needed by the body, lack of stress, and exercise will improve your general condition, as well as increase your immunity and resistance to most diseases , including stomatitis.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags aphthous stomatitis candidal stomatitis transmission routes stomatitis in adults in children
Did you like the article? stay tuned
Previous article
Recommendations for using the Waterpik WP 450 portable irrigator
Next article
Not all toothpastes are created equal
Preventive measures
A very important part of prevention is timely treatment of dental and ENT diseases.
Stomatitis can occur in anyone, regardless of age and lifestyle, but compliance with the following preventive measures can reduce this risk:
- Maintaining oral hygiene and timely treatment of dental diseases.
- Providing a balanced diet to supply the body with the necessary amount of vitamins and nutrients.
- Taking vitamin complexes in spring and autumn.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs and digestive system.
- Rejection of bad habits.